finals review for the worst class on earth
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Charles‘s Law
The volume of a gas increases with increasing temperature as long as the pressure does not change
Pressure
Increasing ____ raises the boiling point of a liquid.
Double covalent bond
covalent bond formed by atoms that share two pairs of electrons
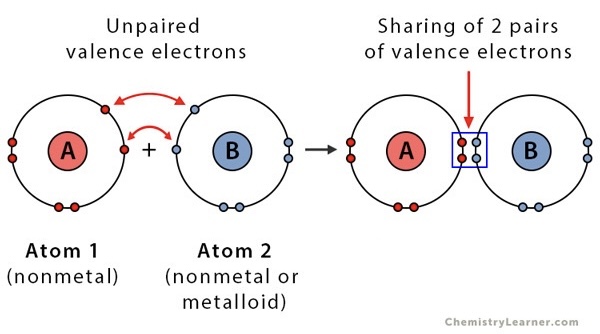
Triple covalent bond
Covalent bond formed by atoms that share three pairs of electrons

Silicon
Which element is most likely to form covalent bonds?
silicon (14)
Oxygen (8)
Chlorine (17)
Sulfur (16)
Identical to
The energy released in the formation of a compound from its elements is always ___ the energy requirements decompose that compound into its elements
Boyle‘s law
The pressure of a gas will increase as the volume of the container decreases provided temperature does not change
Bernoullis principle
Fluid velocity increases when the flow of the fluid is restricted
Pascals principle
Pressure applied to a fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid
Archimedes‘ Principle
Buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
Suspension
Heterogeneous mixture containing a liquid in which you can see particles settle
Kinetic theory of matter
Matter is Made up of small particles that are in constant motion
Amorphous solid
Liquid: soften and gradually turn to liquid over time
Solid: Lacks a crystalline structure and doesn’t have a specific melting temperature
Ex: glass, butter
Liquid crystal
Liquid: flows like a liquid in the liquid phase, but doesn’t lose geometric arrangement
Solid: Retains geometric arrangement in specific directions
Ex: cellphones, calculators
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid begins to turn into a liquid
Heat of fusion
The amount of energy needed to change a substance from a solid to a liquid at its melting point
Boiling point
The temperature at which the pressure of the vapor in a liquid is equal to the external pressure acting on the surface of a liquid
Heat of vaporization
The amount of energy needed for a liquid at its boiling point to become a gas
Requires energy to be added to the substance
Sublimation
The change from a solid to a gas without a liquid state
Plasma
Matter consisting of positively and negatively charged particles
Most abundant matter in the universe
Has enough energy to overcome attractive forces between its particles and within atoms
Thermal expansion
An increase in size of a substance when temperature is increased
Buoyancy
The ability of a fluid (a liquid or gas) to exert an upward force on an object immersed in it
Pressure
force extorted per unit area
Pressure (Pa) = Force (N) / area (m²)
Input force (N) / input area (m²) = output force (N) / output area (m²)
Viscosity
The resistance of a fluid to flowing
Substance
A pure form of matter that has a uniform composition and specific properties
Compound
A substance in which two or more elements are combined in a fixed proportion
Electrically neutral
Dinitrogen oxide
What is the name of N2O?
Greek
____________________ prefixes are used to indicate how many atoms of each element are in a binary covalent compound.
Homogeneous mixture
Contains two or more substances blended evenly throughout
Can be separated by physical changes
Heterogeneous mixture
Mixture in which different materials can easily be distinguished
Solution
Homogeneous mixture of particles too small to see with a microscope and too small to settle
Won’t scatter light
Tyndall effect
Observed When light passes through a colloid
Colloid
A mixture with particles visible under a microscope
not heavy enough to settle
Scatters light
Example: smoke
Not homogeneous
Physical property
A characteristic that can be observed without changing the substance
Examples: odor, color
Physical change
A change in size, shape, or state of matter, but not a change in the substance
Chemical change
A change of one substance to another
Chemical property
A characteristic that indicates whether a substance can change to another substance
Examples: flammability, color change, temperature change
Distillation
The separation of substances in a mixture using evaporation
Law of conservation of mass
The mass of a substance before a chemical change equals the mass of all substances after the change
Atom
The smallest particle of an element that retains the element‘s properties
Nucleus
The small, positively charged center of an atom
Proton
Particles in the nucleus with an electric charge of 1+
Neutron
Electrically neutral particles in the nucleus
Electron
Particles with an electric charge of 1-
Quark
Smaller particles that make up protons and neutrons
Electron cloud
The area around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found
NOT called the negative zone
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Probability cloud
What best represent the location of an electron in an atom according to modern atomic theory
Mass number
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Average atomic mass
The weighted average mass of all naturally occurring isotopes on an element (amu)
Periodic table
The chart that categorizes all known elements in rows and columns, based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties
Period
The horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table that are numbered 1-7
Group
The vertical columns in the periodic table that are numbered 1-18
Halogens
group 17 of periodic table
Form diatomic molecules in gaseous state
Electron dot diagram
Uses the chemical symbol of an element surrounded by dots to represent the number of electrons in the outermost energy level
Selenium
Element in the oxygen group that is needed in trace amounts in your diet
Actinides
Second row of inner transition elements
atomic numbers 90 through 103
named derived from the element actinium.
radioactive, unstable, rare, and nonexistent in nature
Where most synthetic elements are found
Lanthanides
First row of the inner transition elements
atomic numbers 58 through 71
name is derived from the element lanthanum
Metal
Elements that are shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity, solid at room temperature (except for mercury)
1-2 electrons in outer electron shells
Include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, iron triad, boron group, carbon group, and nitrogen group
Malleable
The ability metals have that allows them to be rolled or hammered into sheets
Ductile
The ability metals have that allows them to be drawn into wire
Metallic bonding
Positively charged metallic ions are surrounded by a sea of electrons
Radioactive element
An element in which the nucleus breaks down and gives off particles and energy
Transition element
Elements groups 3-12 in the periodic table
Often occur as uncombined elements in nature
Boron
Only element in group 13 that is NOT a metal
Nonmetal
Element that is usually a gas or solid at room temperature
Found on the far right of the periodic table
Includes halogens and oxygen group
Diatomic molecule
Consists of two atoms in a covalent bond
Can be two of the same element (O2) or one atom of two different elements (CO)
Metalloid
Elements that have both properties of metals and nonmetals
Most likely to be semiconductors
Allotrope
Different molecular structures of the same element
Semiconductor
Elements that conduct electricity under certain conditions only
Transuranium element
Elements that have more than 92 protons
Chemical formula
Shows what elements a compound contains + the exact number of the atoms of each element in a unit of that compound
Chemical bond
The force that holds atoms together in a compound
Ion
A charged particle that has either more or fewer electrons than it has protons
Ionic bond
The force of attraction between a positive ion and a negative ion in an ionic compound
Covalent bond
The force of attraction between two atoms that share electrons
Molecule
The neutral particle that forms when atoms share electrons
Two or more atoms are bonded together
Nonpolar bond
A covalent bond where the electrons are shared equally
Polar bond
A covalent bond where electrons are unequally shared producing charged molecule ends
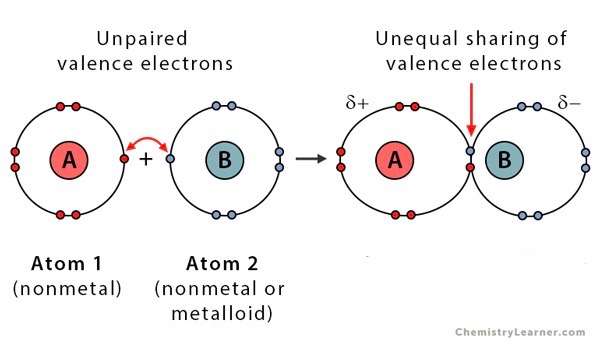
Polar molecule
A molecule that has a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end, but the molecule itself is neutral
Nonpolar molecule
A molecule in which the electrons are shared equally between atoms in the chemical bond
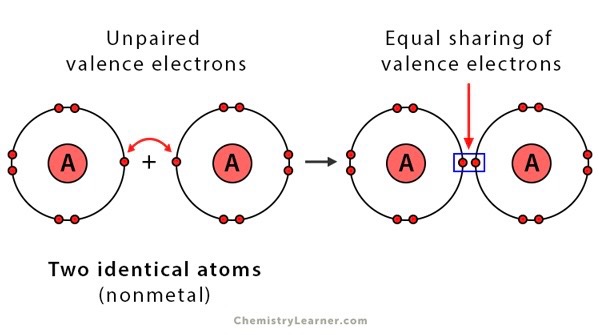
Oxidation number
A positive or negative number that indicates how many electrons an atom has gained, lost, or shared to become neutral
Binary compound
The easiest compounds to write formulas for, composed of two elements
Polyatomic ion
A positively or negatively charged group of covalently bonded groups of atoms
Hydrate
A compound that has water chemically attached to its atoms and written in its chemical formula
Chemical reaction
A change in which one or more substances are converted into new substances
Pure substance
Consists of only one kind of atom or only one kind of molecule
Reactants
The starting substances that react in a chemical reaction
Products
The new substances produced from a chemical reaction
Chemical equation
A way to describe a chemical reaction using chemical formulas and other symbols
Coefficient
Represent the number of units of each substance taking part in a reaction
Balanced chemical equation
A chemical equation with the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the arrow
Mole
The amount of a substance that contains 6.02 × 10²³ particles of that substance
Molar mass
The mass (g) of one mole of a substance
Combustion reaction
A reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light
Synthesis reaction
A reaction in which two or more substances combine to form another substance
Decomposition reaction
A reaction in which one substance breaks down, or decomposes, into two or more substances
Single-displacement reaction
A reaction in which one element replaces another element in a compound
Element + compound = element + compound
Double-displacement reaction
A reaction in which the positive ion of one compound replaces the positive ion of the other compound to form two new compounds