Unit 6 . 1-5 (exam 3)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Pressure
force over area
weight of something on an object
P = force/area
1 atmosphere (atm)
1 atmosphere (atm) = 760 mmHg or 760 torr.
atmosphere (atm) - room air pressure
Category 5 hurricanes often have a central air pressure of 690.1 torr. convert this pressure to atmosphere
1 atmo = 760 torr
690.1 torr x 1 atmo/760 torr = 0.908 atm
suppose blood pressure readings were reported in cm Hg rather than mmHg. convert 140/90 mmHg to cm Hg. (1 in = 2.54cm)
l cm = 10 mm
10-2 10-3 = 101 =10
140 mmHg x 1 cm Hg/10 mmHg = 14 cm Hg
90 mmHg x 1 cm Hg/10 mmHg = 9cm Hg
four measurable quantities of a gas
pressure (p): atm
volume (V) liters
Temperature (T): kelvin (absolute temp scale) no negative kelvin values
amount in moles (n): mol
Boyle’s law
P1V1 = P2V2
Pa 1/v (Boyle’s law is breathing)
a = alpha means proportional
pressure and volume
pressure goes up, volume goes down
pressure goes down, volume goes up
Charles’s law
V1/ T1 = V2/T2
V ∝ T
volume and temperature
volume increases with increasing temp
volume decrease with decreasing temp
sea breeze is created by charles’s law
Guy-Lussac’s law
P1/T1 = P2/T2
pressure and temperature
pressure increases with increasing temp.
pressure decreases with decreasing temp.
P ∝T
proportional
P ∝ V - inversely proportional
P ∝ 1/v - only 1/variable
V ∝ T
V ∝ N
P ∝ T
Directly proportional increase so does the other (increase)
decrease so does the other decrease
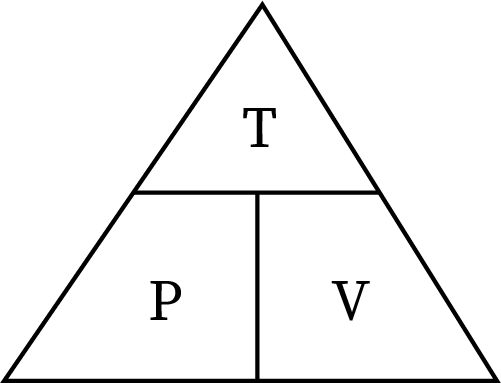
Combined gas law
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
1: state 1 (change) → state 2 (predicts what is 2)
ex. change the temp (T), pressure (P), volume (V)
if a problem provides:
p and V:
P1V1 = P2V2
P and T:
P1/T1 = P2/T2
V and T:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
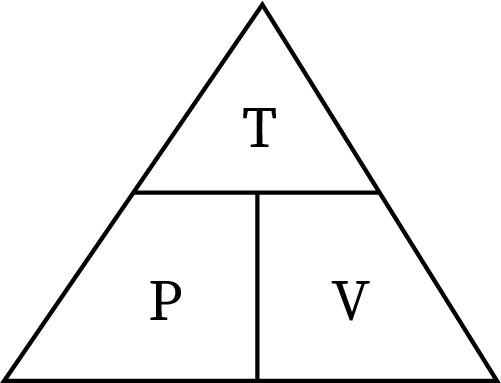
Avogadro’s Law
Volume increase with increasing amount of gas (moles)
V1/ n1 = V2/n2
V∝N
A 4.0-L container of helium gas has a pressure of 10.0 atm, what pressure does the gas exert if the volume is increased to 6.0 L?
ID the variables and derive the gas law
P1V1 =P2V2
match variables
V1= 4.0 L
P1 = 10.0 atm
V2 6.0 L
P2 =?
P2 = P1V1/V2 = 10.0 atm (4.0L)/6.0 L = 40.0/6 = 6.67 atm = 6.7
P ∝ 1/v - v went up and P went down
What volume will a sample of gas occupy at 400 °C, if it occupies 420 mL at 100 °C at constant pressure?
T go up and V go up
K = C + 273
V1 = 420 mL
V1/T1 = V2/T2
420 mL/373 k = v2/673 k
673 × 1.126 =v2/673 × (673) (you times to cancel out the divided) = 758 mL
volume is higher
Argon is an inert gas used in incandescent light bulbs to slow the vaporization of the filament. A certain light bulb containing argon at 1.20 atm and 18 °C is heated to 85 °C at constant volume. What is the final pressure of argon in the bulb in atm?
P1 = 1.20 atm
k = c +273
p1/T1= P2/T2
another way to solve it
P1/T1= P2/T2 (do the criss-cross method)
P1T2 = P2T1
1.20 atm (358k) = p2 (291K)
P2 = 1.20 atm (358K)/ 291 K = 1.48 atm
3 H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g)
How many liters of NH3 would be produced when 2.9 L of H2 reacts with an excess of N2 at constant temperature and pressure?
Avogadro’s law - stoichiometry ( sub volume in liters for the molar coefficient)
V1/n1 = V2/n2
start with the correct ratio
2NH3 liters / 3H2 liters x 2.9 L of H2 = 1.9 L of NH3
solute
in the minority/smallest component in a solution (mixture)
solvent
is the majority largest component in a solution
solution
homogenous mixture, uniform throughout. (all mix well - you cannot see)
small particles size, transparent/translucent - see through
ex. apple juice
colloid
homogenous mixtures, uniform throughout,
large particles size, opaque (cant see through)
the middle largest component
suspension
heterogenous mixtures, non-uniform ( you can see the mixtures)
largest particles. undisturbed, the particles settle to the bottom.
Ex. blood ( it is consitly moving in are body. if not it will clot)
pulp orange juice
weight to volume (w/v)%
g solute/ mL solution x 100
volume to volume (V/V)
volume of solute/ volume of solution x 100
parts per million (ppm)
if you see a chemical given in ppm, its dangerous
ppm= same unit to be (g, mg, mL…) solute / share unit (g, mg, mL…) solvent x 106 → 1,000
Seabirds such as osprey that feed on fish contaminated with the pesticide DDT (sample Problem 7.7) accumulate an average of 25 parts per million of DDT in their fatty tissues. when DDT concentration is high, mother osprey produces eggs with very thin shells that are easily crushed, so fewer osprey chick’s hatch.
25 mg DDT/ 1,000,000 mg mixture x 106 = 25 ppm
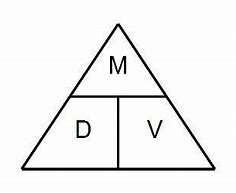
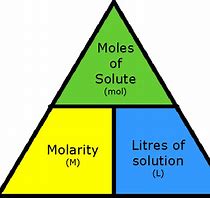
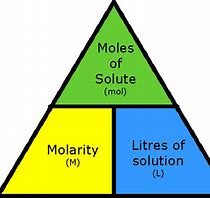
Molarity (M)
molarity in lab reports .
(Moles/L sometimes)
chemists density → M moles/Liters
use those 2 triangles for calculations
Dilution
high concentration add solvent, make a lower concentration solution.
M1V1 = M2V2
M = molarity (for concentrations)
M can also mean mega
V = volume
Calculate the concentration of a solution and prepare a dilute solution - Practice
A saline solution used in intravenous drips contain 0.92% (w/v) NaCl in water. How many grams of NaCl are contained in 250 mL of this solution
G?
0.92 g NaCl/100mL solution x 250/1 mL solution = 2.3 g NaCl
Calculate the concentration of a solution and prepare a dilute solution - Practice
What is the concentration in parts per million (ppm) if 0.038 mg of DDT was found in 1400 g plankton?
convert to the same units
0.038 mg → g or 1400 g to mg
100g x 1 mg/10-3 g = 1,400,00 mg (1.4 × 106 mg)
apply formula
0.038 mg DDT/ 1.4 × 106 mg (106) the two cancel out
and you divide by 0.038 mg DDT/ 1.4 = 0.027 ppm
Calculate the concentration of a solution and prepare a dilute solution - Practice
Calculate the molarity of a solution made from 20.0 g of NaOH in 250 mL of solution.
Molar mass of NaOh is 40.0 g/mol
M?
M=moles/L
moles/L: 1 mole/40.0g x 20.0 g NaOH/2.50 mL x 1000 mL/ 1 L = 2.0 mole/L = 2.0 M
or solve
250 mL/ 1000 mL
20 g/40 g/mol = 0.5 moles
0.5 moles/0.250 L = 2.0 M
Calculate the concentration of a solution and prepare a dilute solution - Practice
What volume in milliliters of a 0.30 M solution of glucose contains 0.025 mol of glucose?
any molarity (M) = moles/L
0.30 M = 0.30 moles/1 L
mL?
1000 mL/ 1L x 1L/0.30 moles x 0.0250 mol/ 1 = 83.3 mL
or
L = mol/M
0.025 moles/0.30 M
= 0.0833 L (1000 mL/1)
= 83.3 mL
Calculate the concentration of a solution and prepare a dilute solution - Practice.
What is the concentration of a solution formed by diluting 5.0 mL of 3.2 M glucose solution to 40.0 mL?
v1 = 5.0 mL
M1 = 3.2 M
v2= 40.0 mL
M2?
M1V1/V2 = M2V2/V2 (the two V2 cancel out)
M2 = M1V1/V2 = 3.2 M (5.0 mL)/ 40.0 mL
= 0.4 M solution
a 25% (wt/vol) solution of mannitol is often used to help patients with head injuries to reduce swelling. What volume, in mL, should be give to a patient requiring 57g?
mL?
100mL/25g x 57g/1 = 228mL