1 Microbial Life Smartwork
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Which of the following organisms are not considered microbes?
A. Fungi
B. Viruses
C. Bacteria
D. Mosquitoes
E. Protozoa
D. Mosquitoes
Adult mosquitoes are eukaryotic arthropods that can be seen without a microscope and are not considered microorganisms. Mosquitoes can serve as biological vectors to transmit microbial parasites, such as bacteria and viruses, causing mosquito-borne diseases. Examples of mosquito-borne diseases include malaria, West Nile virus, and Zika fever.
Rank the following microorganisms from largest to smallest in size.
Pelomyxa - Ameba found in soil
Escherichia coli- Bacteria found in the human colon
Varicella-zoster virus - The virus that causes chickenpox
Spirogyra - Aquatic algae
Prochloroccocus - Photosynthetic marine bacteria
Pelomyxa - Ameba found in soil (Largest)
Spirogyra - Aquatic algae
Escherichia coli - Bacteria found in the human colon
Prochloroccocus - Photosynthetic marine bacteria
Varicella-zoster virus - The virus that causes chickenpox (Smallest)
Classify each of the following groups of organisms as bacteria, archaea, or eukaryotes by dragging the items into the correct categories.
-Proteobacteria
-Plants
-Methanogens
-Animals
-Cyanobacteria
-Protists
-Sulfur thermophiles
-Algae
-Fungi
Bacteria: proteobacteria and cyanobacteria
Eukaryotes: Plants, animals, protists, algae, and fungi
Archaea: methanogens and sulfur thermophiles
Spontaneous generation is the notion that
A. microbes are ubiquitous.
B. antibiotics are produced by microorganisms to defend against other microorganisms.
C. microbes cause disease.
D. living organisms arise from nonliving matter.
D. living organisms arise from nonliving matter.
Spontaneous generation is the notion that living organisms can arise from nonliving matter. This was a long-held belief before scientists started to understand the ubiquity of microorganisms. Spontaneous generation was disproved by Louis Pasteur and others in the 19th century.
Which characteristic of endospores led to confusion when Tyndall tried to replicate Pasteur's experiments regarding spontaneous generation?
Choose one or more:
A. Ability to form biofilms
B. Heat resistance
C. Antibiotic resistance
D. Microscopic size
B. Heat resistance
Endospores are heat resistant, so simply boiling the contents of the flask does not kill endospores. The endospores that contaminated the broth could only be eliminated by repeated rounds of boiling. Not all flasks were contaminated by endospores, which caused the variable results.
Which of the following is true of a pure culture?
A. It is a culture of multiple organisms that cause a single disease.
B. It is a culture of diverse microorganisms obtained from a single diseased patient.
C. It is a culture of diverse microorganisms obtained from a single environmental sample.
D. It is a culture of a single type of organism that can facilitate identification of a pathogen.
D. It is a culture of a single type of organism that can facilitate identification of a pathogen.
A pure culture of microorganisms is one that is grown from a single parental cell. This method revolutionized medical microbiology and helped to establish the germ theory of disease.
Koch’s Postulates
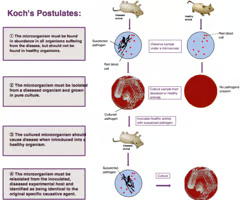
Which criteria of Koch's postulates would not necessarily be met when trying to link a particular bacterium to a latent infection, such as tuberculosis or Lyme disease?
Choose one or more:
A. The microbe is found in all cases of the disease but is absent from healthy individuals.
B. The microbe is isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
C. When the microbe is introduced into a healthy, susceptible host, the same disease occurs.
D. The same strain of microbe is obtained from a newly diseased host.
A. The microbe is found in all cases of the disease but is absent from healthy individuals.
C. When the microbe is introduced into a healthy, susceptible host, the same disease occurs.
Latent infections, such as tuberculosis, only cause symptoms in a fraction of infected individuals. In addition, the period of time before infected individuals show symptoms is variable. Accordingly, it is unlikely that a scientist would only find the microbe in diseased individuals and also unlikely that symptoms would occur in all hosts.
Which of the following is a unique characteristic of viruses that distinguishes them from all major groups of microorganisms in the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains?
A. lack of typical cell structure
B. too small to be seen without a microscope
C. lack of a nucleus
D. ability to cause disease
E. presence of a genome
A. lack of typical cell structure
Viruses lack a typical cellular structure and do not fulfill all necessary life functions. As a result, many scientists do not consider viruses "alive."
Identify which organisms can be infected by viruses.
Choose one or more:
A. Archaea
B. Bacteria
C. Animals
D. Fungi
E. Protists
F. Plants
A. Archaea
B. Bacteria
C. Animals
D. Fungi
E. Protists
F. Plants
All types of organisms can be infected by viruses—even other viruses! Although some viruses can cause disease, many endogenous viruses may benefit their hosts.
Most organisms (including you) break down organic compounds to obtain energy and nutritional building blocks. In contrast, chemolithotrophs are prokaryotes that obtain energy through the oxidation of inorganic compounds. Which of the following inorganic molecules would these microbes also need to build macromolecules for new cell material?
A. CO2
B. N2
C. H2
D. O2
E. H2O
A. CO2
Most chemolithotrophs are able to fix CO2 by using a metabolic pathway, known as the Calvin cycle, in which CO2 is used to ultimately generate glucose. As a result, these microorganisms can obtain all of their cellular carbon from CO2 and grow in the absence of organic compounds or sunlight.
The ocean is the largest biome on planet Earth, and its biomass is dominated by microbes. Aside from their importance to marine ecosystems, photosynthetic marine microbes also play a major role in composing the Earth's atmosphere. How do photosynthetic marine microbes affect Earth's atmosphere?
A. They produce 50% of Earth's oxygen gas.
B. They consume 50% of Earth's oxygen gas.
C. They produce 50% of Earth's nitrogen gas.
D. They consume 50% of Earth's nitrogen gas.
A. They produce 50% of Earth's oxygen gas.
Half of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere is produced by photosynthetic marine phytoplankton, while the other half is produced by land plants.
Early microbial ecologists knew that hydrogen gas is oxidized in soil and that ammonia is oxidized in sewage. How did these scientists determine that microbes are responsible for these ecological reactions?
A. by removing hydrogen gas and ammonia from soil and sewage samples and observing dead microbes under the microscope.
B. by applying heat and antimicrobial treatment to sewage samples and observing that nitrate was no longer formed
C. by adding pure cultures to sewage samples and detecting the formation of nitrate
D. by preparing pure cultures from soil and sewage samples and observing their metabolic reactions in the laboratory
B. by applying heat and antimicrobial treatment to sewage samples and observing that nitrate was no longer formed
Microbial ecologists eliminated microbes from soil and sewage samples by applying heat, acid, and antimicrobial treatments. Destruction of the microbes eliminated the oxidation of hydrogen gas and ammonia, indicating that the microbes were responsible for these reactions.
Microbial endosymbiosis, in a variety of diverse forms, is widespread in all ecosystems. Many interesting cases involve animal or human hosts. Endosymbiotic microbes make essential nutritional contributions to host animals. Ruminant animals such as cattle, as well as insects such as termites, require digestive bacteria to break down cellulose and other plant polymers. Even humans obtain about 15% of their nutrition from colonic bacteria. Intestinal bacteria such as E. coli and Bacteroides species grow as biofilms, organized multispecies communities adhering to a surface. Biofilms play major roles in all ecosystems and within parts of the human body. Microbial enzymes are required for digesting most kinds of plant fibers that we consume.
What is the primary function of ruminant microorganisms?
A. digestion of cellulose to organic acids
B. protection and defense against pathogens
C. fixation of nitrogen gas
D. fixati
A. digestion of cellulose to organic acids
Ruminant microorganisms are endosymbiotic organisms that live in the rumen of certain animals and are responsible for digestion of cellulose and other plant polymers. The breakdown of cellulose results in the production of organic acids, such as acetic acid and propionic acid, which are ultimately used as an energy source for the organisms.
E. intracellular bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, that inhibit macrophage apoptosis
Microbial endosymbiosis exists in a variety of diverse forms and is widespread in all ecosystems. Ruminant animals such as cattle require digestive bacteria to break down cellulose and other plant polymers. Many invertebrates, such as hydras and corals, harbor endosymbiotic phototrophs that provide products of photosynthesis in return for protection and nutrients. Bacteria that normally inhabit the human intestine and skin protect our bodies from infection by pathogens. Gut bacteria regulate development of our immune system and even send signals to the brain.
Astrobiologists study the origin of life in the universe and the possibility of life beyond Earth. Which of the following is not a reason why astrobiology involves microbiology?
A. Microbes were the first and only living organisms on Earth for 2 billion years.
B. Astronauts may have altered immune systems and be susceptible to infections due to long-term space travel.
C. Scientists are trying to colonize Mars with microorganisms from Earth in an effort to determine whether life can survive on other planets.
D. Microorganisms can live in extreme environments that are similar to those found in space.
C. Scientists are trying to colonize Mars with microorganisms from Earth in an effort to determine whether life can survive on other planets.
Microbiology plays a very important role in astrobiology. Not only did life on Earth consist solely of microorganisms for billions of years, but it is also likely that life beyond the planet will be microbial. Furthermore, there are concerns about the potential impact of space travel on the human immune system due to susceptibility to infections as well as bacterial mutations.
Which of the following statements is true about all microbes?
A. All microbes contain a nucleus.
B. All microbes are single cells.
C. All microbes contain a genome.
D. All microbes cause disease.
C. All microbes contain a genome.
All microbes contain a genome, which is the total genetic information contained in an organism's chromosomal DNA. Although viruses may have a DNA- or RNA-based genome, all other microorganism contain a DNA-based genome. The genes in a microbe's genome and the sequence of DNA tell us a lot about how that microbe grows and associates with other species.
Louis Pasteur used a swan-necked flask to demonstrate that
A. microbial fermentation can be used to make beer and wine.
B. dust in the air is a source of living microbes.
C. microorganisms cause disease.
D. microorganisms can arise from nonliving matter.
E. microorganisms can arise from cellular fission.
B. dust in the air is a source of living microbes.
Pasteur demonstrated that, after boiling, the contents in the swan-necked flask remained free of microbes, despite the access to air. As a result, Pasteur's experiments helped to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation.
While repeating Pasteur's experiment with the swan-necked flask, John Tyndall occasionally observed the opposite result. Tyndall noticed that the boiled broth in the swan-necked flask sometimes did give rise to microorganisms. Accordingly, he demonstrated that the broth was contaminated with _____
endospores
Some bacteria, for example, certain Bacillus and Clostridium species, can form endospores when environmental conditions are unfavorable. These endospores are heat-resistant forms of the bacteria that can lay dormant until environmental conditions are more favorable for survival and reproduction. Endospores can be destroyed by repeated cycles of boiling and cooling. These conditions can be attained in an autoclave, which uses steam pressure to reach and maintain temperatures in excess of 100°C.
Koch's postulates are criteria used to establish that
A. microorganisms can arise from nonliving matter.
B. inoculations can be used to prevent disease.
C. microbes can be classified based on genomic similarities.
D. a particular microbe causes a particular disease.
D. a particular microbe causes a particular disease.
Koch's postulates consist of four criteria that are used to establish a causative link between an infectious organism and a specific disease. Koch was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1905 for determining the causative agent of tuberculosis. Although Koch's postulates are still used today to determine whether a specific strain of microorganism causes a specific disease, there are limitations to the postulates, and individual diseases and pathogens may confound one or more of the criteria.
Identify which two of Koch's postulates would most likely not be fulfilled when trying to link a human virus to a particular disease.
Choose one or more:
A. The microbe is found in all cases of the disease but is absent from healthy individuals.
B. The microbe is isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
C. When the microbe is introduced into a healthy, nonhuman experimental host, the same disease occurs.
D. The same strain of microbe is obtained from a newly diseased host.
B. The microbe is isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
C. When the microbe is introduced into a healthy, nonhuman experimental host, the same disease occurs.
Viruses are highly specific, and it is difficult to culture viruses outside of their host target cells. In addition, most human viruses would not be able to infect and cause disease in an animal model host. Accordingly, when trying to link a virus with a specific human disease, it is difficult to culture the virus and find an appropriate susceptible experimental host.
During a period of time outside the host, a virus may become _____ and lose many factors that are required for infections. These viruses stimulate the immune system with much lower mortality than the fully virulent strains.
attenuated
Because attenuated viruses are unable to cause infection in their original hosts, they can be used for immunizations and vaccines. Heat treatment or aging for various periods are common approaches for attenuating a viral strain.
Which of the following is not a reason why opportunistic pathogens, such as Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus, are public health concerns?
A. They can be antibiotic resistant.
B. All individuals who are exposed to the pathogen will develop an infection.
C. They are commonly a part of the normal human microbiota.
D. They can enter a host via contaminated food and water.
E. They are abundant in hospitals and lead to nosocomial infections.
B. All individuals who are exposed to the pathogen will develop an infection.
Although opportunistic pathogens are generally harmless to healthy individuals, immunocompromised individuals are at high risk for the development of an opportunistic infection. These potential pathogens are widespread in the environment and are even a normal component of the human microbiota. Accordingly, it is no surprise that opportunistic infections account for a significant percentage of nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections.
The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine requires refrigeration. mRNA is much less stable than DNA and is prone to degradation. Thus, if Covid vaccine is not properly refrigerated, some of the mRNA may degrade. Based on your understanding of how the vaccine works (as described in the special topic), which of the following will likely result from a patient receiving a vaccine that was not properly stored or refrigerated? (Select all that apply.)
Choose one or more:
A. More antibodies to the spike protein (antigen) will be produced.
B. More SARS-CoV-2 virus particles will be eliminated from the host.
C. Fewer antibodies to the spike protein (antigen) will be produced.
D. Fewer SARS-CoV-2 virus particles will be eliminated from the host.
C. Fewer antibodies to the spike protein (antigen) will be produced.
D. Fewer SARS-CoV-2 virus particles will be eliminated from the host.
If mRNA is degraded, there will be fewer spike proteins produced (transcribed and translated)—and also fewer antibodies to help eliminate the SARS-CoV-2 virus particles.
What percentage of microbial species can be grown in pure culture in the laboratory?
A. 99.9%
B. 10%
C. 1.0%
D. 50%
E. 0.1%
E. 0.1%
Microorganisms are responsible for cycling many minerals essential for all life, including all atmospheric nitrogen gas and much of the oxygen. However, less than 0.1% of all microbial species can be cultured in the laboratory. Unculturable microbes make up the majority of Earth's biosphere, but this does not mean that we cannot study these microbes. Microscopy, PCR, and DNA sequencing are a few of the techniques that we can use to study unculturable microbes.
Compared to eukaryotic microorganisms, bacteria are able to evolve very quickly, which allows these microorganisms to adapt to new environments, use a variety or resources, and develop antibiotic resistance. Which of the following sets of characteristics allow bacteria to evolve so rapidly?
A. Large population, rapid growth rate, transformation
B. Small population, rapid growth rate, anaerobic
C. Large population, rapid growth rate, sexual reproduction
D. Rapid growth rate, anaerobic, sexual reproduction
E. Large population, slow growth rate, anaerobic
A. Large population, rapid growth rate, transformation
Bacteria are ubiquitous and abundant. A rapid growth rate allows for exponential growth under favorable environmental conditions. In addition, the unique characteristic of transformation, or the ability to take up naked DNA, allows antibiotic resistance, as well as other favorable adaptations, to spread through a population and be passed on to daughter cells.
Identify the three domains of life according to the classification system developed by Carl Woese.
Choose one or more:
A. Prokarya
B. Archaea
C. Viruses
D. Eukarya
E. Bacteria
B. Archaea
D. Eukarya
E. Bacteria
According to the taxonomic system developed by Carl Woese in 1977, Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya are the three domains of life.The domains were identified based on analysis of small subunit rRNA sequences. Although bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, rRNA analysis indicates that they belong to two distinct domains. In fact, the genetic sequences of archaea differ as much from those of bacteria as from those of eukaryotes.
Which of the following is true of viruses?
A. They have large genomes.
B. They are eukaryotic.
C. They are prokaryotic.
D. They are not cells.
D. They are not cells.
Viruses are neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic since they are not cells. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites and usually have small genomes.
The figure below shows Louis Pasteur and his swan-necked flask. This apparatus was used to show that
A. bacteria divide by binary fission.
B. boiling kills microbes.
C. living things cannot arise in sealed containers.
D. oxygen does not allow spontaneous generation.
D. oxygen does not allow spontaneous generation.
Redi showed sealed containers prevented maggots from arising in meat and Spallanzani showed that sealed broth that had been boiled also did not spoil, but both experiments were criticized for excluding oxygen. Pasteur's swan-necked flask is explicitly "open to air," so more effectively refuted spontaneous generation.
Which of the following is a difference between antiseptics and antibiotics?
A. Antibiotics can be taken internally but antiseptics cannot.
B. Antiseptics can be taken internally but antibiotics cannot.
C. Antiseptics kill microbial cells but antibiotics do not.
D. Antibiotics kill microbial cells but antiseptics do not.
A. Antibiotics can be taken internally but antiseptics cannot.
Both antiseptics and antibiotics can kill microbial cells. However, antiseptics cannot be taken internally as they are harmful to patients. Antiseptics are used externally on skin, and also on inanimate objects.