Chapter 5, Lesson 3: Connective Tissue
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 5, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Connective tissue
Abundant type of tissue where cells may not be in direct contact; supports, connects, and protects organs with varying avascularity
Functions of connective tissue
Connecting organs
Support and movement
Physical and immune protection
Heat production
Internal transport and storage
Fibrous connective tissue
Connective tissue made up of many types of cells; types include loose, dense regular/irregular, areolar, and reticular
Fibroblasts
Fibers in fibrous connective tissue; the ground substance of the matrix
Macrophages
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that phagocytize (eat) foreign material and activate immune system
Leukocytes
White blood cells in fibrous connective tissue; made of up neutrophils and lymphocytes (anti-bacteria, toxins, and foreign agents)
Mast cells
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that secrete substances to inhibit blood clotting and dilate blood cells
Adipocytes
Cells in fibrous connective tissue that store triglycerides, or fat molecules
Collagenous fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; makes up 25% of the body’s proteins and is tough, flexible, and stretch-resistant to make up tendons, ligaments, and deep skin layers
Reticular fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; made up of collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein to make up spleen and lymph nodes
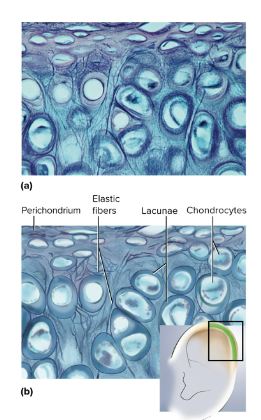
Elastic fiber
A fiber in fibrous connective tissue; made up of elastin to allow stretching and recoiling particularly in elastic cartilage in external ears
Proteoglycans
Part of ground substance in fibrous connective tissue made of brush-shaped molecules; holds tissues together with gravy-like colloids
Adhesive glycoproteins
Part of ground substance in fibrous connective tissue made of protein-carbohydrate complexes; binds tissue components
Loose connective tissue
Fibrous connective tissue with gel-like ground substance between cells; includes areolar and reticular loose tissue
Dense connective tissue
Fibrous connective tissue where the fibers fill in space between cells and fiber orientations vary; regular or irregular
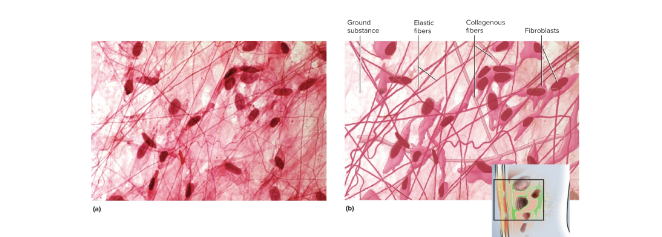
Loose areolar tissue
Loose connective tissue with randomly organized fibers and blood vessels; found in epithelium for nutrition and leukocyte supply and forms layers between skin and organs and in between muscles
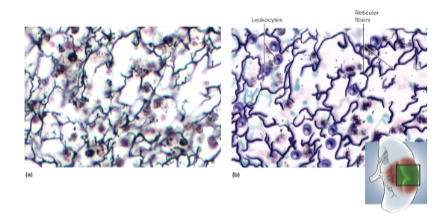
Loose reticular tissue
Loose connective tissue with mesh of reticular fibers and fibroblasts, supports lymphatic organs and found in spleen and bone marrow
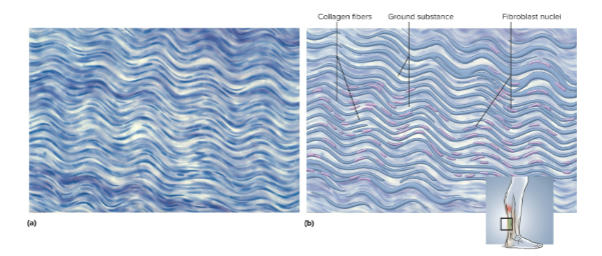
Dense regular connective tissue
Densely packed, parallel collagen fibers with wavy elastic tissue sheets; helps attach muscles and bones with tendons and ligaments
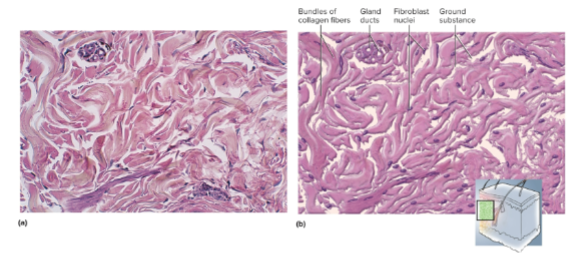
Dense irregular connective tissue
Densely packed, randomly arranged collagen fibers to withstand stresses; found in deeper skin layers and capsules around organs
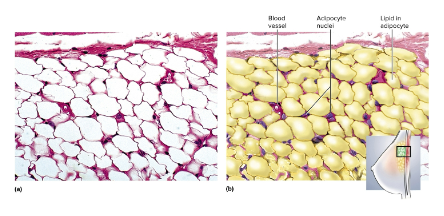
Adipose tissue
Tissue made of fat cells/vacuoles (adipocytes) with nuclei pushed to sides; stores energy, cushions body and organs, and insulates or produces heat
White fat
The main type of fat in adults; provides thermal insulation and cushioning
Brown fat
The main type of fat in children; provides heat generation and colored by blood vessels
Cartilage
Stiff connective tissue with flexible matrix; gives shape to ear, tip of nose, and larynx—avascularity slows healing
Types include hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage
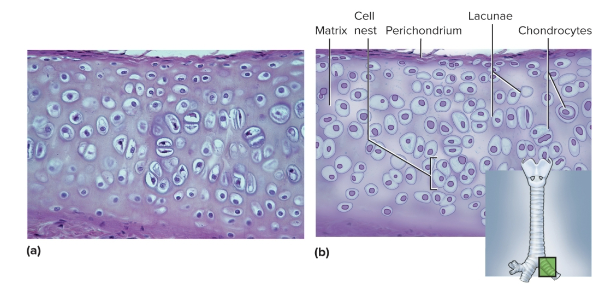
Hyaline cartilage
Cartilage with a clear appearance due to fine collagen fibers; eases joint movement, holds airway open, and moves vocal cords—located in trachea, larynx, fetal skeleton
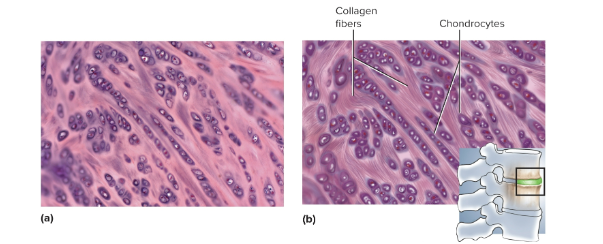
Fibrocartilage
Cartilage with large bundles of collagen fibers; resists compression and absorbs shock in intervertebral discs and meniscus
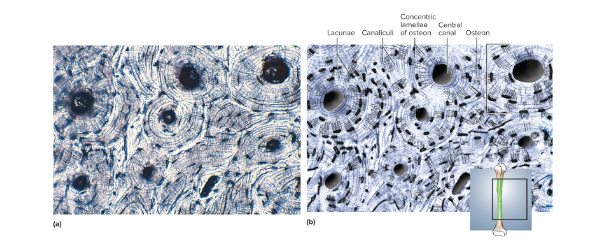
Bone (osseous) tissue
A type of calcified connective tissue with cells arranged around a central canal
Spongy bone
A porous type of bone covered by compact bone; found in heads of long bones and middle of flat bones
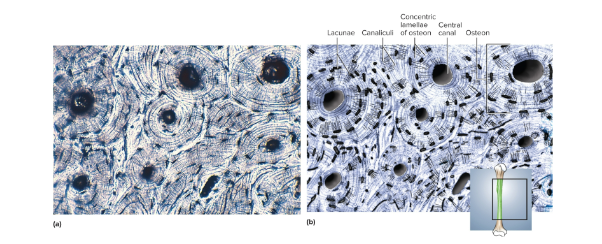
Compact bone
A dense, calcified tissue with no visible space; cylindrical arrangement with canals and vertically oriented blood vessels in central canal
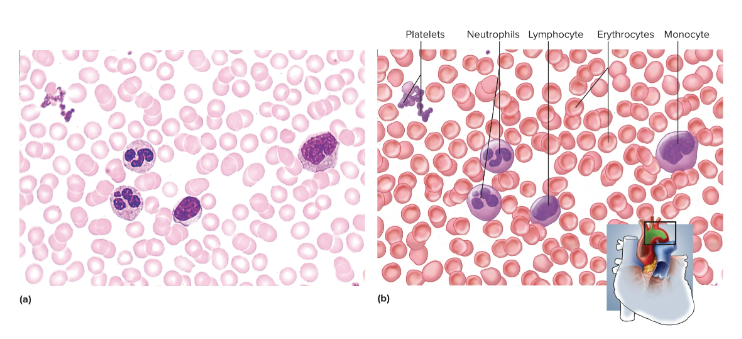
Blood
A type of fluid connective tissue that transports cells and matter from place to place
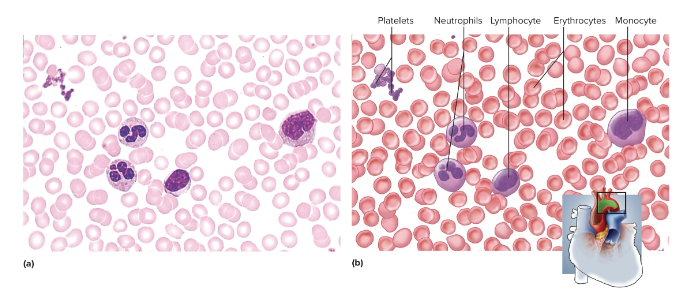
Plasma
Blood’s ground substance; contains red/white blood cells and platelets and synthesizes antibodies