MH Lecture 6 - Schizophrenia and ADHD
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Dopamine
not exactly the “pleasure neurotransmitter”
critical for motivated behaviour and learning
helps us direct our attention to meaningful stimuli
Dopamine and Learning
prior to CS-US training — dopamine (DA) spikes at food/reward delivery (R)
after conditioning — DA spikes at CS presentation
DA helps us learn CS-US associations
What gets our attention — Predictive Stimuli
the predictiveness principle — we pay more attention to stimuli if they are “predictive”
we pay more attention if they predict something that we like or dislike
What do we ignore
ignoring without learning
stimuli that lacks salience
things we learn to ignore
non-predictive stimuli
Schizophrenia Diagnostic Criteria
2 or more of the following (incl at least 1,2, or 3)
delusions
hallucinations
disorganised speech
grossly disorganised or catatonic behaviour
negative symptoms
Symptoms must cause dysfunction
continuous signs of disturbance persist for at least 6 months
exclusions for other conditions
Schizophrenia Symtom Clusters
positive symptoms (added)
negative symptoms (taken away)
cognitive symptoms
Schizophrenia Positive Symptoms
Delusions
persecutory, grandiose, referential
Hallucinations
most commonly auditory, can involve other senses
Disorganised speech/thinking
word salad
Disorganised behaviour
agitated or repetitive motor behaviours, difficulty w basic tasks
Catatonic behaviour
unresponsive/frozen
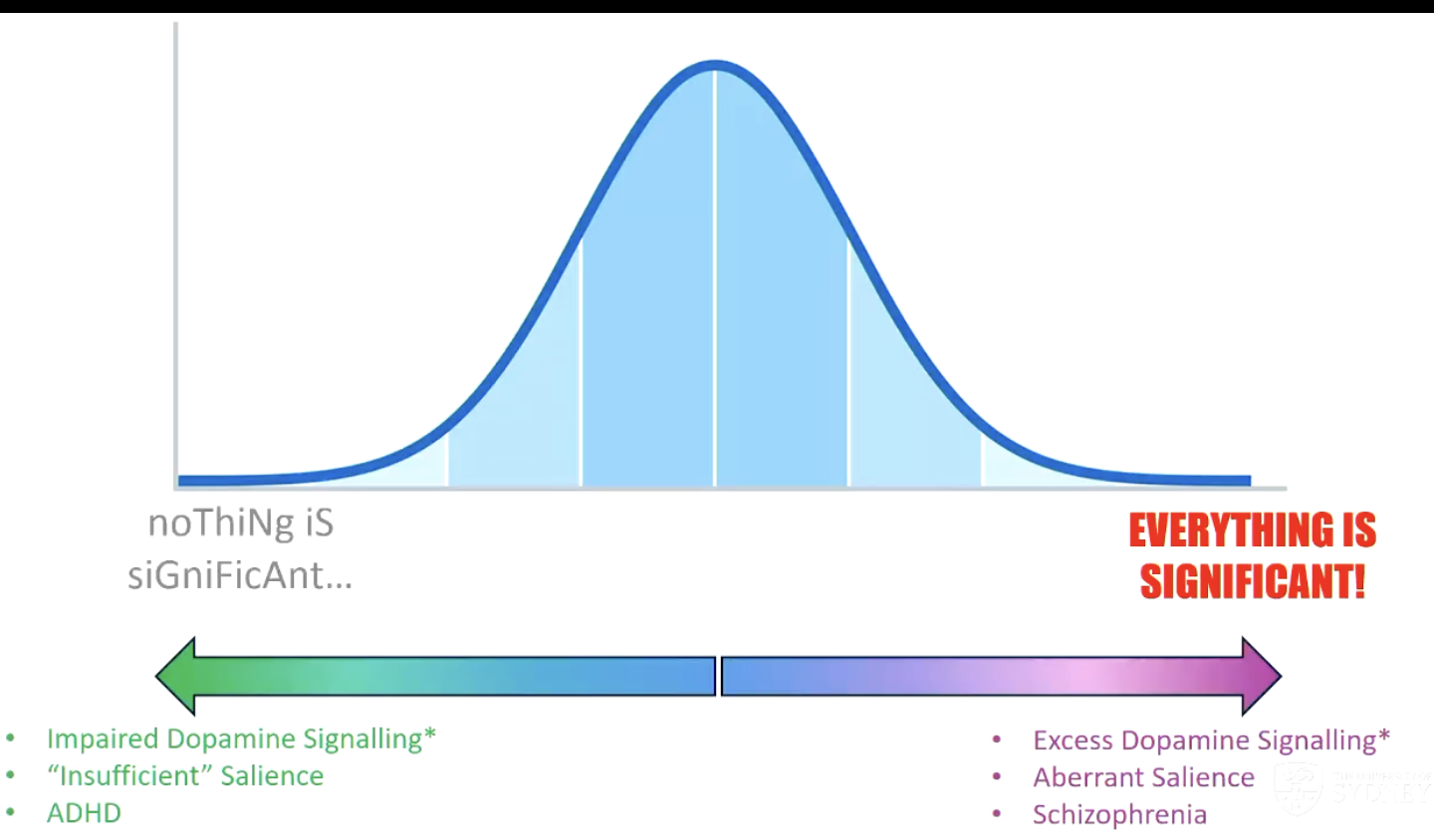
Dopamine hypothesis of Schizophrenia
excess dopamine activity in the striatum causes “aberrant salience” and “failures to ignore”
attention is attracted by meaningless stimuli
hallucinations/delusions develop as a result
Latent Inhibition
tests normal processes of learning to ignore irrelevant stimuli
people w schizophrenia do not show strong latent inhibition effect
failure to ignore is a feature of the condition
ADHD Presentation — Inattention
more than 6 (kids) — more than 5 (adults)
lack of attention to detail
difficulty sustaining attention in play or work
does not appear to attend when spoken to directly
leaves tasks unfinished
difficulties w organisation
avoid tasks that require sustained mental effort
loses things necessary for tasks/activities
easily distracted by extraneous stimuli/unrelated thoughts
forgetful in daily activities
ADHD Presentation — Hyperactivity
more than 6 (kids) — more than 5 (adults)
fidgets
leaves seats in inappropriate situations
runs about or climbs in inappropriate situations
unable to play/engage in leisure activities quietly
on the go
talks excessively
prematurely blurts out answers
difficulty waiting turn
interrupts
ADHD Diagnostic Criteria
persistant pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity
symptoms present before 12 years of age
symptoms present in 2 or more settings
causes dysfunction
not explained by schizophrenia
Dopamine Hypothesis of ADHD
evidence of disrupted DA activity
hyperactive DA transporter
decreased sensitivity of DA receptors
Representation of Dopamine Signalling
SCZ Treatment
Antipsychotics
dopamine antagonists
block activity at a specific subtype of DA receptor (dampens down the excess dopamine and calms down some of the positive symptoms)
ADHD Treatments
Amphetamines
dopamine agonists
increase release and/or prevent reuptake of dopamine
d-amphetamine not methamphetamine given
Problem of Symptom Similarity
prior to onset of first psychotic episode — person w prodromal schizo may experience attentional challenges and be diagnosed w ADHD (many people w SCZ have additional diagnosis of ADHD)
what would happen if person w SCZ given amphetamine — induces psychotic episodes
common symptom of disrupted attentional filtering is the same but biological mechanisms are polar opposites