Geography Chapter 15 - Groundwater & Karst Topography
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Inputs vs Outputs
Inputs = water added to the system
Example: Precipitation
Outputs = water is lost from the system
Example: Evapotransportation
What is evaporation?
moisture is lost to the atmosphere through the wind and sunlight
rates are affected by temperature, wind speed, humidity
What is Transpiration?
biological process by which water is lost from a plant
Rates depend on time of year, type + amount of vegetation, availability of moisture, and the length of the growing season
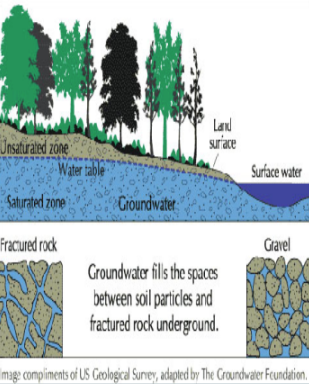
What is Groundwater?
fresh water (from raining or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces between rock
can stay underground for hundreds to thousands of years
What is Groundwater? pt. 2
can come to the surface and help fill rivers, streams, lakes, etc.
can also come to the surface as a spring or be pumped from a well
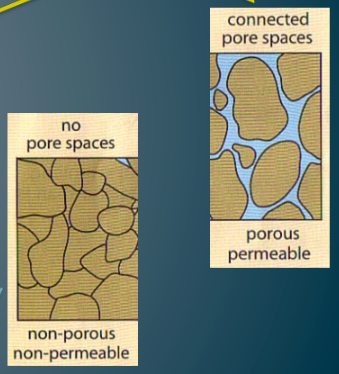
What is Porosity?
In order for groundwater to exist, there has to be porous layers
These are spaces within the soil which allows water to flow through them and be stored

What is Permeability?
Permeable = the ability for water to pass through rock layers
Impermeable = the inability for water to pass through rock layers
What is the Importance of Groundwater?
In the prairies groundwater is used extensively for crop irrigation
Areas with no mountain ranges with no rain rely on groundwater as their water source
What are Groundwater zones?
When water infiltrates the ground a section of rock becomes saturated (zone of saturation)
The top of the saturated rock/soil is the water table
The portion of the rock that is not 100% saturated is called the zone aeration
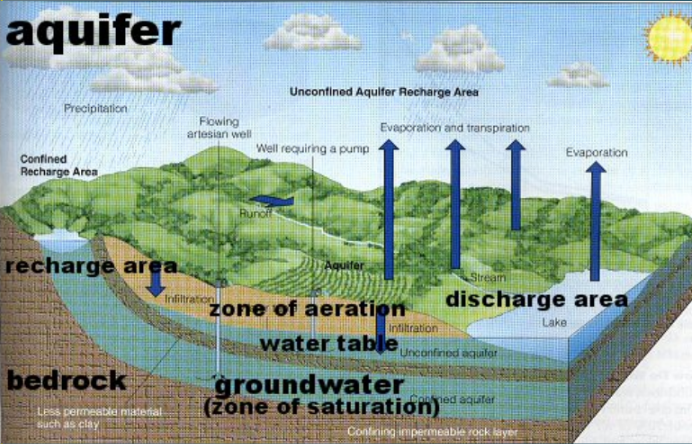
What is an aquifer?
Rock layer that can store and yield water
In dry areas aquifers provide clean water for drinking and irrigation by drilling a well
Recharge vs Discharge Diagram
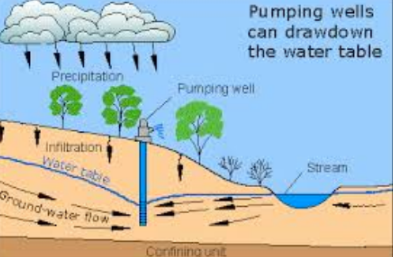
Aquifers: Ordinary Wells
Ordinary Wells are located in-between permeable rock
Water is not under pressure and is forced to rise with a pump
Aquifers: Artesian Well
Artesian Well is drilled through the ground
Confined between two impermeable rock layers which causes a build up of pressure which causes the water to rise on its own

What are some potential threats to our Groundwater?
contamination + Overuse and depletion
How do Karst Landforms form?
Process is called: Carbonation
Limestone and Dolostone
Landforms created by groundwater
Travertine Terraces:
Found in areas in where there is an abundant amount of hot groundwater
Hot water carries dissolved material and when it reaches the surface it quickly cools and deposits minerals on existing rock

Karst Landscapes
Caves or Caverns
Found in areas with highly soluble rock such as limestone
Water moves through the rock, dissolving limestone

Sinkholes
As caverns increase in size the support decreases and the ground collapses
Forms a depression (sinkhole)

Why does Florida have so many sinkholes?
Most of Florida peninsula is made up of limestone and dolostone overlain by sand and clay
Carbonate rocks may dissolve (solution) forming karst terrain