oxidative phosphorylation and lipid metabolism transport
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the chemiosmotic theory?
The proton concentration gradient is the energy reservoir that drives ATP formation
as electrons pass through the ETC, protons get pumped into the intermembrane space. This generates the proton motive force (PMF)
protons move back across the intermembrane space through ATP synthase
How does the proton gradient generated by the ETC drive ATP synthesis?
It serves as an energy reservoir due to differences in H+ concentration
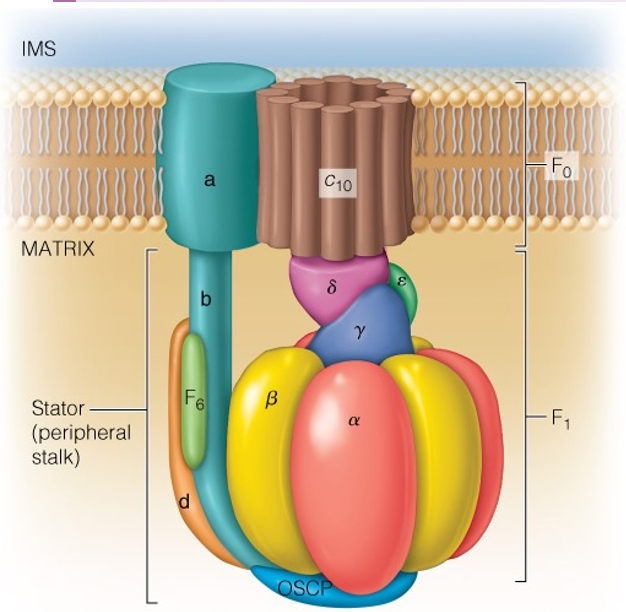
How does the gamma subunit interact with the beta subunits to drive ATP synthesis?
every rotation causes conformational changes in the beta subunits which drives ATP synthesis
Why is it advantageous for there to be three active sites for driving ATP synthesis?
Each subunit has the ability to control ADP binding. This controls the rate of ATP synthesis
How does ATP get out of the matrix?
By an ADP-ATP translocator
What is uncoupling?
The process of releasing H+ back to the matrix without making ATP. Stimulates O2 consumption, therefore, heat is created
Hibernating animals and newborn babies have brown fat. What is this tissue used for, and what does it have to do with uncoupling?
mitochondria rich fat, used as energy storage during hibernation, has a natural uncoupling mechanism that allows for ATP synthesis
why are fats a better source of energy storage than carbohydrates?
They yield more energy and are more compact in storage
Under certain conditions, fatty acids are released from adipose tissue. What are these conditions?
When other sources are not available (?)
How does the fat releasing process work, and how is it controlled?
epinephrine and glucagon are released into the blood when glucose conc and insulin conc are low
They bind to receptors on the surface of adipocytes
when bound, adipocytes activate TAG metabolism
How are fats from our diet transported to other tissues?
exported into the blood by transporter proteins or diffusion
serum albumin binds to the fatty acids
FAs transported to where they are needed
Why is LDL “bad” cholesterol?
It can lead to buildups in your arteries
they mostly contain cholesterol and cholesteryl esters
Why is HDL “good” cholesterol?
They get rid of LDL
They decrease plasma cholesterol
How does ADP get into the matrix?
by an ADP-ATP translocator
How does Pi get into the matrix?
by a phosphate carrier symporter