C6 Rates
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is rate of reaction?
a measure of how quickly reactants form products
What equations are used to calculate the mean rate of reaction? (2)
quantity of reactant used / time
quantity of product formed / time
What are the units of rate of reaction? (2)
g/s
cm³/s
What are the usual units for mass (in chemistry)?
g
What are the units for volume
cm³
A steep gradient on a rate of reaction graph shows what?
fast reaction
What does it mean when a graph showing rate of reaction levels off?
the reaction is complete and no more product is produced
What is concentration?
The number of particles in a given volume
What is pressure?
A measure of how close together gas particles are
What is surface area?
The area of a solid that is exposed to the surface
How could you increase the surface area of a solid reactant?
Break it into smaller pieces
Which has a larger surface area: 10 g of magnesium ribbon or 10 g of magensium powder?
10g of magnesium powder
What happens to the rate of a reaction when the concentration of reactants in solution is increased?
rate increases
What happens to the rate of a reaction when the pressure of reacting gases is increased?
rate increases
What happens to the rate of a reaction when the temperature is increased?
rate increases
What happens to the rate of a reaction when the surface area of solid reactants increases?
rate increases
What happens to the rate of a reacton when a solid reactant is broken into smaller pieces?
rate increases
What methods can you use to collect a gas? (2)
a gas syringe
in an upturned measuring cylinder underwater
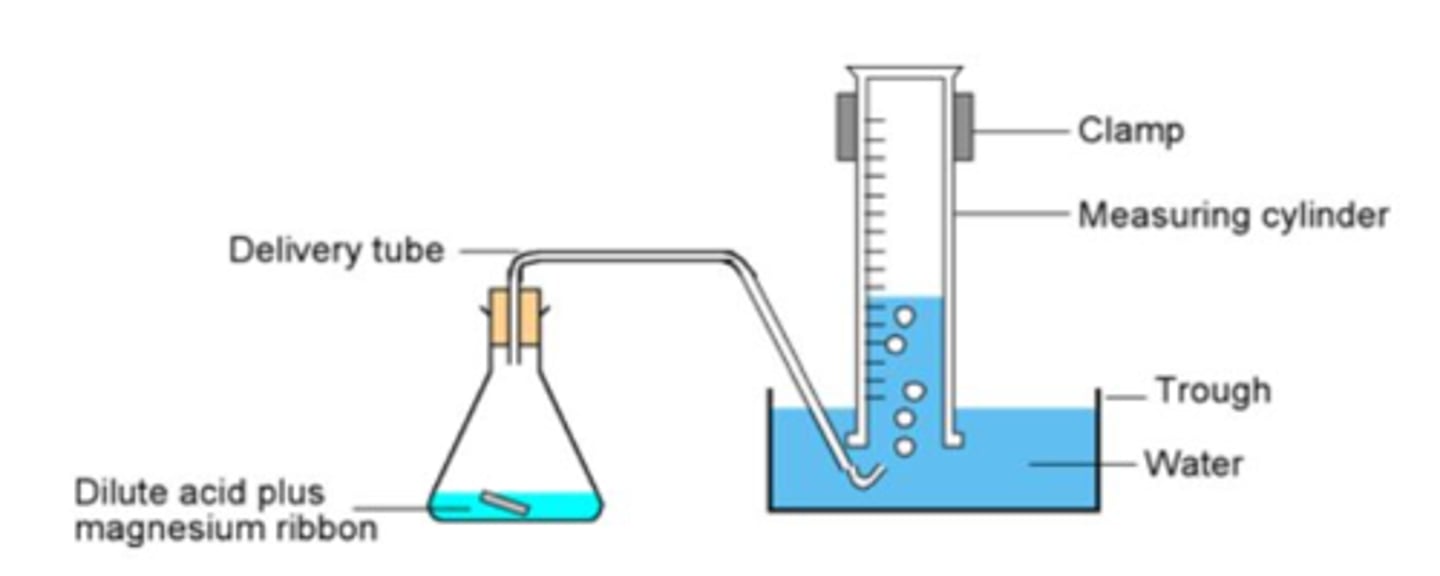
What piece of apparatus should be used to measure 20 cm³ of acid?
a measuring cylinder
When will solutions turn cloudy?
When an insoluble solid is produced
Why can measuring the time taken for a solution to turn cloudy indicate the rate of reaction? (2)
The solution turns cloudy when the product is formed
Measuring the time allows us to use quantity of product formed / time
What is collision theory?
for chemical reactions to occur, reacting particles must collide with sufficient energy
What is the activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy that reacting particles must collide with for a reaction to occur
What happens if reacting particles collide with energy less than the activation energy?
no reaction - they stay as reactants
What happens if reacting particles collide with energy greater than or equal to the activation energy?
the reaction takes place - the reactants form products
What does the term 𝒇𝒓𝒆𝒒𝒖𝒆𝒏𝒄𝒚 𝒐𝒇 𝒄𝒐𝒍𝒍𝒊𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒔 mean?
the number of collisions that occur in a given time period eg. collsions per second
How can you increase the rate of a reaction? (2)
Increase the frequency of collisions
Increase the energy of collisions
Why does increasing the surface area increase the rate of a reaction? (3)
increases the number of particles available for collisions
increases the frequency of collisions
increases the chances of successful collisions with energy greater than the activation energy
Why does increasing the concentration of reactants increase the rate of a reaction? (3)
increases the number of particles in a given volume
increases the frequency of collisions
increases the chances of successful collisions with energy greater than the activation energy
Why does increasing the pressure of reacting gases increase the rate of a reaction? (3)
causes the particles to become closer together
increases the frequency of collisions
increases the chances of successful collisions with energy greater than the activation energy
Why does increasing the temperature increase the rate of a reaction? (3)
increases the kinetic energy of particles
increases the frequency and energy of collisions
increases the chances of successful collisions with energy greater than the activation energy
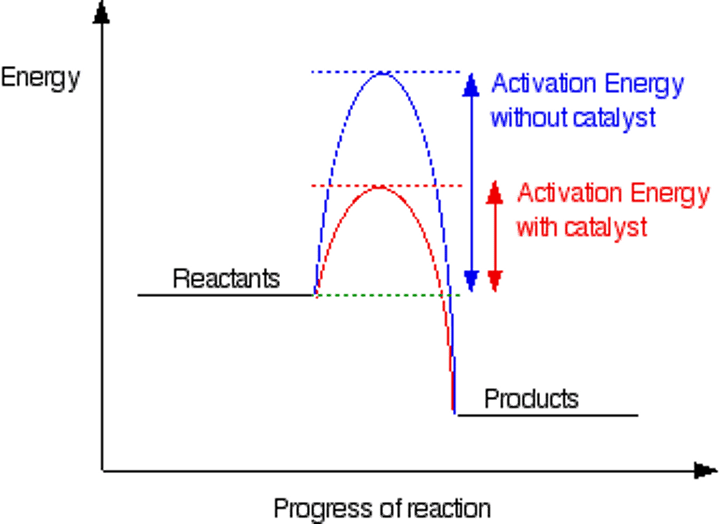
What are catalysts?
Substances that increase the rate of chemical reactions without getting used up themselves
Why does using a catalyst increase the rate of a reaction? (2)
they offer a different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
this increases the chances of succesful collisions with energy greater than the activation energy
What does a reaction profile for a catalysed reaction look like?
a profile with a lower energy reaction pathway for the reaction with a catalyst
What does this symbol ⇌ mean?
a reversible reaction
What is a reversible reaction?
A reaction in which reactants form products and the products can react to form the reactants
How can the direction of a reversible reaction be changed?
by changing the conditions (e.g. heat for one direction, cool for the other direction)
What is an exothermic reaction?
A reaction that transfers energy to the surroundings
What is an endothermic reaction?
A reaction that takes in energy from the surroundings
If a reversible reaction is exothermic in one direction, what type of reaction is the reverse reaction?
Endothermic