Lesson 3 - Community Ecology
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What makes up a realized niche?
The result of species interactions
Competition
Predation
Parasitism
Mutualism
What is Competition?
An interaction in which two species that depend on the same limited resource(s) each have a negative effect on the other
Interspecific – between species
Intraspecific – within a species
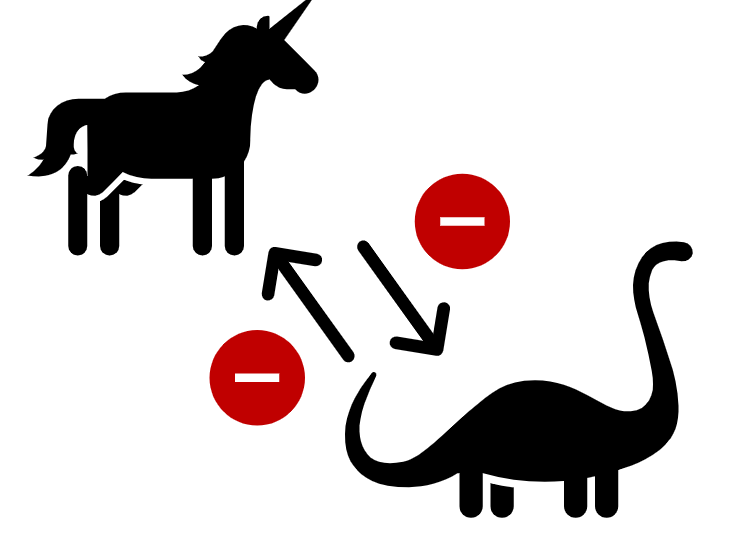
Exploitative Competition
Indirect
Refers to the indirect competition between individuals or species for limited
resources within an environment.If one competitor uses a resource, it is not available for other competitors.
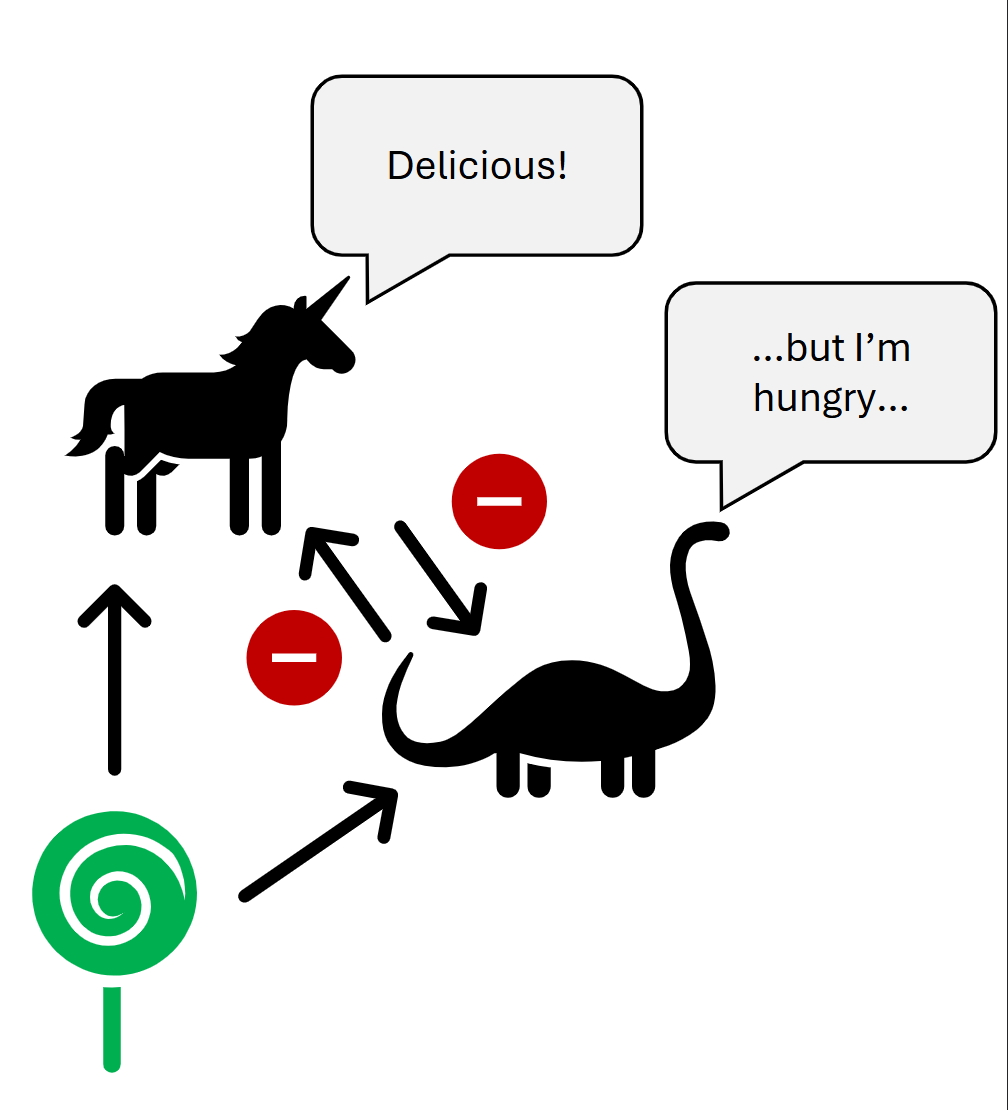
Interference Competition
Direct
Refers to direct interactions between individuals or species that impede the access of competitors to essential resources.
Physical interference between individuals, usually for a resource.
Competitive Exclusion Principal
States that if two species with identical niches compete, then one will inevitably drive the other to extinction.
So how do competitors co- exist?
What three things can happen when competitors overlap?
1) Temporary co- existence (at reduced carrying capacity)
2) Competitive exclusion
3) Niche partitioning
Temporary Co-existence
Both species continue to live in the area, but at lower numbers.
But this tends to only last in the short term.
i.e., temporary
Competitive Exclusion
One of the species disappears from that area.
Not usually random
Some species are better competitors than others.
If two species’ niches perfectly overlap, the species that is better adapted to the niche will eventually outcompete the other.
One species might arrive before the other.
Priority effects refer to the influence that the order and timing of species arrival have on a community
Competitors may inhibit other species from establishing
Chance
Disturbance events may impact the abundance of one species more than the other
Niche Partitioning
Both species continue to co-exist, but they diverge to occupy slightly different ecological niches within the shared habitat.
i.e., a change in the realized niche
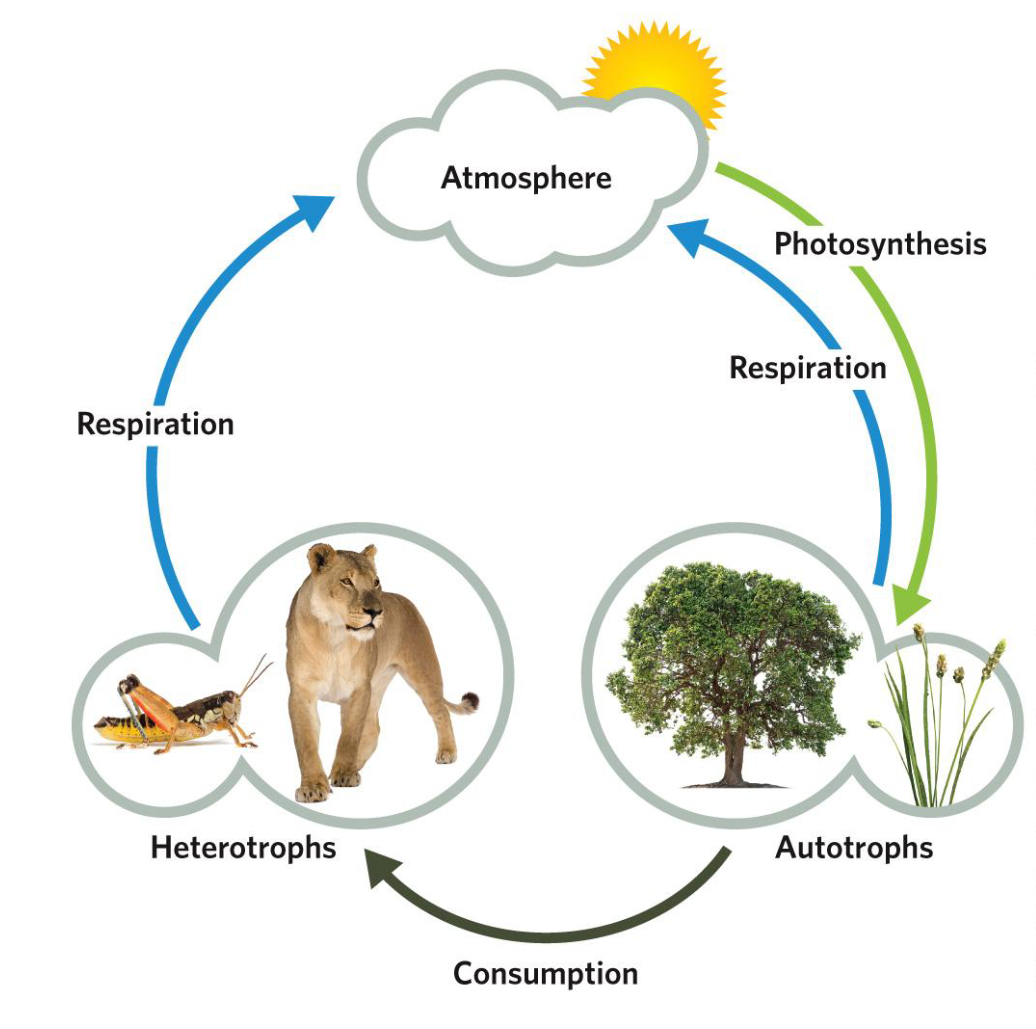
What are plants role in an ecosystem?
Plants are mostly primary producers
They provide the food that almost all of the other organisms present depend on
Autotrophs
Photosynthesis results in oxygen in aquatic environments and the atmosphere
Carbon storage in plant tissues
Also provide the physical structure of a community. In a forest, for example, root systems create a structure inhabited by mycorrhizal fungi
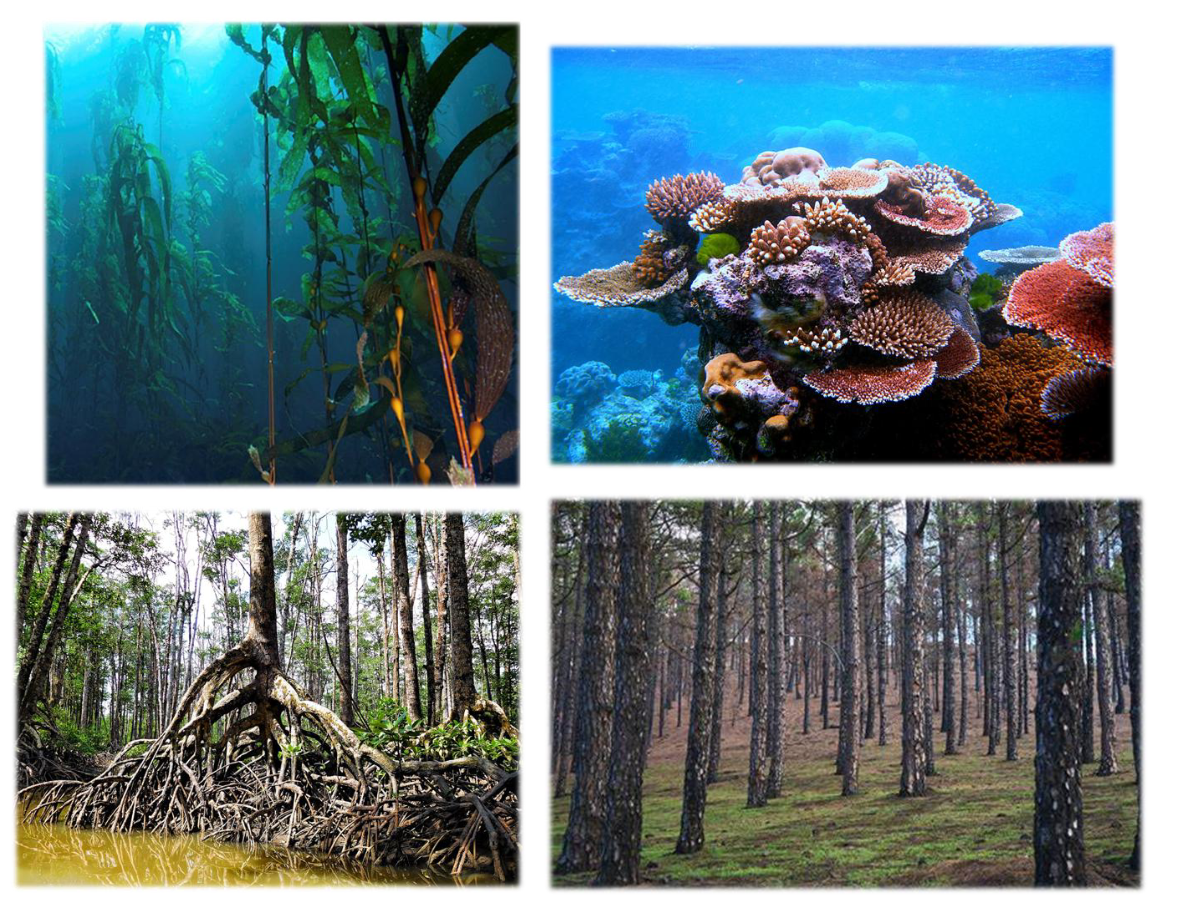
Foundation Species
Shape their community!
Provide an ecological foundation for many other species, even though they might not benefit from the interactions.
e.g., physical foundation or infrastructure for a community or ecosystem
Often highly abundant
Examples
Many trees, Corals, Kelp

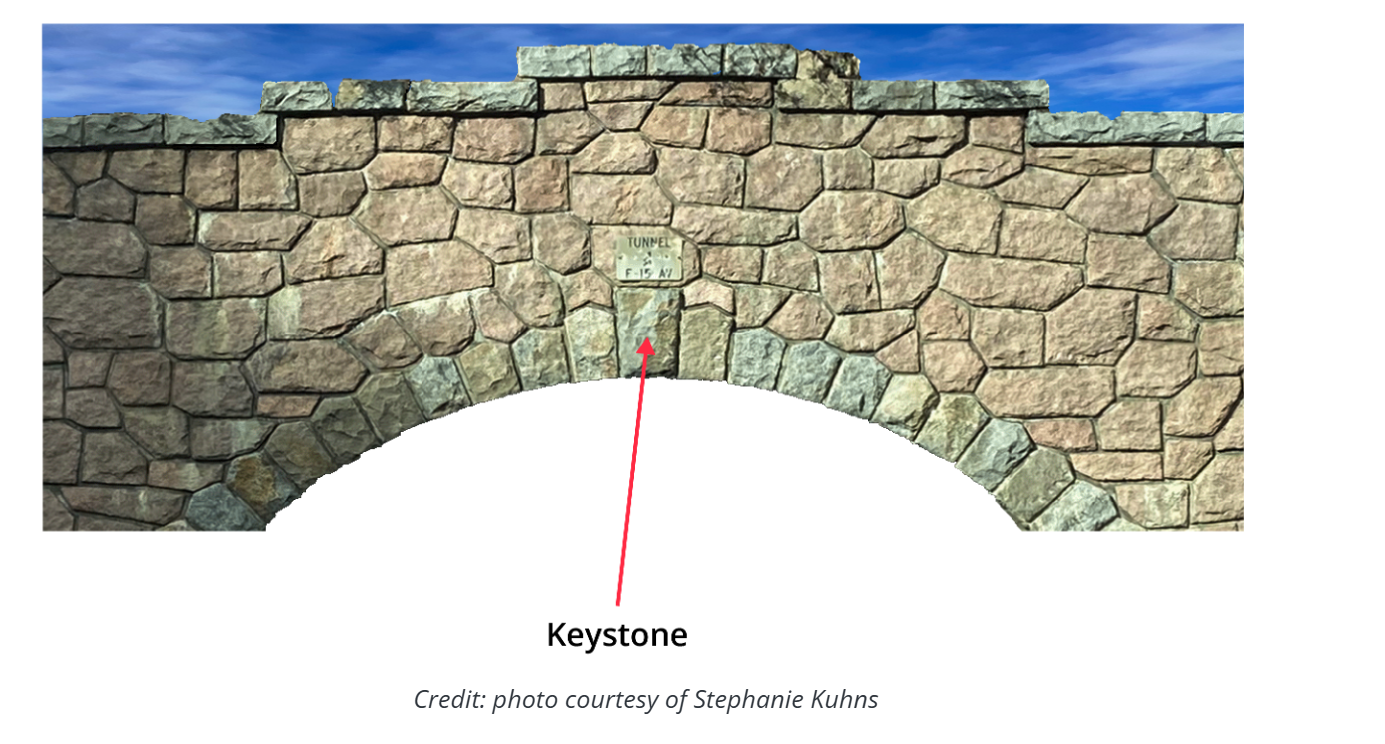
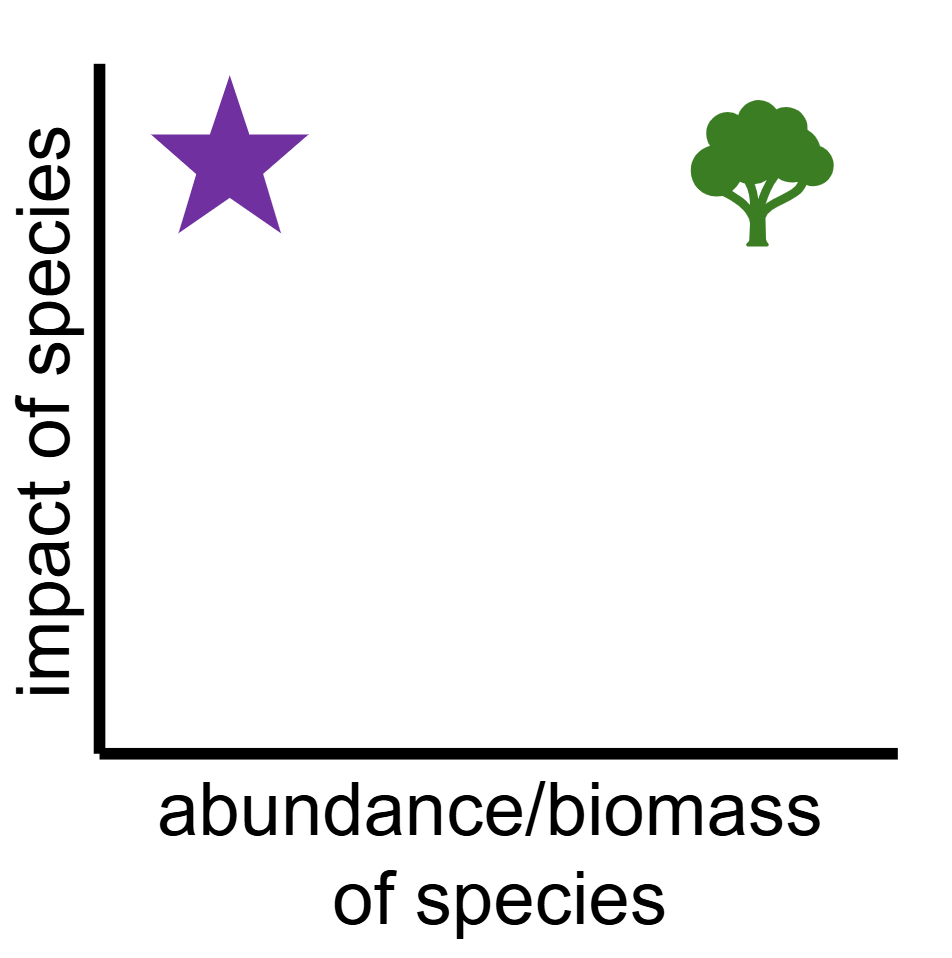
Keystone Species
A disproportionately large impact on its environment relative to its abundance or biomass
Can be species in many types of ecological roles (Predators, Mutualists)
Examples: (Wolves, Otters, Starfish)
Biomass
The total mass of living organisms in a specific area
Foundational Species (High Biomass + High Impact!)
Keystone Species (Low Biomass + High Impact!)
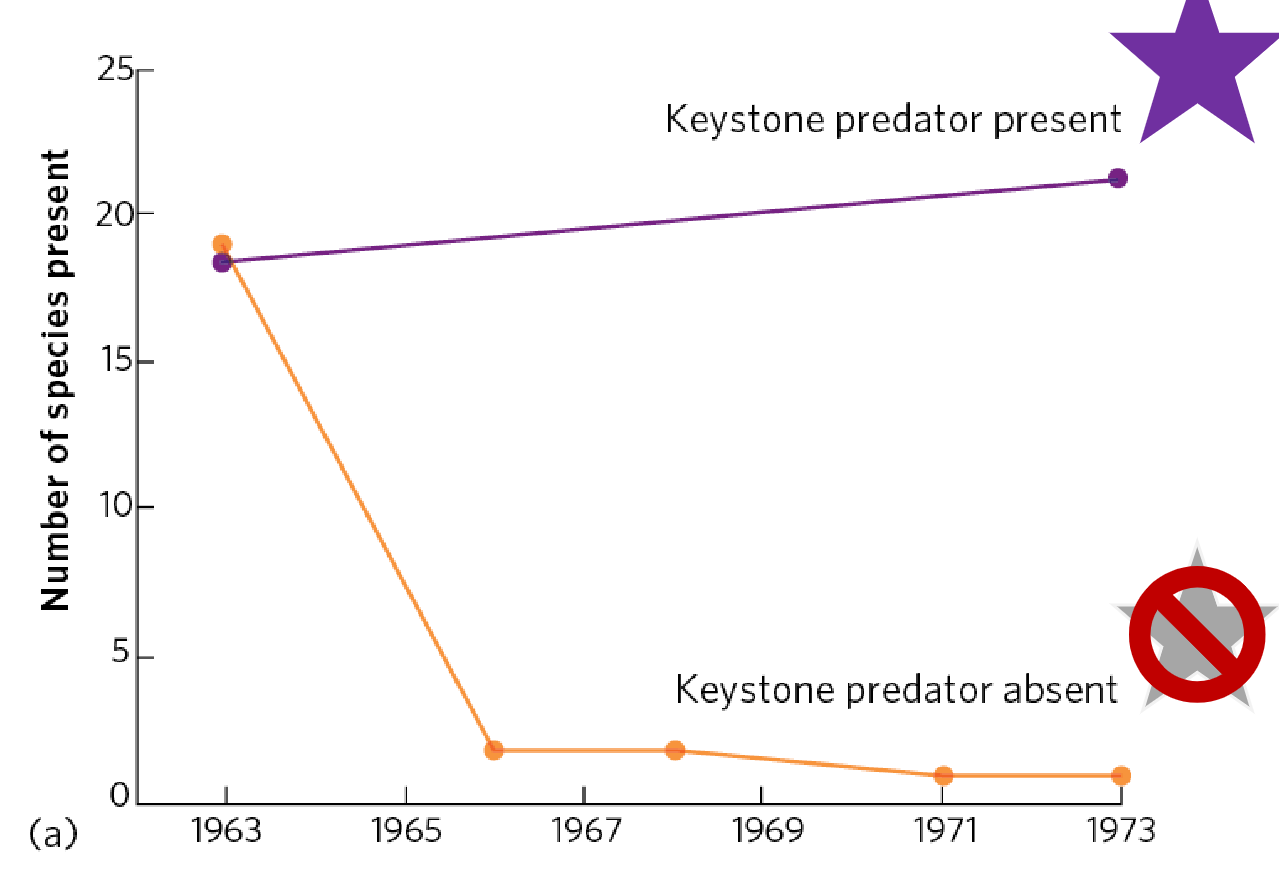
Example of a Keystone Species (Starfish)
When Pisaster was removed from the ecosystem
The population of mussels dramatically increased and dominated space on the rocks
Invertebrate community shifted from diverse assemblage of species to a dense mussel bed
Reduced overall biodiversity
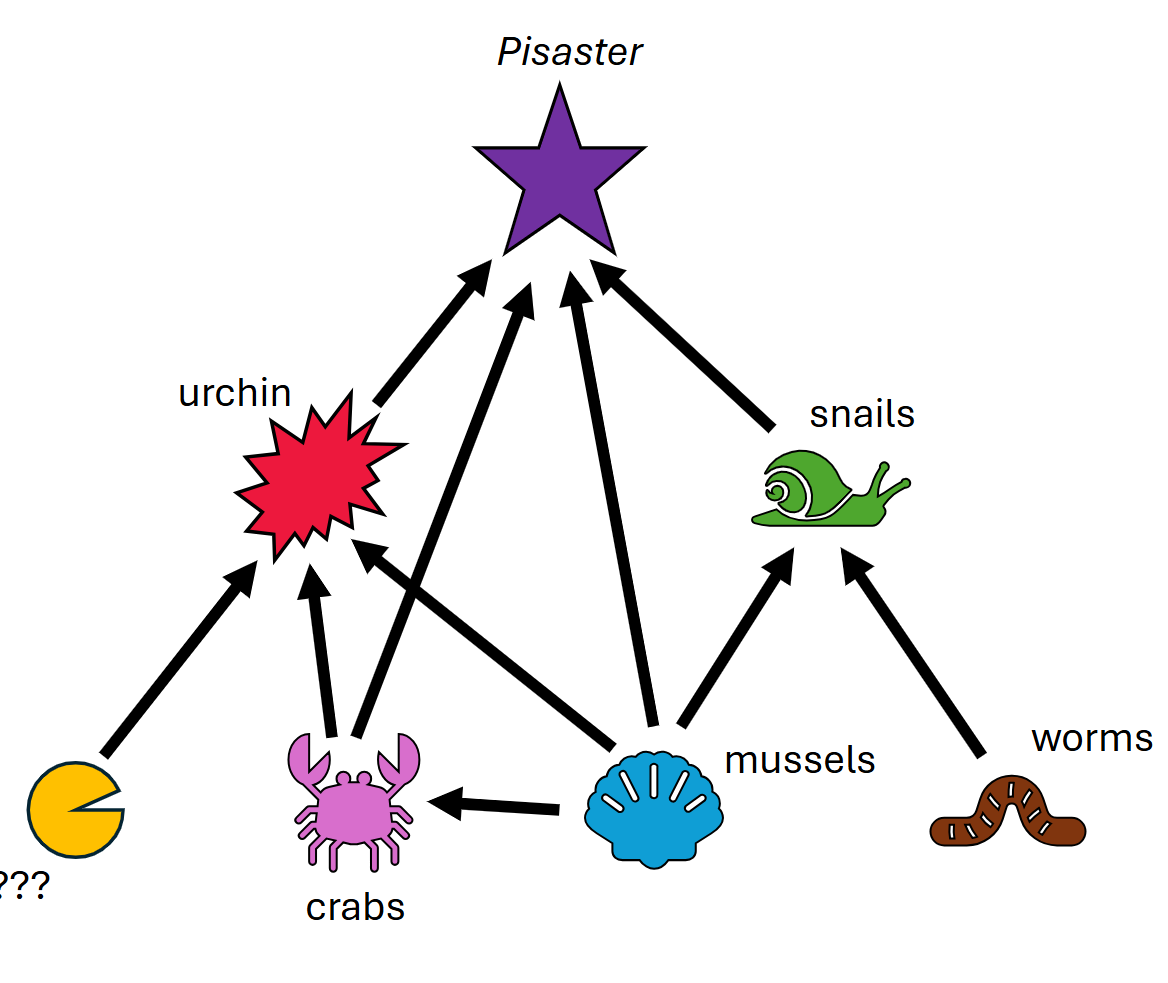
Interactions Within A Food Web
Direct interactions occur between two species where one directly affects the other
Predation or mutualism
Indirect interactions occur when the relationship between two species is mediated by one or more additional species
Trophic cascade → A change in a food web—usually caused by a change in an important predator—that causes changes in the abundance of other species in the web
Ecological Network
A representation of the biotic interactions in an ecosystem, in which species are connected by interactions
Organisms are interconnected via the various relationships within an ecological network
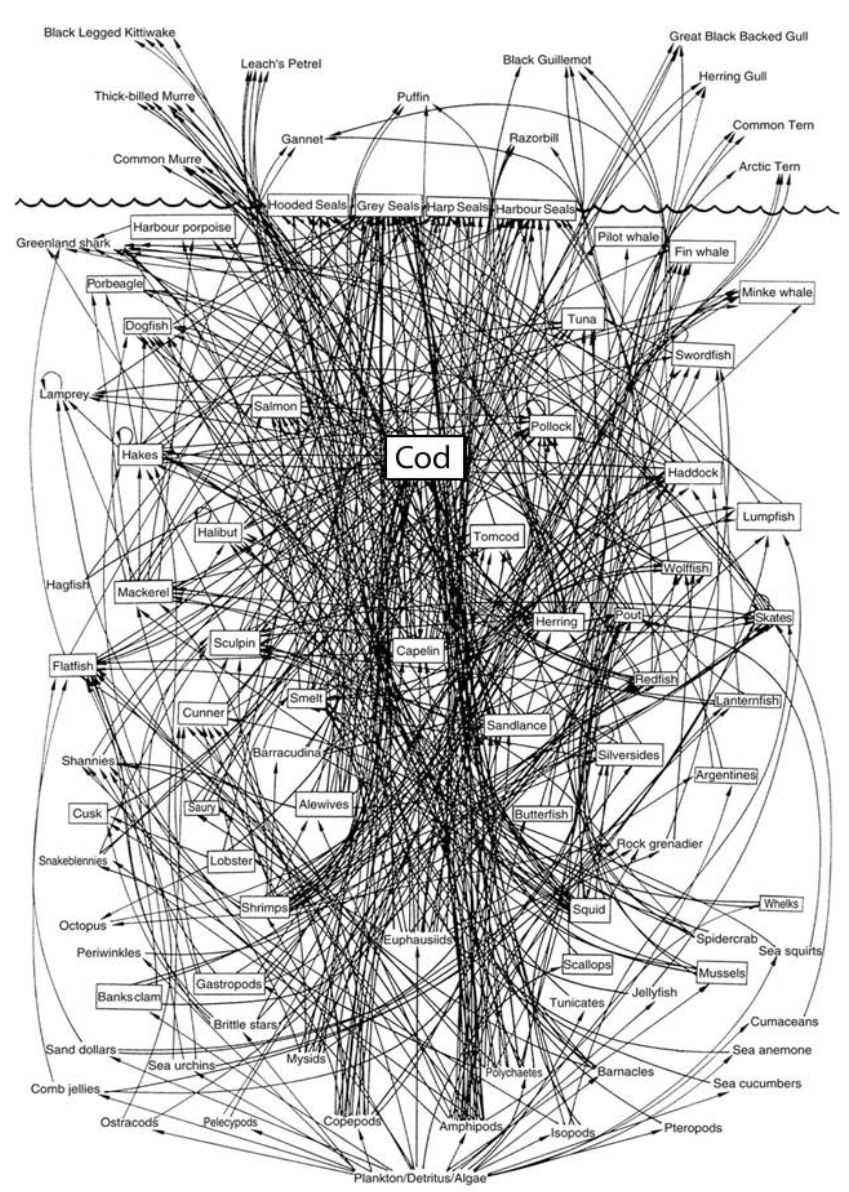
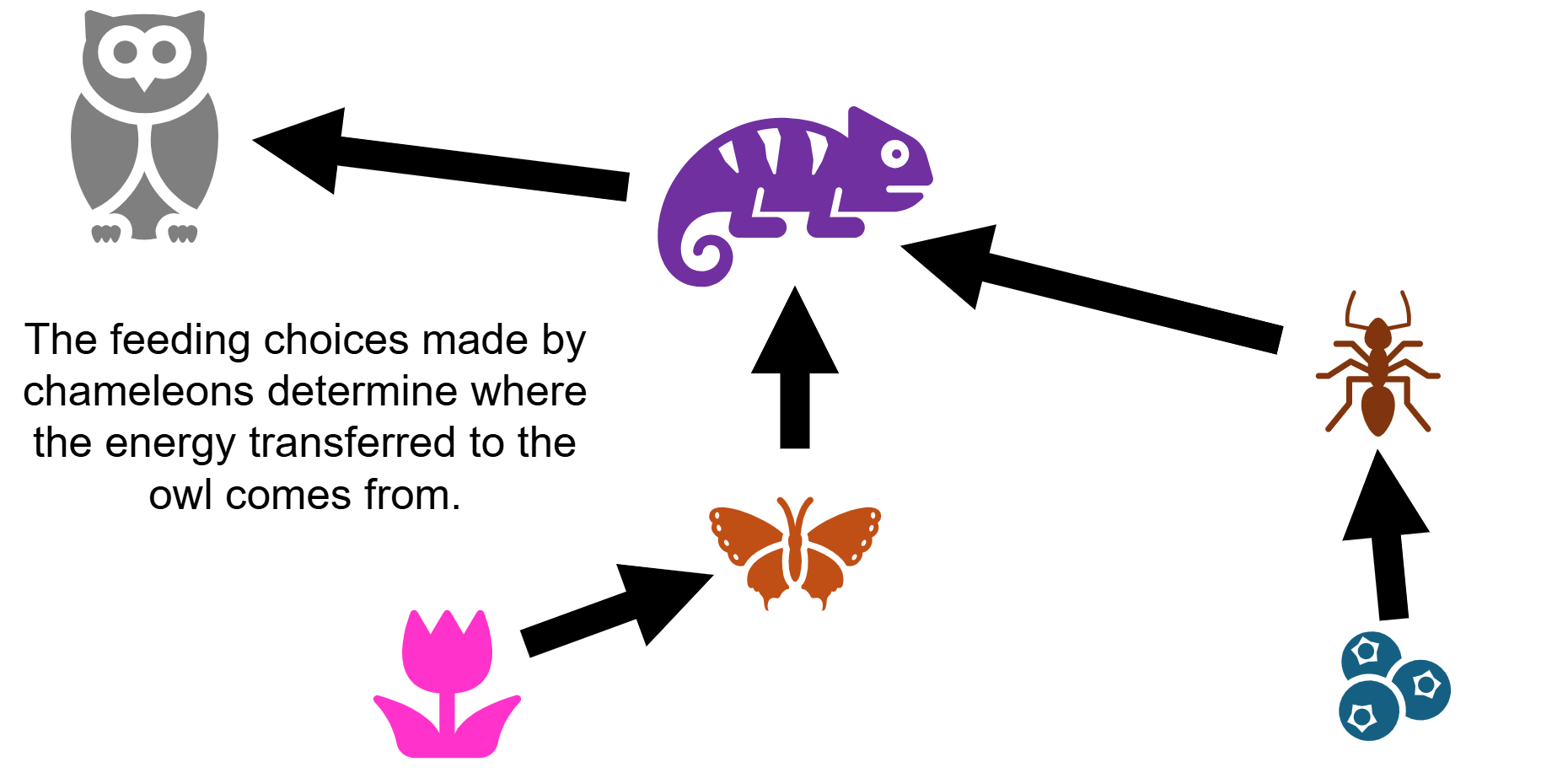
Food Webs
A type of ecological network that shows who eats whom and how much
Organisms mediate the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems
Organisms sometimes eat more of certain resources and less of others
Matter and energy can move through multiple pathways
Are also a map for how pollutants and toxins flow through an ecosystem!
Multiple Choice Tips