2. Coronary Circulation and Electrical Activity of the Heart
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
coronary circulation
The heart is an organ so it needs a source of nutrients & oxygen and a way to get rid of wastes. This is called…
blood flow…
is NOT continuous
systole
When coronary vessels are compressed, the heart is in [term] (contracts), so the flow is diminished
diastole
Regular flow resumes when the heart is in [term] (relaxes)
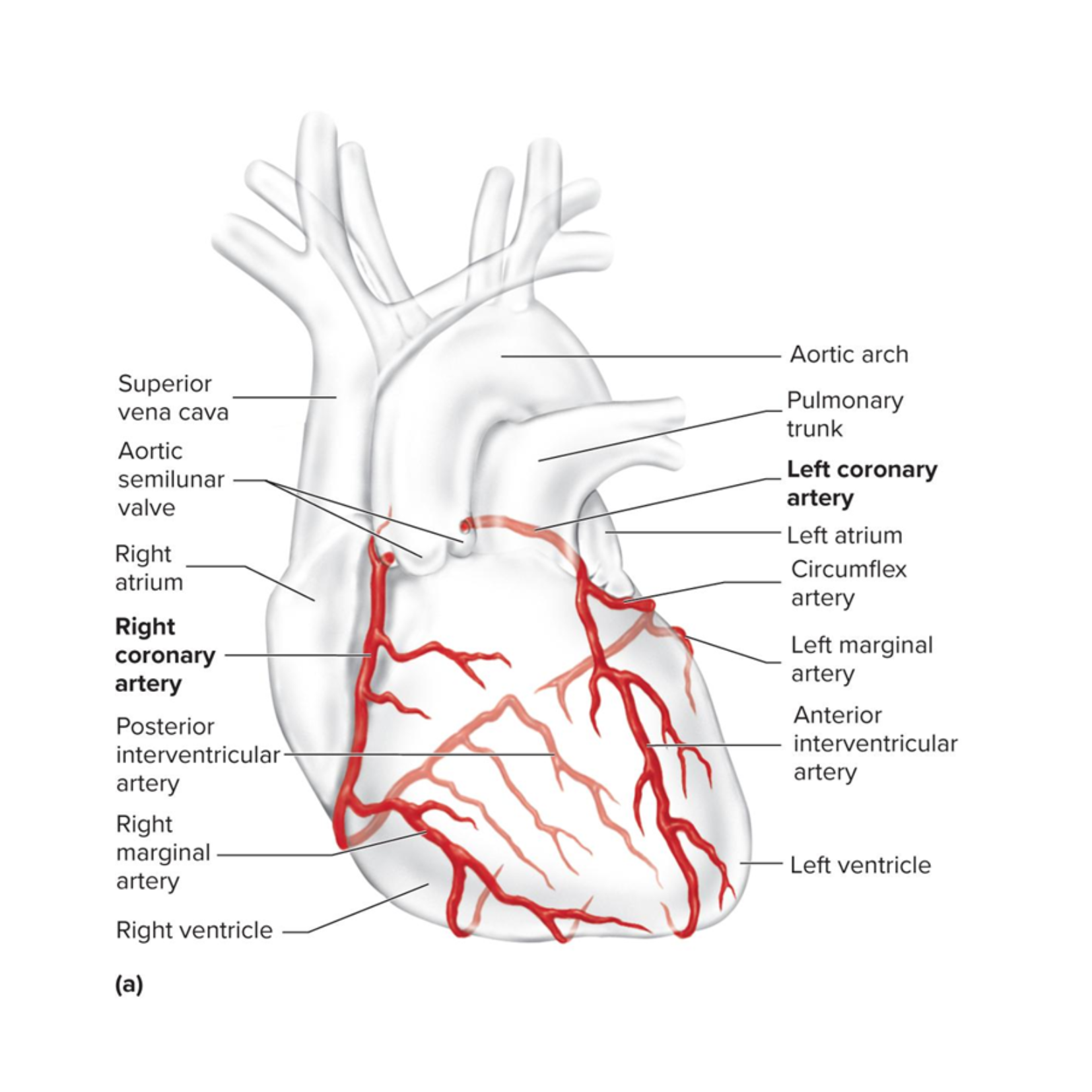
coronary arteries
delivers oxygenated blood to the heart wall during diastole
the left and right ones are the first branches of the aorta
have many anastomoses (connections between vessels)
major coronary veins
drains the deoxygenated blood from the heart wall during diastole
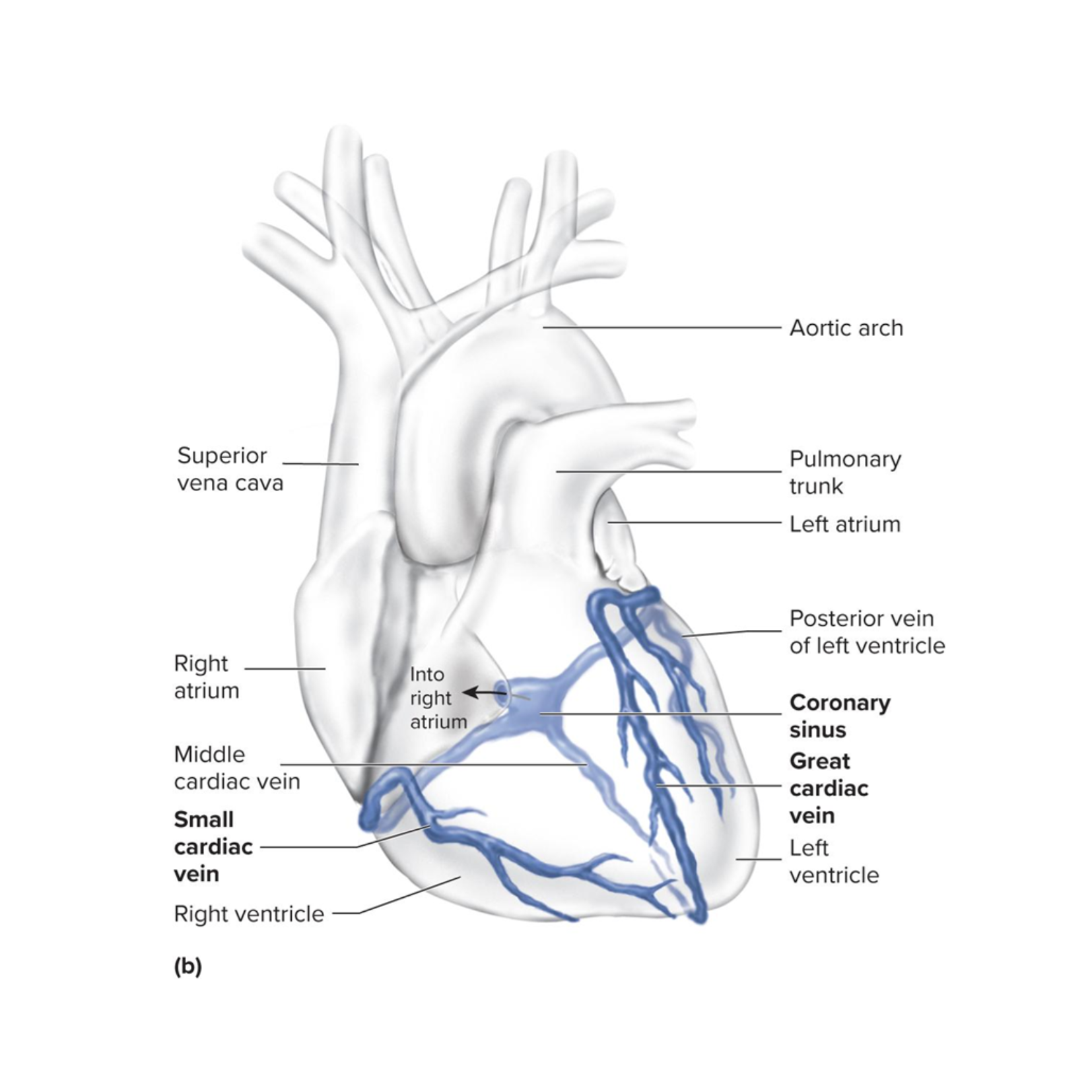
great cardiac vein
drains the left side of the heart
small cardiac vein
drains the right margin of the heart
coronary sinus
all of the veins empty here
empties blood into the right atrium
autorhythmic
the heart stimulates itself to contract at regular intervals
pacemaker cells
generate action potentials (APs) spontaneously
pacemaker potential
movement of K+, Na+, and Ca2+ causes spontaneous development of local potential
AP is generated
once the threshold is reached…
conducting cells
specialized cells
able to pass the AP through the heart
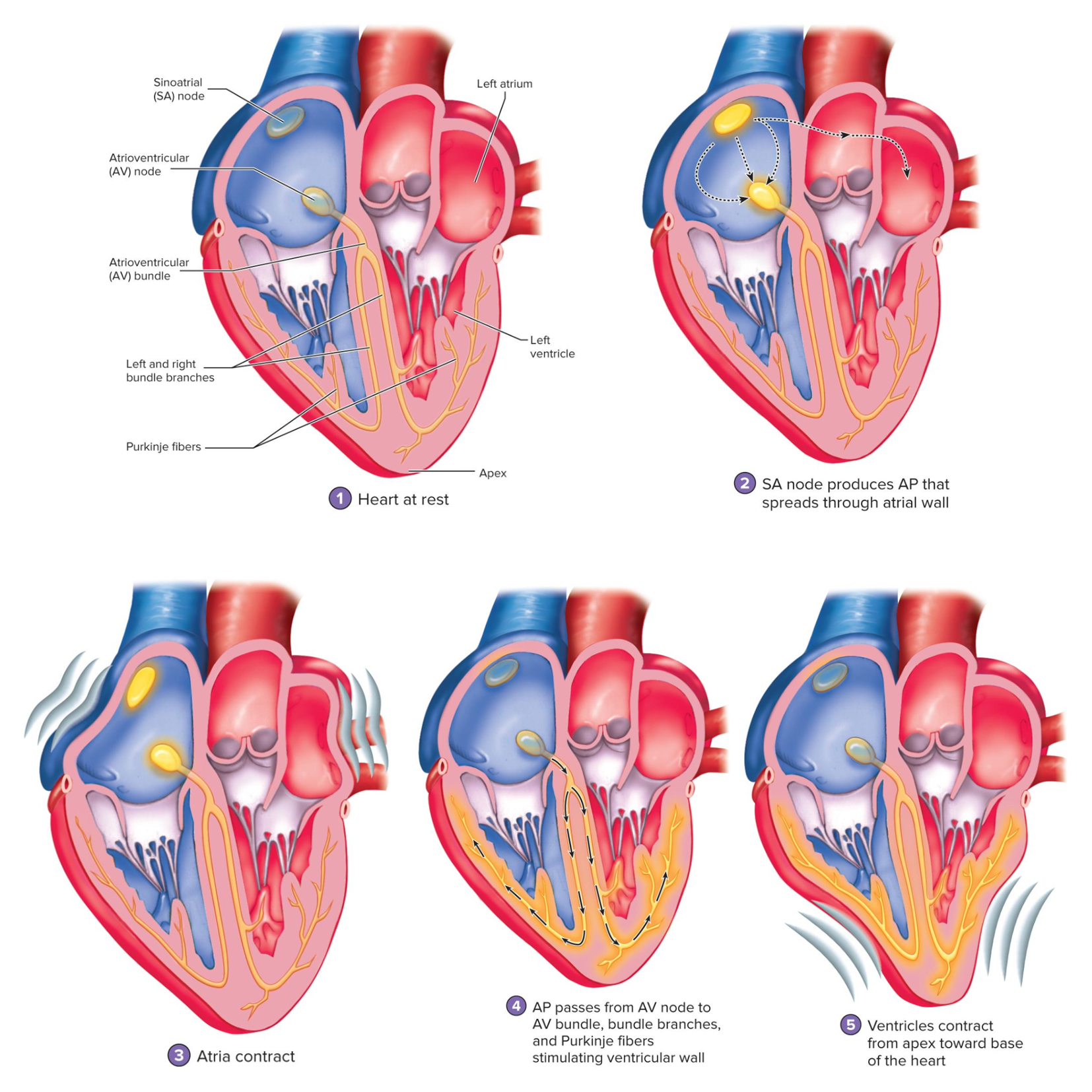
Sinoatrial node (SA node)
Located in the right atrium just medial to the opening of the superior vena cava
This is the pacemaker of the heart – origin of our heartbeat
Generates AP that pass into the atrial muscle cells and then to the AV node
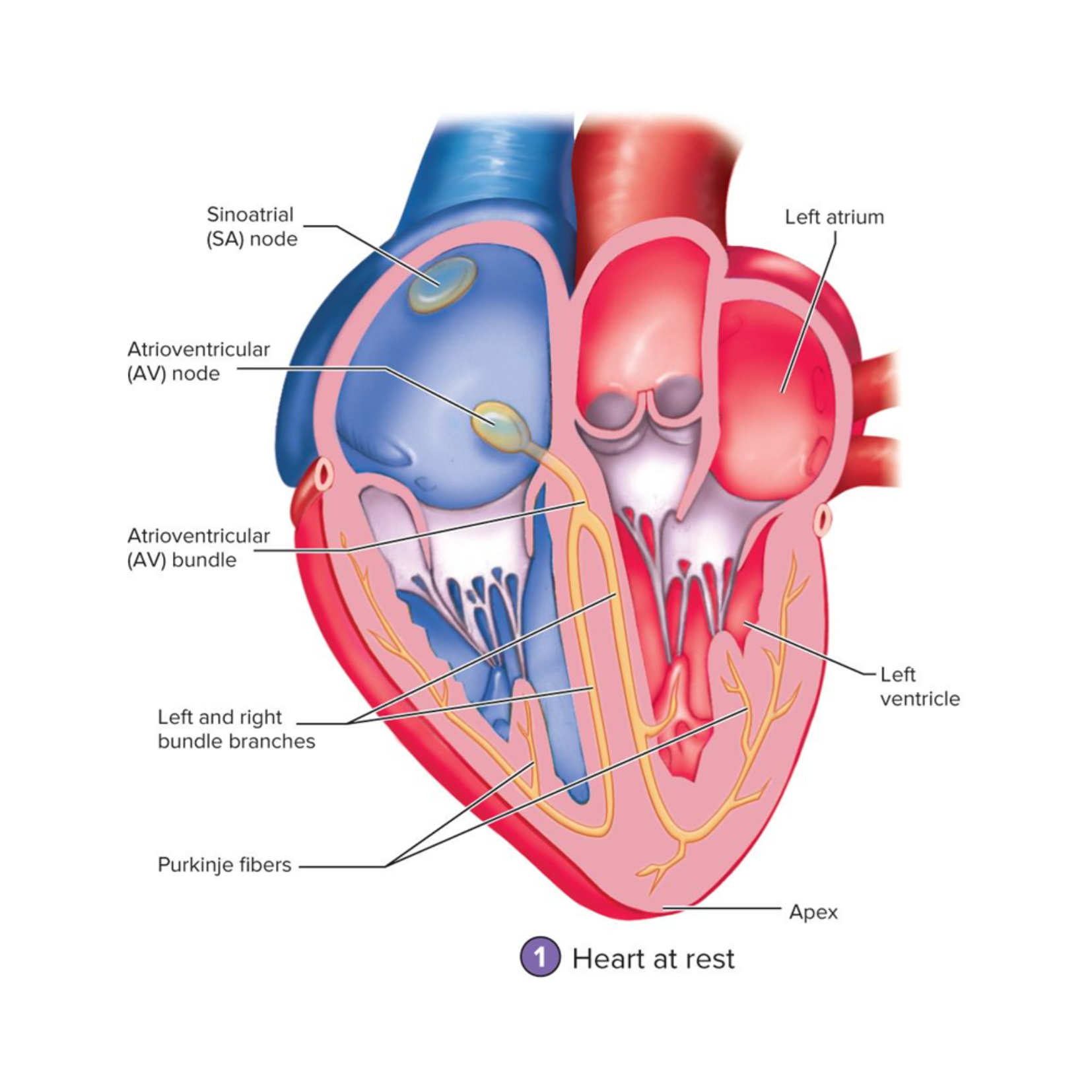
AV node
in right atrium, near tricuspid valve;
slowest conduction—delays signal so atria finish contracting
APs are conducted here more slowly that anywhere else in the conducting system
Gives the atria time to finish contracting before the signal is received by the ventricles
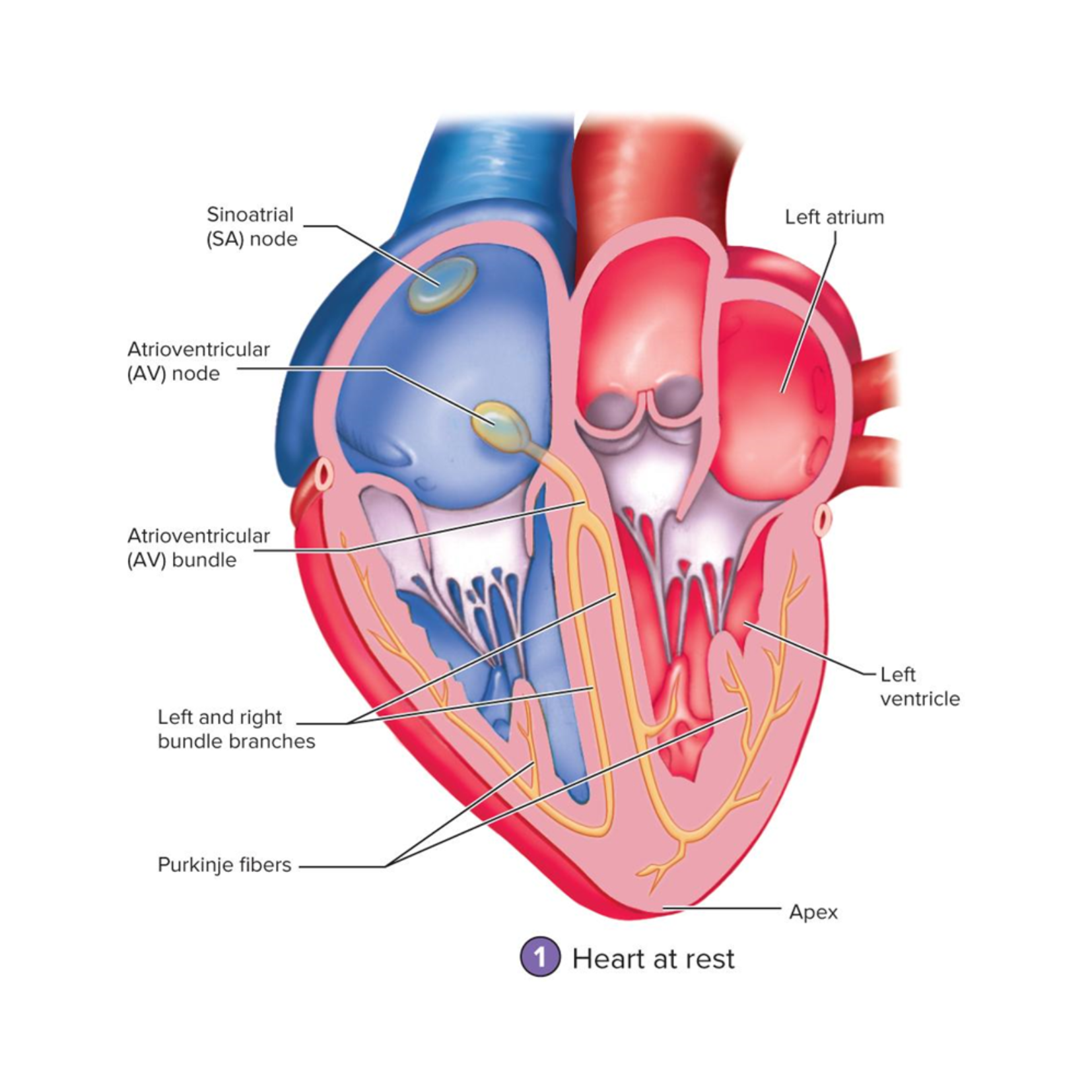
Atrioventricular bundle (AV bundle)
Located in the superior part of the interventricular septum
the only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles
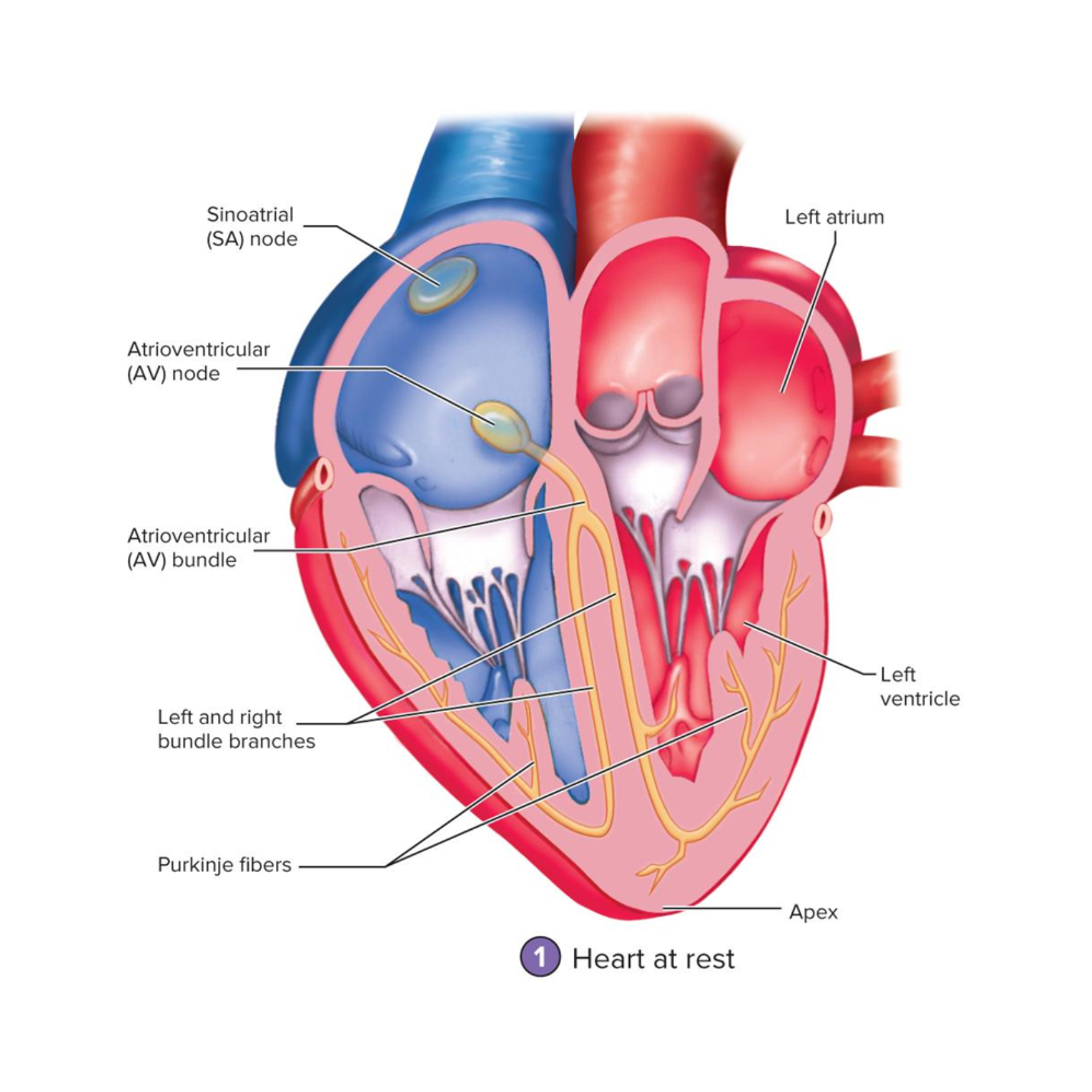
right and left bundle branches
Begin where the AV bundle splits into two branches
Extend through the interventricular septum down to the apex
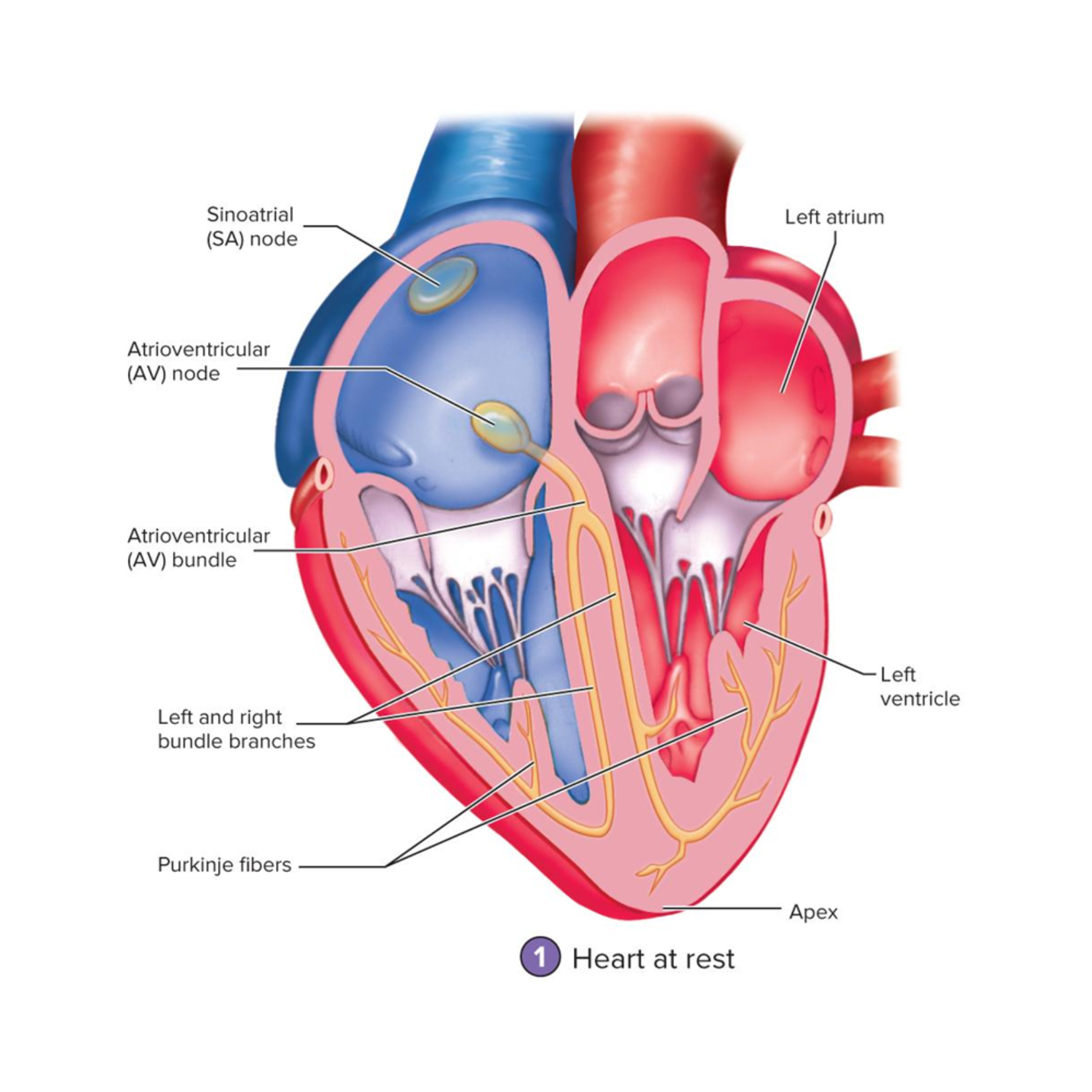
Purkinje fibers
large myofibers of the Conducting Network
located in the ventricle walls
conduct the AP to the ventricular muscle cells
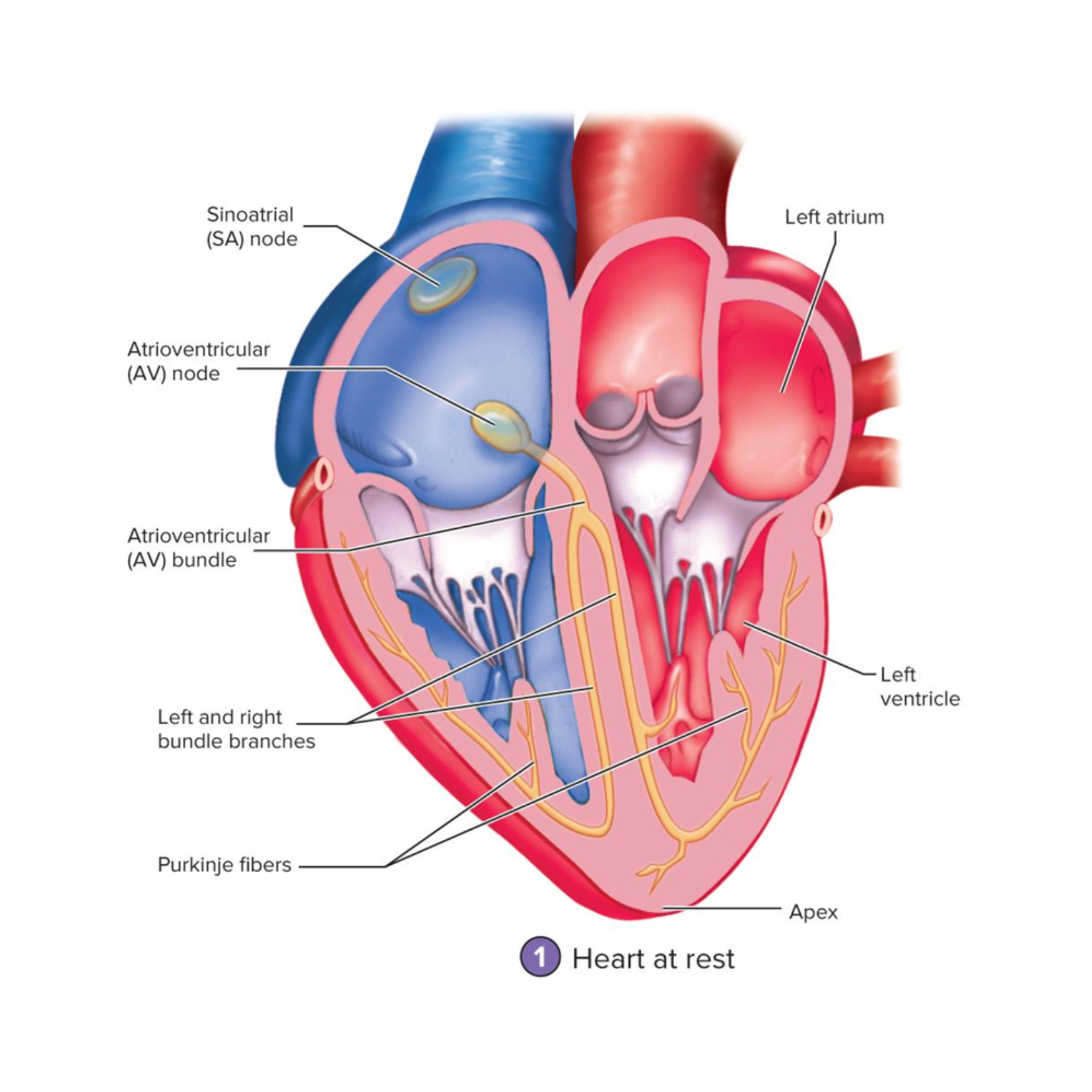
AP through the heart
what do these images show (study it)
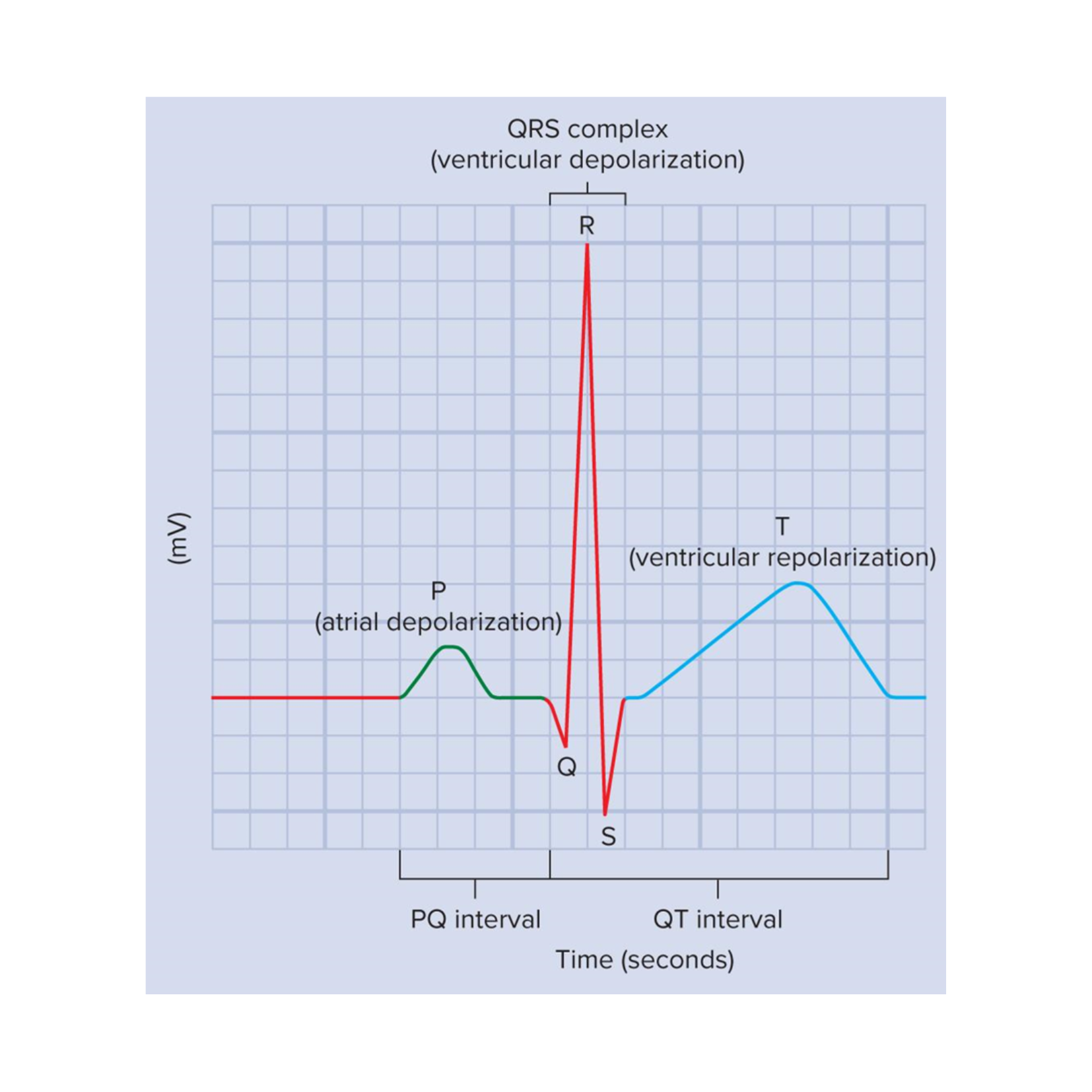
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
graphical record of the electrical events of the myocardium
we can correlate the electrical events to the mechanical events
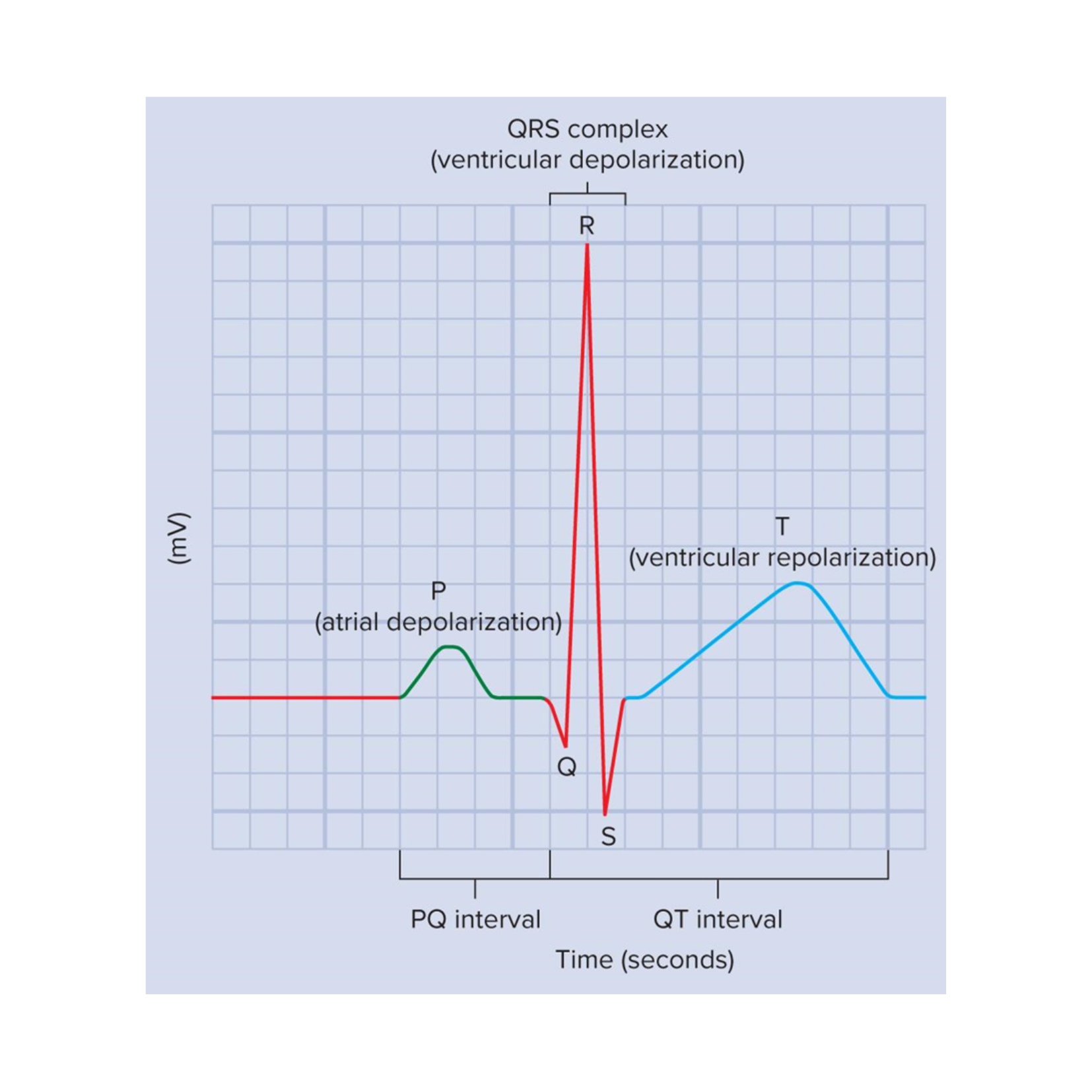
Important EKG events
P wave, QRS complex, and T wave
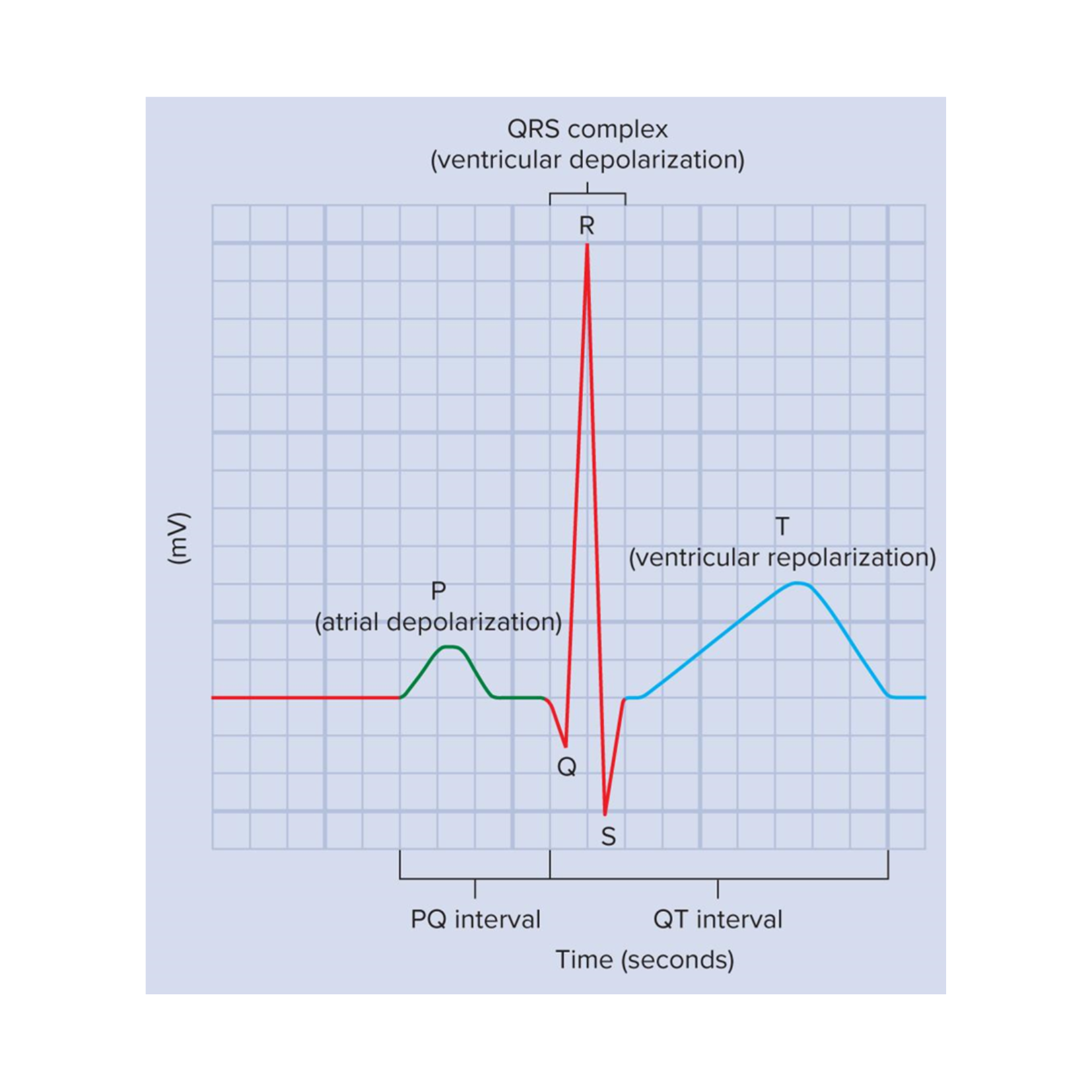
P wave
atrial depolarization
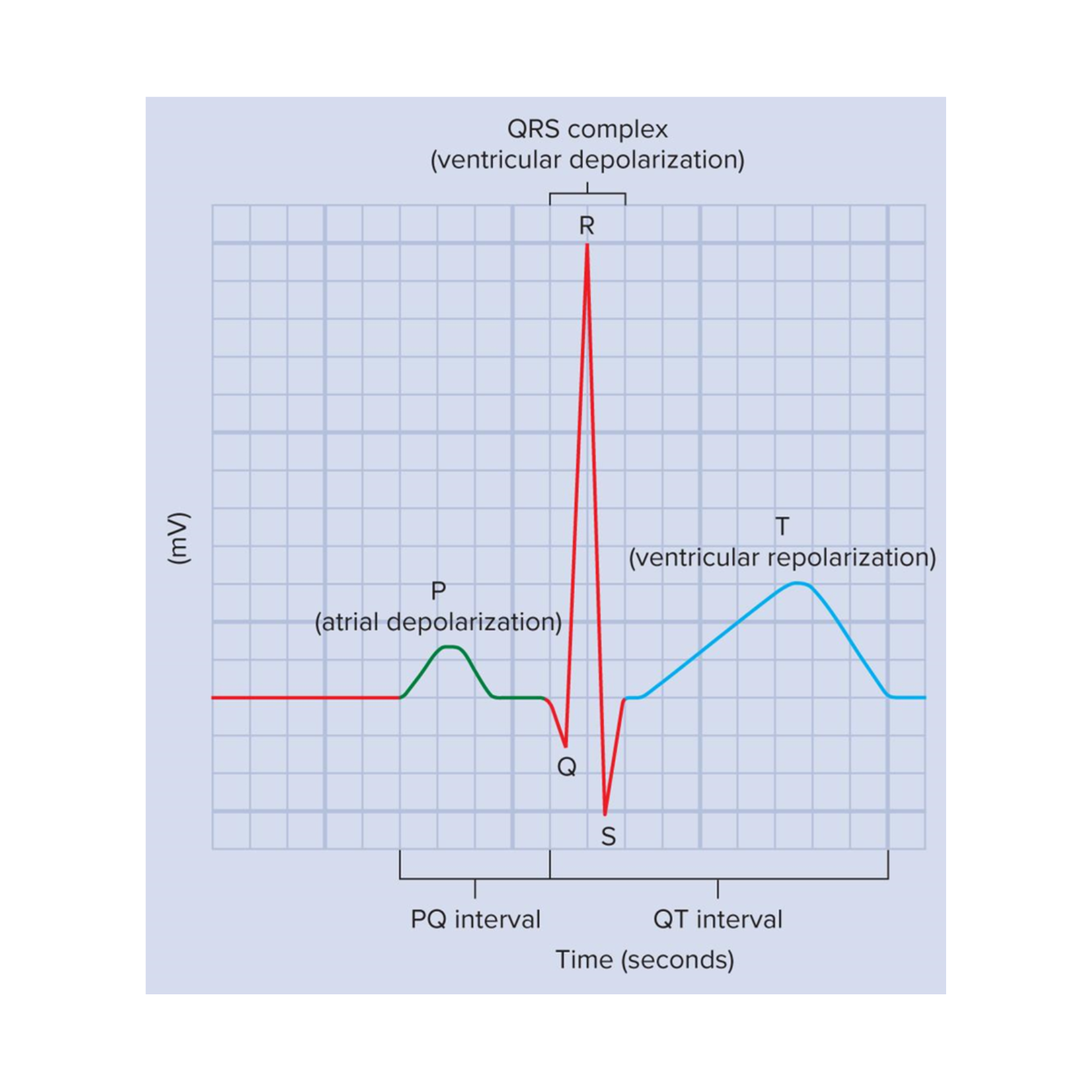
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
At this time, the atria are undergoing repolarization, but it cannot be seen on an EKG because ventricular depolarization is a stronger electrical event
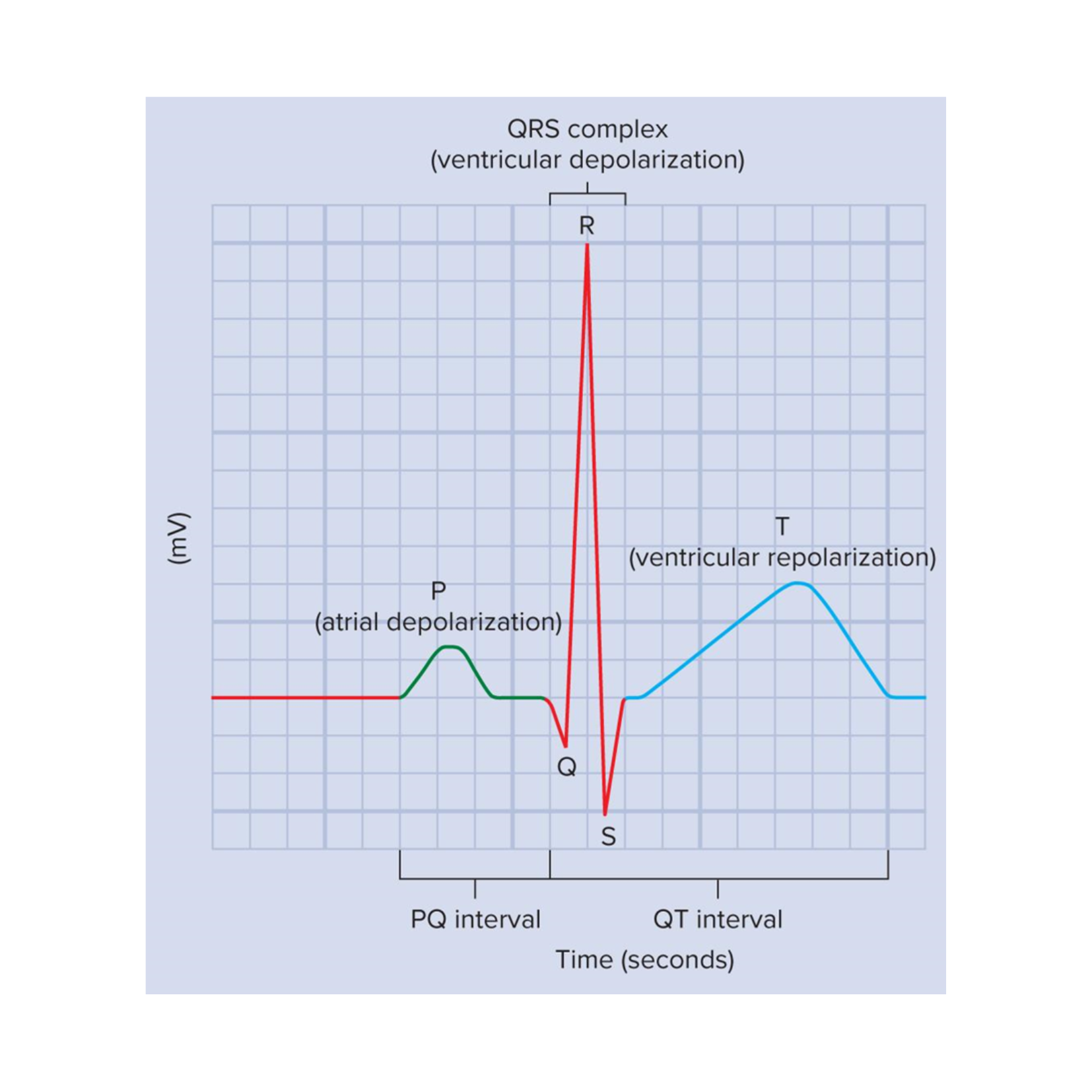
T wave
ventricular repolarization