Peptides and Peptide Bonds
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
A polypeptide is formed by the _____ interaction of two amino acids
covalent
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds’
A polypeptide is formed by the covalent interactions of two _____ ______
amino acids
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
A molecule of _____ is eliminated for each peptide bond formed and the product is called a peptide
water
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
A molecule of _____ is eliminated for each peptide bond formed and the product is called a peptide
The remaining portion of the AA in the peptide is called an ____ ___ _____
amino acid residue
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
A molecule of water is eliminated for each peptide bond formed and the product is called a peptide
The remaining portion of the AA in the peptide is called an amino acid residue
The _______ and _____ ends are available for further reaction
N-terminal and C-terminal
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
The condensation reaction to form peptide bonds is catalyzed by the _________
ribosome
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
The condensation reaction to form peptide bonds is catalyzed by the _________
How do amino acids get into the ribosome?
tRNA molecules transport amino acids to the ribosome
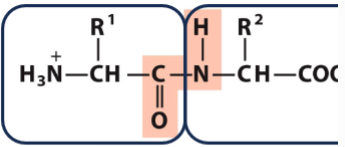
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
What is happening in the highlighted orange
The amino group from the amino acid is added to the carboxyl group of the growing peptide aka amino acids are added successfully to the carboxyl terminal end of the growing peptide
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
The _____ _____ _____ is the primary structure of the protein
amino acid sequence
Topic: Peptide Bond
Peptides and Peptide Bonds
The amino acid sequence is the _____ ______ of the protein
primary structure
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
________ and ________ analyzed the geometry and dimensions of peptide bonds in crystal structures of molecules containing one or a few peptide bonds
Linus Pauling and Robert Corey
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
_______ bond length is 10% shorter than found in usual amines
C-N
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
The C-N bond length is _____ shorter than found in usual amines
10%
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Planar Structure of Peptide Bonds
Why is the peptide bond (C-N) shorter than the others
because the C-N bond has some double bond character, resonance with the C=O group
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Planar Structure of Peptide Bonds
The peptide bond is short because the C-N bond has some double-bond character (40%) due to resonance with the C=O group
All peptide bonds are approximately _______
coplanar
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Planar Structure of Peptide Bonds
The peptide bond is short because the C-N bond has some double-bond character (40%) due to resonance with the C=O group
All peptide bonds are approximately coplanar
The ______ of the peptide bond reduces the degrees of freedom durin gfolding
rigidity
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
The 3 main torsion angles of a polypeptide backbone are
______, C-N
_______, C=O to C (α)
________, peptide bond
phi ( ϕ)
psi (Ψ)
omega (ω)
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
The three main torsion angles of a polypeptide backbone are phi ( ϕ), C (α)- N ; psi (Ψ), C=O to C (α), and omega (ω) peptide bond
The planarity of peptide bonds restrict ω to _____ (trans) in nearly all the main chain peptide bonds
180 degrees
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
The three main torsion angles of a polypeptide backbone are phi ( ϕ), C (α)- N ; psi (Ψ), C=O to C (α), and omega (ω) peptide bond
The planarity of peptide bonds restrict ω to 180 (trans) in nearly all the main chain peptide bonds
In rare cases, ω=0 degrees for a ___ peptide bond which usually involves proline
cis
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
The three main torsion angles of a polypeptide backbone are phi ( ϕ), C (α)- N; psi (Ψ), C=O to C (α), and omega (ω) peptide bond
The planarity of peptide bonds restricts ω to _180_ (trans) in nearly all the main chain peptide bonds
In rare cases, ω=0 degrees for a cis peptide bond which usually involves _____
proline
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
what does the phi ϕ torsion angle connect to in a polypeptide backbone
C (α)- N
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
what does the psi Ψ torsion angle connect to in a polypeptide backbone
C=O to C(α)
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bond Torsion Angles
what does the omega torsion angle connect to in a polypeptide backbone ω
peptide bond (C-N)
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Cis and Trans Configuration
The two C(α) carbons , C=O and N-H are nearly _______
coplanar
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Cis and Trans Configuration
The _____ _____ is always nearly in the trans configuration because it is favorable over cis
peptide bond
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Cis and Trans Configuration
The peptide bond is nearly always in the ________ configuration because it is favorable over cis
trans
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Cis and Trans Configuration
The peptide bond is nearly always in the trans configuration because it is favorable over cis
C(α) atom sare on the opposite sides of the C-N peptide in the ______ ______ and the same side in the _____ _____
trans isomer; cis isomer
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Cis and Trans Configuration
The peptide bond is nearly always in the trans configuration because it is favorable over cis
C(α) atoms are on the opposite sides of the C-N peptide in the trans isomer and the same side in the cis isomer
_______ ________ between fucntional groups attached to C(α) atoms are greater in the cis configuration
steric hinderance
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Involving Proline
The _________ nature of the proline chain allow both the cis and trans configurations to have nearly equivalent energies. Thus, proline is found in the cis configuration
cyclic nature
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Peptide Bonds Involving Proline
The cyclic nature of the proline chain allow both the cis and trans configurations to have nearly equivalent energies. Thus, proline is found in the _____ configuration
cis
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Formation and Stability of Peptide Bonds
In aqueous solution, formation of a peptide bond is ___ _______ ___________ (Δ)G = 10kJ/mol at room temperature )
not favored thermodynamically
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Formation and Stability of Peptide Bonds
In aqueous solution, formation of a peptide bond is ___ _______ ___________ (Δ)G = 10kJ/mol at room temperature )
Instead, the reverse reaction, ________ of a peptide bond is favored
hydrolysis
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Formation and Stability of Peptide Bonds
In aqueous solution, formation of a peptide bond is not thermodynamically (Δ)G = 10kJ/mol at room temperature )
Instead, the reverse reaction, hydrolysis of a peptide bond, is favored
The energy _____ is used during translation
ATP
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Polypeptide Nomenclature
The convention is always to represent the ____ terminus on the left and the ___ terminus on the right
N; C
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Polypeptide Nomenclature
The convention is always to represent the ____ terminus on the left and the ___ terminus on the right
Short peptides of a few residues are called ______ peptides , while longer peptides are called polypeptides, and proteins are very long-chain polypeptides folded into regular structures
oligopeptides
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Polypeptide Nomenclature
The convention is always to represent the N terminus on the left and the C terminus on the right
Short peptides of a few residues are called oligopeptides, while longer peptides are called ______ , and proteins are very long chain polypeptides folded into regular structures
polypeptides
Topic: Peptide Bond Structure
Polypeptide Nomenclature
The convention is always to represent the N terminus on the left and the C terminus on the right
Short peptides of a few residues are called oligopeptides, while longer peptides are called polypeptides , and proteins are very long chain polypeptides folded into regular structures
The term polypeptide refers simply to a chain of amino acids while the term protein refers to ________ ________ and is ( in some cases ) modified. Proteins may consist of more than one polypeptide chain ( multimer)
the chain of amino acids after it folds properly
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Protein Size
the avergae molecular weight of an amino acid is about 138. When accoutning the abundance of AA’s in known proteins, the molecular weight of an average AA in protein is about ___
128
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Protein Size
The average molecular weight of an amino acid is about 138. When accounting for the abundance of AA’s in known proteins, the molecular weight of an average AA in protein is about 128
Peptide bond formation removes a water molecule ( molecular weight of 18) so the avergae weight of an amino acid reside in a protein is ___
110
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Protein Size
The average molecular weight of an amino acid is about 138. When accounting for the abundance of AA’s in known proteins, the molecular weight of an average AA in protein is about 128
Peptide bond formation removes a water molecule ( molecular weight of 18) so the average weight of an amino acid reside in a protein is 110
Estimate the number of residues in a protein by dividing the molecular weight by 110
ex- 619,000/110=
5627
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Peptide Sequence
____________________. Simply choosing the most common amino acids as monomers is a polypeptide, the number of sequences possible is given by the following
Number of sequence = ( number of possible AAd)^( peptide length)
The number of unique sequences possibilities is enormous
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Peptide Sequence
. Simply choosing the most common amino acids as monomers is a polypeptide, the number of sequences possible is given by the following
Number of sequence = ( number of possible AA)^( peptide length)
Ex- For any of the 20 common amino acids in a tetrapide ( four amino acid residues ) results inthe following number of possible peptide sequences ______
20^4= 160,000
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Peptide Sequence
The number of unique sequences possibilities is enormous.. Simply choosing the most common amino acids as monomers is a polypeptide, the number of sequences possible is given by the following
Number of sequence = ( number of possible AA)^( peptide length)
Ex- For any of the 20 common amino acids in a tetrapide ( four amino acid residues ) results inthe following number of possible peptide sequences 20^4= 160,000
Organisms typically rely on _____ to ______ sequences, so necessary function will determine which sequences are constructed. As we will see, polypeptides ( proteins) do not contain an equal distribution of amino acids
30,000- 35,000
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
AA’s sequence in Polypeptide Chain Define Structure
Each of the amino acids, joined together by peptide bonds, in proteins ( or polypeptides ) have different properties determine dby their __ group side chains:
acidic, basic, neutral, hydrophobic
R
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
AA’s sequence in Polypeptide Chain Define Structure
Each of the amino acids, joined together by peptide bonds, in proteins ( or polypeptides ) have different properties determined by their _R_ group side chains:
acidic, basic, neutral, hydrophobic
The amino acid side chains direct the folding of the nascent polypeptide into___________ and ________
a functional protein and stabilize its final conformation
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Some proteins Contain Chemical Groups Other Than Amino Acids
Conjugated proteins:___________
non amino acid part = prosthetic group
contain permanently associated chemical components
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Some proteins Contain Chemical Groups Other Than Amino Acids
Conjugated proteins: contain permanently associated chemical components
non amino acid part = ______
prosthetic group
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Some proteins Contain Chemical Groups Other Than Amino Acids
Conjugated proteins:contain permanently associated chemical components
non amino acid part = prosthetic group
lipoproteins:______
contain lipids
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Some proteins Contain Chemical Groups Other Than Amino Acids
Conjugated proteins:contain permanently associated chemical components
non amino acid part = prosthetic group
Lipoproteins contain lipids
glycoproteins:_______
contain sugars
TOPIC: Ionization of Peptides and Proteins
Some proteins Contain Chemical Groups Other Than Amino Acids
Conjugated proteins:contain permanently associated chemical components
non amino acid part = prosthetic group
lipoproteins
glycoproteins: contain sugars
metalloproteins: ______
contain specific metals