CARBS (MAIN)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Last updated 5:01 PM on 12/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
Glucose
Most important carbohydrate in the body is
2
New cards
(CnH2O)n or “hydrate of carbon”
The empiric for many of the simpler carbohydrates is
3
New cards
Glycosidic bond
Type of bonding of carbohydrates
4
New cards
3. Hormones
Carbohydrates are components of the following except?
1. Cell membranes
2. Nucleic acids
3. Hormones
4. Bacterial cell wall
1. Cell membranes
2. Nucleic acids
3. Hormones
4. Bacterial cell wall
5
New cards
carbohydrates
Serve as intermediates for the biosynthesis of
biochemical entities such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid
biochemical entities such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid
6
New cards
1 and 2
Which of the following is an example of monosaccharide?
1. Ribose 2. Galactose 3. Amylose 4. Lactose
1. Ribose 2. Galactose 3. Amylose 4. Lactose
7
New cards
Lactose and Cellobiose
Which has/have β (1,4) linkages
1. Lactose 2. Maltose 3. Cellobiose 4. Sucrose
1. Lactose 2. Maltose 3. Cellobiose 4. Sucrose
8
New cards
Carbohydrate
Part of the structural framework of DNA and RNA molecules
9
New cards
T
T OR F?
Every carbon (C) contains your hydroxyl group
(OH) except the carbon that is double bonded
with your oxygen.
Every carbon (C) contains your hydroxyl group
(OH) except the carbon that is double bonded
with your oxygen.
10
New cards
Polysaccharides
has more than 10 sugar units
11
New cards
Oligosaccharides
3-10 sugar units
12
New cards
Disaccharide
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Sucrose
Lactose
13
New cards
Glyceraldehyde ; Dehydroxyacetone
Trioses
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
14
New cards
Erythrose, Threose ; Erythlurose
Tetroses
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
15
New cards
Xylose, Ribose, Arabinose ; Ribulose
Pentoses
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
16
New cards
Glucose Galactose Mannose ; Fructose
Hexoses
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
Aldose _________ ; Ketose ___________
17
New cards
Glucose
a known aldose
18
New cards
Fructose
a known ketose
19
New cards
Isomers
are molecules that have the same chemical
formula but different structures
formula but different structures
20
New cards
Stereoisomers
differ in the 3-D orientation of atoms
21
New cards
optical isomers
Most biologically important chemicals exist as
stereoisomers or also called
stereoisomers or also called
22
New cards
D/L Isomerism
are also called enantiomers or mirror images of
each other.
each other.
23
New cards
ASYMMETRIC OR CHIRAL CARBON
Carbon attached to four
different groups
different groups
24
New cards
ANOMERIC CARBON
Carbon in the carbonyl
group
group
25
New cards
PENULTIMATE CARBON
The highest numbered chiral carbon or the last chiral carbon
26
New cards
Bel-van't Hoff rule
states that the number of stereoisomers of an organic compound is 2
n, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms.
n, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms.
27
New cards
D-TALOSE
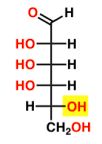
28
New cards
D-Gulose
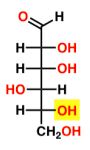
29
New cards
D-Galactose
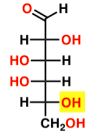
30
New cards
D-ALLOSE
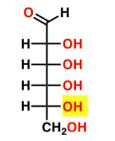
31
New cards
Name in order
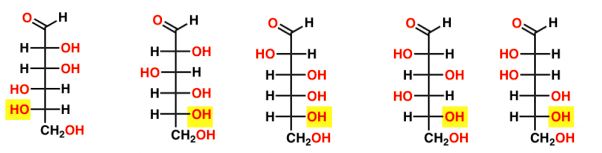
32
New cards
EPIMERS
Stereoisomers with more than one chiral carbon which differ in chirality at ONLY ONE chiral center.
33
New cards
EPIMERASE; EPIMERIZATION
Interconversion of epimers catalyzed by
enzyme ___________ and the process is called ________
enzyme ___________ and the process is called ________
34
New cards
Solid
Soluble
Solubility
Soluble
Solubility
_________at room temperature
_________in water
_________helps carbs to be transported
quickly
_________in water
_________helps carbs to be transported
quickly
35
New cards
same
Molecules which are enantiomers of each other have _______ (same or diff) physical properties (melting point, boiling point, index of refraction, etc.)
36
New cards
Polarized
vibrates only in one plane; it results from passing light through a polarizing filter.
37
New cards
Dextrorotatory (+)(d)(r)
- Rotate the light to the right or clockwise
38
New cards
Levorotatory (-)(l)(s)
- Rotate the light to the left or counterclockwise
39
New cards
A racemic mixture, or racemate
is a solution in which both enantiomers of a substance are present in equal proportions
40
New cards
Light Source, Unpolarized light, Polarizer, Tube with chemicals, Analyzer, Polarized Light, Observer
Process of Optical Activity
41
New cards
FISCHER PROJECTION
Specific type of formula that designates the
orientation of groups
orientation of groups
42
New cards
two crossed lines
To construct a 3D based on Fischer projections, atetrahedral carbon atom is represented by
43
New cards
RING CONFIGURATION
is formed as a self-reaction when the carbonyl atom forms a hemiacetal linkage for aldoses and hemiketal linkage for ketoses
44
New cards
pYRANOSE
a six-membered ring
45
New cards
FURANOSE
A five-membered ring
46
New cards
ANOMERS
Are formed when sugars assume a cyclic form. This is an isometric form of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon atom.
47
New cards
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
The carbon atom where a carbonyl or functional group is present is now called the anomeric carbon.
The carbon atom where a carbonyl or functional group is present is now called the anomeric carbon.
48
New cards
Mutarotation
epimers: epimerization; anomers __________
- When the alpha or beta anomers are interconverted
- When the alpha or beta anomers are interconverted
49
New cards
define whether alpha or beta
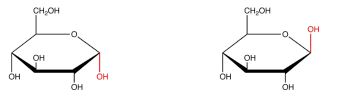
50
New cards
Right side
If the cyclic structure is alpha, on what side is the OH located in its Fischer projection?
51
New cards
BETA
Define whether the structure is beta or alpha when it cyclicize
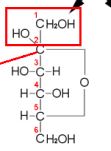
52
New cards
. HAWORTH PROJECTION
is considered as more realistic than fischer projection
53
New cards
Haworth Projection
Biochemists prefer what type of projection?
54
New cards
NEWMANN OR CHAIR
Organic Chemists prefers which type of structure?
55
New cards
__________ is the carbon immediately to the right of the oxygen atom
56
New cards
Last carbon is drawn below/above the plane
below: L-Sugar mnemonic (L-ow)
above: D-sugar
below: L-Sugar mnemonic (L-ow)
above: D-sugar
How do we determine if the Haworth projection is D or L?
57
New cards
a-l-glucopyranose
Determine if alpha/beta and D/L
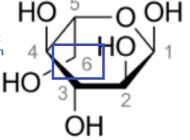
58
New cards
NEWMAN/CONFORMATIONALCHAIR FORM
The configuration that best represents the
three-dimensional conformation of sugars with 5 or more carbons
three-dimensional conformation of sugars with 5 or more carbons
59
New cards
D-Glucose
can be obtained from fruit juices, hydrolysis of starch, cane sugar, maltose and lactose
60
New cards
D-fructose
From fruit juice, honey, can sugar, and INULIN
61
New cards
D-GALACTOSE
From hydrolysis of lactose
62
New cards
D-RIbose
-sourced from Nucleic Acid
- structural components of nucleic acid and coenzymes and flavoprotein
- an intermediate in the PPP
- structural components of nucleic acid and coenzymes and flavoprotein
- an intermediate in the PPP
63
New cards
D-Galactose
can be changed in the liver and be metabolized and synthesized in the mammary gland to make lactose of milk
components of glycolipids and glycoprotein
components of glycolipids and glycoprotein
64
New cards
D-Galactose
associated with cataract and galactosemia
65
New cards
D-Fructose
can be changed into glucose int he liver
66
New cards
PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY
is able of converting something into energy like glucose
67
New cards
F
T OR F All reducing sugars are monosaccharides
68
New cards
D-Mannose
Constituent of glycoprotein and sourced from hydrolysis of plant mannan gums
69
New cards
carbohydrates are completely oxidized
to carbon dioxide and water molecules
to carbon dioxide and water molecules
In carbs as reducing agents, the highest energy yield from carbohydrates occurs
when...
when...
70
New cards
true
*Reverse complete oxidation of sugars is the
reduction of CO2 and water molecules to
produce sugar which happens in the process of
photosynthesis. T OR F?
reduction of CO2 and water molecules to
produce sugar which happens in the process of
photosynthesis. T OR F?
71
New cards
ferric (Fe3+) or cupric (Cu2+).
Monosaccharides can be oxidized by relatively mild oxidizing agents such as...
72
New cards
reducing sugars.
Sugars capable of reducing ferric or cupric ion are
73
New cards
OXIDATION
What type of reaction is involved when a carbonyl group forms carboxylic acid
74
New cards
First one is an aldose/aldehyde (the carbonyl group) being converted to carboxyl
Second one (R-CH2OH to R-COOH) is the terminal carbon
Note: Ketoses are resistant to oxidation since they do not have Hydrogen in their carbonyl group (oxidation removes hydrogen)
Second one (R-CH2OH to R-COOH) is the terminal carbon
Note: Ketoses are resistant to oxidation since they do not have Hydrogen in their carbonyl group (oxidation removes hydrogen)
R-CHO -> R-COOH
R-CH2OH -> R-COOH
explain
R-CH2OH -> R-COOH
explain
75
New cards
TRUE
Acidic sugar contains a carboxylate group which confers that negative charge at neutral pH is true for that monosaccharide
76
New cards
true
When these aldehydes are oxidized, the oxidizing agent must be reduced and that is the time when we detect if the sugar is non-reducing.
true or false
true or false
77
New cards
Uronic Acid
Aldonic Acid
Aldaric
Aldonic Acid
Aldaric
Three products/examples of oxidation
78
New cards
Uronic Acid
when an aldehyde group is left intact and primary alcohol at the other end is oxidized to COOH
79
New cards
Aldonic Acid
when the aldehyde group is converted to carboxyl group
80
New cards
Aldaric Acid
when both ends of a monosaccharide
is oxidized
is oxidized
81
New cards
Gluconic Acid
Identify what type of oxidation product and what name
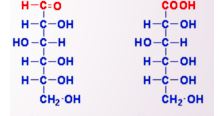
82
New cards
glucuronic acid
glucuronic acid Identify what type of oxidation product and what name
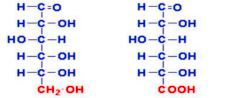
83
New cards
Identify what type of oxidation product and what name
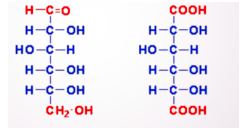
84
New cards
.
NAME THE FF
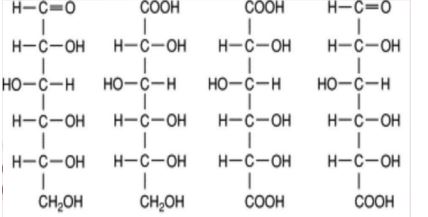
85
New cards
REDUCTION OF CARBONYL
- It is the gain of electrons
- The resultant product is a polyol or sugar alcohol
(alditol)
- The resultant product is a polyol or sugar alcohol
(alditol)
86
New cards
Sugar Alcohol
erythritol, lactitol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol, and xylitol are examples of
87
New cards
Glucose from sorbitol
- Most important sugar alcohol
- Associated with cataracts with diabetes
- Associated with cataracts with diabetes
88
New cards
Mannose from mannitol
- Important as diuretic
- Glyceraldehyde gives glycerol
- Glyceraldehyde gives glycerol
89
New cards
Formation of Glucitol though Reduction of Carbonyl Group
Wat reaction and product is formed here
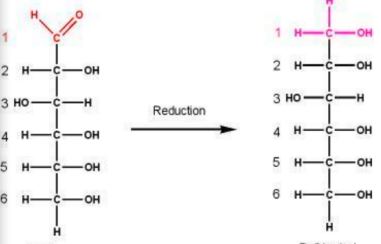
90
New cards
Esters through ESTERIFICATION
__________ are formed by reaction of hydroxyl groups (alcohols) with acids.
91
New cards
ESTERIFICATION OF THE HYDROXYL GROUP (in CH2OH) OF CARBOHYDRATE
Explain the reaction below
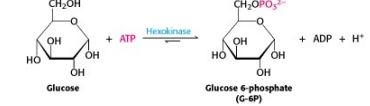
92
New cards
AMINO DERIVATIVES
- Sugar + Amin group (NH2
- Monosaccharides in which the alcoholic hydroxyl group is replaced by an amino acid
- Monosaccharides in which the alcoholic hydroxyl group is replaced by an amino acid
93
New cards
Amino dERIVATIVE
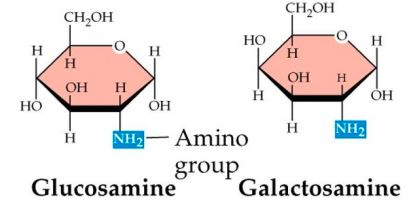
94
New cards
FERMENTATION
- Used for food industry
- For bacterial identification
- GLUCOSE contributes to this reaction by converting ADP to ATP
- For bacterial identification
- GLUCOSE contributes to this reaction by converting ADP to ATP
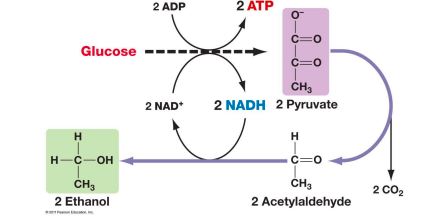
95
New cards
OSAZONE FORMATION
- It is seldom used for identification as we now use HPLC or mass spectrometry
- It consists of monosaccharide with phenylhydrazone to form a crystalline compound D-fructose and D-mannose
- It consists of monosaccharide with phenylhydrazone to form a crystalline compound D-fructose and D-mannose
96
New cards
dehydration synthesis
Disaccharides are formed by joining two simple sugars through__________ forming a covalent bond between them
97
New cards
DISACCHARIDE
The hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide
combines with the hydrogen of another
forming a glycosidic linkage
combines with the hydrogen of another
forming a glycosidic linkage
98
New cards
TRUE
Even though disaccharides are soluble in water, they are too large to pass through the cell membrane
99
New cards
DISACCHARIDES
Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose, Cellobiose are examples of
100
New cards
Lactose
Sucrose
Maltose
Cellobiose
Sucrose
Maltose
Cellobiose
NAME THE DISACCHARIDES
Linkage between galactose and glucose ______
Linkage between Fructose and Glucose_____
Linkage between two glucose (beta) ______
Linkage between two glucose (alpha) ________
Linkage between galactose and glucose ______
Linkage between Fructose and Glucose_____
Linkage between two glucose (beta) ______
Linkage between two glucose (alpha) ________