4.1.6 - protectionism
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
what is protectionism
restrictions on free trade
reasons for protectionism
infant industries
sunset industries
strategic industries
dumping
employment
current account deficit
labour/environmental regulations
(I Saw Some Drivers Eating Doner Regularly)
infant industries
new firms unlikely to succeed if they are competing globally
sunset industries
declining industries with firms on their way out (usually primary industries in first world countries)
government tries to limit the economic damage that could occur from closing abruptly
strategic industries
eg. military, energy, agriculture
u kind of have to be able to make those yourself to avoid sabotage
dumping
when foreign firms sell products at low prices in foreign markets to price out other firms
can even be below their own costs of production
employment
avoid structural unemployment caused by outsourcing production abroad
current account deficit
reduce number of imports
labour/environmental regulations
apply pressure to other countries with a lack of labour/environment regulation that makes their costs of production so cheap
4 main types of protectionism
tariff
quota
domestic subsidies
non-tariff barriers
define tariff
a tax imposed on imported g+s
show a tariff diagram
results in an overall loss in welfare
(watch uplearn if u don’t get how this had been drawn!)
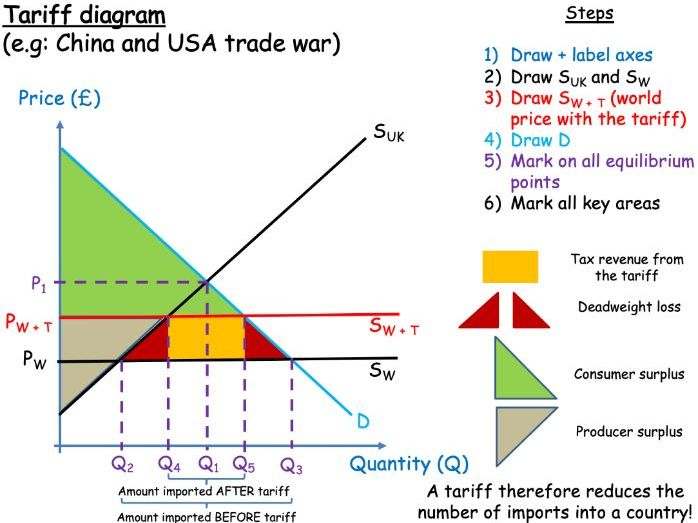
tariff impact on domestic producers
increase in producer surplus
tariff impact on domestic consumers
loss of consumer surplus
tariff impact on government
tax revenue
tariff impacts on standard of living
worse for consumers
better for employees of domestic firms
define quota
a physical limit on imports
how do quotas work
the limit is set below the free market level of imports
market price goes up
domestic firms can supply more
quota impact on domestic producers
higher revenue
quota impact on foreign producers
lower output but higher price if they do manage to export
quota impact on consumers
higher prices, less choice
quota impact on government
maybe corporation tax revenue from domestic firms, but no tariff revenue
quota impact on standards of living
lower - higher prices for everyone = lower purchasing power
how do subsidies work
lower costs of production = lower prices (for domestic firms)
more internationally competitive
subsidy impact on domestic producers
more internationally competitive
subsidy impact on foreign producers
harder to compete
subsidy impact on consumers
lower prices
subsidy impact on government
costs them the amount of the subsidy
and opportunity cost
subsidy impact on standards of living
improve - lower prices
what’s the point of non-tariff barriers
creating barriers to trade instead of taking drastic measures like tariffs, quotas and subsidies
examples of non tariff barriers
health and safety regulations (eg. banning chemicals widely used in another country)
environmental regulations (eg. banning stuff made in certain ways that are used in another country)
NTB impacts on domestic producers
limits foreign competition
NTB impact on foreign producers
disincentive to export
OR
they meet the requirements but it costs them so lower profit
NTB impact on consumers
less choice
NTB impact on government
lose WTO credibility
expensive/difficult to enforce the barriers
NTB impact on standards of living
lower - less choice, higher prices
higher - banning certain chemicals