Botany - 2d: Secondary Growth Internal Anatomy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
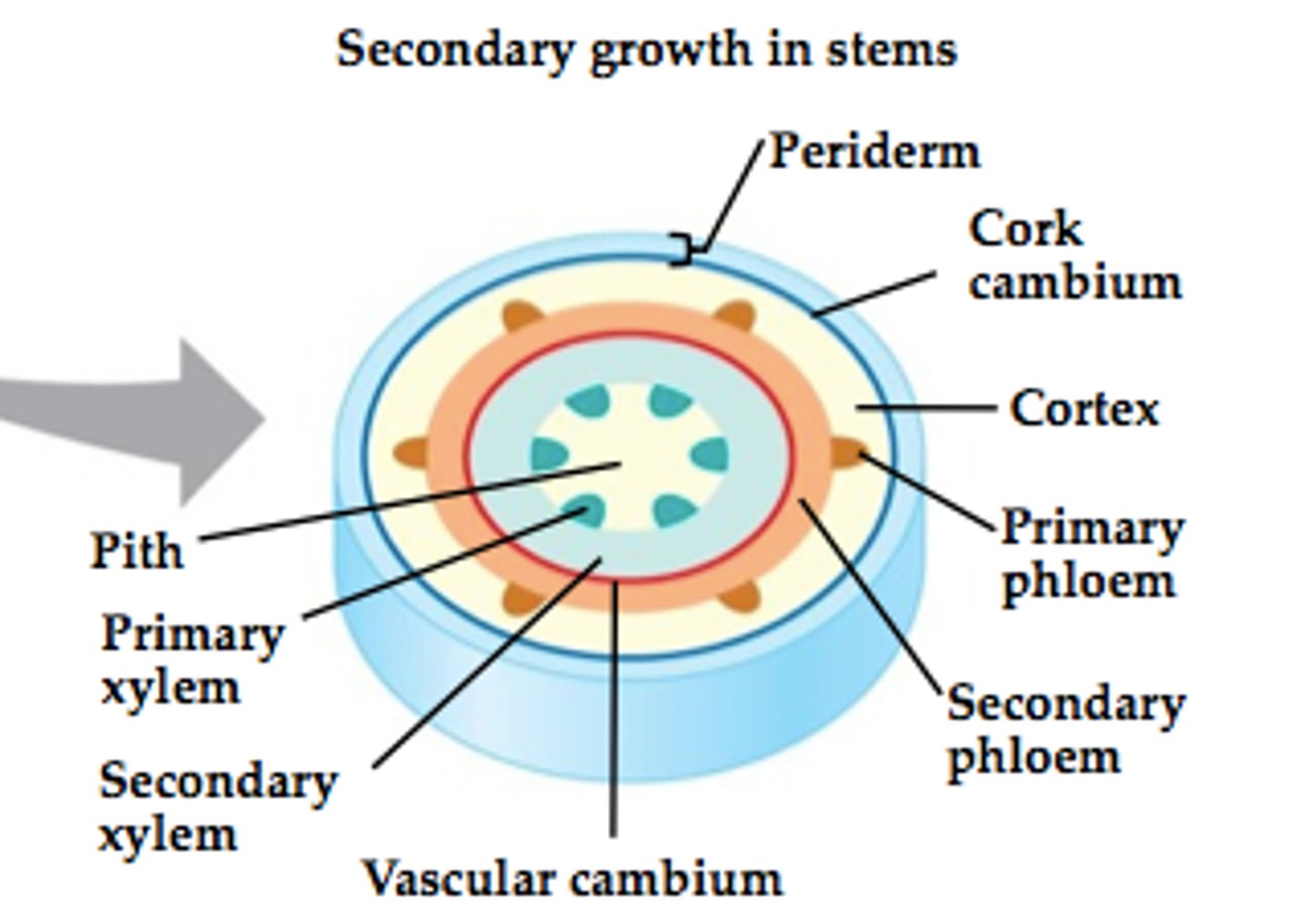
2 new meristems for increasing girth
1. vascular cambium
2. cork cambium
girth
diameter of stem
vascular cambium
A cylinder of meristematic tissue in woody plants that adds layers of secondary vascular tissue:
- secondary xylem (wood on inside)
- secondary phloem (inner bark on outside)
secondary xylem
wood inside stem
secondary phloem
produces the inner bark on outside of stem
in secondary growth, the primary xylem and phloem....
are not functioning
cork cambium
A cylinder of meristematic tissue that produces cork cells
- periderm replaces the epidermis
periderm
The protective coat that replaces the epidermis in plants during secondary growth
- bunch of cork cells
- outer bark
wood is...
secondary xylem produced by the vascular cambium
secondary growth internal anatomy
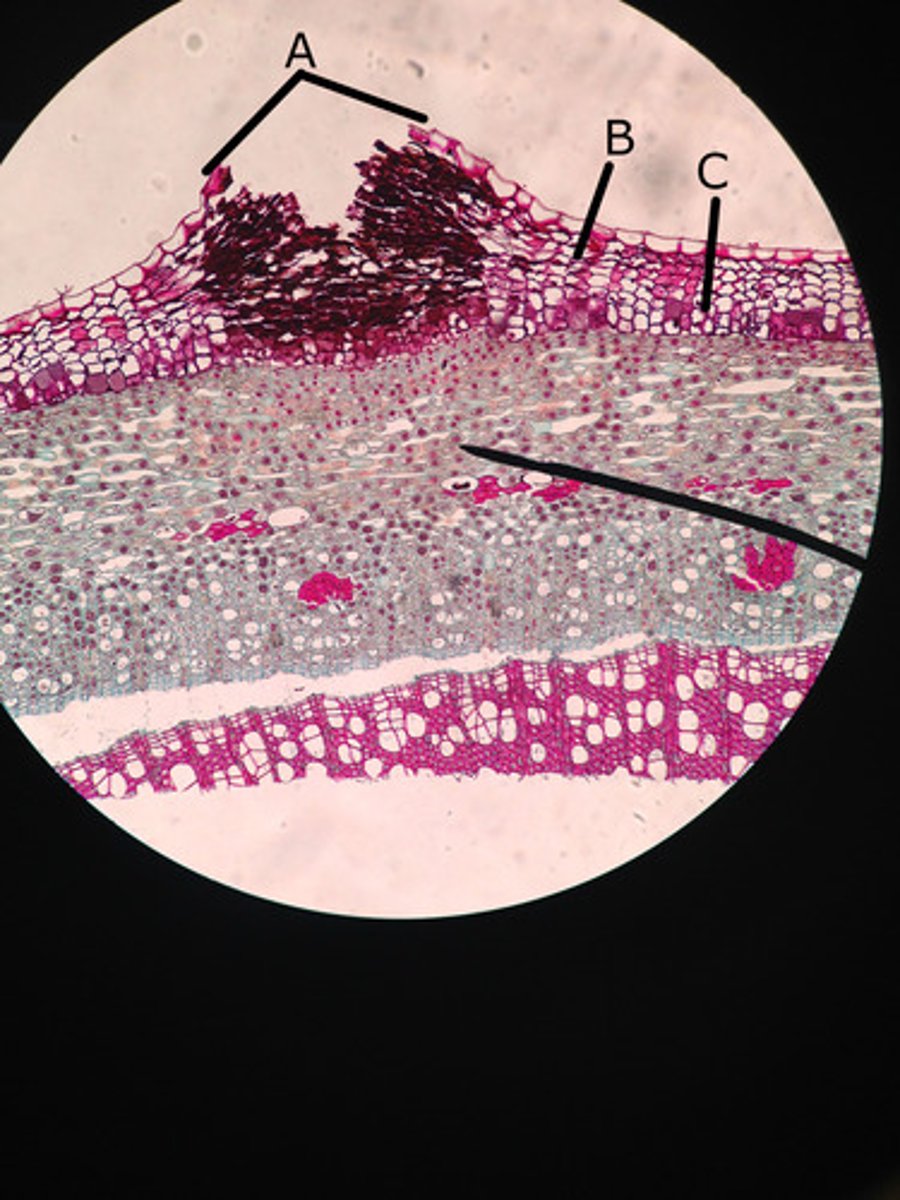
lenticel
ruptures (raised openings) in the periderm/cork cells (outer bark) that enables gas exchange
(A in pic)
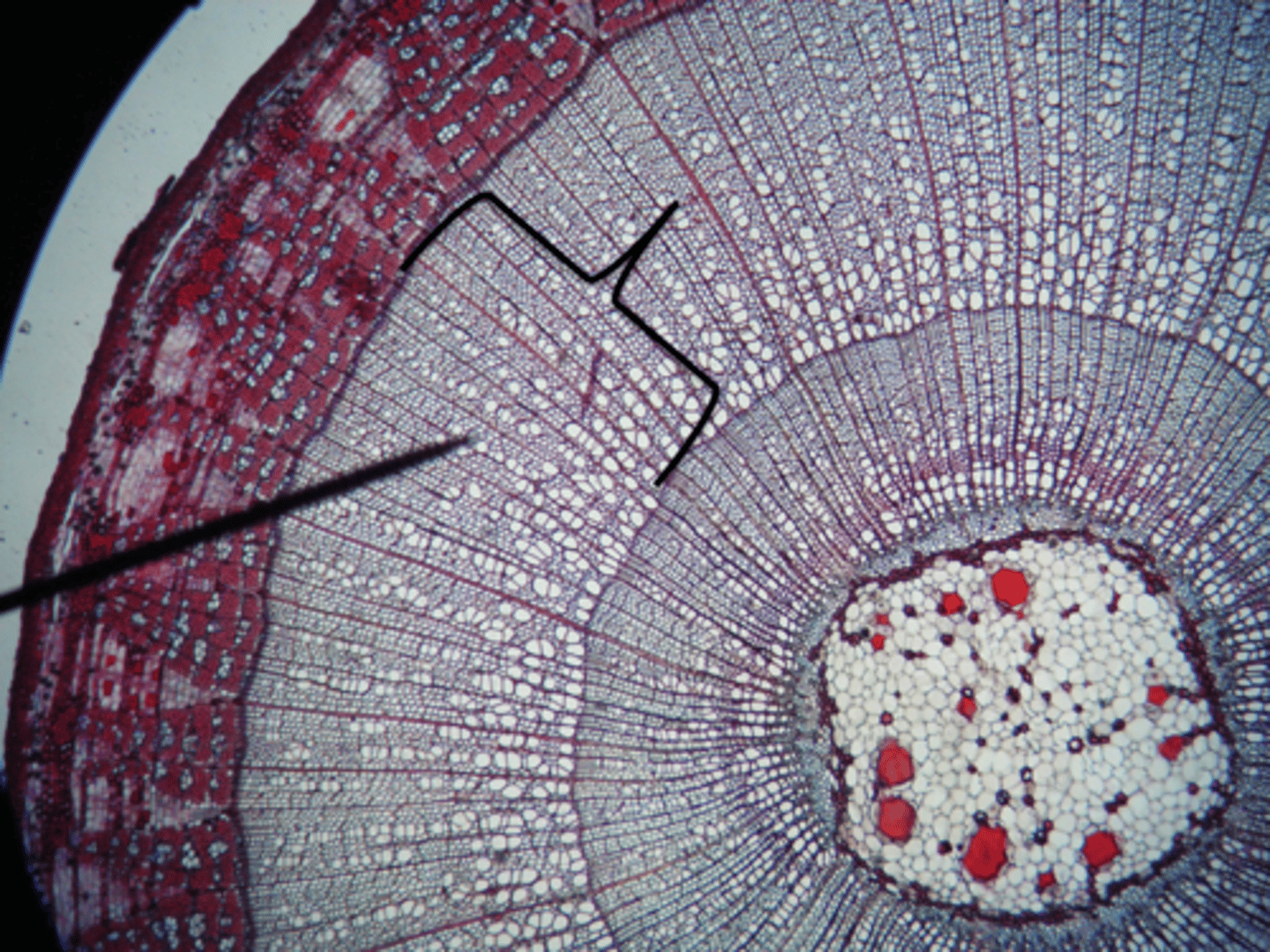
wood =
secondary xylem
secondary xylem =
wood
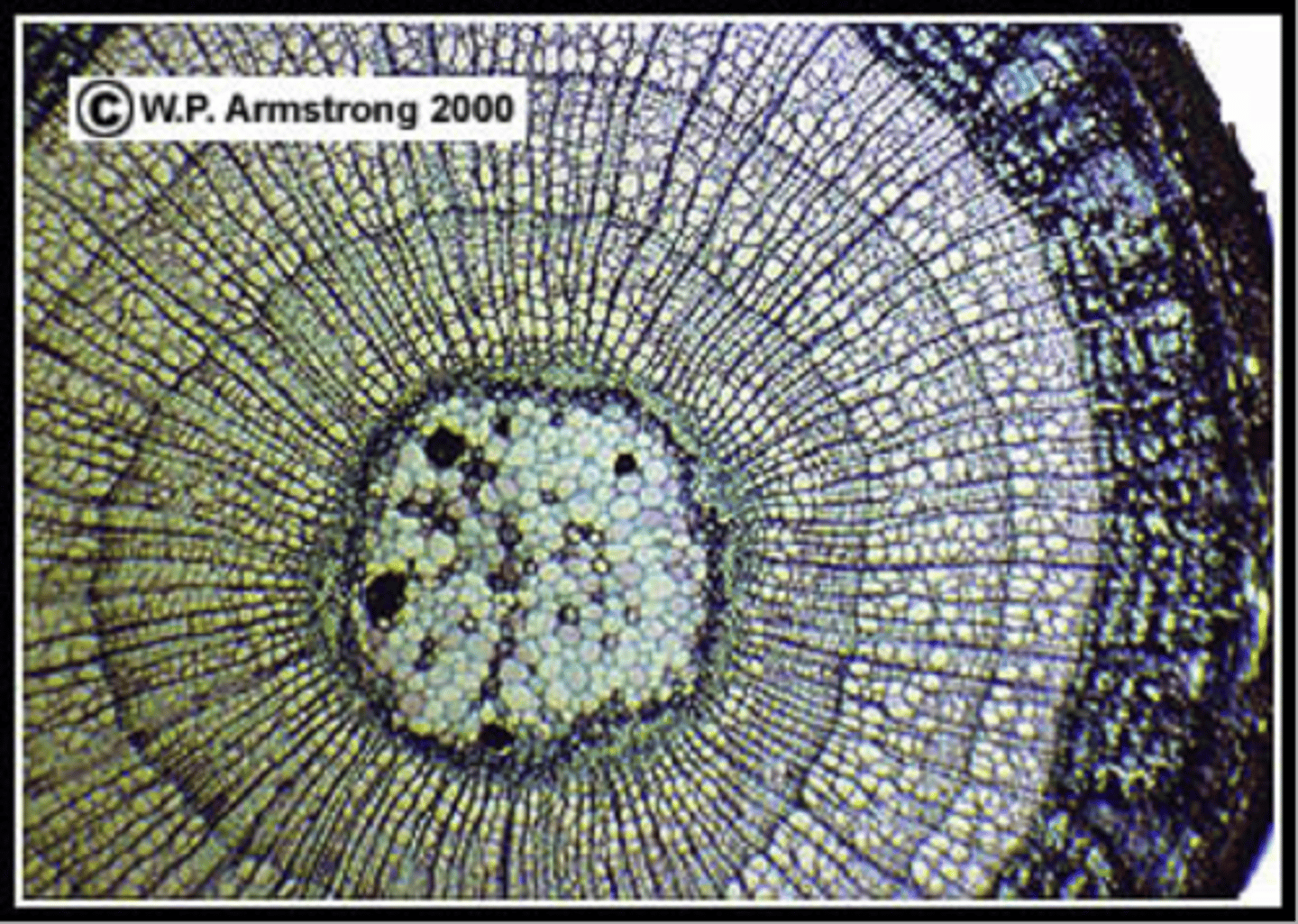
annual growth rings
The distinct layers of xylem that result from the patterns of seasonal growth in a tree
- 1st ring secondary xylem = 1st season of growth
- 2nd ring secondary xylem = 2nd season of growth
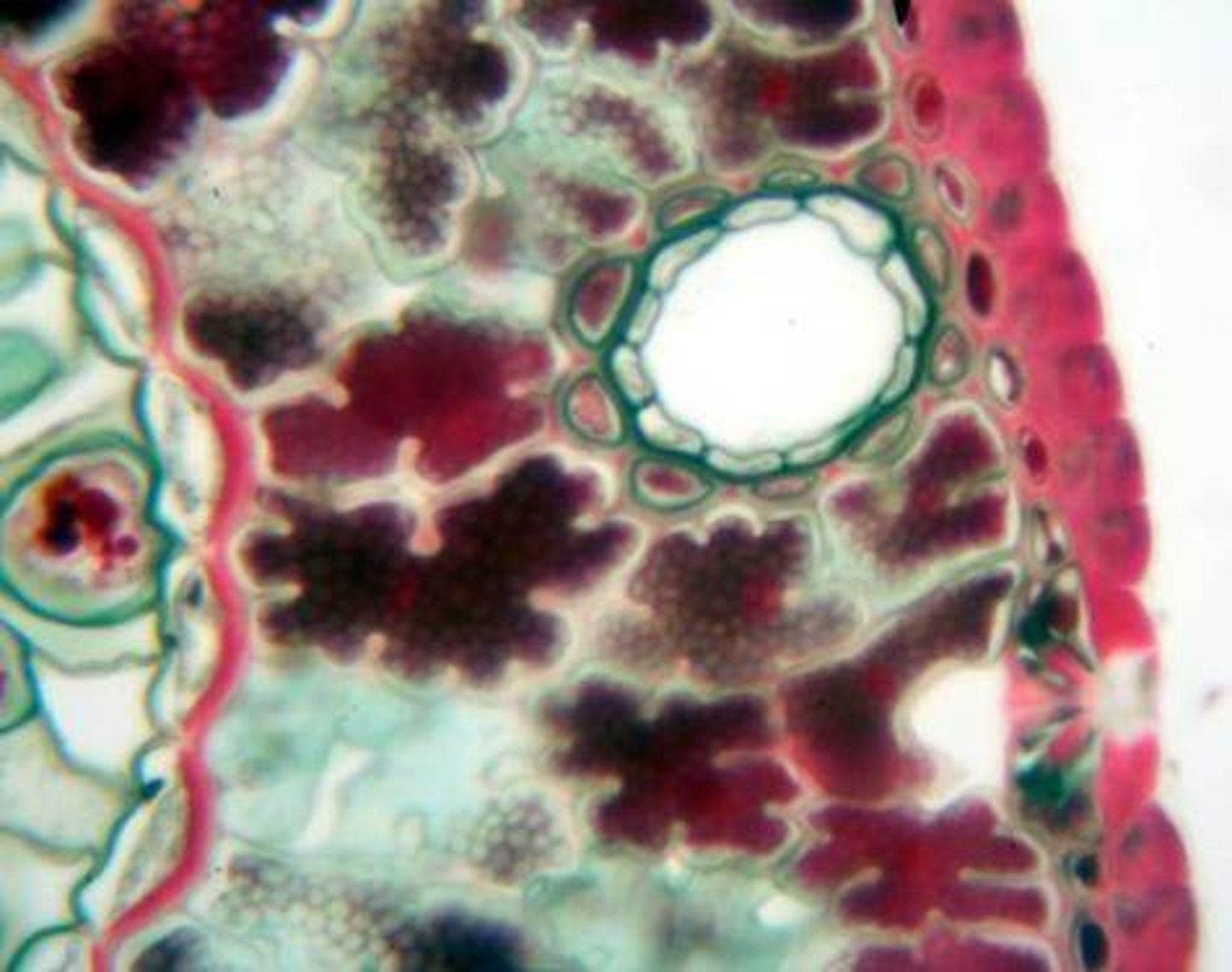
resin duct
A tubelike intercellular space that contains a clear, viscous liquid (resin) that protects the plant against herbivores and pathogens
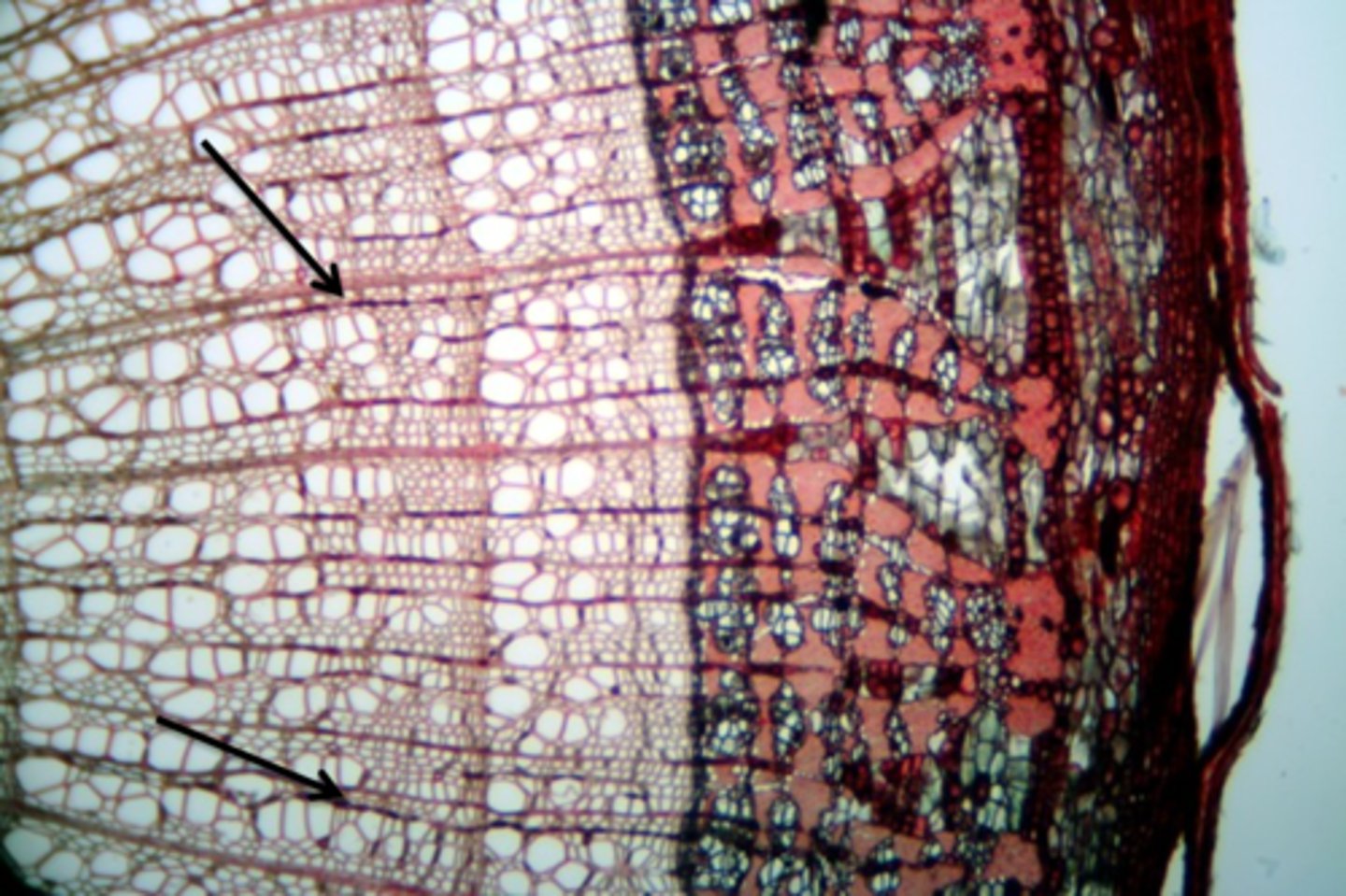
Late wood
formed in late summer and is harder (thick-walled cells) and less porous

early wood
formed in the spring and has thin cell walls to maximize water delivery
- less dense because cells are larger and walls are thinner

sapwood
layer of secondary phloem that surrounds the heartwood; usually active in fluid transport
- usually lighter in color
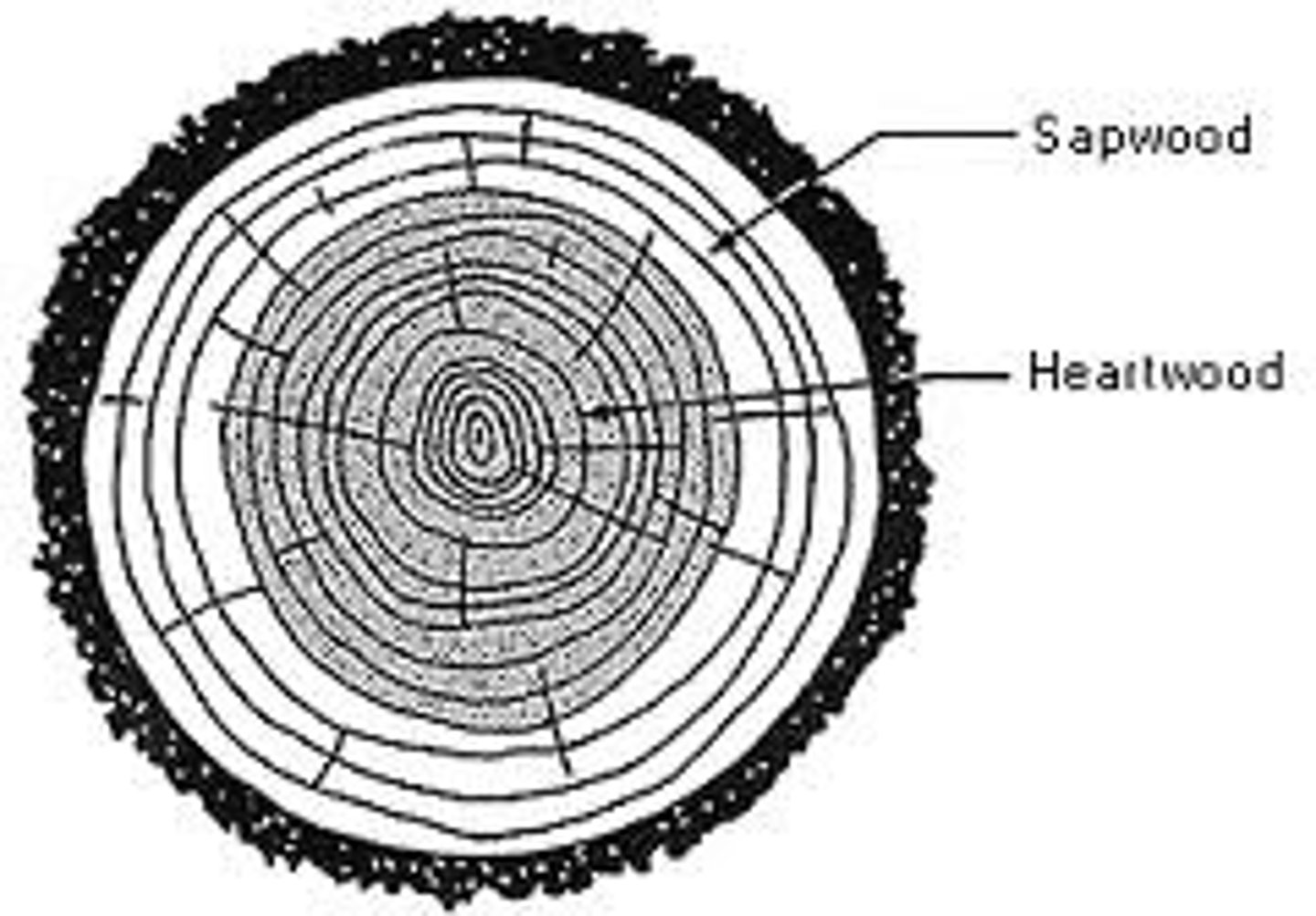
heartwood
older xylem near the center of the stem that no longer conducts water
- usually darker
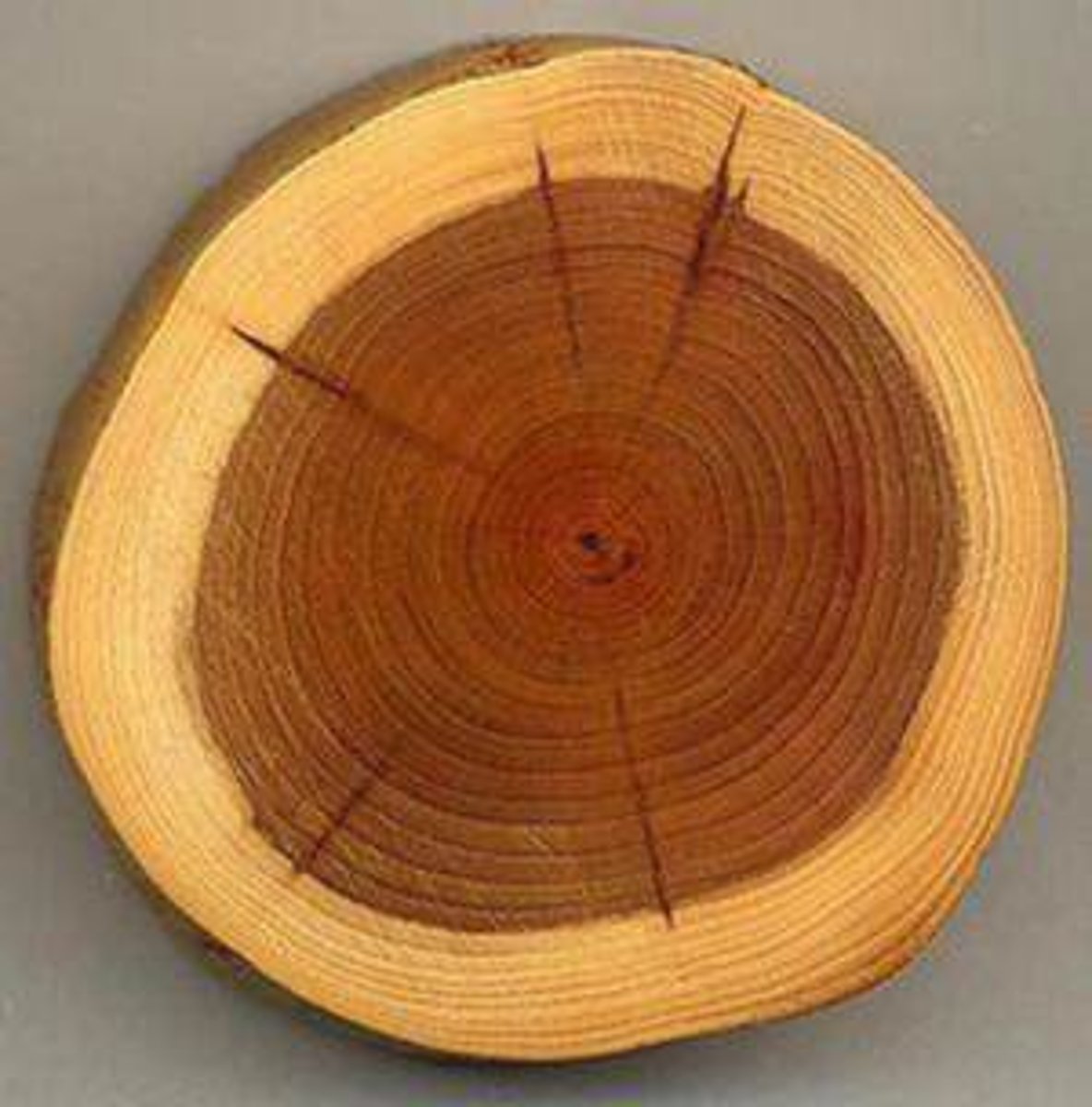

girdling
Removing a strip of bark from around a tree
xylem ray
a vascular ray located in the xylem
- Provides lateral movement of water and minerals in woody stems
phloem ray
a vascular ray located in the phloem
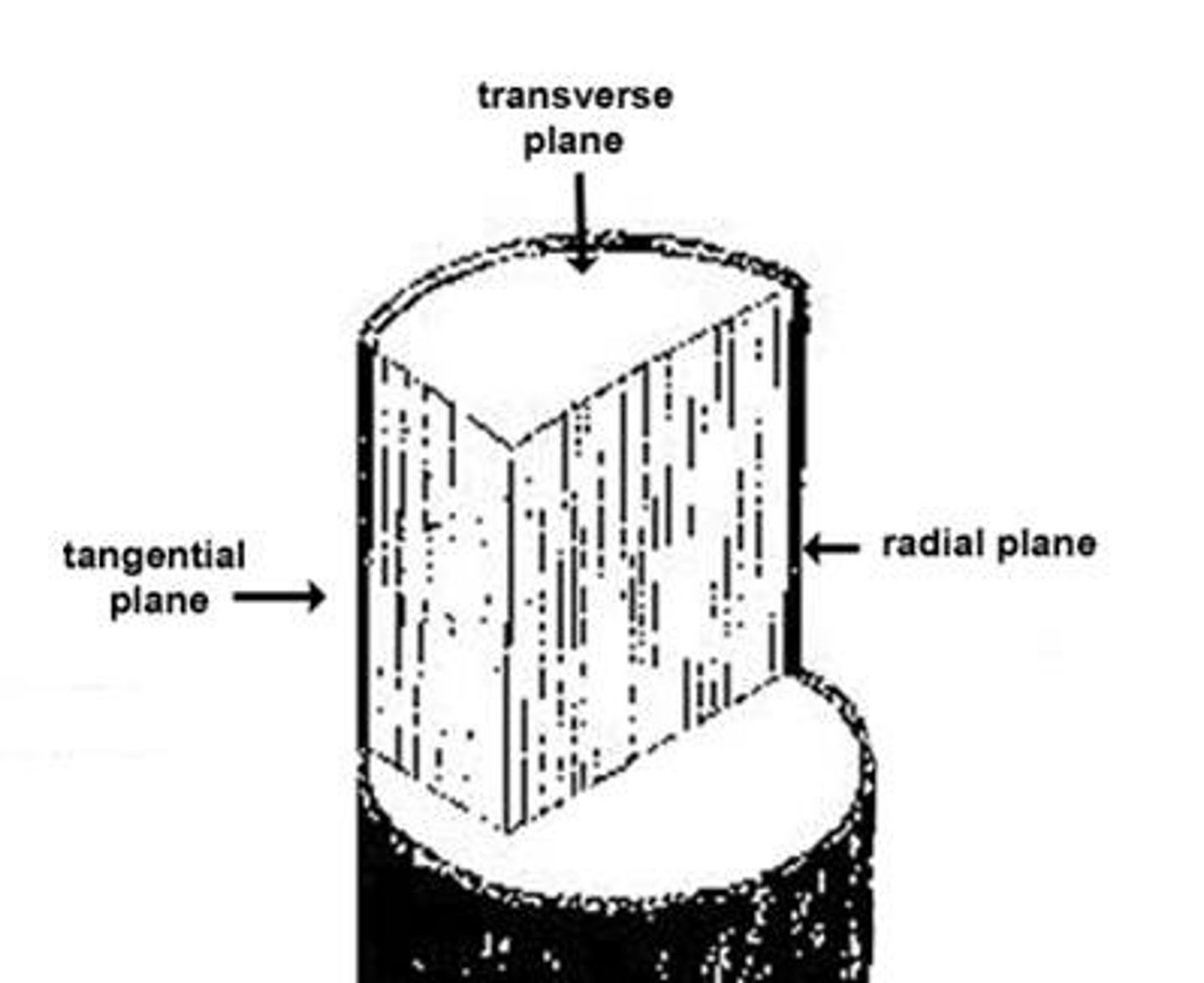
surfaces of wood
transverse, tangential, and radial surface
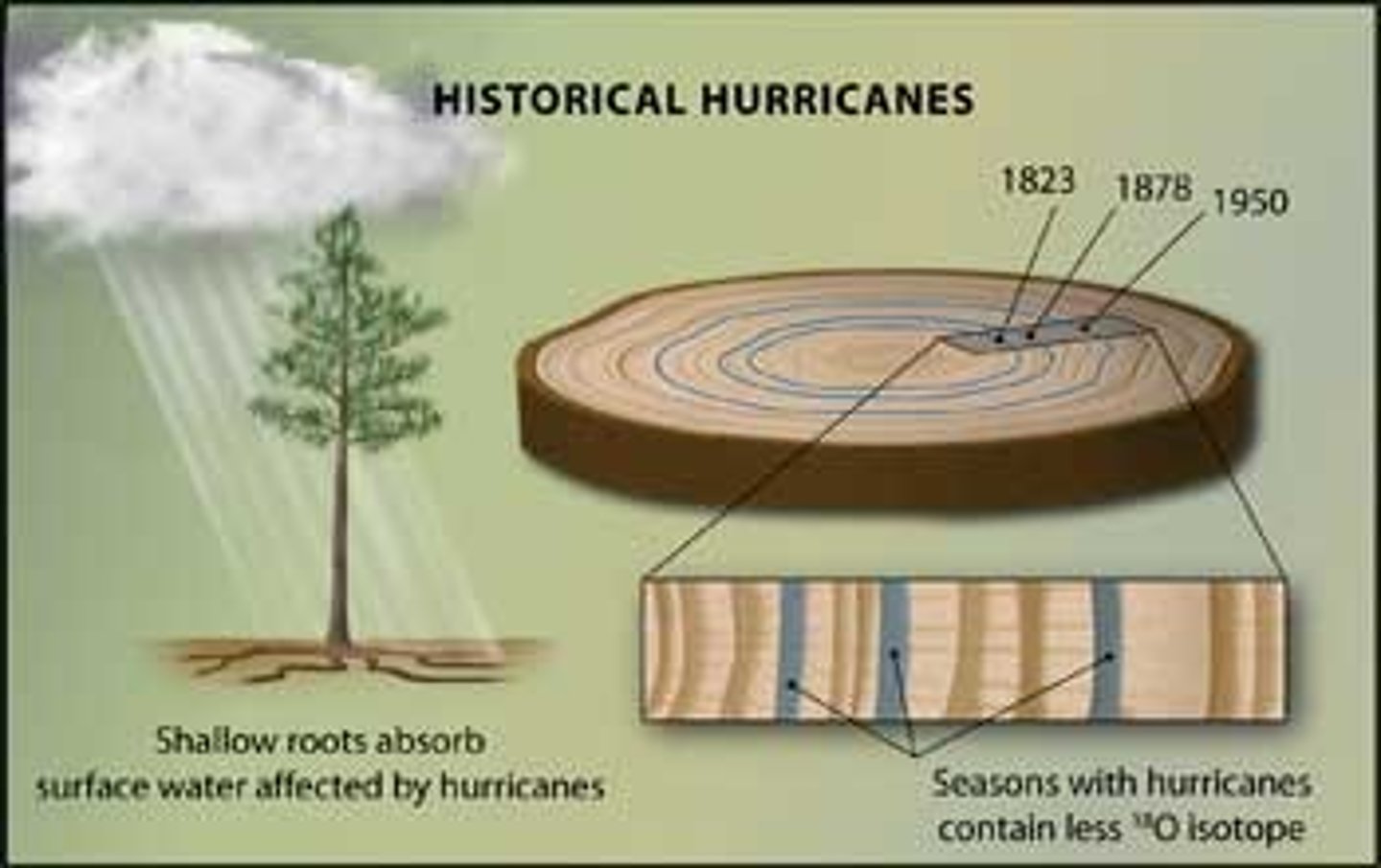
dendrochronology
process of counting tree rings to determine the age of a tree
- inferring something about the past based on growth rings
- can detect drought, fire, insect damage, and climate cycles
- wide rings = wet years
bristlecone pine
the world's oldest known living tree (5,068 years in 2018)
- dendrochronology ≈ 9000 years exists

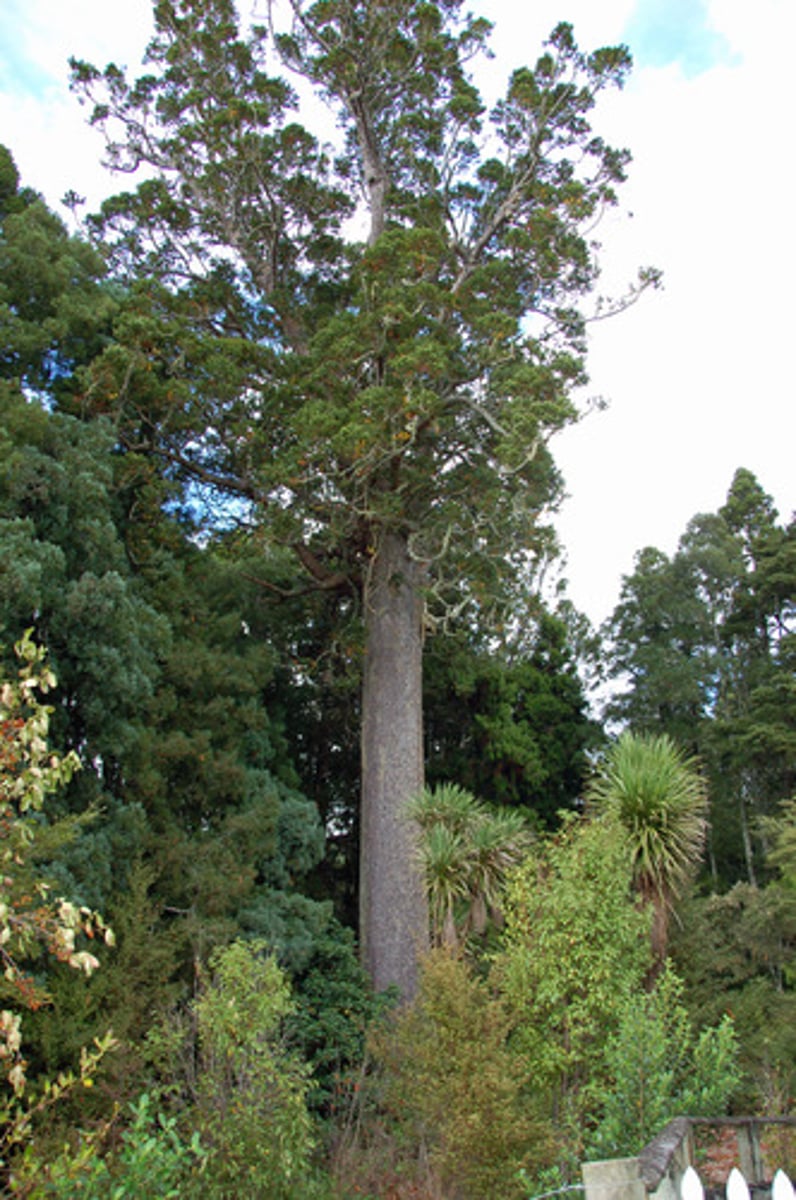
kauri tree in New Zealand
- live about 2000 years
- swamp-preserved trees to 60,000 yrs
- 14C dating calibration

14C Dating
absolute dating technique which measures the amount of C14 in sample, must be organic
NOAA (International Tree Ring Data Bank)
where dendrochronology is done
- over 1500 sites
hardwood
Angiosperm wood
- vessel members present, also tracheids and fibers
- tough, heavy timber with a compact texture; any deciduous tree (tree that loses its leaves annually)
- typically used for making cabinets
- ex: Oak, Maple, Cherry, etc.

softwood
Gymnosperm wood
- vessel members absent, tracheids and fibers only
- any light, easily cut wood (cone bearing or coniferous)
- typically used for decks (easier to hammer nails in)
- ex: Pine, Cedar, Redwood, etc.
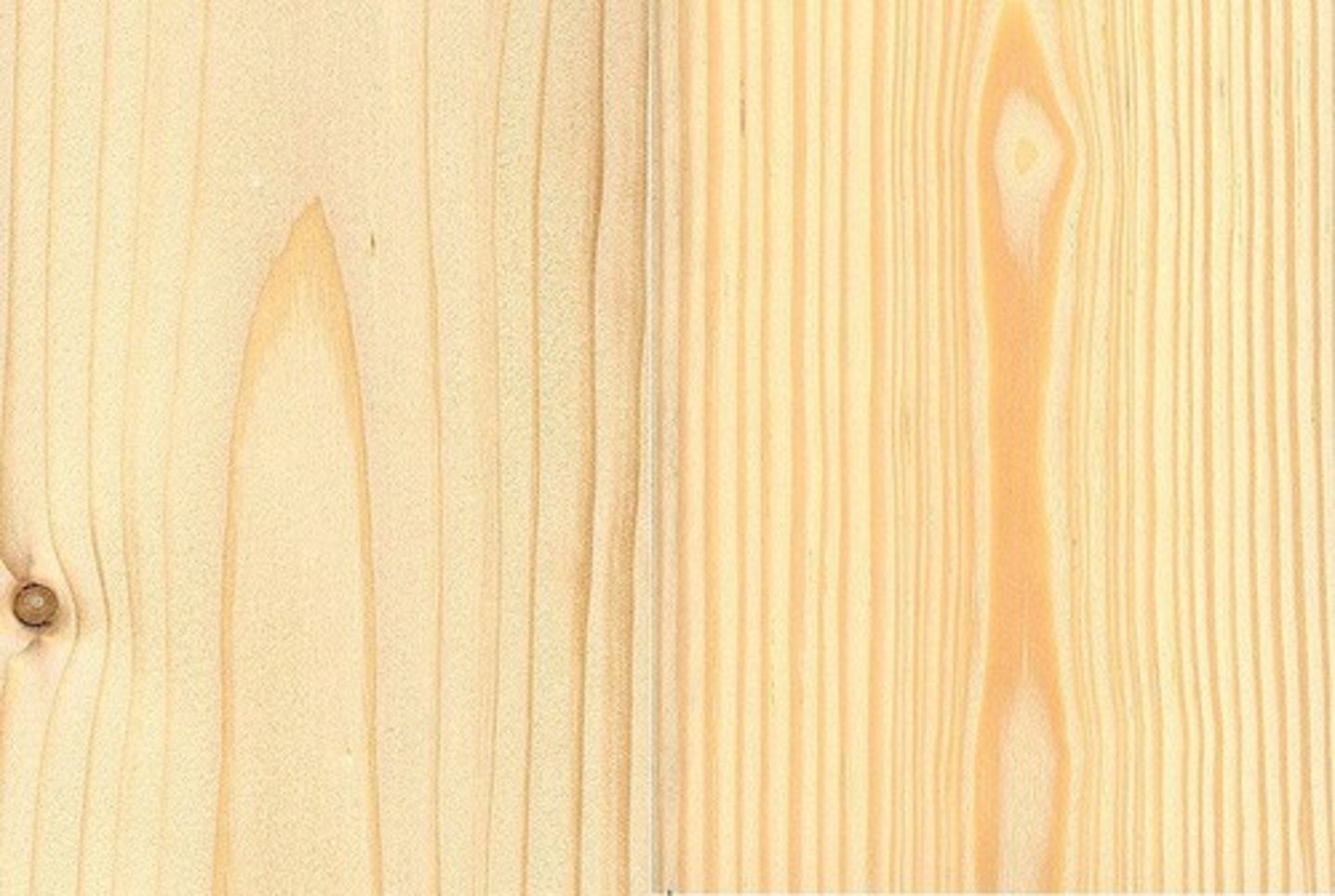

in hardwood, the vessel members are...
present, along with tracheids and fibers
in softwood, the vessel members are...
absent, only tracheids and fibers present
hardwood =
angiosperm wood
softwood =
gymnosperm wood
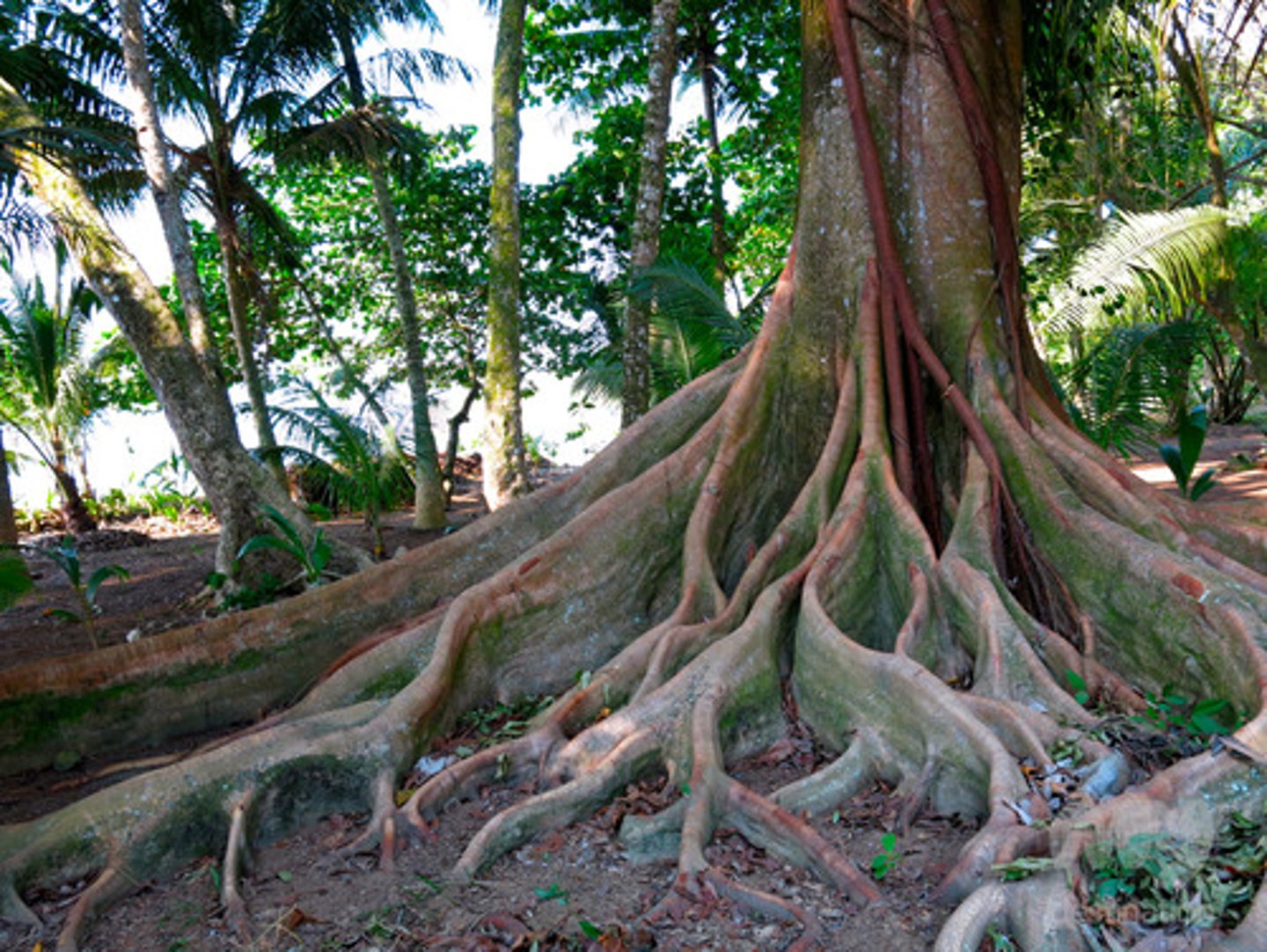
wood modifications
- buttresses
- reaction wood
- knot
buttresses
-Trunk spreads wide at bottom to keep tree straight
-Deep roots not necessary because not much nutrients
- ex: Cyprus

reaction wood
wood of abnormal growth due to inclination (mechanical stress) of the trunk
- uneven thickening, keeps branch from breaking

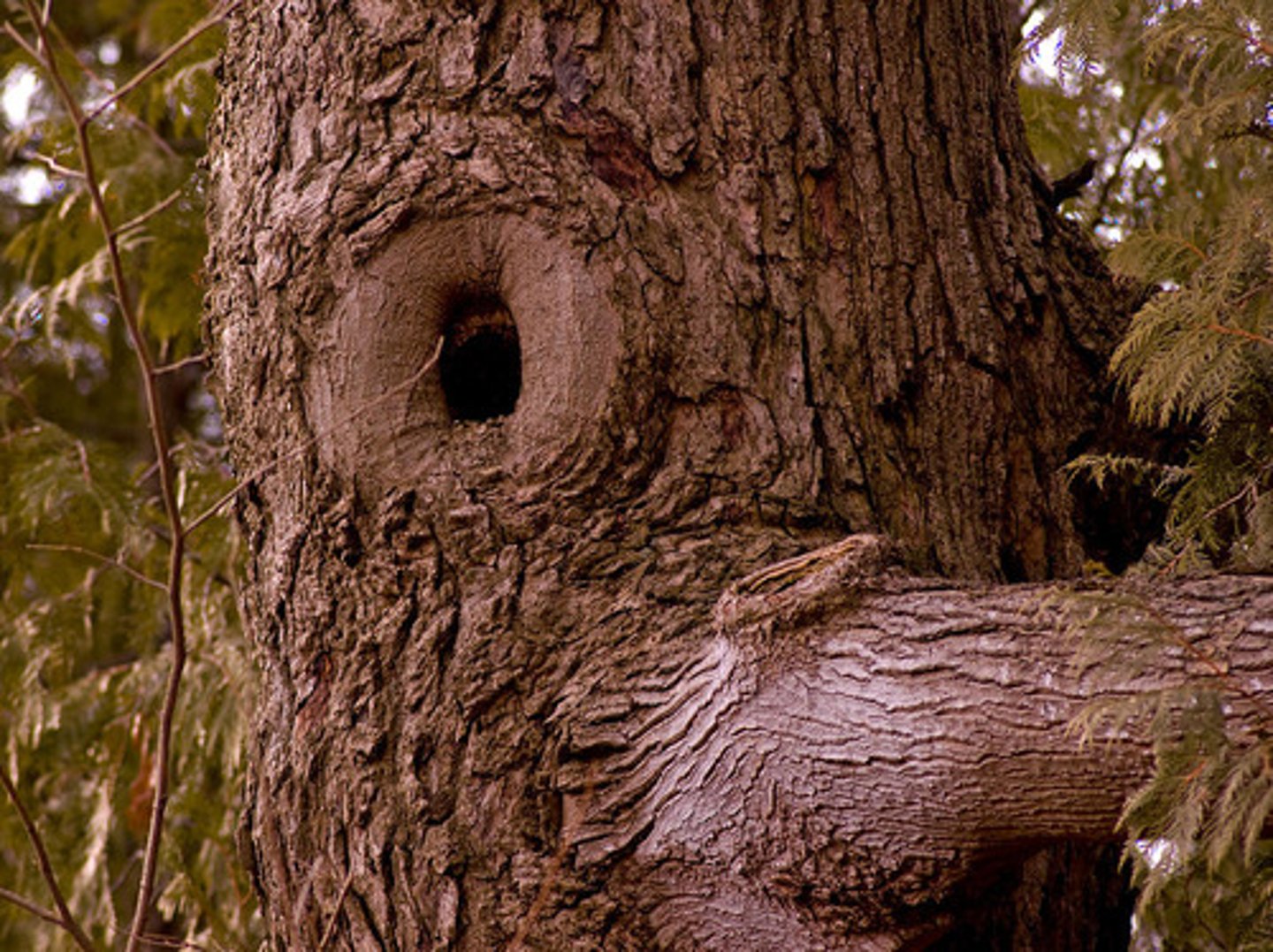
knot
branch is imprisoned/incorporated in the wood as it grew
- ex: chain in tree becomes included in the tree as it grows, -
- horse shoe that was hung on a branch becomes embedded in the tree

Do monocots have secondary growth?
very few do
- ex: Joshua trees