Topic 4- Biodiversity and Natural Resources
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
cellulose function and structure
structural component of plant cell walls to provide strength and support
made of β-glucose, bonded together by 1,4-glycosidic bonds, joined in a condensation reaction
every alternate β-glucose is inverted, and it is unbranched
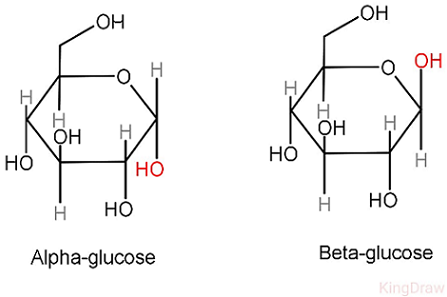
alpha and beta glucose- isomers
—> alpha glucose has two hydroxyl groups adjacent
cellulose microfibril structure
contains β-glucose
joined by 1,4-glycosidic bonds and alternate glucose molecules are inverted
microfibril is composed of many (60-70) cellulose molecules held together by hydrogen bonds
structure of the plant cell wall
made of cellulose molecules
bundles of cellulose molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds to form cellulose microfibril
layers of microfibrils are laid down at different angles to form a mesh, which is then embedded in a matrix of hemicelluloses and pectins to form the primary cell wall
secondary thickening involves lignin being added to form the secondary cell wall
xylem vessels
cellulose microfibrils in cell walls
walls thickened with lignin, often in spirals or rings
continuous column made of hollow, dead cells with no cell contents
pits in walls
vessels have open ends
at the innerpost point of the vascular bundle
function: transport of water and disolved mineral ions from roots to leaves, and provides structural support
phloem
cellulose cell wall
seive tube elements have thin peripheral cytoplasm and few organelles
have seive plates and pores
a companion cell is linked to each seive tube element by plasmodesmata
living tissue
in the middle of the vascular bundle
function: transport of organic solutes eg sucrose or amino acids from source to sink, in translocation
sclerenchyma fibres
fibres have cellulose cell walls which are thickly lignified
dead and hollow cells when mature
often have pits in their walls
long, narrow cells, usually pointed at both ends
at the outer point of the vascular bundle
function: structural support only
linking structural components of xylem to its function
lignin and cellulose microfibrils in cell walls- for strength to prevent the vessel collapsing
lignin in walls- to make the vessel waterproof
lignin in rings or spirals- allow stretching and flexibility as plant grows
no end walls- forms a continuous, dead, hollow tube with no cytoplasm to reduce resistance or obstruction to water flow
pits in walls- allow lateral/sideways movement of water between xylem vessels
large cross sectional area- allows a larger volume of water to be transported
transpiration
water evaporates from the surface of the leaf cells into the air spaces and exits the leaf by transpiration- water vapour diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata down a concentration gradient
this creates a low hydrostatic pressure in leaves which draws water out of the xylem vessels by osmosis
a continuous column of water molecule (transpiration stream) is pulled, under tension, up the xylem by capillary action
due to cohesion- hydrogen bonding between polar water molecules in xylem, and adhesion- hydrogen bonding between water and the cellulose in xylem walls
water moves into roots by osmosis, creating a high hydrostatic pressure
water moves along the high hydrostatic pressure gradient, from high pressure in roots to low pressure in leaves, by mass flowrol
role of water in plants
act as a reactant in photosynthesis
keep plant turgid for support
needed for hydrolysis reactions eg breakdown of starch
as a solvent to dissolve and transport mineral ions
calcium ions
needed to make calcium pectate for making the middle lamella which holds plant cells together, plays a role in permeability
deficiency exhibits symptoms such as young leaves turning yellow and crinkly, growng points die back, stunted growth
magnesium ions
needed for making chlorophyll, which is required for photosynthesis. also needed for nucleic acid synthesis and activation of some plant enzymes
deficiency exhibits symptoms such as less glucose being made and stunted growth (due to lack of chlorophyll synthesis and therefore photosynthesis), yellowing of leaves between the veins
nitrate ions
needed to make amino acids for the synthesis of proteins including enzymes, and also found in chlorophyll, nucleic acids, ATP, growth hormones
deficiency exhibits symptoms such as older leaves turning yellow and dying, lack of side shoots, and stunted growth due to lack of enzymes/proteins
phloem structure related to its function
transfer cell for loading sucros into the sieve tube at the source, or unloading at the sink
sieve tube has sieve plates with sieve pores, so fluid and flow through
companion cell has organelles including mitochondria that provide metabollic support for the sieve tube element cells
peripheral cytoplasm of sieve tube has few organelles so less resistance to fluid flow
translocation
at the source eg leaf, sucrose is produced from glucose and fructose
transfer cells actively pump sucrose into phloem sieve tubes against a concentration gradient, using energy in the form of ATP from respiration
there is a high sucrose concentration in the sieve tube at the source
this draws water into the sieve tube by osmosis from adjacent xylem vessels, increasing hydrostatic pressure at the loading end of the sieve tube
fluid in the sieve tube flows from high to low hydrostatic pressure by mass transport
sucrose is activeky unloaded using ATP in sinks where the sugars are needed, so solute concehtration decreases in the sieve tube at the sink.
water moves back into the xylem by osmosis, decreasing hydrostatic pressure
bacterial growth- optimum temperature (varies with species)
for optimum enzyme activity, rate of reaction and growth metabolism
bacterial growth- optimum pH
for optimum enzyme activity, rate of reaction and growth metabolism
bacterial growth- optimum oxygen concentration
for respiration to release energy
bacterial growth- optimum concentrations of glucose, nitrogen, etc
glucose for respiration to release energy
nitrogen for making amino acids to make proteins for growth and DNA
bacterial growth- moisture/water
for cell function eg hydrolysis reactions g
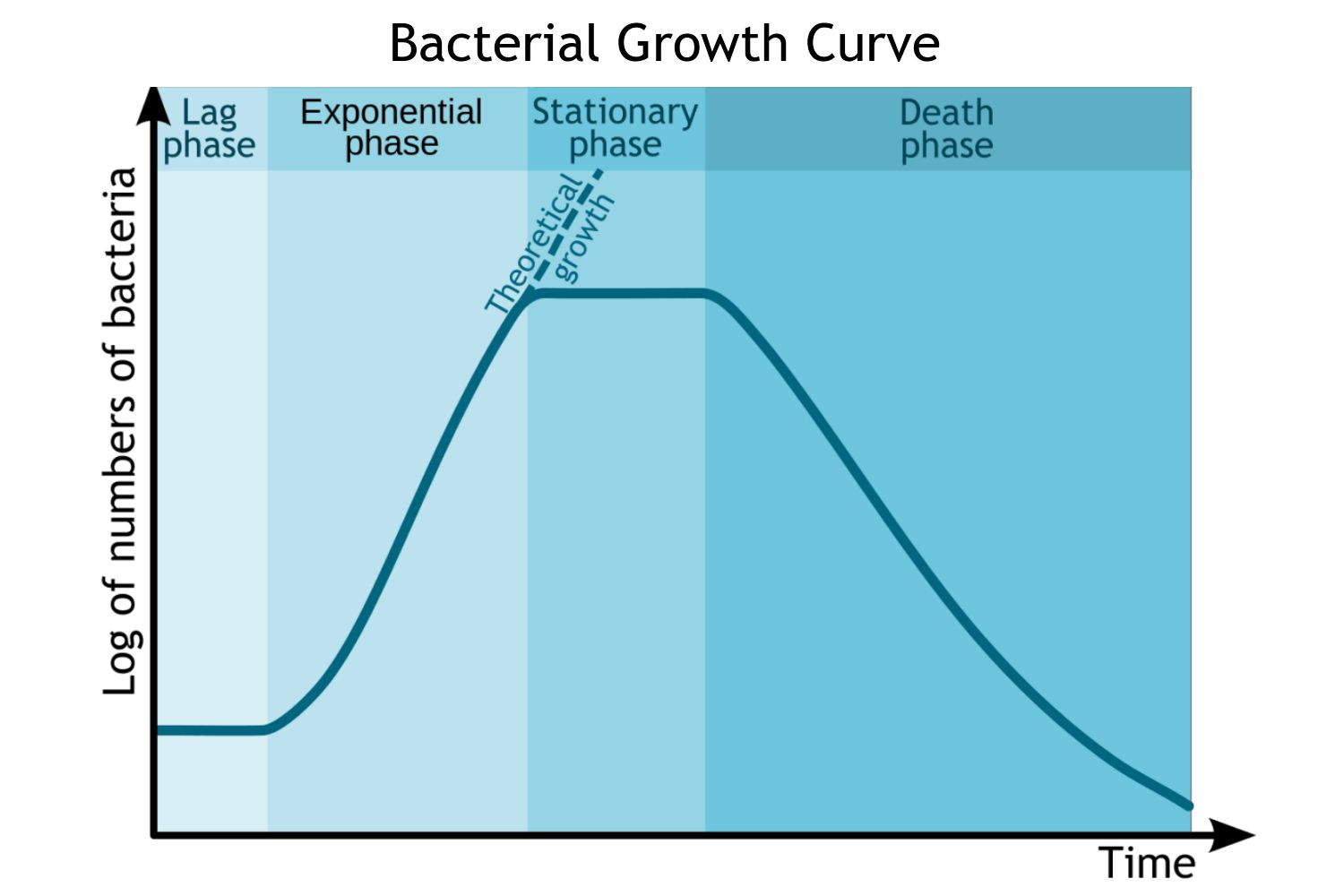
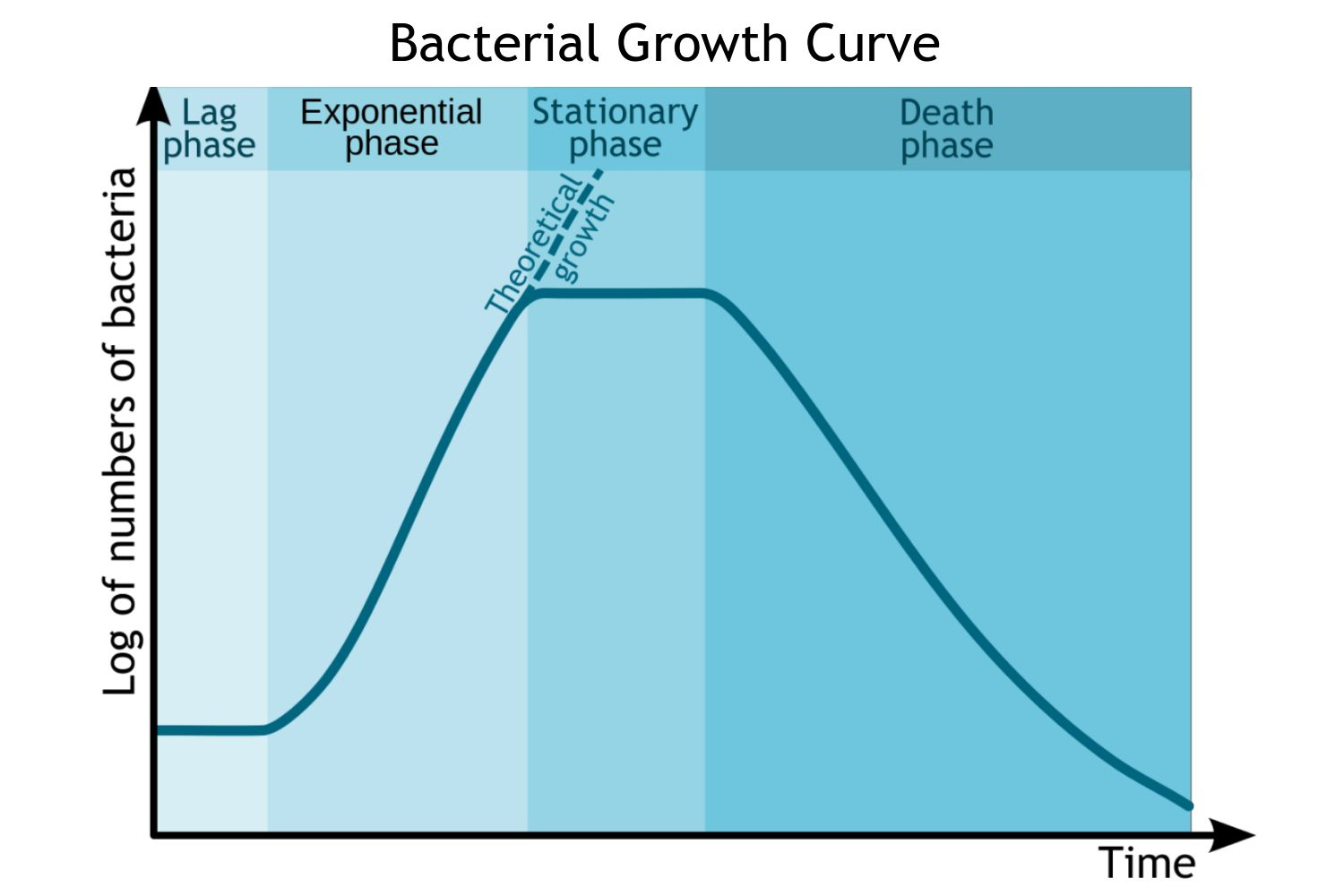
growth of a bacterial culture graph
lag phase- no change/increase in number of cells as they adjust to conditions
log phase- number of cells increases as cells divide at the fastest rate possible for the conditions, doubling each time
stationary phase- no change/increase in number of cells as glucose is depleted and waste products build up, causing a change in pH
death phase- number of cells decreases as cells dying are more than cells being formed
starch structure
alpha-glucose joined by glycosidic bond in condensation reactions
made of amylose and amylopectin
amylose: 1,4- glycosidic bonds, straight chained, spiralled
amylopectin: 1,4 and 1,6- glycosidic bonds, branched
uses of starch from seeds
stiffening agents eg fabric or paper
thickning agents for custard or wallpaper paste
starch foam for packaging
superabsorbants eg for nappies
sustainable resource
a resource that is renewable and will not run out so s therefore available for future generations
plastic/petrol sustainability
come from crude oil which is a fossil fuel, so is non-renewable and will run out
why is starch renewable
made from plants, which are a renewable resource as more plants are grown to replace those used
they biodegrade/decompose more quickly, so will not contribute to landfill
drug testing: William Withering’s protocol
potentially useful plant chemical/ substance identified
trial on a small group of patients with the disease- side effects recorded
trial on a larger group to discover the effective dose
results recorded and published
pre-clinical trials
lab testing on animals or cells/tissue cultures to assess safety/side effects and determine if drug is effective against the disease
clinical trials phase 1
small group of healthy human volunteers are given the drug to look for side effects in humans. different doses are trialled to find one which is both safe and effective. is the drug absorbed, distributed, metabolised, excreted as expected?
clinical trials phase 2
does the drug work?- it is tested on a small group (100-300) of volunteer human patients who have the disease
clinical trials phase 3
a double blind randomised controlled trial
a larger group (1000-3000) of patients are assigned randomly either to either a test group, who are given a new drug or a control group, who are given the existing drug (or a placebo/sugar pill if no existing drug is available)- checks for effectiveness (efficacy) and side effects
control group is for comparison with the test rgroup, to prove any improvement is due to the new drugs to improve validity
statistical analysis of data- checks if drug is effective by seeing if there is significant difference/improvement in patients taking it compared to those taking the existing drug
clinical trials after licensing
drug licenced. data on efficacy and safety continues to be collected and monitored
placebo
an inactive substance which does not contain the drug. used as a control to compare to the actual drug and removes the psychological effect taking a drug
double-blind trial
some people are given the drug and sme are given a placebo, or existing drug, and neither the patient nor the doctor know who has been given the actualy drug and who has been given the placebo, removing bias from the trial