Reproductive strategies
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what does asexual reproduction show
that sex is not essential to produce offspring
binary fission
a process in which one individual produces a copy of all its DNA, grows to 2x its original size, then splits in two
asexual (or vegetative) propagation
a new plant is produced from the roots, stem, or leaves of a single parent
parthenogenesis
females lay unfertilized eggs, which develop into offspring; can lead to an all female species
what is a major cost of asexual reproduction
if a deleterious mutation is present in a chromosome, all offspring produced would inherit this detriment because offspring are clones of the parent
true or false: asexual organisms do not undergo recombination or independent assortment
true
What is Muller’s Ratchet
in asexual reproduction, once a mutation evolves in a lineage, it becomes permanent
what does sexual reproduction require
gametes, which are formed during meiosis
what is a benefit of sexual reproduction
once a mutation evolves in lineage, it does not become permanent
t/f: asexual reproduction avoid muller’s ratchet
false; sexual reproduction avoids this
how is sexual reproduction defined
by a union of gametes
isogamous vs anisogamous
species differ in the size of gametes
isogamy
all individuals within a species produce gametes of the same size (no genetic sexes, but different mating types)
anisogamy
individuals within a species produce gametes of different sizes (i.e., genetic sexes)
under isogamy, if gametes are the same size, but different types does fertilization occur
yes
under isogamy, if gametes are the same size and the same mating type does fertilization occur
no
under isogamy, gametes from each mating type contain
DNA, as well as nutrients for developing zygote (yolk)
what is the ancestral state of sexual reproduction
isogamy
in anisogamy gametes are different types and sizes therefore
fertilization occurs
smaller gametes are
mobile, provide no nutrients (DNA only), and can be produced in great number
larger gametes are
generally immobile, provide essential nutrients for the developing zygotes and are few in number
anisogamy evolves from isogamy due to
competition
small low investment gametes can be
mass produced and spread far
large immobile gametes ensure
offspring survival and rely on the numerous, mobile gametes to fertilize them
what does anisogamy lead to
differential parental investment
pre-fertilization under anisogamy
egg production requires a greater energy investment than sperm production
post-fertilization under anisogamy
gestation or incubating and defending eggs requires much energy. these tasks are generally carried out by females who have already invested more.
under anisogamy natural selection promotes the defense of what sex
women as they invest more than men
how does anisogamy cause males and females to differ
in their potential rate of reproduction
the difference in the potential rate of reproduction is demonstrated by what
Bateman’s curve
are males limited when it comes to reproduction
no, due to the production of small cheap sperm males can increase reproductive success by seeking multiple partners
are female limited when it comes to reproduction
yes, by the production of large, expensive eggs. because of this females cannot increase reproductive success by seeking multiple partners per reproductive cycle
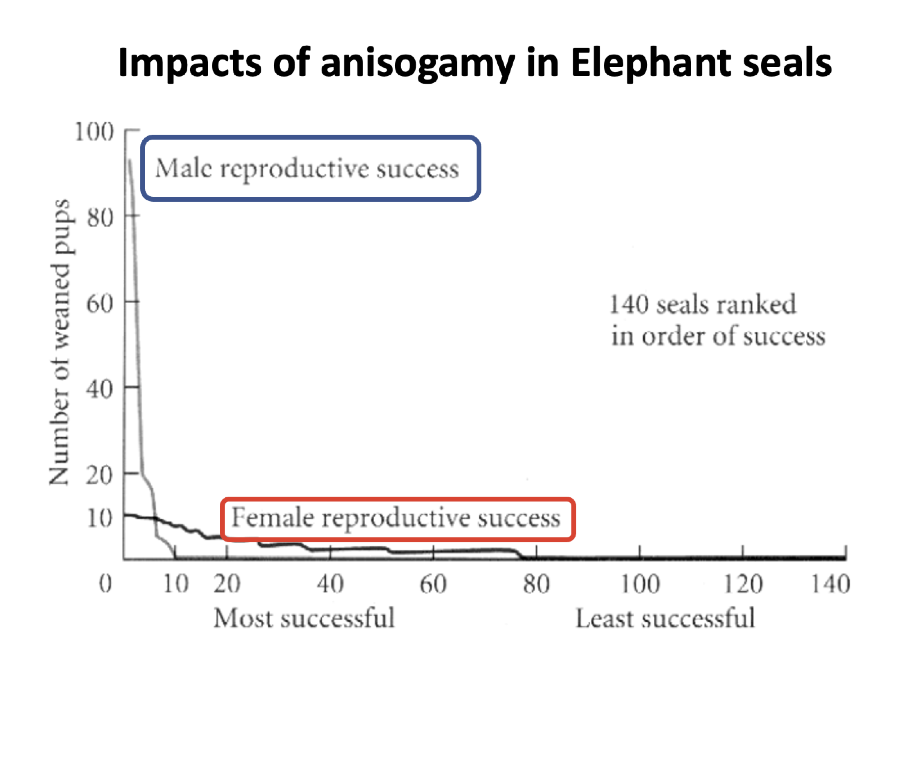
what does this graph show
there is high variation between reproductive success of males, few males are highly success but most males are highly unsuccessful
there is low variation between reproductive success of females, most females are somewhat successful