ASTR Exam 1
1/645
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
646 Terms
Earth's Cosmic Address
Earth, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy, Local Group, Local Super Cluster
solar system
the sun and all of the planets and other bodies that travel around it
galaxy
an island of stars in space all held together by by gravity and orbiting a common center
The Milky Way
-the galaxy our solar system is in
-relatively large, one of the two largest in our local group
Where is our solar system located within the Milky Way Galaxy?
a little over halfway from the galactic center to the edge of the galactic disk
local group
-the group of about 40 galaxies that the Milky Way belongs to
-located on outskirts of our local supercluster (Laniakea)
Galaxy cluster
cluster of galaxies
superclusters
-largest known structures in the universe
-region where galaxies and galaxy clusters are more tighly placed
universe
The sum total of all matter and energy; that is, everything within and between all galaxies along with all of the different structures (planets, galaxies, stars, superclusters, voids, etc)
Astronomical Unit
-average distance of Earth from the Sun
- 1 AU = 150 million km
-mainly used for distances in our solar system
Light year
-distance light travels in one year
- 1 ly = 10 trillion km
-used to describe distances of stars and galaxies
in what way do we "look back in time" when observing space?
-since certain objects in space are so far away it can take light years to reach us
- however many ly away = how many years ago from the present we are seeing something
- Ex. Andromeda is 2.5 mil ly away so we see it as it was 2.5 mil years ago
why are snapshots of galaxies pictures of space and time?
- the shape of galaxies give them a far and near side which are different ly lengths
- allows us to see different parts of a galaxy over a spread out time period
- In Andromeda galaxy the light we see from the far side left 100,000 years before the light on the near side
observable universe
-The portion of the entire universe that can be seen from Earth, at least in principle
-The observable universe is probably only a tiny portion of the entire universe.
-14 billion ly
-anything further than 14 billion of ly technically does not exist yet
what can the number of stars in the observable universe be compared to on Earth
counting every grain of sand on every beach on Earth
universe is expanding principle
-means distances between galaxies increase with time
-implies galaxies were once close together in the past
the big bang
-name of the event thought to mark the birth of the universe
-starting point of the universe's expansion
what happens when gravity overpowers the universe's expansion
forms galaxies and galaxy superclusters
-the gravitational pull of these does not expand with the universe and stays constant in size
how do stars and planets form?
Space stuff (dust, gas etc) is pulled together by gravity and forms a tight clump
when do stars "die"
when they exhaust their usable fuel from fusion
supernova
-a massive explosion that occurs when a star dies
-returns matter to space becoming parts of new clouds of gas and dust allowing new stars to be born
what were the two main chemical elements present in the early universe
hydrogen and helium
why are people "star stuff"?
because we are made of elements that were manufactured by the deaths of stars
what way does Earth rotate around its axis?
counterclockwise (west to east)
rotation
The spinning of Earth on its axis
-one rotation a day
orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space
-one year around Sun
ecliptic plane
The plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun
what is the tilt of Earth's axis?
23.5 degrees
what is axis tilt?
the amount by which a planet's axis is tilted with respect to a line perpendicular to the ecliptic plane
what way does Earth orbit the Sun?
counterclockwise (west to east)
why don't we see other stars racing in the sky?
-they are so far away their movement is not noticeable
-everything in the galaxy is still moving relative to one another
dark matter
matter that emits no light at any wavelength
-makes up most of space
dark energy
name given to energy that could be causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate
how do galaxies move relative to one another in the local group?
-galaxies either move towards or away from us
-some orbit other galaxies
how did we determine the age of the universe?
We based it on how quickly it is expanding
-exponential expansion
is there a center to the universe?
no
how does astronomy affect human history?
revolutions in astronomy have gone hand in hand with revolutions in science and technology that have shaped modern life
how many stars are visible to the naked eye on a moonless night away from city light?
2,000 stars
constellations
patterns in the sky that have been given names throughout history
what purpose do constellations serve for astronomers?
depict regions of the sky with self-defined borders
are stars in constellations close together
no they just appear close because of human's lack of depth perception
celestial sphere
the imaginary sphere on which objects in the sky appear to reside when observed from Earth
important points on the celestial sphere
-North Celestial Pole
-South Celestial Pole
-Celestial Equator
-Ecliptic
North Celestial Pole
point directly over Earth's North Pole
South Celestial Pole
point directly over Earth's South Pole
Celestial Equator
projection of Earth's equator into space, makes a complete circle around the celestial sphere
ecliptic
the path the Sun follows as it appears to circle the celestial sphere annually
-crosses at 23.5 angle due to Earth's tilt
features of the local sky
-horizon
-zenith
-meridian
horizon
boundary between Earth and sky
zenith
point directly overhead
meridian
imaginary half circle scratching from horizon due south through the zenith to the horizon due north
what do you need to pinpoint objects in the local sky?
-direction along horizon (azimuth)
-altitude above horizon
azimuth
An angle measured from due north clockwise
-N = 0 degrees
-E = 90 degrees
-S = 180 degrees
W = 270 degrees
altitude
angle above the horizon
angular size
angle an object appears to span in your field of view
can you use angular size to tell the true size of an object?
no
angular distance
angle that appears to separate objects
what is the angular size used to find?
apparent size
what is the angular distance used to find?
measure distance between stars
what direction do the stars appear to move through our sky?
east to west
circumpolar stars
stars that never set
where do stars rise and set?
rise in the east and set in the west
Does the sky vary with latitude or longitude?
latitude
why does latitude effect the constellations we see?
because it impacts where our horizon is
what is the altitude of the celestial pole equal to?
your latitude
why does the night sky change throughout the year?
because Earth changes position in its orbit
In what direction does the Sun appear to move through our sky?
east to west (westward)
what determines what constellations we see at night?
the Sun's apparent location along the ecliptic
during a zodiac's paired month can you see that constellation?
-no because it is where the Sun is located so it is only visible in the daytime sky
-instead we see opposite constellations
what causes the seasons?
the tilt of Earth's axis
- causes sunlight to fall differently on Earth at different times
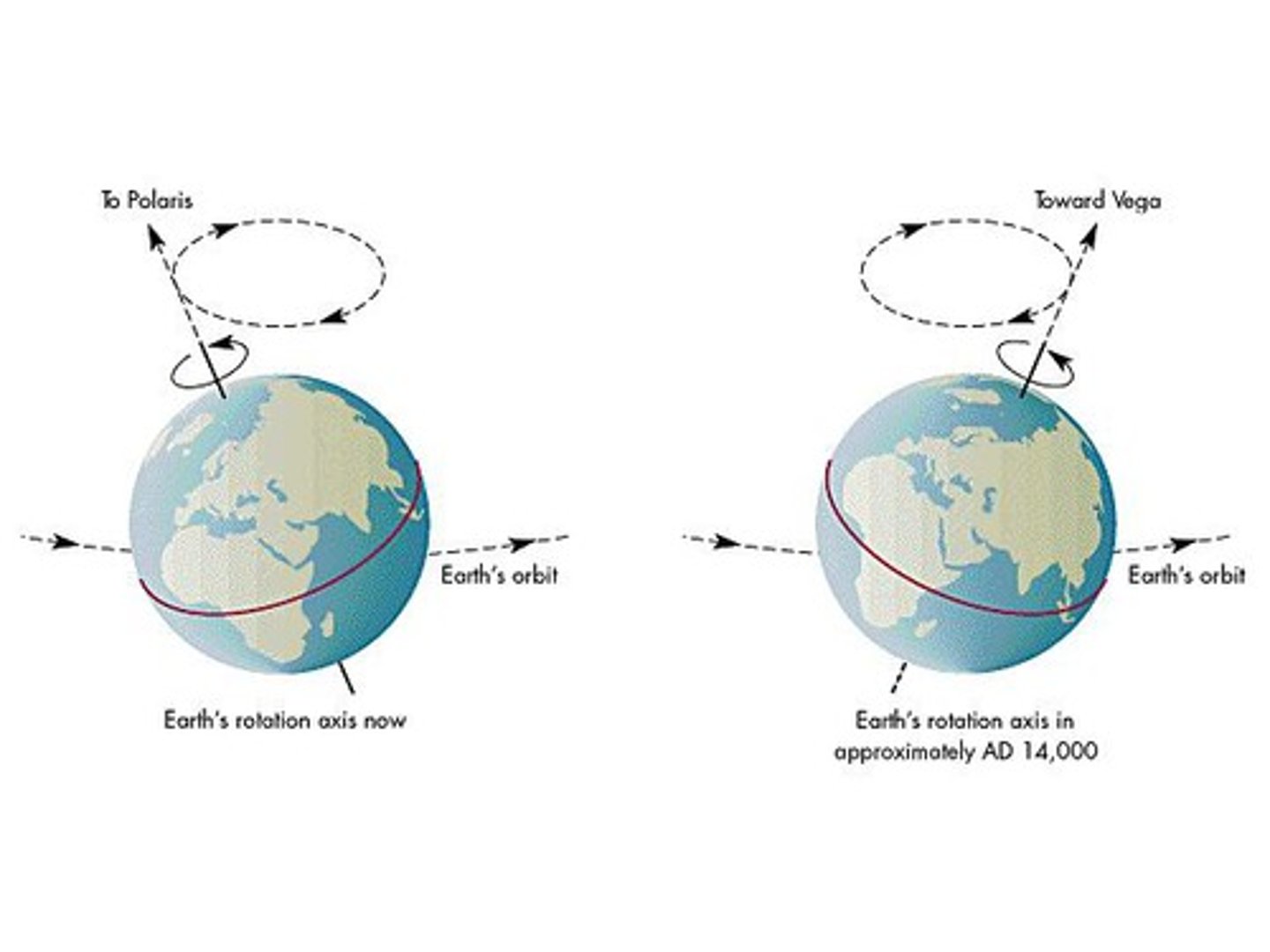
does Earth's tilt direction ever change
No, always pointed towards Polaris
When is the NH tipped toward and away from the Sun
toward in June and away in December
When is the SH tipped toward and away from the Sun
toward in December and away in June
Earth's orientation in June
sun hits at steep angle for NH and shallow angle for SH
what season does a steep angle cause
Summer
-More concentrated light, makes it warmer
-Means the Sun follows a longer and higher path through sky, more hours of daylight, more time to be warmed by Sun
what season does a shallow angle cause
Winter
Sunlight is less concentrated
Sun follows a shorter, lower path through sky
Earth's orientation in December
sunlight hits Earth at steep angle in SH and shallow angle in NH
When are the NH and SH illuminated equally
March and September
-mark the transitional seasons
what season is March in the NH
spring
what season is March in the SH
fall
what season is September in the NH
fall
what season is September in the SH
spring
what would happen if Earth did not have an axis tilt
there would be no seasons
June solstice
-summer solstice for NH
-winter solstice for SH
-June 21
-NH tipped most directly toward Sun and receives most direct sunlight
December solstice
-winter solstice for NH
-summer solstice for SH
-December 21
-NH receives least direct sunlight
March equinox
-spring/vernal equinox in NH
-fall/autumnal equinox in SH
-March 21
-NH goes from being slightly tipped away from Sun to being tipped slightly toward Sun
-winter to spring NH
-summer to fall SH
September Equinox
-fall/autumnal equinox in NH
-spring/vernal equinox in SH
-September 22
-NH first starts to tip away from the Sun
-summer to fall NH
-winter to spring SH
what do solstice and equinox dates depend on?
where we are in leap year cycle
what is the purpose of leap years
to keep solstices and equinoxes around the same dates
-add one day (Feb 29) every 4th year
when do equinoxes occur?
-On the two days of the year which the Sun rises precisely due east and sets precisely due west
-When sun is above and below horizon for equal time-12 hours
when does the June solstice occur?
-the day in which the Sun follows its longest and highest path through NH sky
-Shortest and lowest for SH
-Day when Sun rises and sets farther to the north of due east and due west
-NH has longest hours of daylight and Sun rises highest in the midday sky
when does the December solstice occur?
-When the Sun rises and sets farthest to the south
-the NH has its shortest hours of daylight and lowest midday Sun
-SH has longest hours of daylight and Sun rises highest in midday sky
What do solstices and equinoxes mark?
first day of a season
what does the June solstice mark
-NH: first day of summer
-SH: first day of winter
what does the December solstice mark
-NH: first day of winter
-SH: first day of summer
what does the March equinox mark
-NH: first day of spring
-SH: first day of fall
what does the September equinox mark
-NH: first day of fall
-SH: first day of spring
how does latitude affect seasons?
-higher latitudes have more extreme seasons
-equator regions do not have 4 seasons, only rainy and dry ones
why does latitude affects seasons?
-NH has more land and less ocean which allows it to heat and cool more easily leading to extreme seasons
-SH has more ocean which moderates its climate
precession
the gradual wobble of the axis of a rotating object around a vertical line