Topic 6: Immunity, Infection and Forensics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/186
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
1
New cards
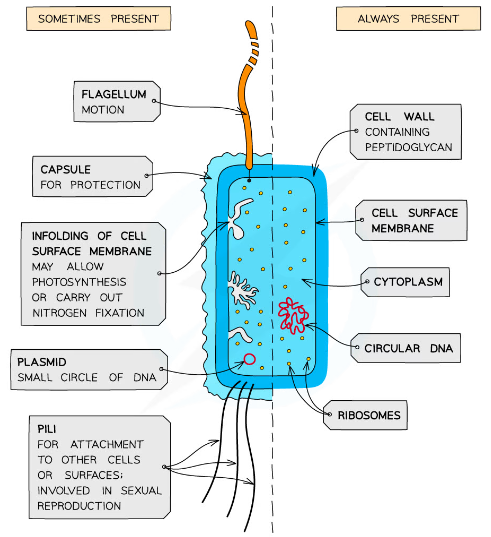
What is the structure of bacteria?
-Can only be 5 shapes
-Small, single celled prokaryotes
-Smaller than eukaryotic cells
-Cytoplasm without membrane bound organelles
-Smaller ribosomes
-no nucleus
-Cell wall that contains glycoprotein murein
-Small, single celled prokaryotes
-Smaller than eukaryotic cells
-Cytoplasm without membrane bound organelles
-Smaller ribosomes
-no nucleus
-Cell wall that contains glycoprotein murein
2
New cards
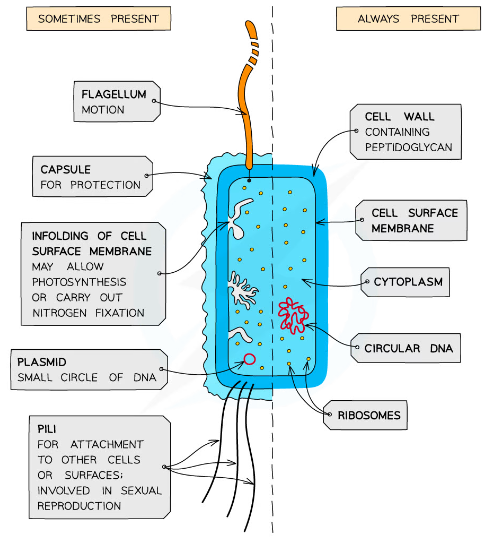
What features of bacteria are only sometimes present?
-Cell membrane contains folds known as mesosomes
-Plasmids
-Capsules
-Flagella
-Pili
-Plasmids
-Capsules
-Flagella
-Pili
3
New cards
What is the capsule?
-It helps to protect bacteria from drying out and from attack by cells of the immune system of the host organism
4
New cards
What is a flagella?
-Long, tail-like structures that rotate, enabling the prokaryote to move
-Some prokaryotes have more than one
-Some prokaryotes have more than one
5
New cards
What is pili?
-Thread-like structures on the surface of some bacteria that enable the bacteria to attach to other cells or surfaces
>Involved in gene transfer during sexual reproduction
>Involved in gene transfer during sexual reproduction
6
New cards
What is a virus?
\- Viruses are non-cellular infectious particles
-They are relatively simple in structure, and much smaller than prokaryotic cells
-They are relatively simple in structure, and much smaller than prokaryotic cells
7
New cards
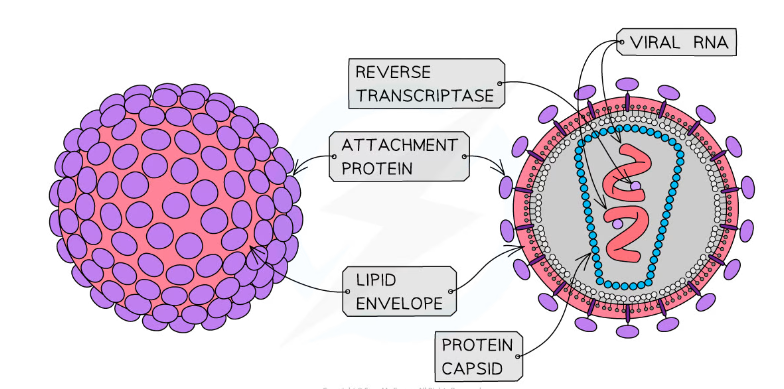
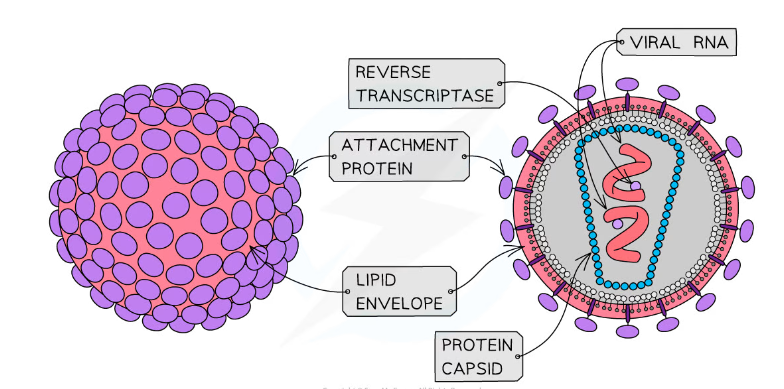
What is the structure of a virus?
-Large variety of different shapes
-Nucleic acid core
>Genomes either DNA or RNA, single or double stranded
-Protein coat (capsid)
-Attachment proteins
>Enables the virus to attach itself to the host cell
-Nucleic acid core
>Genomes either DNA or RNA, single or double stranded
-Protein coat (capsid)
-Attachment proteins
>Enables the virus to attach itself to the host cell
8
New cards
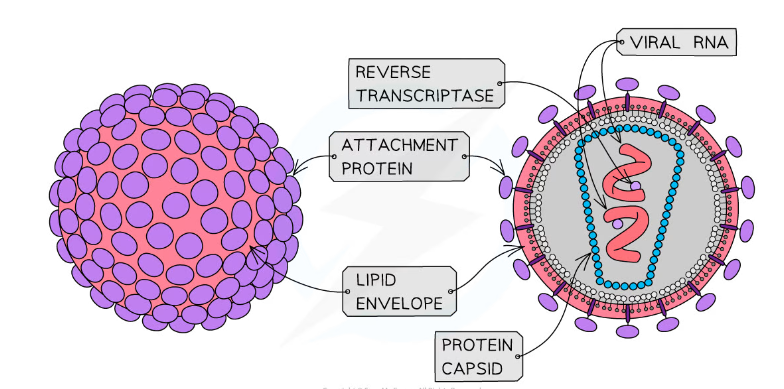
What features do viruses not have?
-Plasma membrane
-Cytoplasm
-Ribosomes
-Cytoplasm
-Ribosomes
9
New cards
What features are only present in some viruses?
-Envelope: formed from the membrane-phospholipids of the cell they were made in
-Various proteins inside the capsid
-Various proteins inside the capsid
10
New cards
What is a disease?
* An illness or disorder of the body or mind that leads to poor health
* Each disease is associated with a set of signs and symptoms
* Each disease is associated with a set of signs and symptoms
11
New cards
Infectious Diseases
-Caused by pathogens and are transmissible, meaning that they can be spread between individuals within a population
12
New cards
What is a pathogen?
-An organism that causes disease to the host
-Pathogens may include certain species of bacteria, some fungi and all viruses
>Not all viruses are pathogenic to humans
-Pathogens may include certain species of bacteria, some fungi and all viruses
>Not all viruses are pathogenic to humans
13
New cards
What is mycobacterium tuberculosis?
-A pathogen that causes the disease TB
14
New cards
How is TB transmitted?
-When infected people cough or sneeze, droplets of liquid containing TB will be released form the lungs into the air
-When uninfected people inhale these droplets, TB is transmitted
> TB spreads more efficiently in overcrowded conditions
-When uninfected people inhale these droplets, TB is transmitted
> TB spreads more efficiently in overcrowded conditions
15
New cards
What is the process of TB infection?
-Once inside the lungs, TB bacteria are engulfed by macrophages and encased in a phagosome
-Lysosomes are supposed to fuse with the phagosome and release enzymes that break down the bacteria
-The TB mycobacterium release an enzyme that inhibits the fusion, meaning that TB can proliferate inside the phagosome
> Individuals with healthy immune system will not develop TB at this stage
-infected phagocytes will eventually become encased in structures called tubercles in the lungs where the bacteria will remain dormant
-Lysosomes are supposed to fuse with the phagosome and release enzymes that break down the bacteria
-The TB mycobacterium release an enzyme that inhibits the fusion, meaning that TB can proliferate inside the phagosome
> Individuals with healthy immune system will not develop TB at this stage
-infected phagocytes will eventually become encased in structures called tubercles in the lungs where the bacteria will remain dormant
16
New cards
TB Active Phase
-When the immune system is compromised, the bacteria can become activated and overpower the immune system
-The length of time between infection and developing the disease can vary from a few weeks to a few years
-The length of time between infection and developing the disease can vary from a few weeks to a few years
17
New cards
What are the symptoms of TB?
-The first symptoms of TB will include developing a fever, fatigue, coughing and lung inflammation
-If left untreated the bacteria will cause extensive damage to the lungs which can result in death due to respiratory failure
-TB may also spread to other parts of the body where it can lead to organ failure if not treated promptly
-If left untreated the bacteria will cause extensive damage to the lungs which can result in death due to respiratory failure
-TB may also spread to other parts of the body where it can lead to organ failure if not treated promptly
18
New cards
What is HIV?
-Human immunodeficiency virus
-HIV contains RNA and is a retrovirus
-HIV contains RNA and is a retrovirus
19
New cards
What is a retrovirus?
-A group of viruses that have the ability to make DNA from RNA
-This is because they contain an enzyme called reverse transcriptase
-This is because they contain an enzyme called reverse transcriptase
20
New cards
Transmission of HIV
-Sexual Intercourse
-Blood donation
-Sharing of needles used by intravenous druggies (injecting into the vein)
-From mother to child across the placenta
-Mixing of blood between the mother and child during birth
-Breastfeeding
-Blood donation
-Sharing of needles used by intravenous druggies (injecting into the vein)
-From mother to child across the placenta
-Mixing of blood between the mother and child during birth
-Breastfeeding
21
New cards
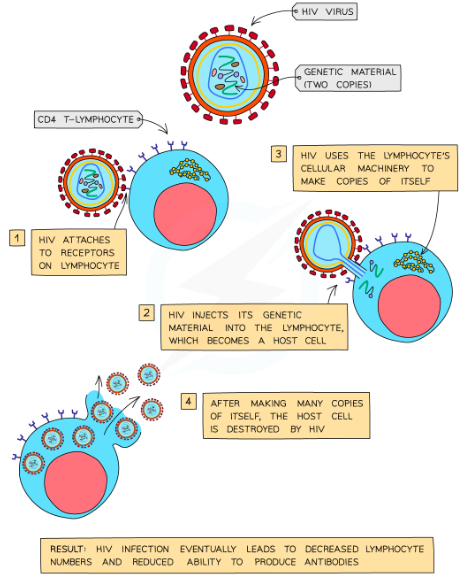
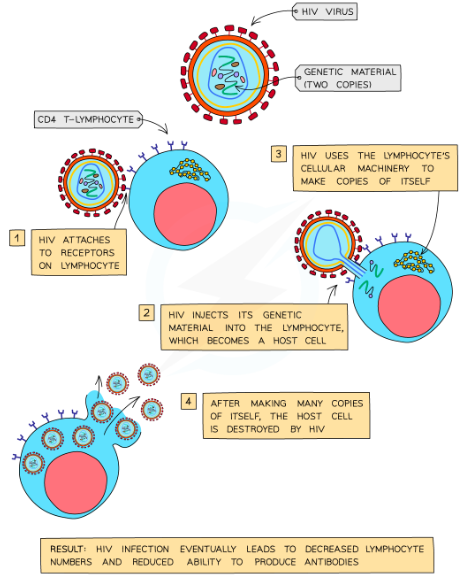
How does HIV spread/replicate in the body?
-When the virus enters the bloodstream it infects helper T cells
-It enters the helper T cells by attaching to a receptor molecule on the host cell membrane
-The capsid enters the helper T cell and releases the RNA it contains
-The viral RNA is used as a template by reverse transcriptase enzymes to produce a complementary strand of DNA
-Once this single-stranded DNA molecule is turned into a double-stranded molecule it can be successfully inserted into the host DNA
-From here it uses the host cell's enzymes to produce more viral components which are assembled to form new viruses
-These bud from the host cell and enter the blood, where they can infect other helper T cells and repeat the process
-At this stage the individual is HIV +ve and may experience flu-like symptoms
-It enters the helper T cells by attaching to a receptor molecule on the host cell membrane
-The capsid enters the helper T cell and releases the RNA it contains
-The viral RNA is used as a template by reverse transcriptase enzymes to produce a complementary strand of DNA
-Once this single-stranded DNA molecule is turned into a double-stranded molecule it can be successfully inserted into the host DNA
-From here it uses the host cell's enzymes to produce more viral components which are assembled to form new viruses
-These bud from the host cell and enter the blood, where they can infect other helper T cells and repeat the process
-At this stage the individual is HIV +ve and may experience flu-like symptoms
22
New cards
Initial Infection Period
-Rapid HIV replication
23
New cards
Latency Period
-Rate of replication drops
-The individual will not show any symptoms (often for years)
-The individual will not show any symptoms (often for years)
24
New cards
How can HIV progress to AIDS?
* Gradually the virus reduces the number of helper T cells in the immune system
* B cells are no longer activated
* No antibodies are produced
* This decreases the body’s ability to fight off infections (immunocompromised), eventually leading to AIDS (Acquired immune deficiency syndrome)
* B cells are no longer activated
* No antibodies are produced
* This decreases the body’s ability to fight off infections (immunocompromised), eventually leading to AIDS (Acquired immune deficiency syndrome)
25
New cards
What are the effects of being immunocompromised?
* They begin to suffer from diseases that would usually cause very minor issues in healthy individuals
* These diseases are described as opportunistic
* *Tuberculosis* (TB) is a common example
* An HIV infection will progress to AIDS when
* An individual starts suffering from constant opportunistic infections
* The helper T cell count drops below a critical level
* These diseases are described as opportunistic
* *Tuberculosis* (TB) is a common example
* An HIV infection will progress to AIDS when
* An individual starts suffering from constant opportunistic infections
* The helper T cell count drops below a critical level
26
New cards
What are the symptoms of AIDS?
* Length of time for HIV→ AIDS varies
* Initially only have mild infections of the mucous membranes due to the low helper T numbers
* Over time, however, infections will become more severe e.g. diarrhoea, TB
* During the final stages of AIDS a person will suffer from a range of more serious opportunistic infections
* It is these opportunistic diseases that cause an individual with advanced AIDS to die
* Initially only have mild infections of the mucous membranes due to the low helper T numbers
* Over time, however, infections will become more severe e.g. diarrhoea, TB
* During the final stages of AIDS a person will suffer from a range of more serious opportunistic infections
* It is these opportunistic diseases that cause an individual with advanced AIDS to die
27
New cards
What factors affect how quickly HIV → AIDS
* The number of existing infections
* The strain of HIV the person is infected with
* Their age
* Access to healthcare
* The strain of HIV the person is infected with
* Their age
* Access to healthcare
28
New cards
Which four ways can pathogens enter the body?
* Broken skin
* Provides direct access to the tissues and bloodstream
* The digestive system
* When we consume contaminated food and drink
* The respiratory system
* Every time we inhale
* Mucosal surfaces
* The lining of body cavities e.g. inside of nose, mouth, genitals
* Provides direct access to the tissues and bloodstream
* The digestive system
* When we consume contaminated food and drink
* The respiratory system
* Every time we inhale
* Mucosal surfaces
* The lining of body cavities e.g. inside of nose, mouth, genitals
29
New cards
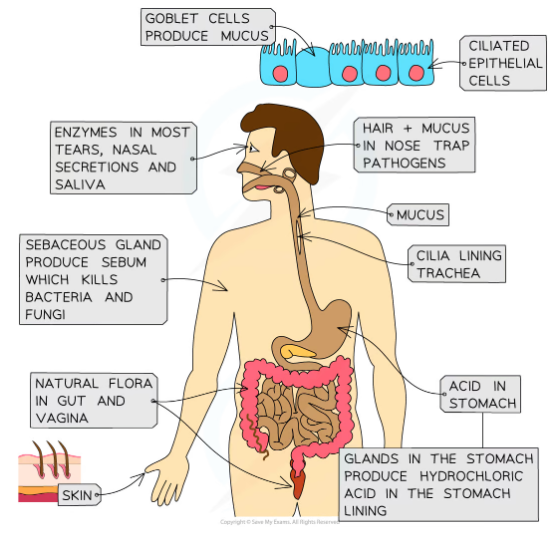
Barriers to infection: skin
* Physical barrier against infection
* If the skin is damaged it leaves the exposed tissue beneath vulnerable to pathogens
* The blood clotting mechanism of the body plays an important role in preventing pathogen entry in the case of damage to the skin
* A few pathogens may still enter before a clot forms as blood clotting takes time
* If the skin is damaged it leaves the exposed tissue beneath vulnerable to pathogens
* The blood clotting mechanism of the body plays an important role in preventing pathogen entry in the case of damage to the skin
* A few pathogens may still enter before a clot forms as blood clotting takes time
30
New cards
Barriers to infection: microorganisms in the gut and skin
* Collectively these harmless microorganisms are known as the gut or skin flora
* They compete with pathogens for resources, thereby limiting their numbers and therefore their ability to infect the body
* They compete with pathogens for resources, thereby limiting their numbers and therefore their ability to infect the body
31
New cards
Barriers to infection: stomach acid
* The hydrochloric acid in the stomach creates an acidic environment that is unfavourable to many pathogens present on food and drink
* Sometimes a few of these pathogens may survive and make their way to the intestines where they infect the gut wall cells and cause disease
* Sometimes a few of these pathogens may survive and make their way to the intestines where they infect the gut wall cells and cause disease
32
New cards
Barriers to infection: Lysozyme
* Secretions of the mucosal surfaces, e.g. tears, saliva, and mucus, contains an enzyme called lysozyme
* This enzyme will damage bacterial cell walls, causing them to burst, or lyse (cell disintegrating due to rupture of the cell membrane)
* This enzyme will damage bacterial cell walls, causing them to burst, or lyse (cell disintegrating due to rupture of the cell membrane)
33
New cards
What is a non-specific immune response?
* When the response is the same, regardless of the pathogen that invades the body
34
New cards
What is a specific immune response?
* This is a response specific to a particular pathogen
35
New cards
How does the immune system recognise the specific pathogens
* Because of the presence of antigens on their cell surface
36
New cards
Antigens
* Antigens are molecules such as proteins or glycoproteins located on the surface of cells; their role is to act as an ID tag, identifying a cell as being 'self' or 'non-self'
37
New cards
What does ‘self’ and ‘non-self’ mean?
* Self means that they are body cells
* Non-self means that they are foreign cells
* Pathogens have non-self antigens, so the immune system recognises them as not belonging to the body
* Non-self means that they are foreign cells
* Pathogens have non-self antigens, so the immune system recognises them as not belonging to the body
38
New cards
Non-specific immune response
* The first step in the immune response that happens as soon as the pathogen invades the tissue, this includes;
* Inflammation
* Interferons
* Phagocytosis
* Inflammation
* Interferons
* Phagocytosis
39
New cards
What is inflammation?
* When the surrounding area of a wound can sometimes become swollen, warm and painful to touch
40
New cards
Inflammation: mast cells
* Body cells called mast cells respond to tissue damage by secreting the molecule histamine
41
New cards
What is histamine?
* Histamine is a chemical signalling molecule that enables cell signalling, or communication between cells
42
New cards
Which responses does histamine stimulate?
* Vasodilation increases blood flow through capillaries
* Capillary walls becomes more permeable, allowing fluid to enter the tissues and creating swelling
* Some plasma proteins leave the blood when the capillaries become more permeable
* Phagocytes leave the blood and enter the tissue to engulf foreign particles
* Cells release cytokines, another cell signalling molecule that triggers an immune response in the infected area
* Capillary walls becomes more permeable, allowing fluid to enter the tissues and creating swelling
* Some plasma proteins leave the blood when the capillaries become more permeable
* Phagocytes leave the blood and enter the tissue to engulf foreign particles
* Cells release cytokines, another cell signalling molecule that triggers an immune response in the infected area
43
New cards
Interferons
* These are anti-viral proteins that are released by infected cells
* Interferons prevent viruses from spreading to uninfected cells
* Interferons prevent viruses from spreading to uninfected cells
44
New cards
What do interferons do?
* They inhibit the production of viral proteins, preventing the virus from replicating
* They activate white blood cells involved with the specific immune response to destroy infected cells
* They increase the non-specific immune response e.g. by promoting inflammation
* They activate white blood cells involved with the specific immune response to destroy infected cells
* They increase the non-specific immune response e.g. by promoting inflammation
45
New cards
Phagocytes
* Phagocytes are a type of white blood cell responsible for removing dead cells and invasive microorganisms; they do this by engulfing and digesting them
* The process of engulfing and digesting is known as phagocytosis
* Phagocytes travel throughout the body and can leave the blood by squeezing through capillary walls
* During an infection they are released in large numbers
* The process of engulfing and digesting is known as phagocytosis
* Phagocytes travel throughout the body and can leave the blood by squeezing through capillary walls
* During an infection they are released in large numbers
46
New cards
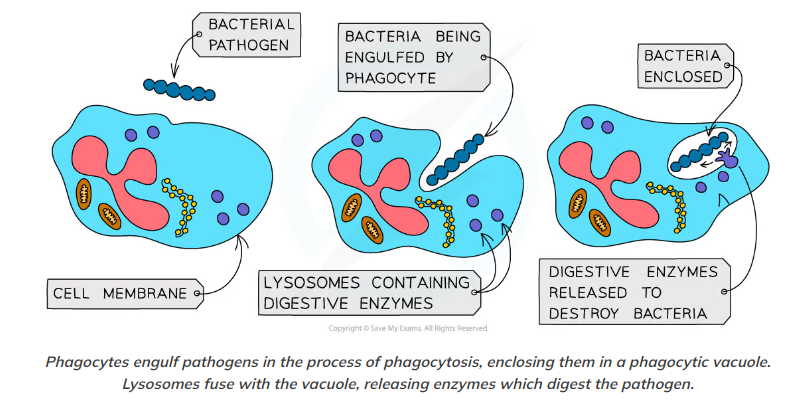
Process of phagocytosis
* Chemicals released by pathogens, as well as chemicals released by the body cells under attack, e.g. histamine, attract phagocytes (macrophages) to the site where the pathogens are located
* They move towards pathogens and recognise the antigens on the surface of the pathogen as being non-self
* The cell surface membrane of a phagocyte (macrophage) extends out and around the pathogen, engulfing it and trapping the pathogen within a phagocytic vacuole
* This part of the process is known as endocytosis
* Enzymes are released into the phagocytic vacuole when lysosomes fuse with it
* These digestive enzymes, which includes lysozyme, digest the pathogen
* After digesting the pathogen, the phagocyte will present the antigens of the pathogen on its cell surface membrane
* The phagocyte becomes what is known as an antigen presenting cell
* The presentation of antigens initiates the specific immune response
* They move towards pathogens and recognise the antigens on the surface of the pathogen as being non-self
* The cell surface membrane of a phagocyte (macrophage) extends out and around the pathogen, engulfing it and trapping the pathogen within a phagocytic vacuole
* This part of the process is known as endocytosis
* Enzymes are released into the phagocytic vacuole when lysosomes fuse with it
* These digestive enzymes, which includes lysozyme, digest the pathogen
* After digesting the pathogen, the phagocyte will present the antigens of the pathogen on its cell surface membrane
* The phagocyte becomes what is known as an antigen presenting cell
* The presentation of antigens initiates the specific immune response
47
New cards
Macrophage
* macrophages are a type of phagocytic white blood cell
* Most common cell in phagocytosis probably?
* Most common cell in phagocytosis probably?
48
New cards
What are antigens?
* Markers on the surface membranes of cells that allow cell recognition
* Microorganisms have their own unique antigens
* Found on cell surface membranes, bacterial cell walls, or the surfaces of viruses
* Some glycolipids and glycoproteins on the outside of cell surface membranes act as antigens
* Microorganisms have their own unique antigens
* Found on cell surface membranes, bacterial cell walls, or the surfaces of viruses
* Some glycolipids and glycoproteins on the outside of cell surface membranes act as antigens
49
New cards
Self antigens
* Antigens produced by the organism's own body cells are known as self antigens
* Self antigens do not stimulate an immune response
* Self antigens do not stimulate an immune response
50
New cards
Non-self antigens
* Antigens not produced by the organism’s own body cells are known as non-self antigens
* Non-self antigens stimulate an immune response
* E.g. the antigens found on pathogenic bacteria and viruses, or on the surface of a transplanted organ
* Non-self antigens stimulate an immune response
* E.g. the antigens found on pathogenic bacteria and viruses, or on the surface of a transplanted organ
51
New cards
Activating the specific immune response
Antigen presenting cells such as macrophages activate the specific immune response
* This occurs when the white blood cells of the specific immune response, known as lymphocytes, bind to the presented antigens with specific receptors on their cell surface membranes
* This occurs when the white blood cells of the specific immune response, known as lymphocytes, bind to the presented antigens with specific receptors on their cell surface membranes
52
New cards
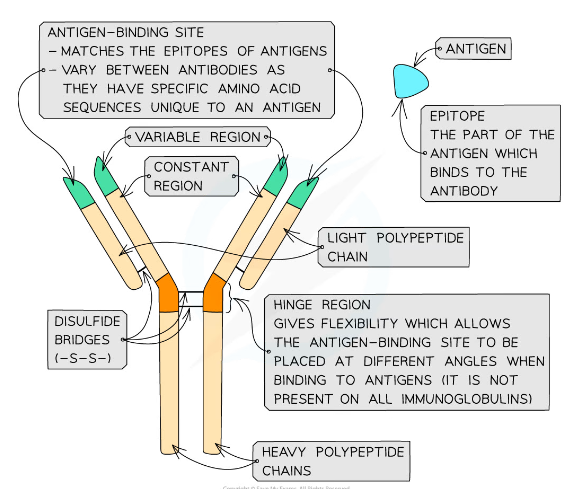
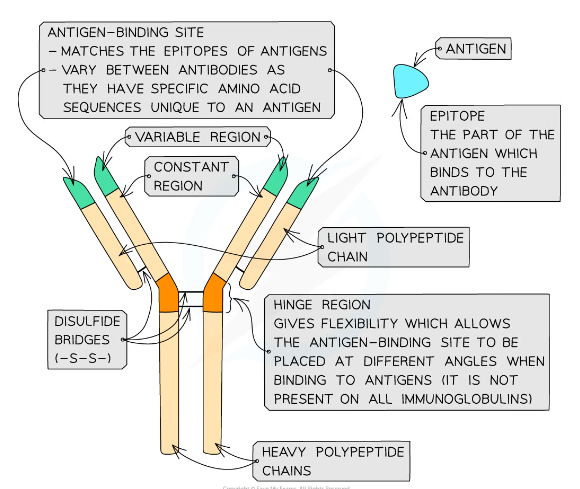
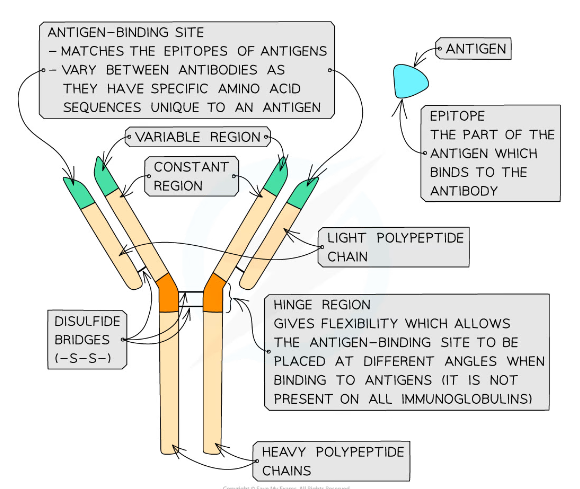
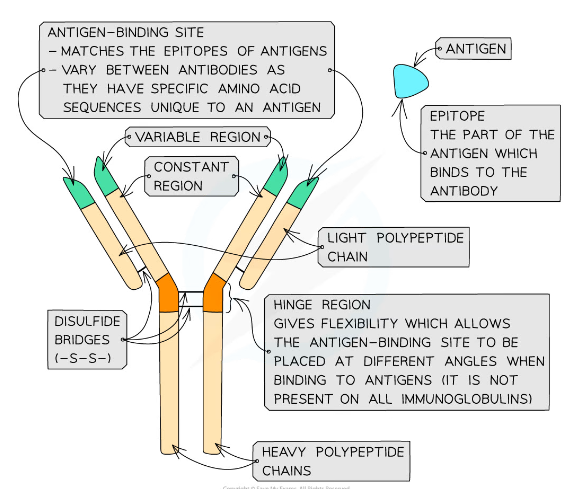
Structure of an antibody
* Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules sometimes known as immunoglobulins
53
New cards
Antibody chains
* Antibodies consist of four polypeptide chains; two ‘heavy’ chains attached by disulfide bonds to two ‘light’ chains
* 'Heavy' chains are long while 'light' chains are short
* 'Heavy' chains are long while 'light' chains are short
54
New cards
Constant region and variable region
* Each polypeptide chain has a constant region and variable region
* The constant regions do not vary within a class of antibody
* There are 5 classes of mammalian antibodies, each with different roles
* The amino acid sequences in the variable region are different for each antibody
* The variable region is where the antibody binds to an antigen to form an antigen-antibody complex
* At the end of the variable region is a site called the antigen binding site
* The antigen binding sites **vary** greatly, giving the antibody its **specificity** for binding to **antigens**
* The constant regions do not vary within a class of antibody
* There are 5 classes of mammalian antibodies, each with different roles
* The amino acid sequences in the variable region are different for each antibody
* The variable region is where the antibody binds to an antigen to form an antigen-antibody complex
* At the end of the variable region is a site called the antigen binding site
* The antigen binding sites **vary** greatly, giving the antibody its **specificity** for binding to **antigens**
55
New cards
The hinge region of the antibody
* The ‘hinge’ region, where the disulfide bonds join the heavy chains, gives flexibility to the antibody molecule, allowing the antigen binding site to be placed at different angles when binding to antigens
* This region is not present in all classes of antibodies
* This region is not present in all classes of antibodies
56
New cards
Antibodies: membrane bound or secreted directly into blood
Antibodies can be either membrane-bound or secreted directly into the blood
* Membrane-bound antibodies are attached to the surface of lymphocytes
* The membrane-bound antibodies have an extra section of polypeptide chain within their heavy chains which forms the attachment to lymphocytes
* This extra section of polypeptide is not required in antibodies that are not bound to lymphocytes
* Membrane-bound antibodies are attached to the surface of lymphocytes
* The membrane-bound antibodies have an extra section of polypeptide chain within their heavy chains which forms the attachment to lymphocytes
* This extra section of polypeptide is not required in antibodies that are not bound to lymphocytes
57
New cards
Alternative splicing
* The gene which codes for the antibody heavy chains can undergo a process called alternative splicing to remove this extra section in non-bound antibodies
* Splicing removes non-coding sections of mRNA called introns, while alternative splicing removes coding sections called exons; in this case the exons that code for the the extra section of the heavy chains are removed
* Splicing removes non-coding sections of mRNA called introns, while alternative splicing removes coding sections called exons; in this case the exons that code for the the extra section of the heavy chains are removed
58
New cards
Antibody function
* Antibodies bind to specific antigens that trigger the specific immune response
* Antibodies function to disable pathogens in several ways
* Antibodies function to disable pathogens in several ways
59
New cards
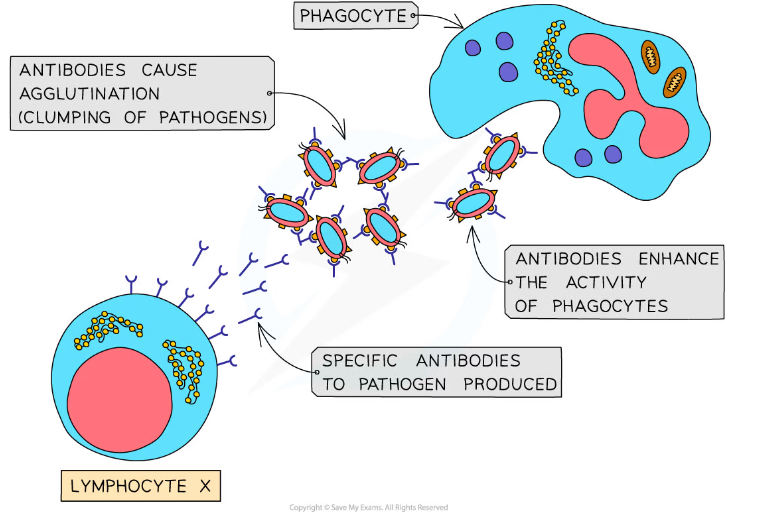
How do antibodies disable pathogens
* Pathogens enter host cells by binding to them using receptors on their surface; antibodies can bind to these receptors, preventing pathogens from infecting host cells
* Antibodies can act as anti-toxins by binding to toxins produced by pathogens, e.g. the bacteria that cause diphtheria and tetanus; this neutralises the toxins
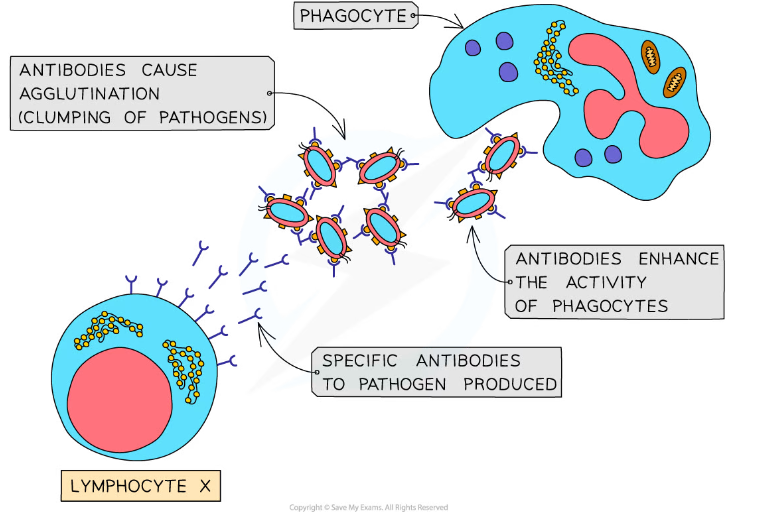
* Antibodies cause pathogens to clump together, a process known as agglutination; this reduces the chance that the pathogens will spread through the body and makes it possible for phagocytes to engulf a number of pathogens at one time
* Antibodies can act as anti-toxins by binding to toxins produced by pathogens, e.g. the bacteria that cause diphtheria and tetanus; this neutralises the toxins
* Antibodies cause pathogens to clump together, a process known as agglutination; this reduces the chance that the pathogens will spread through the body and makes it possible for phagocytes to engulf a number of pathogens at one time
60
New cards
Note about secondary immune response
* Watch a video and look at diagrams before reading the notes, don’t get this bit without a video
* Links:
* Links:
61
New cards
What are T cells?
T cells, sometimes known as T lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell involved with the specific immune response
62
New cards
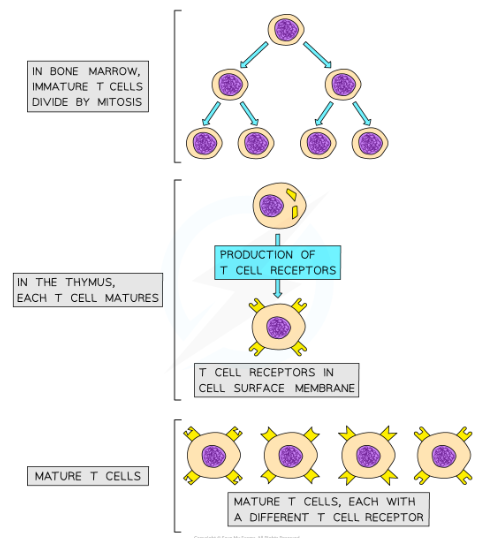
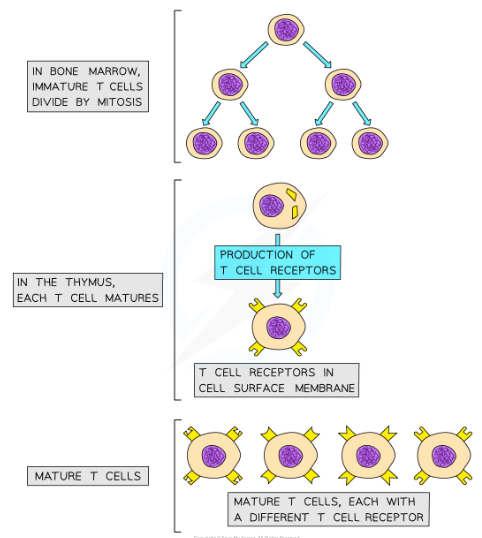
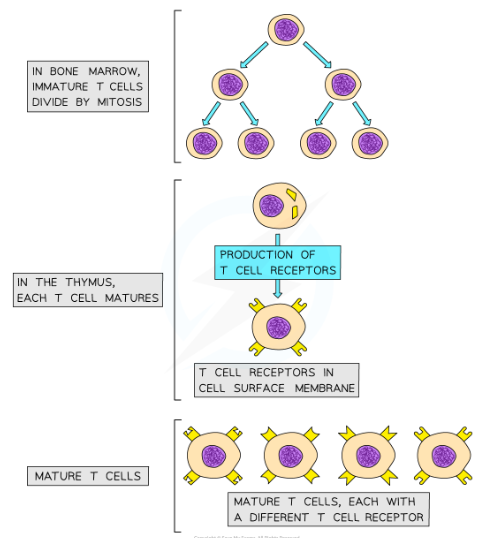
Where are T cells produced
* They are produced in the bone marrow and finish maturing in the thymus, which is where the T in their name comes from
63
New cards
T cell receptors
* Mature T cells have specific cell surface receptors called T cell receptors
* These receptors have a similar structure to antibodies and are each specific to a particular type of antigen
* These receptors have a similar structure to antibodies and are each specific to a particular type of antigen
64
New cards
How are T cells activated?
* T cells are activated when they encounter and bind to their specific antigen on the surface of an antigen presenting cell
* This antigen-presenting cell might be a macrophage, an infected body cell, or the pathogen itself
* This antigen-presenting cell might be a macrophage, an infected body cell, or the pathogen itself
65
New cards
Activated T cells
* These activated T cells divide by mitosis to increase in number
* Dividing by mitosis produces genetically identical cells, or clones, so all of the daughter cells will have the same type of T cell receptor on their surface
* As they divide by mitosis the T cells differentiate into four types of T cell
* Dividing by mitosis produces genetically identical cells, or clones, so all of the daughter cells will have the same type of T cell receptor on their surface
* As they divide by mitosis the T cells differentiate into four types of T cell
66
New cards
Different types of T cells
* T helper cells
* Release chemical signalling molecules that help to activate B cells
* T killer cells
* Bind to and destroy infected cells displaying the relevant specific antigen
* T memory cells
* Remain in the blood and enable a faster specific immune response if the same pathogen is encountered again in the future
* *T suppressor cells (don’t have to know)*
* *A type of immune cell that blocks the actions of some other types of lymphocytes, to keep the immune system from becoming over-active*.
* Release chemical signalling molecules that help to activate B cells
* T killer cells
* Bind to and destroy infected cells displaying the relevant specific antigen
* T memory cells
* Remain in the blood and enable a faster specific immune response if the same pathogen is encountered again in the future
* *T suppressor cells (don’t have to know)*
* *A type of immune cell that blocks the actions of some other types of lymphocytes, to keep the immune system from becoming over-active*.
67
New cards
What are B cells?
* B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a second type of white blood cell in the specific immune response
68
New cards
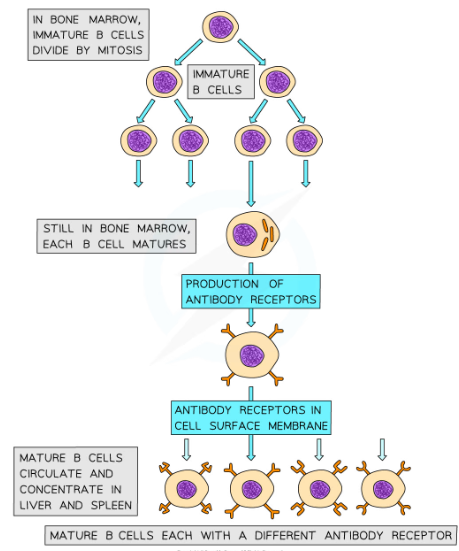
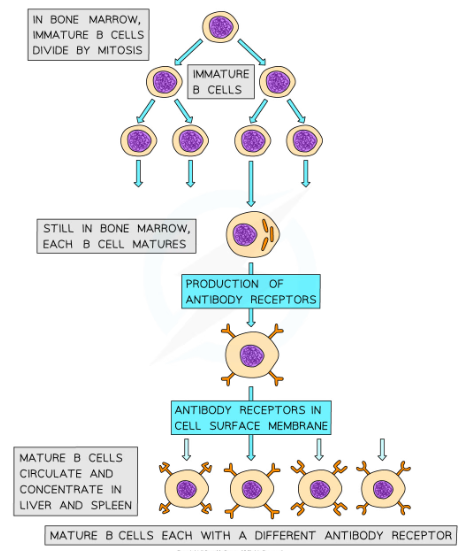
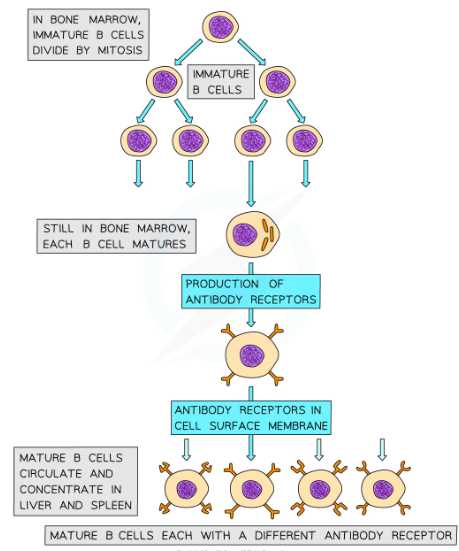
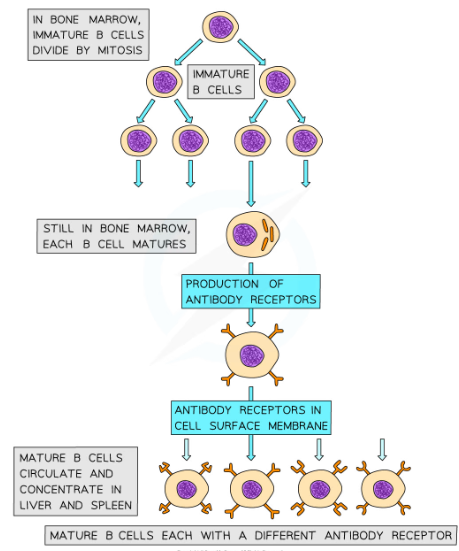
Where are B cells produced?
* B cells are produced and remain in the bone marrow as they mature, hence the B in their name
69
New cards
B cell receptors
* B cells have many specific receptors on their cell surface membrane
* The receptors are in fact antibodies, and are known as antibody receptors
* Each B cell has a different type of antibody receptor, meaning that each B cell can bind to a different type of antigen
* The receptors are in fact antibodies, and are known as antibody receptors
* Each B cell has a different type of antibody receptor, meaning that each B cell can bind to a different type of antigen
70
New cards
Antigen-antibody complex
* If the corresponding antigen enters the body, B cells with the correct cell surface antibodies will be able to recognise it and bind to it
* When the B cell binds to an antigen it forms an antigen-antibody complex
* When the B cell binds to an antigen it forms an antigen-antibody complex
71
New cards
Activation of B cell
* The binding of the B cell to its specific antigen, along with the cell signalling molecules produced by T helper cells, activates the B cell
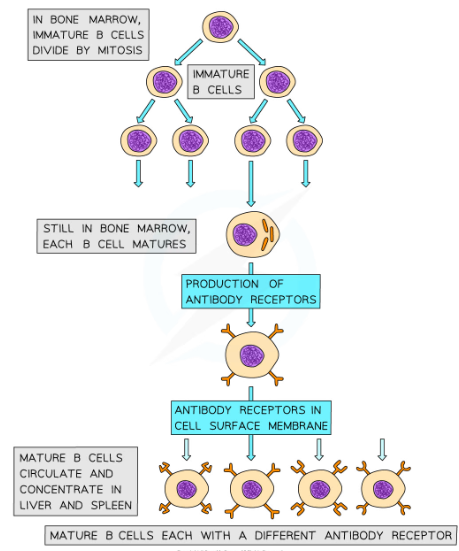
* Once activated the B cells divide repeatedly by mitosis, producing many clones of the original activated B cell
* The daughter cells differentiate into two main types of cells
* *(Basically T cell in previous step stimulated B cell)*
* Once activated the B cells divide repeatedly by mitosis, producing many clones of the original activated B cell
* The daughter cells differentiate into two main types of cells
* *(Basically T cell in previous step stimulated B cell)*
72
New cards
Two main types of B cells
* Effector cells, which go on to form plasma cells
* Plasma cells produce specific antibodies to combat non-self antigens
* Memory cells
* Remain in the blood to allow a faster immune response to the same pathogen in the future
* Plasma cells produce specific antibodies to combat non-self antigens
* Memory cells
* Remain in the blood to allow a faster immune response to the same pathogen in the future
73
New cards
*Antibody structure recap (just for context for the following flashcards)*
* *Antibody molecules consist primarily of protein*
* *They contain four separate polypeptide chains, two of which are longer, heavy chains, and two of which are shorter, light chains*
* *The structure of the heavy chain determines whether an antibody will be bound to the membrane of a white blood cell, or secreted directly into the blood*
* *Some heavy chains contain an extra section which allows the antibody to bind to the surface of a white blood cell*
* *They contain four separate polypeptide chains, two of which are longer, heavy chains, and two of which are shorter, light chains*
* *The structure of the heavy chain determines whether an antibody will be bound to the membrane of a white blood cell, or secreted directly into the blood*
* *Some heavy chains contain an extra section which allows the antibody to bind to the surface of a white blood cell*
74
New cards
Post-transcriptional modification
* White all heavy chains are coded for by the same gene, post-transcriptional modification determines whether or not this extra section of protein is present in the heavy chain of an antibody
* Post transcriptional modification mechanisms include
* Splicing
* Alternative splicing
* Post transcriptional modification mechanisms include
* Splicing
* Alternative splicing
75
New cards
Define Intron
Sections of non-coding DNA
76
New cards
Define exons
Sections of coding DNA
77
New cards
Producing pre-mRNA molecules
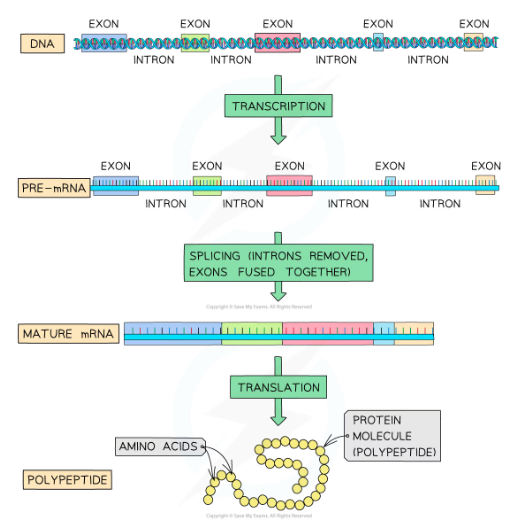
* Polypeptides are made during the process of protein synthesis, during which the DNA base code is transcribed and translated
* The DNA code within eukaryotic cells contains many non-coding sections
* Non-coding DNA can be found within genes; these sections are called introns, while sections of coding DNA are called exons
* During transcription eukaryotic cells transcribe both introns and exons to produce pre-mRNA molecules
* The DNA code within eukaryotic cells contains many non-coding sections
* Non-coding DNA can be found within genes; these sections are called introns, while sections of coding DNA are called exons
* During transcription eukaryotic cells transcribe both introns and exons to produce pre-mRNA molecules
78
New cards
What is the Splicing process?
* Occurs before the pre-mRNA exits the nucleus
* The non-coding intron sections are removed
* The coding exon sections are joined together
* The resulting mRNA molecule contains **only the coding sequences** of the gene
* The non-coding intron sections are removed
* The coding exon sections are joined together
* The resulting mRNA molecule contains **only the coding sequences** of the gene
79
New cards
Why are they called post-transcription modifications
* Because they happen after transcription has occurred
80
New cards
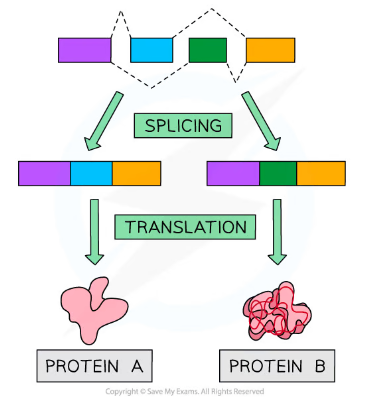
Alternative Splicing
* The exons of genes can be spliced in many different ways to produce different mature mRNA molecules through alternative splicing
* This means that a single eukaryotic gene can code for more than one polypeptide chain
* E.g. depending on the exons that are removed from the gene coding for the antibody heavy chain, it can produce either a membrane-bound or a directly secreted antibody
* This means that a single eukaryotic gene can code for more than one polypeptide chain
* E.g. depending on the exons that are removed from the gene coding for the antibody heavy chain, it can produce either a membrane-bound or a directly secreted antibody
81
New cards
When is the immune system activated?
* The immune system is activated when a new antigen is encountered
82
New cards
What is the first step when the immune system is activated?
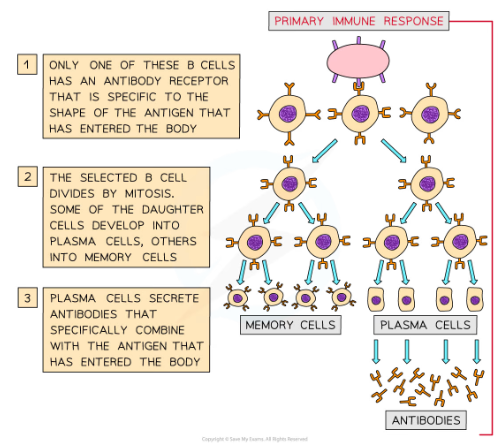
* This launches a primary immune response consisting of a non-specific immune response followed by a specific immune response
* The primary response occurs the first time an antigen is encountered by the immune system
* The primary response occurs the first time an antigen is encountered by the immune system
83
New cards
Why does the immune response take longer the first time?
* the numbers of T and B cells with the correct membrane receptors present in the blood will be low
* It will take time for the correct T and B cells to be activated and to divide and differentiate into different cell types
* It can take several days before plasma cells develop and are able to start producing antibodies against an antigen
* This is the reason why an infected person will experience symptoms of the disease the first time they contract it
* It will take time for the correct T and B cells to be activated and to divide and differentiate into different cell types
* It can take several days before plasma cells develop and are able to start producing antibodies against an antigen
* This is the reason why an infected person will experience symptoms of the disease the first time they contract it
84
New cards
How do you gain immunity from the primary immune response?
* Both T and B cells produce memory cells during the primary response, which will remain in the blood after an infection is over
* The presence of memory cells means that a person is said to be immune to the pathogen
* The presence of memory cells means that a person is said to be immune to the pathogen
85
New cards
Encountering the same antigen in the future
* Should the immune system encounter the same antigen again in the future it will launch a secondary immune response which will be much faster and stronger than the primary response
* Memory cells are present in larger quantities than the mature lymphocytes at the start of the primary response, so the correct memory cells are able to detect an antigen, activate, divide by mitosis, and differentiate much more quickly
* Antibodies are produced more quickly and in larger quantities in a secondary response
* This will often eliminate the pathogen before the infected person can show symptoms
* Memory cells are present in larger quantities than the mature lymphocytes at the start of the primary response, so the correct memory cells are able to detect an antigen, activate, divide by mitosis, and differentiate much more quickly
* Antibodies are produced more quickly and in larger quantities in a secondary response
* This will often eliminate the pathogen before the infected person can show symptoms
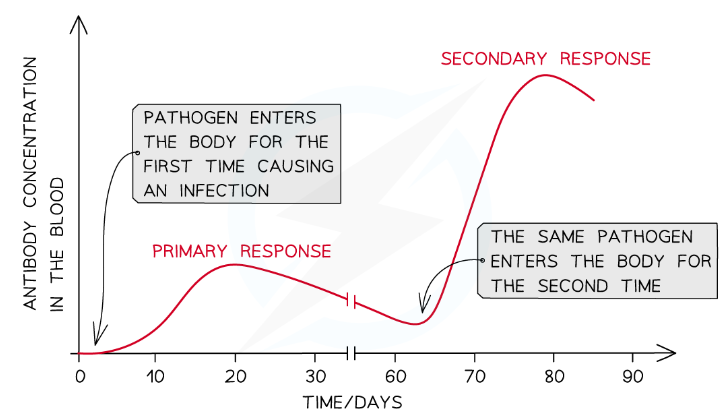
86
New cards
What is active immunity?
* Happens when an antigen enters the body which triggers a specific immune response
* It can be natural or artificial
* The body produces memory cells which gives the person long term immunity
* It can be natural or artificial
* The body produces memory cells which gives the person long term immunity
87
New cards
Natural immunity (active)
* Acquired through exposure to pathogens
88
New cards
Artificial immunity (active)
* Acquired through vaccination
89
New cards
Passive immunity
* Acquired without immune response as antibodies are gained from another source
* Can be natural or artificial
* The person’s immune response has not been activated so there are no memory cells that can enable antibody productions in a secondary response; if a person is reinfected they would need another infusion of antibodies
* Can be natural or artificial
* The person’s immune response has not been activated so there are no memory cells that can enable antibody productions in a secondary response; if a person is reinfected they would need another infusion of antibodies
90
New cards
Natural immunity (passive)
* Foetuses receive antibodies across the placenta from their mothers
* Babies receive antibodies in breast milk
* Babies receive antibodies in breast milk
91
New cards
Artificial immunity (passive)
* Injection/ transfusion of antibodies
* Antibodies collected from people or animals whose immune system had been triggered by a vaccine to produce antibodies
* Antibodies collected from people or animals whose immune system had been triggered by a vaccine to produce antibodies
92
New cards
What are vaccines?
* It contains antigens that are put into the body to induce artificial active immunity
93
New cards
What can vaccines contain?
* Dead or weakened pathogens
* Less harmful strains of a pathogen
* Antigens Alone
* A piece of genetic material that codes for the antigens
* Less harmful strains of a pathogen
* Antigens Alone
* A piece of genetic material that codes for the antigens
94
New cards
How are vaccines administered?
* Injection
* By mouth (digestion)
* By mouth (digestion)
95
New cards
How do vaccines produce long-term immunity?
* They cause memory cells to be created
* The immune system recognises the antigen when re-encountered and produces antibodies in a faster, stronger **secondary response**
* This is the main reason why vaccinated individuals typically do not show symptoms of the diseases they were vaccinated against
* The immune system recognises the antigen when re-encountered and produces antibodies in a faster, stronger **secondary response**
* This is the main reason why vaccinated individuals typically do not show symptoms of the diseases they were vaccinated against
96
New cards
Antigenic variation
* The pathogen may mutate frequency and develop resistance to vaccinations
* This means that vaccinations need to be constantly modified to keep up with the changes to a pathogen’s antigens
* Antigenic changes are the result of mutations
* This means that vaccinations need to be constantly modified to keep up with the changes to a pathogen’s antigens
* Antigenic changes are the result of mutations
97
New cards
How has evolution affected pathogens and vertebrates?
* Vertebrates have developed immune systems able to deal with a wide range of different pathogens
* Pathogens have developed different ways of evading the host’s immune system
* Pathogens have developed different ways of evading the host’s immune system
98
New cards
What is the evolutionary race?
* When each organism develops new ways to have an advantage over the other
99
New cards
What evidence is there to support the evolutionary race?
* Evasion mechanisms developed by pathogens
100
New cards
What evasion methods has HIV developed?
* The virus kills helper T cells
* reduces number of cells that could detect the presence of the virus and activate the production of antibodies
* Prevents infected cells from presenting their antigens on the cell surface
* very difficult for the relevant white blood cells to recognise and destroy the infected cells
* High antigenic variability
* Because high mutation rate
* reduces number of cells that could detect the presence of the virus and activate the production of antibodies
* Prevents infected cells from presenting their antigens on the cell surface
* very difficult for the relevant white blood cells to recognise and destroy the infected cells
* High antigenic variability
* Because high mutation rate