Biology
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen
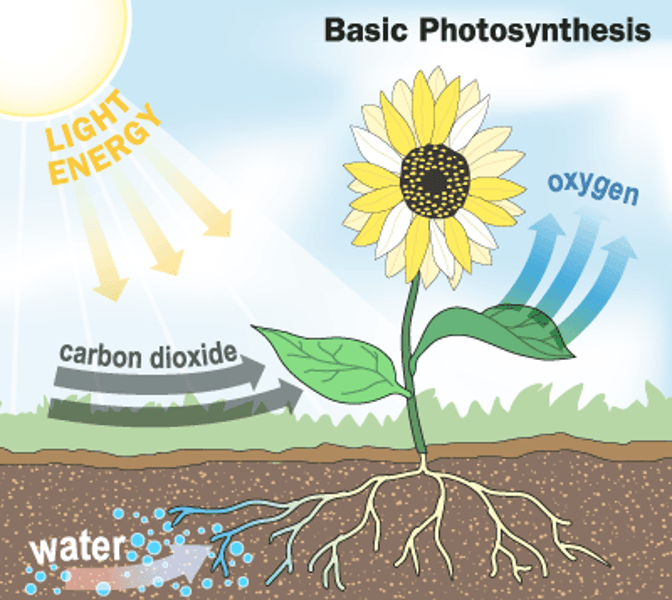
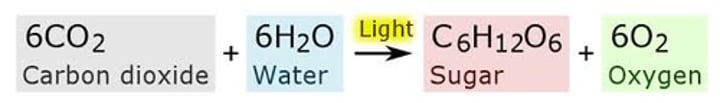
photosynthesis equation(very important)
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
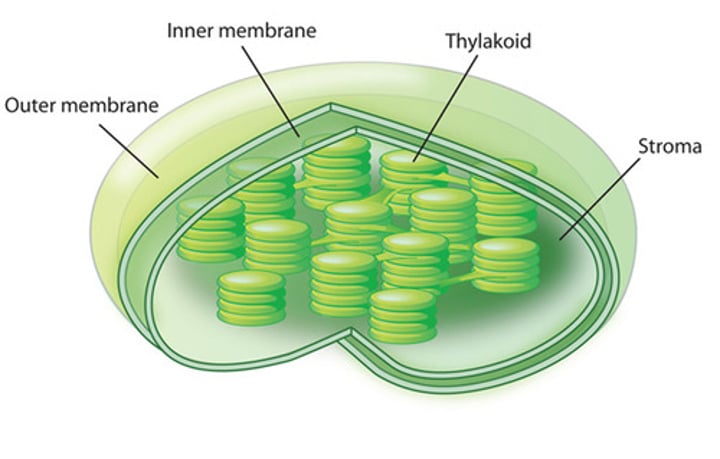
chloroplasts
A structure in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food.
glucose
another name for sugar C6H12O6
sunlight
main source of energy
cellular respiration
C6H1206->CO2 + H20+ ENERGY (released)
goal is to create ATP
occurs in all living things
cell
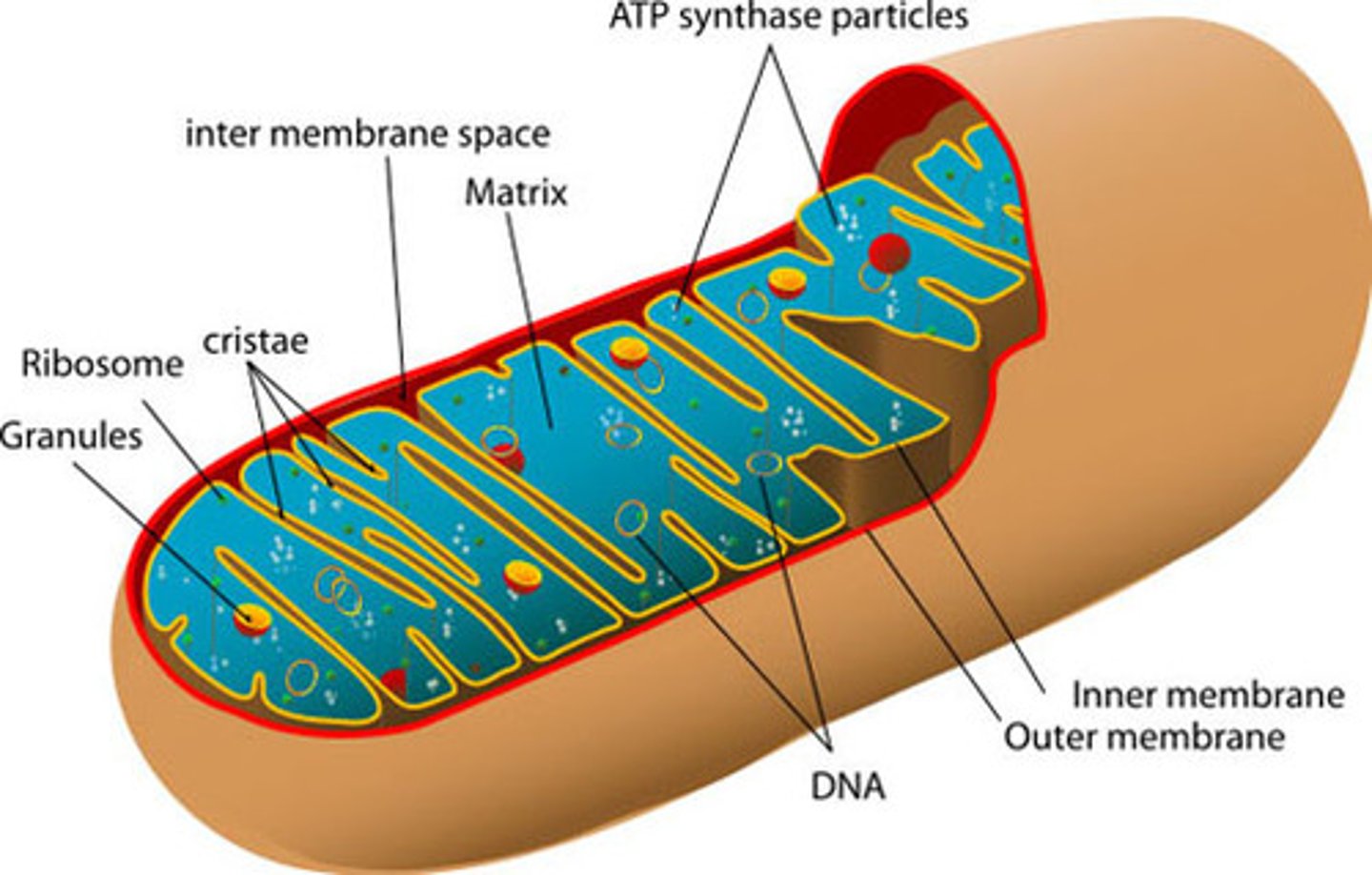
mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
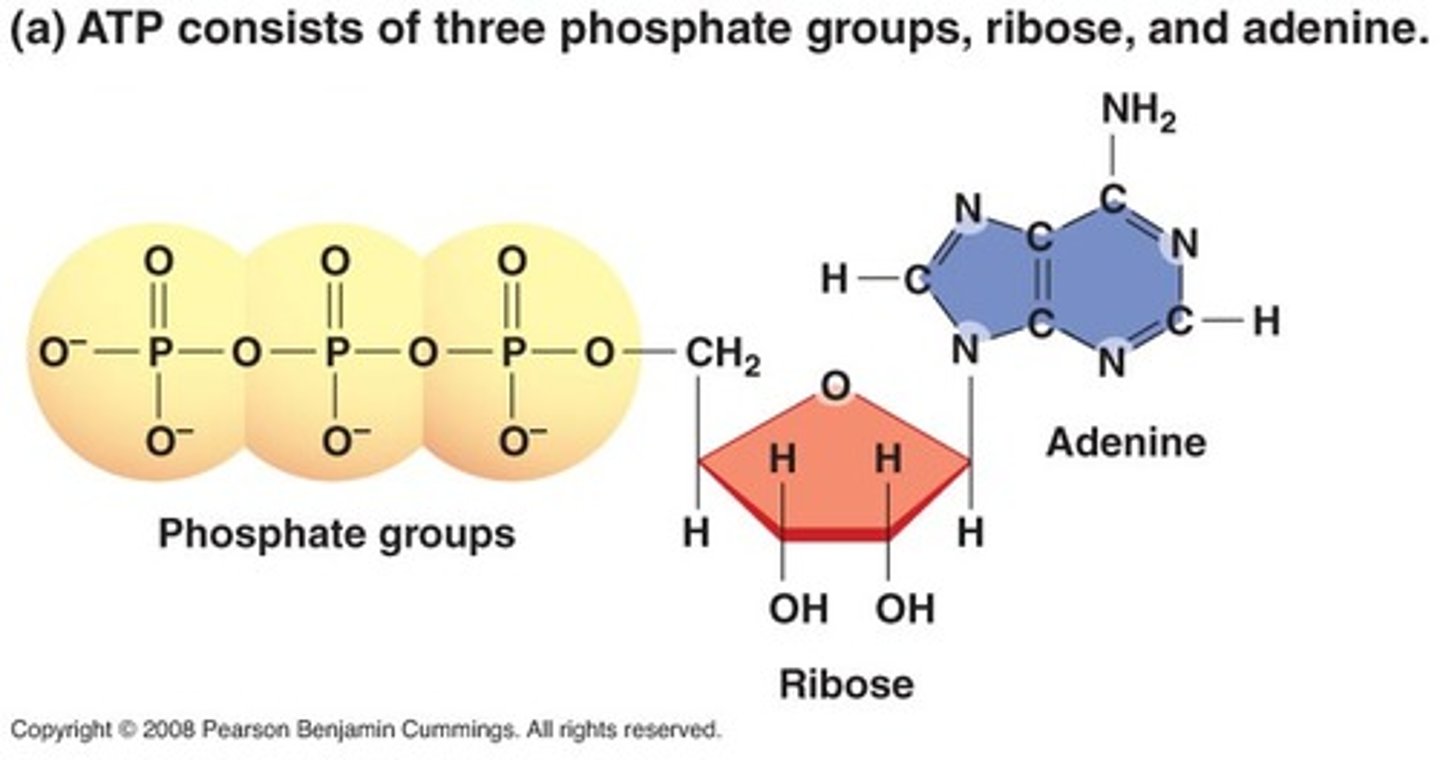
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
the energy is stored in ATP until it is released by the reactions remove a phosphate from ATP
a simple way of remembering it is just that it's just energy
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use the energy of sunlight and simple chemicals to produce their own food.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction accomplished by a single organism.
Sexual reproduction
Reproduction that requires two organisms
Inheritance
The process by which physical and biological characteristics are transmitted from the parent (or parents) to the offspring.
Mutation
An abrupt and marked change in the DNA of an organism compared to that of its parents
Hypothesis
An educated guess that attempts to explain an observation or answer a question.
Theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data.
Scientific law
A theory that has been tested by and is consistent with generations of data.
Prokaryotic cell
A cell that has no distinct, membrane-bounded organelles.
Eukaryotic cell
A cell with distinct, membrane-bounded organelles.
Species
A unit of one or more populations of individuals that can reproduce under normal conditions, produce fertile offspring, and are reproductively isolated from other such units.
Taxonomy
The science of classifying organisms.
Binomial nomenclature
Naming an organism with its genus and species name.
Aerobic organism
An organism that requires oxygen.
Anaerobic organism
An organism that does not require oxygen.
Exponential growth
Population growth that is unhindered because of the abundance of resources for an ever-increasing population.
Logistic growth
Population growth that is controlled by limited resources.
Plasmid
A small, circular section of extra DNA that confers one or more traits to a bacterium and can be reproduced separately from the main bacterial genetic code.
Nucleus
The region of a eukaryotic cell that contains the cell's main DNA.
Vacuole
A membrane-bounded "sac" within a cell.
Chloroplast
An organelle containing chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll
A pigment necessary for photosynthesis.
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion.
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms.
Chitin
A chemical that provides both toughness and flexibility.
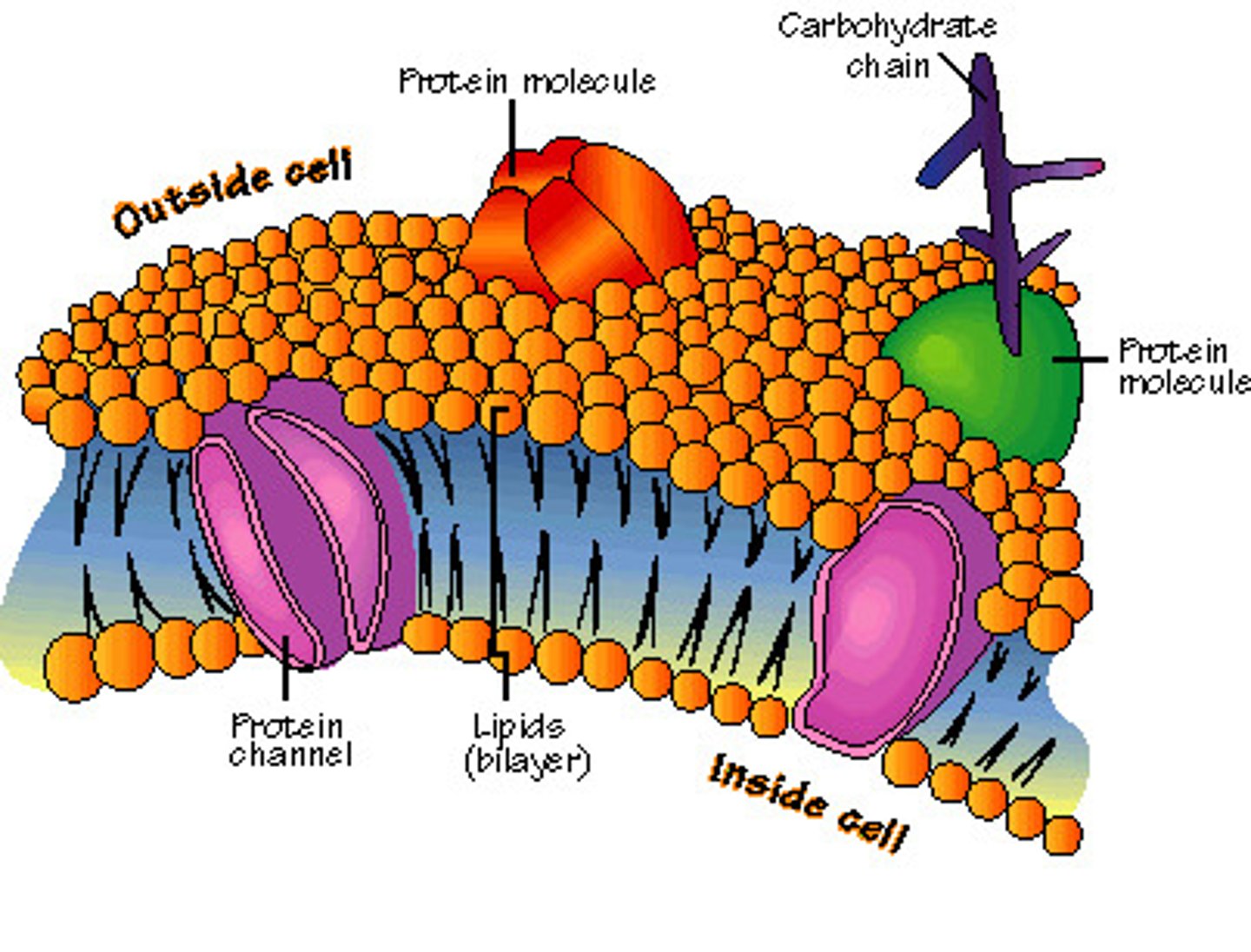
Membrane
A thin covering of tissue.
Fermentation
The anaerobic breakdown of sugars into smaller molecules.
Zygote
The result of sexual reproduction when each parent contributes half of the DNA necessary for the offspring.
Antibiotic
A chemical secreted by a living organism that kills or reduces the reproduction rate of other organisms.
Atoms
The basic building blocks of matter.
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Model
An explanation or representation of something that cannot be seen.
Molecules
Chemicals that result from atoms linking together.
Diffusion
The random motion of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent.
Semipermeable membrane
A membrane that allows some molecules to pass through but does not allow other molecules to pass through.
Osmosis
The tendency of a solvent to travel across a semipermeable membrane into areas of higher solute concentration.
Catalyst
A substance that alters the speed of a chemical reaction but is not used up in the process.
Organic Molecule
A molecule that contains only carbon and any of the following: hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and/or phosphorous.
Monosaccharides
Simple carbohydrates that contain 3 to 10 carbon atoms.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides.
Dehydration reaction
A chemical reaction in which molecules combine by removing water.
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water.
Hydrophobic
Lacking any affinity to water.
Saturated fat
A lipid made from fatty acids that have no double bonds between carbon atoms.
Unsaturated fat
A lipid made from fatty acids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
Peptide bond
A bond that links amino acids together in a protein.
Hydrogen bond
A strong attraction between hydrogen atoms and certain other atoms (usually oxygen or nitrogen) in specific molecules.
Respiration
The breakdown of food molecules with a release of energy.
Homeostasis
Maintaining the status quo.
Reproduction
Producing more cells.
Cell Wall
A rigid structure on the outside of certain cells, usually plant and bacteria cells.
Plasma membrane
The semipermeable membrane between the contents and either the cell wall or the cell's surroundings.
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended.
Mitochondria
The organelles in which nutrients are converted to energy.
Lysosome
The organelle in animal cells responsible for hydrolysis reactions that break down proteins, polysaccharides, disaccharides, and some lipids.
Ribosomes
Non-membrane-bounded organelles responsible fore protein synthesis.
Endoplasmic reticulum
An organelle composed of an extensive network of folded membranes that performs several tasks within a cell.
Rough ER
ER that is dotted with ribosomes.
Smooth ER
ER that has no ribosomes.
Central vacuole
A large vacuole that rests at the center of most plant cells and is filled with a solution that contains a high concentration of solutes.
Golgi bodies
The organelles where proteins and lipids are stored and then modified to suit the needs of the cell.
Microtubules
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tubelike structure.
Nuclear membrane
A highly-porous membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement.
Phospholipid
A lipid in which one of the fatty acid molecules has been replaced by a molecule that contains a phosphate group.
Passive transport
Movement of molecules through the plasma membrane according to the dictates of osmosis or diffusion.
Active transport
Movement of molecules through the plasma membrane (typically opposite the dictates of osmosis or diffusion) aided by a process that requires energy.
Isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in a solution.
Hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution.
Hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution.
Activation energy
Energy necessary to get a chemical reaction going.
Genetics
The science that studies how characteristics get passed from parent to offspring.
Genetic factors
The general guideline of traits determined by a person's DNA.
Environmental factors
Those "nonbiological" factors that are involved in a person's surroundings such as the nature of the person's parents, the person's friends, and the person's behavioral choices.
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for the production of a protein of a portion of protein, thereby causing a trait.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
The RNA that performs transcription.
Anticodon
A three-nucleotide base sequence on tRNA.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotide bases on mRNA that refers to a specific amino acid.
Chromosome
DNA coiled around and supported by proteins, found in the nucleus of the cell.
Mitosis
A process of asexual reproduction in eukaryotic cells.
Interphase
The time interval between cellular reproduction.
Mother cell
A cell ready to begin reproduction, containing duplicated DNA and centrioles.
Centromere
The region that joins two sister chromatids.
Diploid cell
A cell with chromosomes that come in homologous pairs.
Haploid cell
A cell that has only one representative of each chromosome pair.
Diploid number (2n)
The total number of chromosomes in a diploid cell.
Haploid number (n)
the number of homologous pairs in a diploid cell.
Meiosis
The process by which a diploid (2n) cell forms gametes (n).