carina supply/demand + surplus
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
any kind of arrangement where buyers and sellers of goods, services, or resources are linked together to carry out an exchange.
markets definition
composed of a large number of sellers and buyers acting independently, so that no one individual seller or small group of sellers has the ability to control the price of the product sold. The price of the product is then set by the interaction of many sellers and buyers and the forces of both supply and demand.
competitive market definition
the individual consumers willingness and ability to buy goods or services at different prices during a specific period of time (all else being equal)
demand definition
behaviour of buyers
concerns of demand
the amount of goods and services customers are willing and able to pay for.
quantity demand definition
there is a negative causal relationship between a goods price and its quantity demand in a particular time period, ceteris paribus
What is the law of demand?
a change in price = a change in quantity demand
meaning of a negative causal relationship
1) changes in income (normal and inferior goods)
2) tastes and preferences
3) future price expectations
4) price of related good (substitutes and compliments)
5) size of market (number of consumers)
What are the non-price determinants of demand? (5)
if demand will decrease or increase
what do the non-price determinants of demand indicate
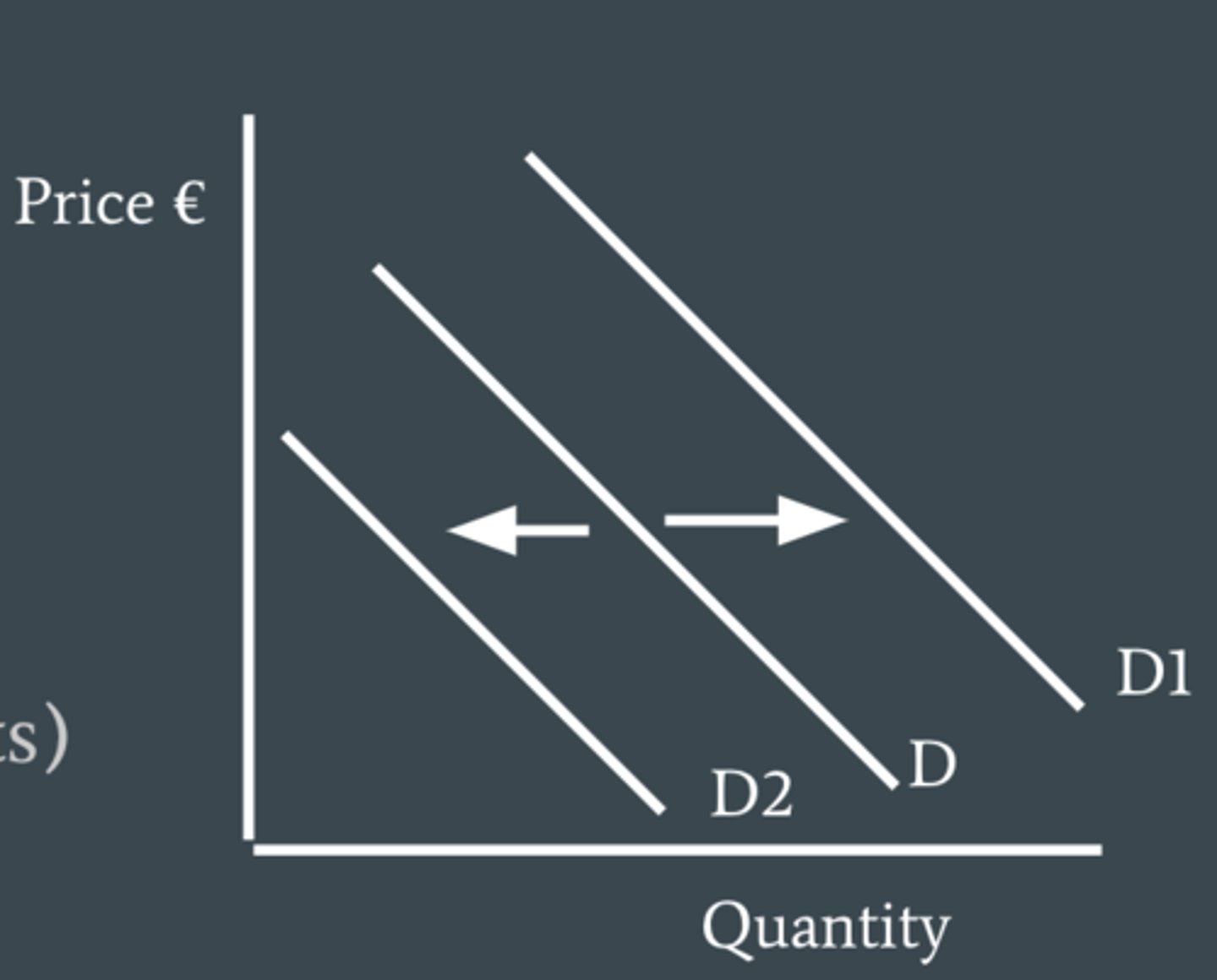
if income increases the demand for normal goods will also increase.
if income decreases the demand for normal goods will also decrease
how do changes in income affect the demand of normal goods?
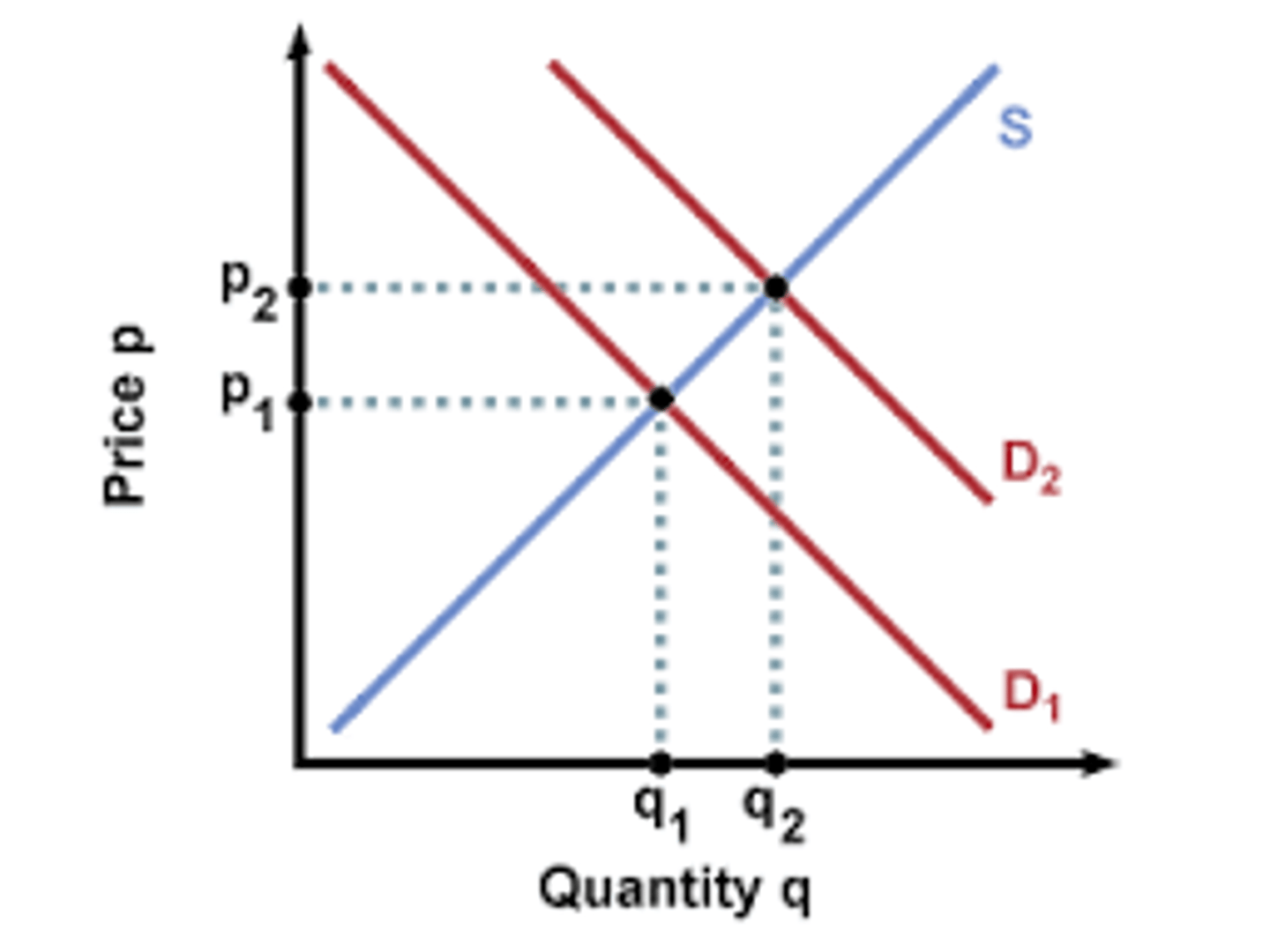
if income increases the demand for inferior goods will decrease
if income decreases the demand for inferior goods will increase
how do changes in income affect the demand of inferior goods?
if a celebrity endorses a product or if news/studies say something either good of bad about a product
increases/decrease demand
what are examples that can affect tastes and preferences? and how does that affect demand
demand will increase today as people want to buy things at the cheaper price, and same vice versa.
future price expectations - if P will increase tomorrow how will D change today?
goods that can be used in place of others
What are substitute goods?
goods that are consumed together
what are complimentary goods?

if the price for good A increases, the demand for it's substitute also increase. if the price of good A decreases the demand for its substitute will decrease and vice versa
how do substitute goods affect demand? (price and QD)
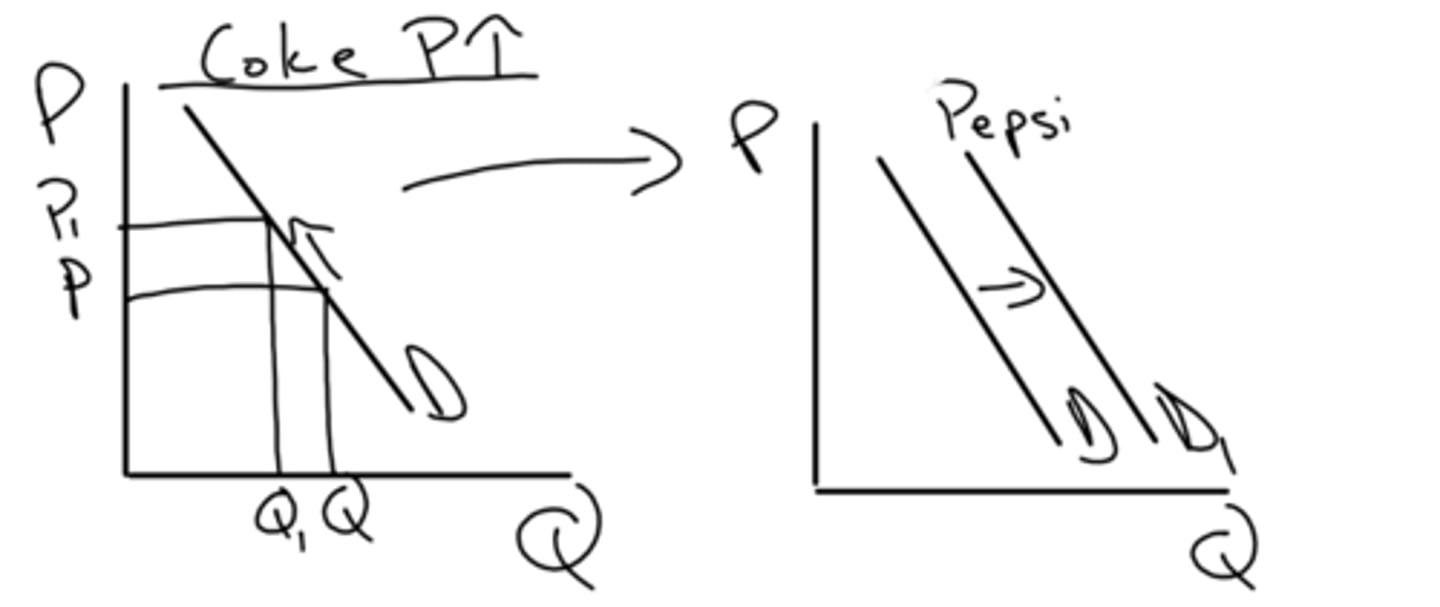
if the price for good A increases the demand for its compliment will also decrease. if the price of good A decreases the demand for its compliment will increase, and vice versa.
How do complimentary goods affect demand? (price and QD)
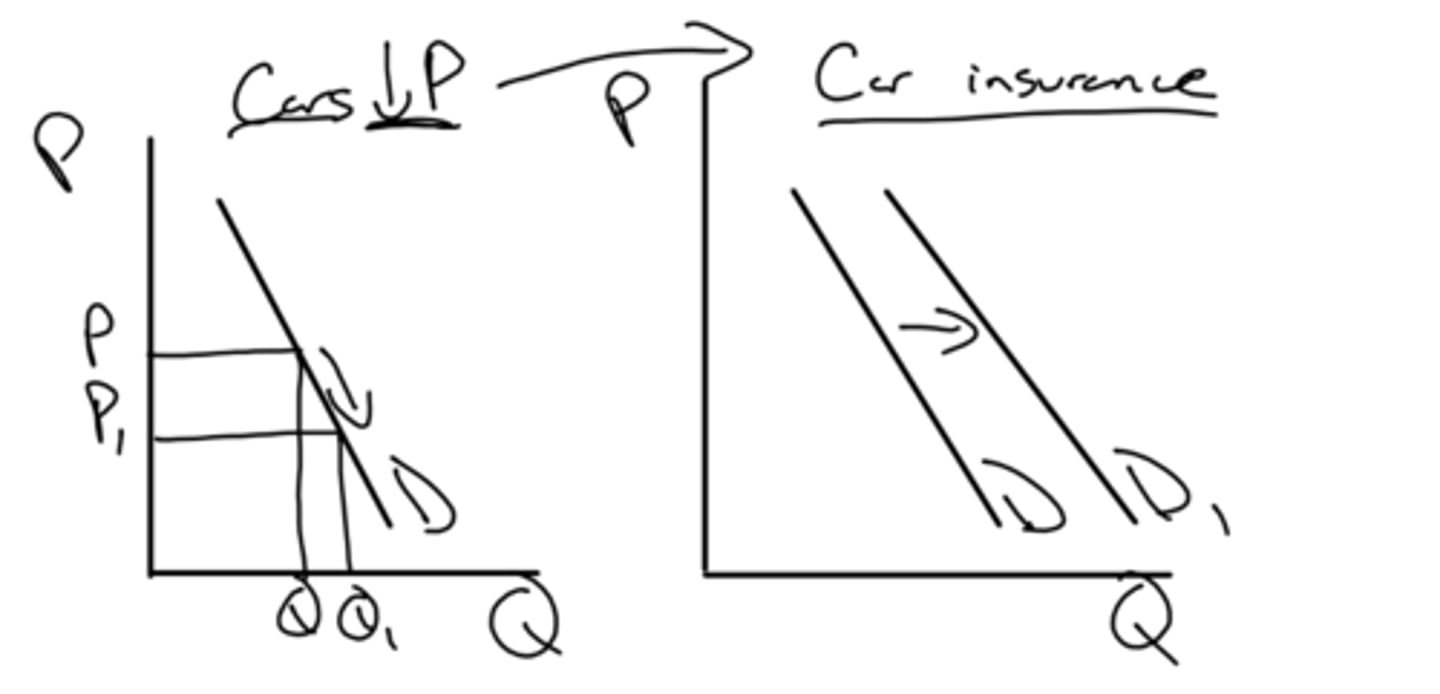
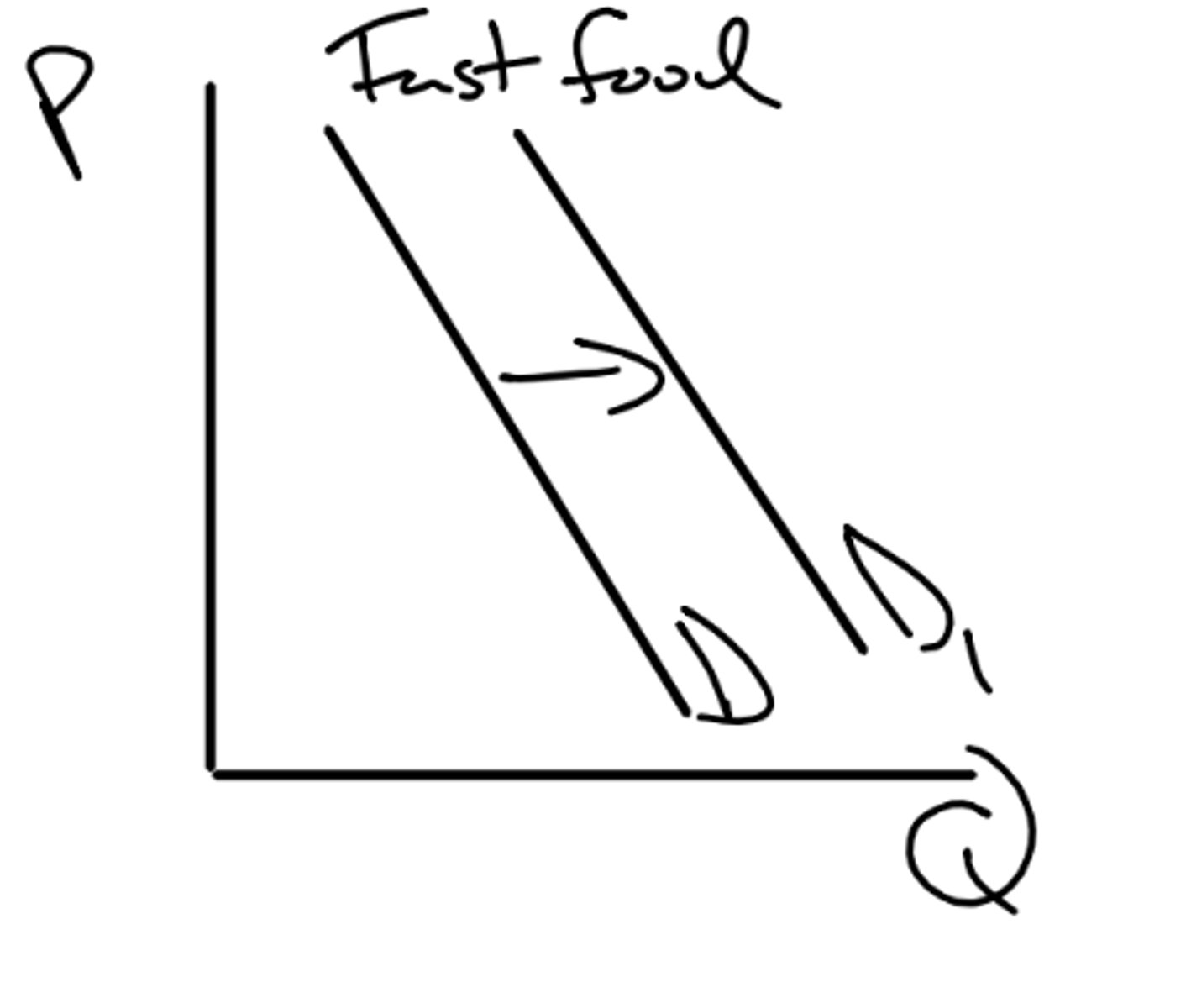
a big concert in vienna, more people coming in, meaning more consumers and thus the demand for things such as fast food increase
what is an example of when size of market would affect demand?
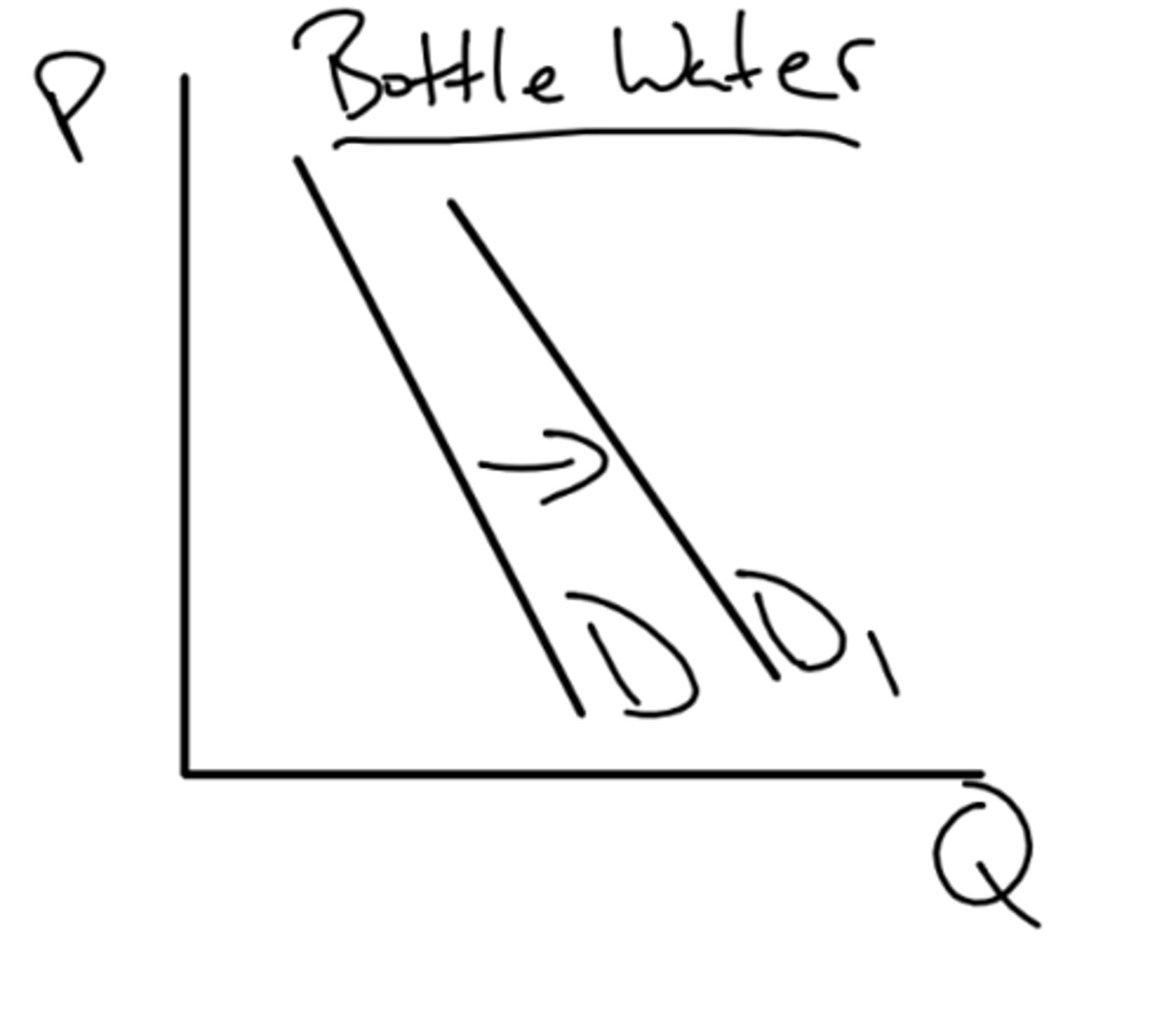
natural disasters, hurricane is expected to hit and thus creating an effect on water supply meaning people will be unable to drink tap water -> demand for bottled water would increase
an example of a special circumstance that might affect demand?
individuals firms willingness and ability to produce various quantities of goods/services at different prices during a specific period of time, ceteris paribus.
definition of supply
behaviour of sellers, such as firms in product markets and households in resources markets
concerns of supply
refers to the amount of goods and services producers willing and able to produce at a given market price.
quantity supply definition
there is a positive causal relationship between a goods price and its quantity supplied in a particular time period, ceteris paribus
what is the law of supply?
STORES
what is the acronym of the non-price determinants of supply?
1 - subsidies and taxes
2 - Technological advances
3 - other related goods prices (joint and competitive supply)
4 - resource costs
5 - expectation of future prices
6 - size of market (number of producers)
What are the non-price determinants of supply? (6)
increase or decrease supply
what do non-price determinants of supply do?
per-unit payment from the government to producers that decreases the firms cost of production
Subsidies definition
payment to the government thats shared by producers and consumers (they increase the costs of production of producers)
Indirect tax definition
subsidies - increase supply (producers can produce more goods and services)
taxes - decrease supply (firms are less willing or able to supply the same quantity of goods or services as before)
how do subsidies and taxes affect supply?
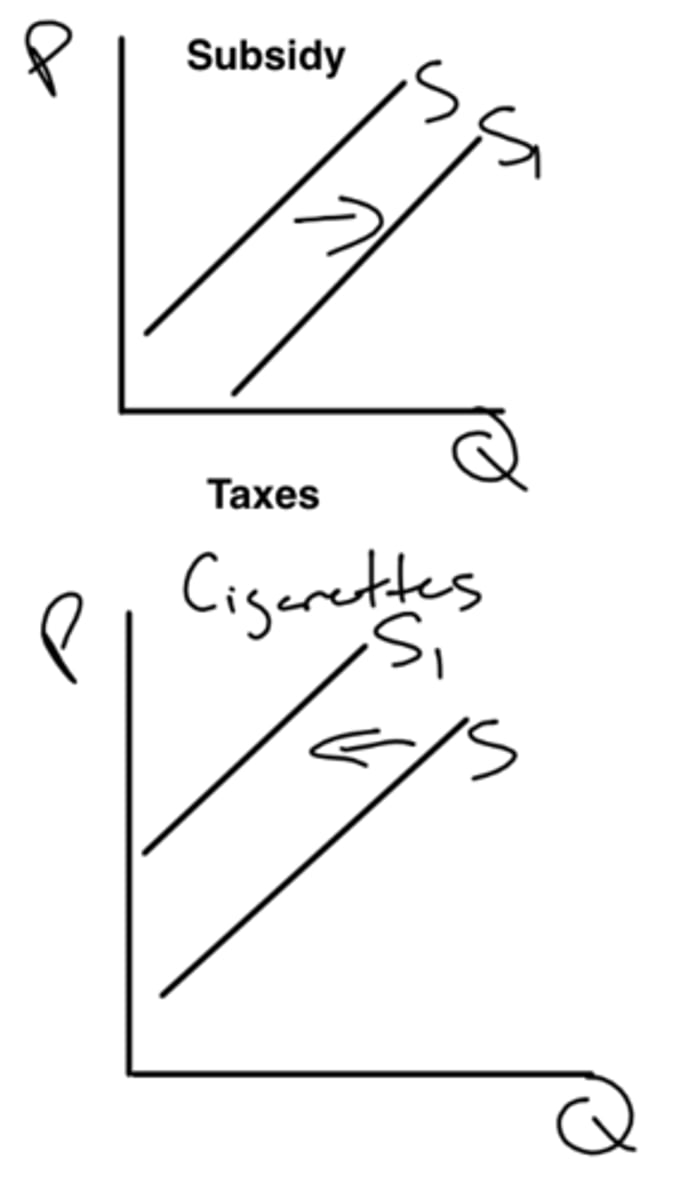
increases supply (only works one way)
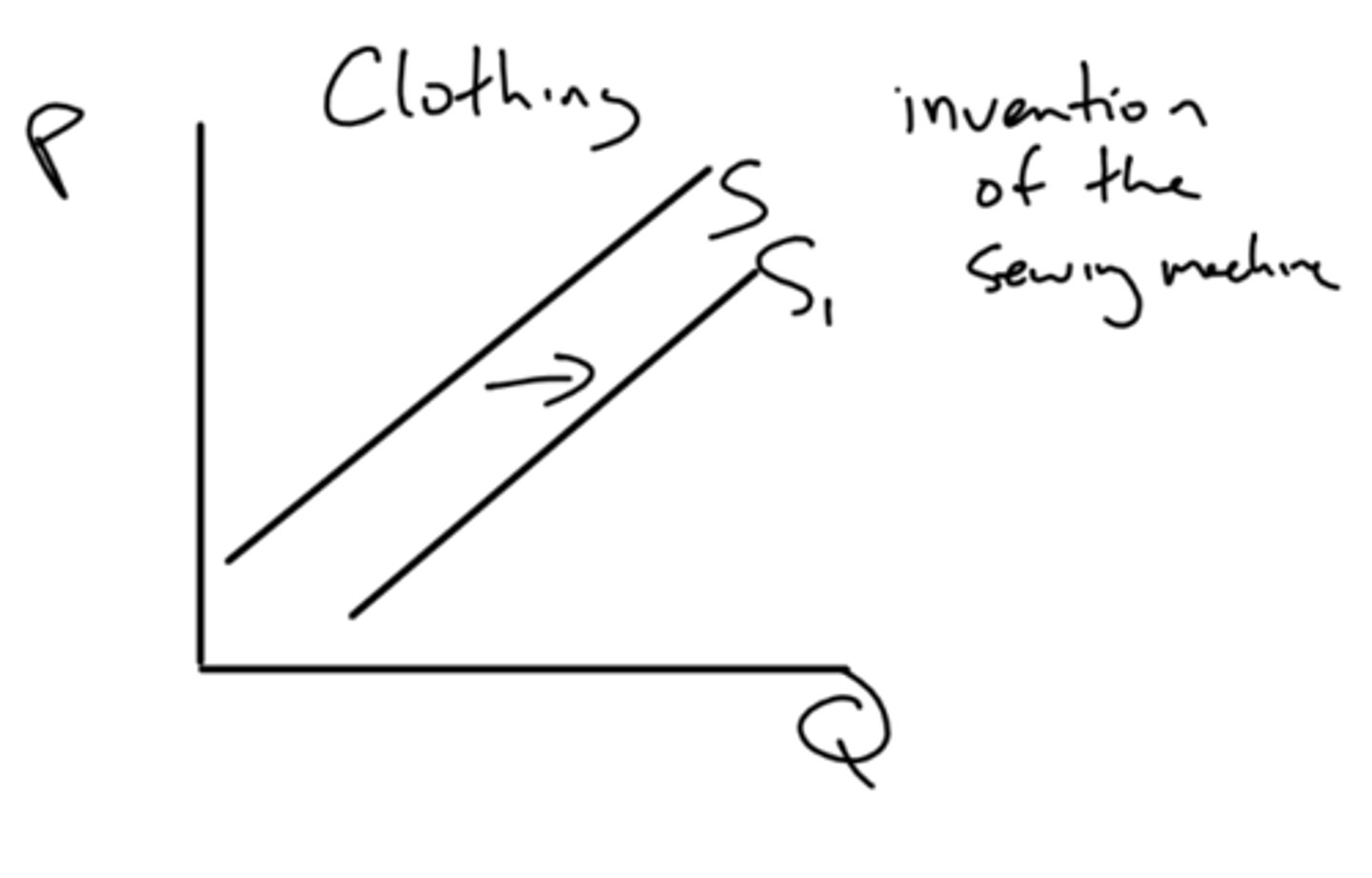
- productivity increases
how do technological advancements affect supply?
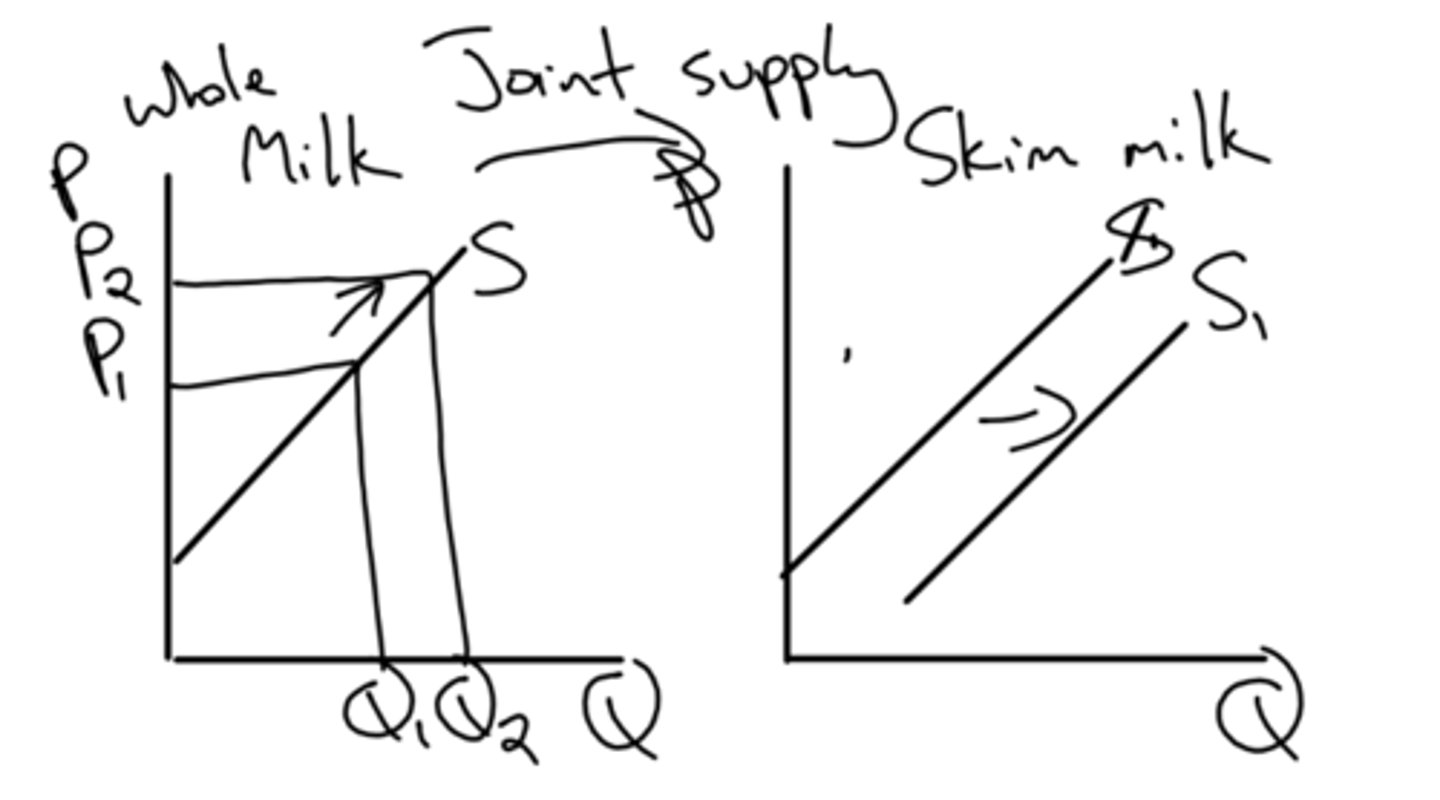
refers to a manufacturing or production process that results in the production of two goods (you cannot make one without the other)
joint supply definition
if more lamb meat is produced then you have the ability to also make more wool. thus an increase in the supply of lamb meat would also increase the supply of wool
example of joint supply
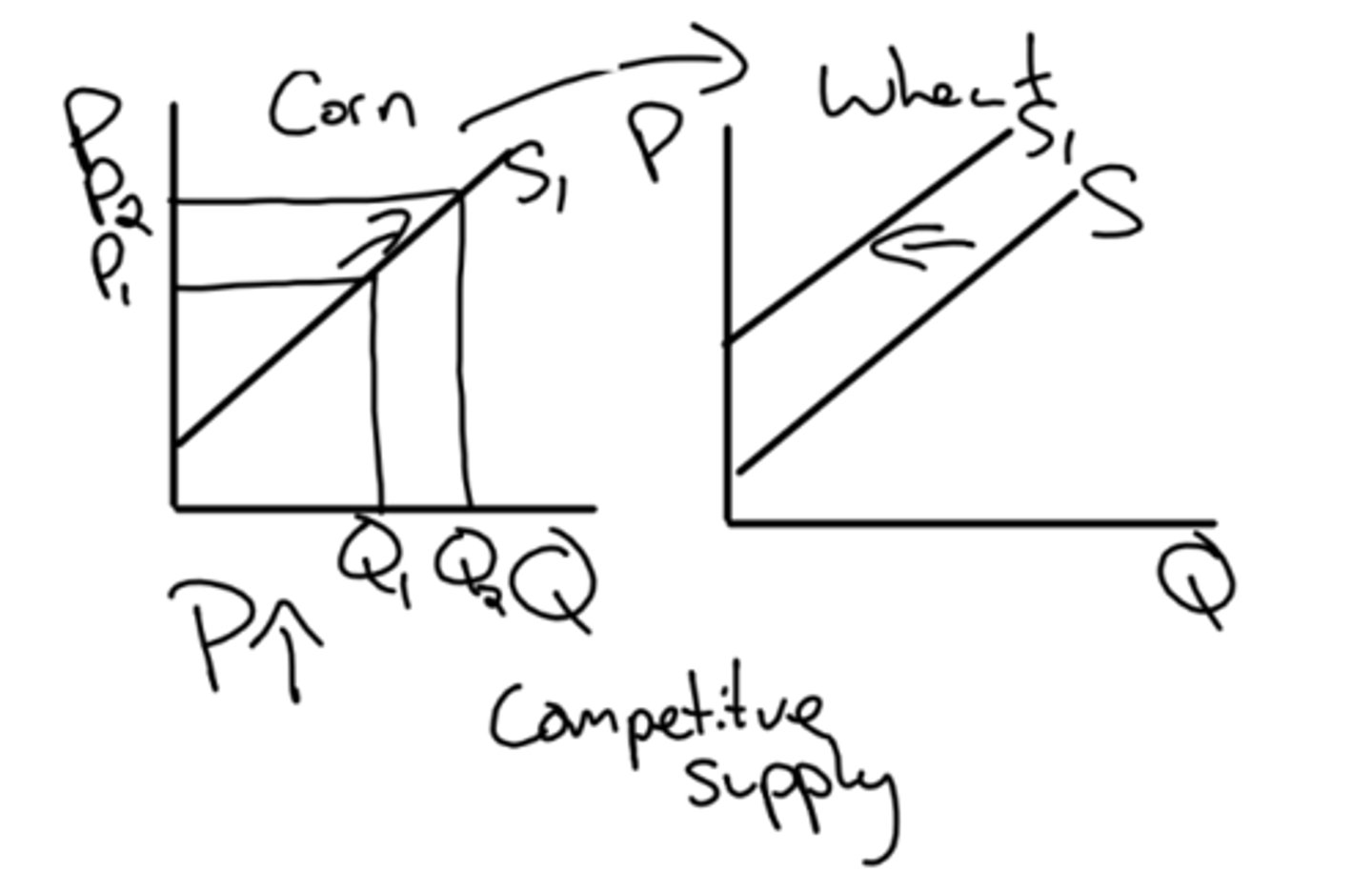
alternative products a firm could make with its resources
competitive supply definition
corn and wheat a considered agricultural substitutes. if there is a price increase of corn there is an incentive to reallocate resources to produce more corn and therefore the supply of wheat would decrease.
example of competitive supply
input prices (what goes into the making of a good/service)
resource costs definition
when the price of resource costs increase, supply decreases
when the price of resource costs decrease, supply increases
how do resource costs affect supply?
if the price of a good/service is going to increase tomorrow, supply will decrease today
if the price of a good/service is going to decrease tomorrow, supply will increase today
how does the expectation of future prices affect supply?
an increase in number of producers = increase of supply
a decrease in number of producers = decrease of supply
how does the size of market (number of producers) affect supply?
a flooding in austria will decrease the supply of pumpkins and thus may increase prices as well.
an example of a special circumstance that can affect supply
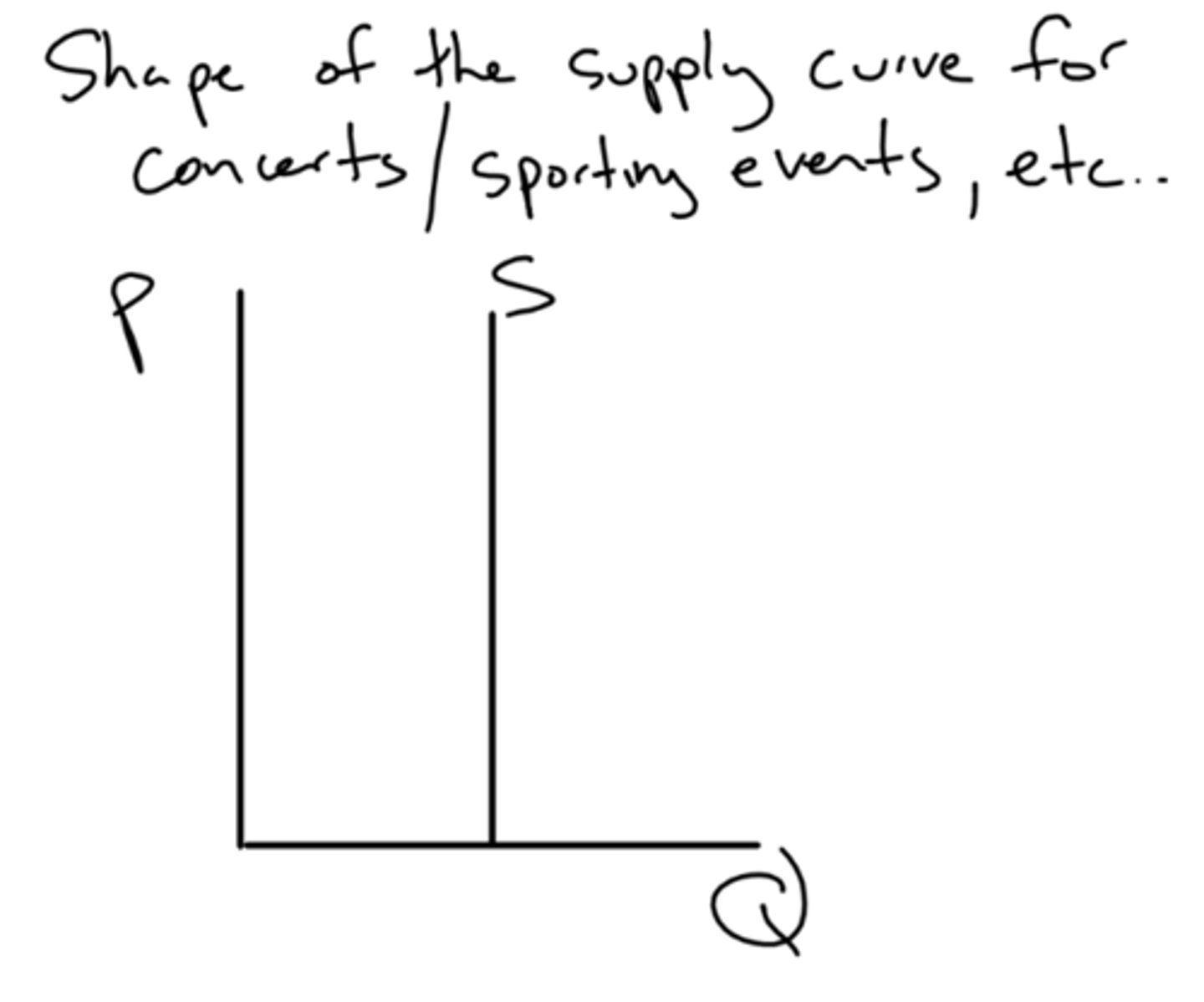
straight line up
what is the shape of the supply curve when a concert has a certain amount of seats?
when market quantity supply equals to market quantity demand and there is no tendency for a change in price
equilibrium definition
the market "clears" meaning that every unit being produced is being consumed
what does it mean when a market is in equilibrium?
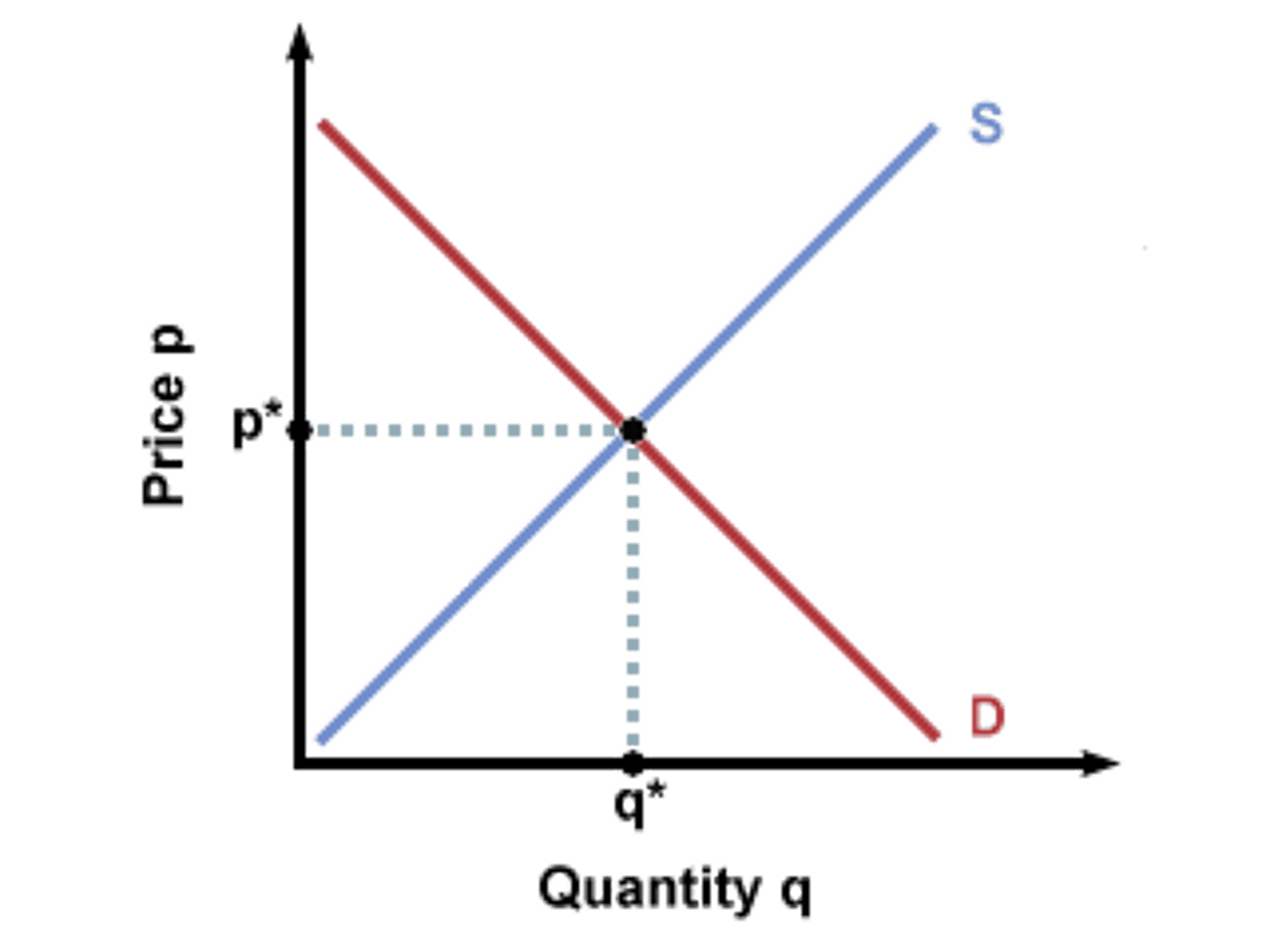
there will be a surplus or shortage
what happens when a market is at disequilibrium?
when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded, excess supply
surplus definition
when quantity demand is greater than quantity supplied, excess demand
Shortage definition
producers will decrease prices in order to encourage consumers to buy more. with a surplus there is a downward pressure on prices until market clears.
what will producers do to try and get rid of surplus?
producers will increase prices, due to the fact the product is selling out very quickly. as with a price increase consumers will demand less quantity -> upward pressure on prices untill market clears
what will producers do to try and overcome shortage?
a change in one of the non-price determinants of demand or supply
what will causes a market in equilibrium to change?
prices can help alleviate or ration scarce resources
and act as incentives for producers or consumers
what can prices help with?
refers to the way in which price determines the allocation of resources and influences the quantity supplied and quantity demanded of goods/services.
what are price mechanisms?
1 - signaling
2 - Rationing
3 - Incentives
what are the 3 price mechnisms?
any piece of data or information which allows people to optimize their decision-making process and make comparatively better decisions economically.
economic signals definition
When the supply of a good is limited, its price increases, which can help to reduce demand and allocate the available quantity to those who are willing and able to pay the higher price.
How does rationing act as a price mechanism?
a reason/purpose to do something
incentive definition
When there is a surplus of a good/service it will incentivize producers to decrease their prices in order to get rid of it. this will then also incentivize consumers to buy more of the good/service
example to do with incentives
Quantity supply - quantity demand
how to calculate surplus?
quantity demand - quantity supply
how to calculate the quantity of the shortage?
Price x Quantity
how to calculate revenue?
it also increases
what happens to total revenue when price and quantity increase?
since supply has decreased the price increases and thus you lose some of the quantity supplied but you gain more revenue due to the increased prices.
e.g - flooding in austria, what is the effect on TR in the market of pumpkins
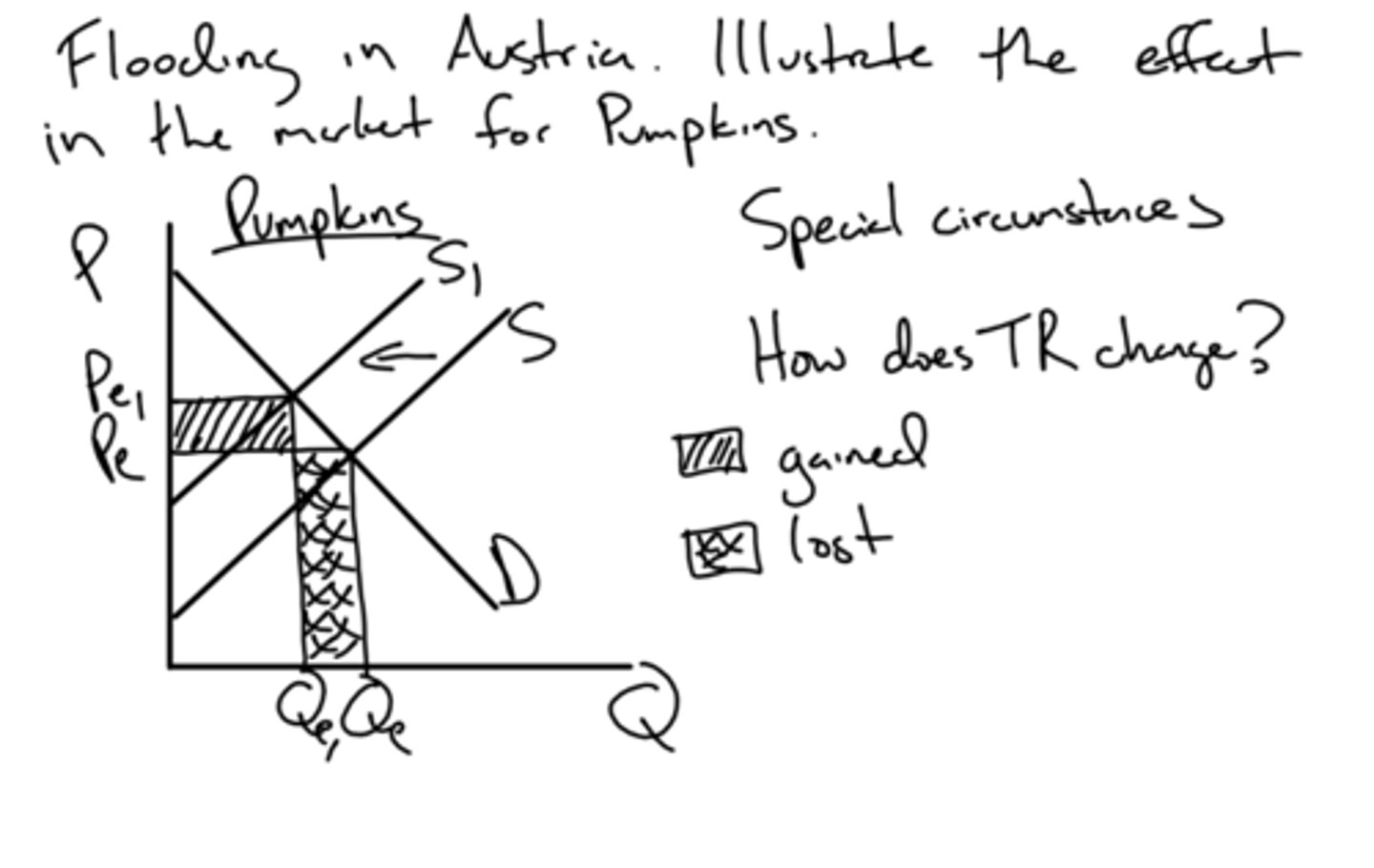
that there was an initial surplus at the original equilibrium price after the change in supply/demand
what does it mean if the new equilibrium price is lower than the original?
there has been a shortage at the original equilibrium price after the change in supply/demand
what does it mean if the new equilibrium price is higher than the original?
Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
what is demand equal to?
the benefit society obtains from the consumption of a good/service. At higher levels of output MSB decreases because additional units of a good/service bring benefits to fewer people and the less people the more of that good/service there is.
what is marginal social benefit?
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
what is supply equal to?
the cost to society for producing an additional unit of a good or service. the cost of producing more of a good/service increases for most goods/services
what is marginal social cost?
refers to producing the combination of goods that are mostly wanted by society.
achieved when economy allocates resources in a way so that no one can become better off from their consumption without someone else becoming worse off.
allocative efficiency definition and how is it achieved?
when goods are produced using the fewest possible resources and lowest possible cost.
achieved when allocative efficiency is
productive efficiency definition and how is it achieved?
when MSC = MSB
when does allocative efficiency take place
the benefit consumers obtain when they pay a lower price than the highest price they are willing to pay.
consumer surplus definition
the benefit producers receive from receiving a price higher than the lowest price they would be willing to sell at.
producer surplus definition
the sum of both consumer and producer surplus
social surplus definition
when the market is in equilibrium.
when is social surplus maximized in a competitive market?
consumers are worse off while producers are better off
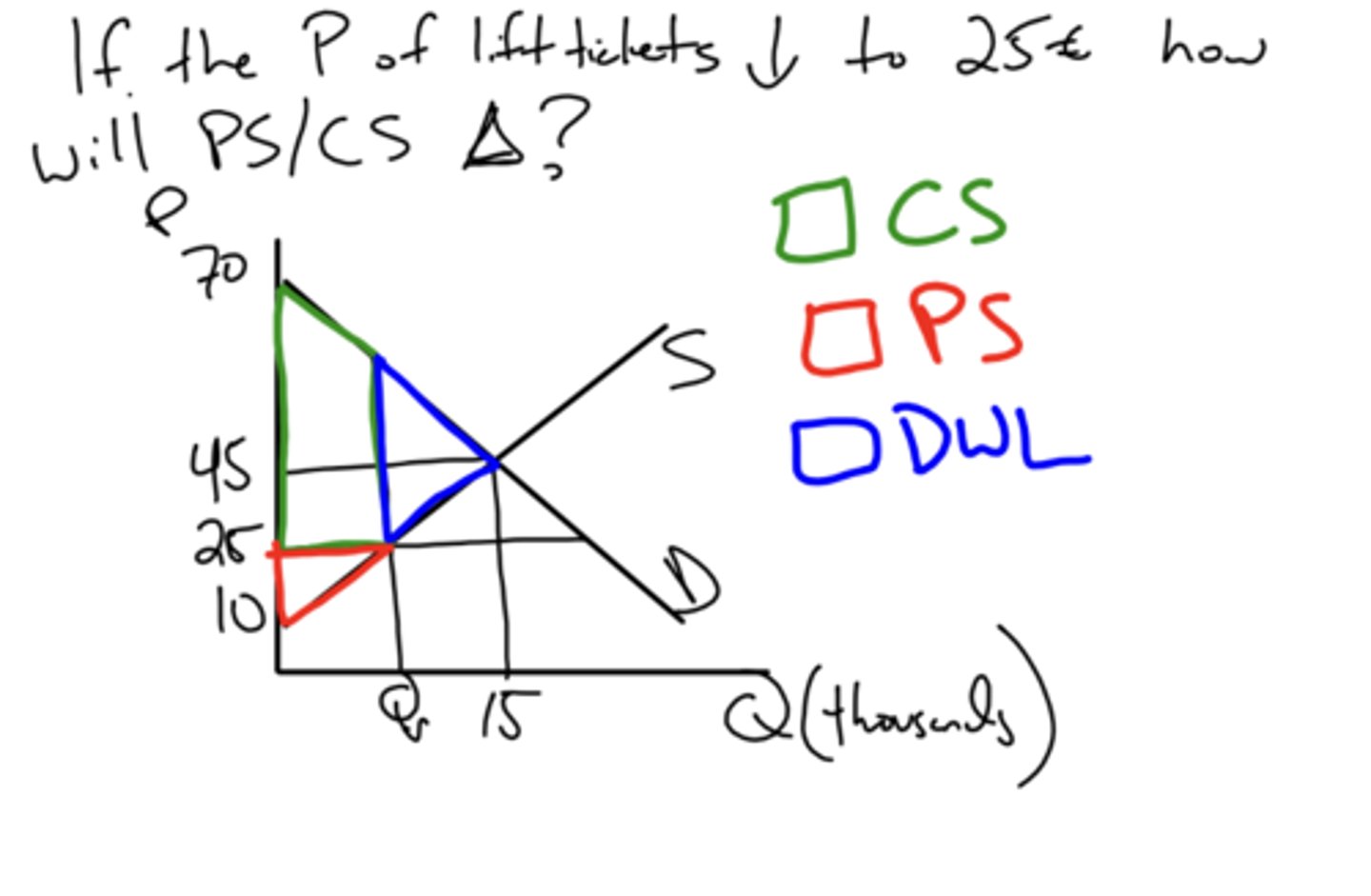
e.g - if price increases how does that affect consumer and producer surplus?
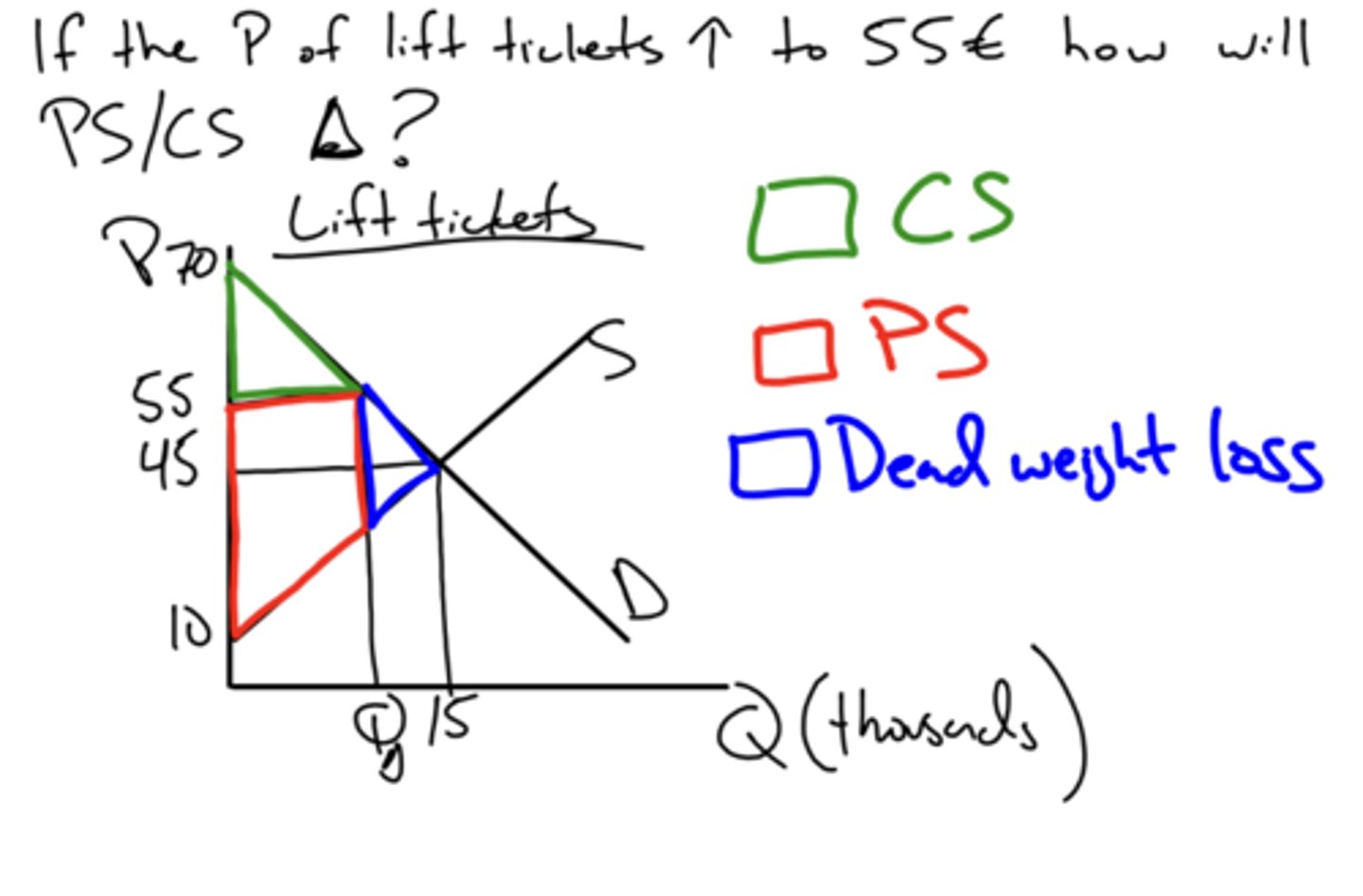
consumers are better off while producers are worse off
e.g - if price decreases how does that affect consumer and producer surplus?