MIDTERM OPS KILL ME
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
The Operation realities
Better quality, high productivity, lower costs and the ability to respond quickly to customer needs
Organizational strategies
Overall strat. That relate to the entire org
Support the achievement of organizational goals and mission
Functional level strategies
Strategies that relate to each of the functional areas and that support achievement of the organizational strategy
Tactics vs Operations
Tactics:
The methods and actions taken to accomplish strategies
The “how to” part of the process
Operations
Actual “doing” part of the process
Order qualifiers
Characteristics that customers perceive as minimum standards of acceptability for them to consider purchase
Order winners
Characteristics that lead customers to prefer one product over another, providing a competitive advantage.
Have/ offering that causes you to get the order (transaction to happen)
Competitive Dimensions
Cost or price
Quality
Delivery speed
Delivery reliability
Responsiveness to demand changes
New products and flexibility
Support functions (after sale)
Risk Mitigation Framework
Identify the source of potential disruptions
a. Look @ highly unlikely events— that cause significant disruption to normal ops
Assess the potential impact of the risk (risk mapping)
a. Quantify probability and potential impact of risk (prob frequency & amount of loss)
Develop plans to mitigate the risk
a. Detailed strat. for minimizing the impact of risk (could take many diff. forms)
FMEA
Failure
Modes
Effects
Analysis
Productivity
Relative measure
Measure of effective use of resources
Normally dimensionless number (unless specified)
Efficiency
Quality
How well do you perform
Look 4 underlying costs
Refined measure
Doing something at the lowest possible cost
Getting the most out of a given set of resources
Productivity
Quantity
Performance
No look 4 underlying costs
Raw measure
Looks at alternative easy to increase the output or reduce the input
Phases of product development
Phase 0: Planning
Corporate strategy /// Tech. assessment
Mission: What will we develop?
Phase 1: Concept Development
Market needs identified /// Alternative concepts generated and evaluated
Concept(s) selected for further development
Phase 2: System-Level Design
Product architecture /// Sub-systems and components
Layout, functional specifications, production process flow
Phase 3: Design Detail
Complete specification of geometry, materials, and tolerances /// Suppliers and tooling for parts
Drawings, process plan
Phase 4: Testing and Refinement
Prototypes tested to evaluate product performance /// Multiple preproduction versions evaluated
Phase 5: Production Ramp-up
Production system used for final product /// Pre-production samples sent to customers
Worker training
Complexity:
# of steps involved in a service & the possible actions that can be taken at each step
Divergence
# of ways a customer/service provider interaction can vary at each step according to the needs & abilities of each
Complexity and Divergence Determine:
The resources (worker skills)
Layout changes that might be required
Process controls needed for the new service
Steps to determine capacity requirement
Forecast to predict sales
Calculate equipment and labor requirements
Project labor and equipment availability
Operating capacity:
Volume of output that can be sustained that minimizes the average unit cost (Involves tradeoffs, fixed costs, equipment wear, etc.)
Sometimes called rated capacity
Capacity utilization rate:
a measure of how close the firm is to its best possible operating level
Economies of scale:
as a plant gets bigger and volume increases, & average cost per unit drops
Diseconomies of scale:
at some point, the plant becomes too large & average cost per unit begins to increase
How to fix capacity Imbalances
Add capacity (overtime, equipment leasing)
Add buffers to ‘smooth’ out fluctuations
Decouple operations
Where is best operating point?? (service utilization)
Best operating point is near 70 percent of maximum capacity
Fixed cost:
An expense that remains constant regardless of output level
Variable cost:
Expenses that are directly proportional to the level of output
Sunk cost:
Past expenses/ investment with no salvage value or current expenses that will have no bearing on the decision
Opportunity cost:
Benefits foregone bc of choosing an action as opposed to the “best” known action
Capital Expenditure (CAPEX):
Spending associated increases in plant, property and equipment
Expected Value
The likelihood of a particular outcome happening is its probability
The ________ Value = expected outcome X the probability of that outcome happening
NPV
_ _ _ is the value today of money you’ll receive or pay in the future
It’s the difference between Pv of money coming in and Pv of $ going out over time.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Is a discount that make the NPV of all cash flows equal 0
At a minimum IRR should be > WACC
Payback Period
the length of time required for an investment to recover its initial outlay in terms of profit savings
Learning Curves?
As output doubles, there is a fixed percentage reduction in the time needed to produce each unit
3 Assumptions:
Time required to complete a given task will be less each time the task
is undertakenUnit time will decrease at a decreasing rate
Reduction in time will follow a predictable pattern
Individual learning:
Improvement that results when people repeat a process and gain skill or efficiency from their own experience
Practice makes perfect
Organizational learning:
Biz learning
Can come from changes in administration, equipment, and product design
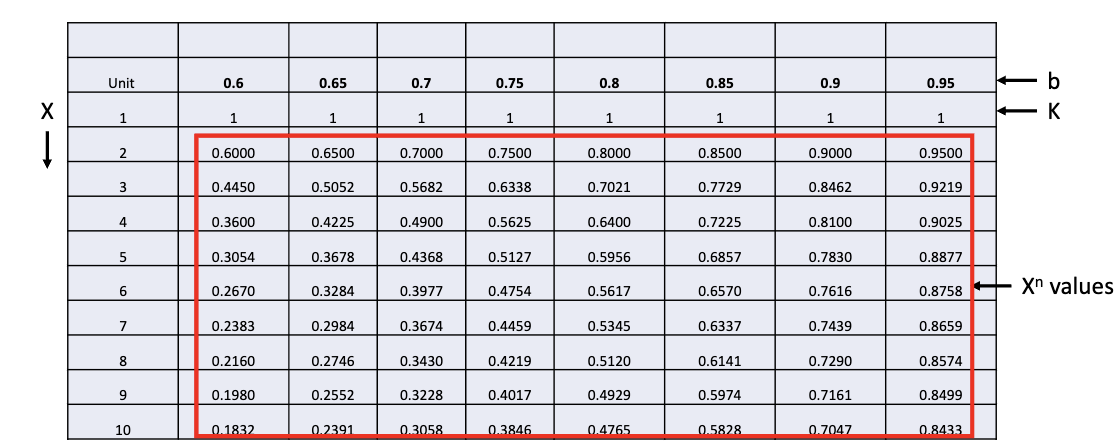
Improvement Factor Table
Job Shop
Nature of business: Customized goods or services
Pros: Able to handle a wide variety of work.
Cons: Slow, high cost per unit, complex planning, and scheduling.
Organization: Product areas.
ie. operating room
Batch
Nature of business: Semi-standardized goods or services.
Pros: Flexible, easy to add or change.
Cons: Moderate cost per unit, moderate scheduling complexity.
Organization: Processes are continuous, but ____es can differ in flow and duration.
ie mas catering
Repetitive
Nature of business: Standardized goods or services.
Pros: Low unit cost, high volume.
Cons: Low flexibility, high cost of downtime.
Organization: Assembly lines.
ie Auto manufacturing
Continuous
Nature of business: Highly standardized goods or services.
Pros: Very efficient, very high volume.
Cons: Very rigid, lack of variety, costly to change, very high cost of downtime.
Organization: Runs continuously, materials are typically gases, liquids, powders, slurries.
ie Plant??
Lead Time:
Time from when an order is placed to when customer receives the order
The sum of all the cycle times in process from start to finish (assume no parallel processes)
Types of Manufacturing Environments
Make to stock: Customer purchases from existing finished goods inventory
Trade-off between the costs of inventory and level of customer service
Assemble to Order: Product is assembled from limited set of options upon receipt of order
Computers ordered online with selection of options
Make to Order: Higher degree of customization than assemble to order
Aircraft manufacturing
Engineer to Order: Designed to customer specifications
Satellites
Variety Leads to Complexity
N1 x N2 x N3 x N4 ....x Ni
4 different models, each model with 3 different case colors, 3
different memory configurations
Total combinations 4 x 3 x 3 = 36 possible configurations
Breakeven Analysis
The choice of equipment or process involves a cost tradeoff
General purpose (do many different things slower) vs. special purpose (few things fast)
________ _______ compares choices in processes/ equipment on the basis of TC,
which will vary with Volume of productionThe point of indifference between them because total cost is the same
Process technology
Methods, procedures, and equipment used to produce goods and provide services
Information technology
The science and use of computers and other electronic equipment to store, process and send information
Product layouts: _______ line
Layout that uses standardized processing operations to achieve smooth,
rapid, high-volume flowSubway or Car build lines
Pro: High output, low unit cost, high utilization equip/labor
Con: Boring, no changes, shutdowns
Process layouts: Work Center, Functional or Job-shop layout
Non-repetitive
Layouts allocate similar machines or activities into an area
Fixed-position layout: Project layout
Layout in which the product or project remains stationary, and workers,
materials, and equipment are moved as neededLarge construction projects: Shipbuilding/ aircraft manufacturing, Space mission
(very specific sequence of task order)
Combination layouts: Manufacturing cells
Some operational environments use a combination of the three basic layout types:
Hospitals
Supermarkets
Shipyards
Cells: allocate dissimilar machines into cells
Cycle time
It is the average elapsed time between any two parts
In ACTUAL production the cycle time SHOULD be < the Takt time in order to meet demand
BC there will always be delays and variation when doing things
Takt time
Maximum allowable cycle time in order to meet the production goals
Line Balancing
The sequence and process times are ordered to keep the line balanced and flowing
The longest process time (including wait time) are early in the sequence
The operations with the longest process time will be the bottleneck
Mixed-Model Line Balancing
Objective is to meet demand and avoid high inventories when you
have more than one product being made on the same lineOne means scheduling this varied production
Information needed
1. Total amount of time available for prod
2. Total quantity needed in that time
3. Cycle times
4. Ratio of different models (calculated based on total quantity)
5. Changeover time
Service Layout
Categorized as: product, process, or fixed position
Requirements:
Degree of customer contact
Degree of customization
Retail Layout
Goal is to maximize net profit per square foot of floor space
One-piece
Shorter lead time when finished Inventory is not carried!!!
Fast casual restaurants
Can get same OR higher output w/ less capital equipment
Batch
Used where setup time/ costs are high (more efficient to produce more per setup)