lab 14 - isolation/identification of an unknown bacteria
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
how do we identify an etiologic agent (the cause of an infectious disease)?
isolate the organism in pure culture to eliminate other potential pathogens (do this by streaking for isolation)
take growth from a single CFU and aseptically transfer it to grow in pure culture
incubate, and now it is the stock culture which is used for all future testing
what is selective medium/agar?
media that contains inhibitory agents that inhibit the growth of specific microorganisms, thereby allowing for the growth of only other specific microorganisms
what is differential agar media?
media that provides preliminary results that logically direct the next biochemical tests and the ultimate definitive identification. most selective agars are also differential
what is macconkey agar?
a medium that is commonly used to select for the growth of gram-negative bacteria and to differentiate those organisms according to their ability to ferment lactose
organisms that grow on macconkey agar are
bile-tolerant and crystal violet tolerant, so they can grow in the presence of inhibitory agents
what is columbia cna agar?
medium that is used to select for the growth of gram-positive bacteria
organisms that grow on cna agar are
resistant to the antibiotics colistin and naladixic acid. they can also lyse erythrocytes through hemolysis, and that is how differentiation is often observed
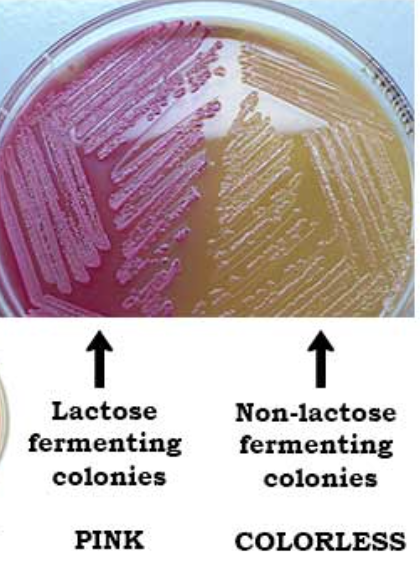
for macconkey’s agar…
what are the inhibitory agents?
it tests for the selective growth of…
what are the differential agents?
differential activity?
what is the indicator?
differential reaction?
bile salts, crystal violet
gram-negative bacteria
lactose
lactose fermentation to acid
neutral red
pink/red colonies (acid) = lactose fermented; colorless/tan colonies (neutral/alkaline) = non-lactose fermenters
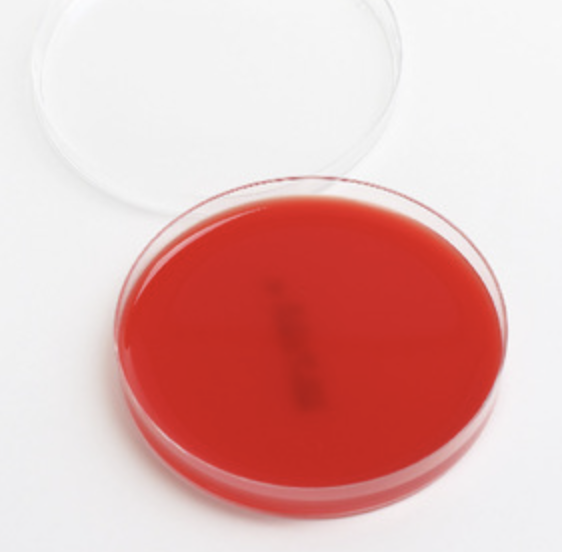
for columbia blood agar (cna)…
what are the inhibitory agents?
it tests for the selective growth of…
what are the differential agents?
differential activity?
what is the indicator?
differential reaction?
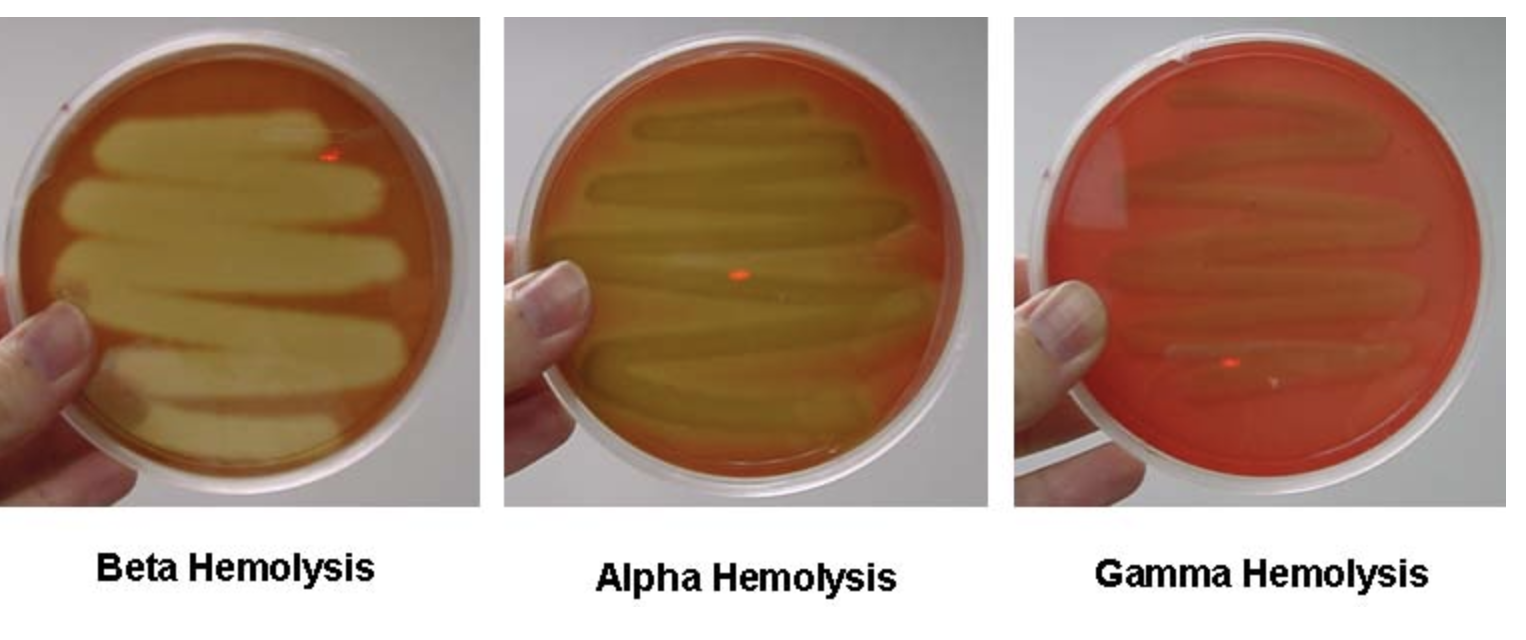
colistin, naladixic acid
some gram-positive bacteria
RBCs
hemolysis of RBCs
none
gamma, alpha, or beta hemolysis
for mannitol salt agar (msa)…
what are the inhibitory agents?
it tests for the selective growth of…
what are the differential agents?
differential activity?
what is the indicator?
differential reaction?
7.5% NACl
salt-tolerant bacteria (mainly staphylococcus)
mannitol
mannitol fermentation to acid
phenol red
yellow colonies & agar (acid) = mannitol fermented
for bile esculin agar…
what are the inhibitory agents?
it tests for the selective growth of…
what are the differential agents?
differential activity?
what is the indicator?
differential reaction?
bile salts
enterococcus & gram-negative enteric bacteria
esculin
esculin hydrolysis by esculinase
ferric citrate
blackening of medium = esculin hydrolysis

for desoxycholate agar (DOC)…
what are the inhibitory agents?
it tests for the selective growth of…
what are the differential agents?
differential activity?
what is the indicator?
differential reaction?
desoxycholate & citrate salts
gram-negative enteric bacilli
lactose & peptone source of amino acids
lactose fermentation to acid; amino acid metabolism to alkaline
neutral red
pink/red colonies (acid) = lactose fermented = fecal coliforms; colorless/tan colonies (alkaline) = NLF = non-coliforms
what is the carbohydrate fermentation series tests?
its the 1st step in the biochemical identification of gram-negative bacteria. most organisms use carbohydrates as the primary nutrient catabolized to provide glycolytic substrates and energy.
_ is often the preferred carbohydrate
glucose. however many organisms alternatively use lactose and/or sucrose. some metabolize these organisms through aerobic respiration, but many use fermentative metabolism. the end products vary, but fall into 2 categories: acidic end products and non-acidic end products. gas (such as O2) can be produced as a by-product
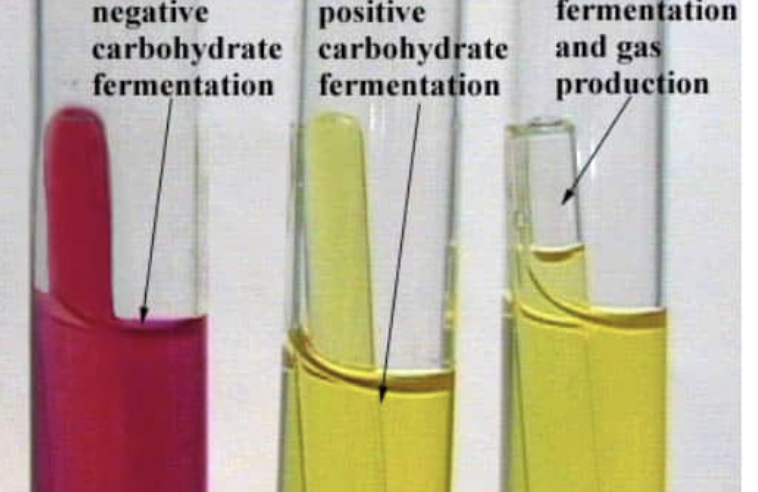
in the carbohydrate tests, how are organisms identified?
by the types of carbohydrates they ferment and whether they produce an acidic end product with/without the production of gas (collected in an inverted durham tube)
in the carbohydrate tests, what is the indicator?
phenol red. if the organism can ferment the carbohydrate to acid, the indicator will change from red to yellow
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is escherichia coli…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, pink colonies
lactose fermenter
no growth
salt-sensitive
for all, produced acid and fermented sugar; CO2 was captured in durham tube
same as 6
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is enterobacter aerogenes…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, pink mucoid colonies
lactose fermenter
no growth
salt-sensitive
for all, produced acid and fermented sugar; CO2 was captured in durham tube
same as 6
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is salmonella enterica…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, colorless colonies
non-lactose fermenter
no growth
salt-sensitive
for glucose and sucrose, produced acid and fermented sugar; CO2 was captured in durham tube. for lactose, sugar wasn’t fermented so phenol red remained red/orange
doesn’t ferment lactose
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is serratia marcescens…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, colorless/slightly pink colonies
non-lactose fermenter
no growth
salt-sensitive
for glucose, produced acid and fermented sugar; CO2 was captured in durham tube. for lactose and sucrose, produced acid and fermented sugar without gas.
ferments all sugars
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is pseudomonas fluorescens…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, colorless colonies
non-lactose fermenter
no growth
salt-sensitive
for all, didn’t ferment sugar so phenol red remained red/orange
is alkaline
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is neisseria sicca…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
no growth
fastidious organism
no growth
salt-sensitive
for glucose, produced acid and fermented sugar without gas. for lactose and sucrose, sugar wasn’t fermented so phenol red remained red/orange
only ferments glucose
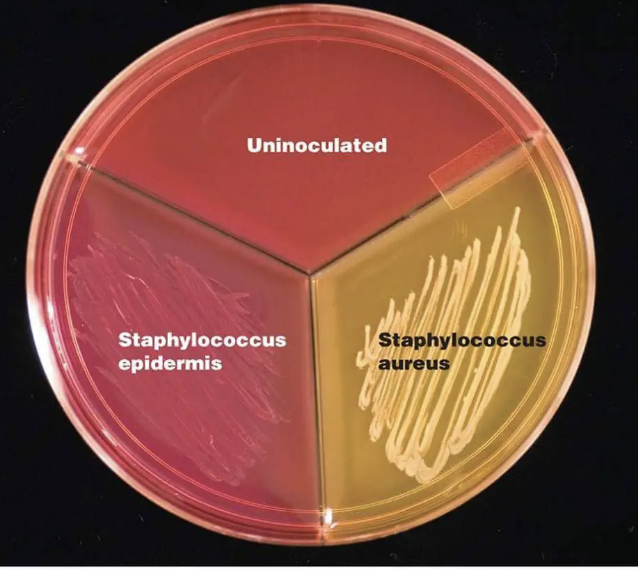
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is staphylococcus epidermidis…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
positive
no growth
can’t tolerate bile salts & crystal violet
growth, small white colonies
not sensitive to salt
for glucose and sucrose, produced acid and fermented sugar without gas. for lactose, didn’t ferment sugar so phenol red remained red/orange
can only ferment glucose and sucrose
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is enterococcus durans…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
positive
no growth
can’t tolerate bile salts & crystal violet
growth, small grayish colonies
not salt sensitive
for all, produced acid and fermented sugar without gas
same as 6
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is staphylococcus aureus…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
positive
no growth
can’t tolerate bile salts & crystal violet
growth, yellow/golden colonies with beta hemolysis
not salt sensitive
for all, produced acid and fermented sugar without gas
same as 6
on macconkey’s agar, cna agar, and the carbohydrate fermentation test, is pseudomonas aeruginosa…
gram positive or negative?
growth/no growth & appearance on macconkey?
interpretation of results on macconkey?
growth/no growth & appearance on cna?
interpretation of results on cna?
results in glucose, lactose, and sucrose?
observations from carbohydrate fermentation tests?
negative
growth, colorless colonies
non-lactose fermenter
no growth
salt sensitive
for all, sugar wasn’t fermented so phenol red remained red/orange
non-fermenter
difference between presumptive/preliminary and definitive/confirmatory identification?
presumptive - relies on observable characteristics and basic tests to narrow down possibilities. for example, a gram stain indicates whether a bacteria is gram positive or negative
definitive - requires more extensive, specific tests to confirm the species/genus of an organism
compare and contrast presumptive/preliminary and definitive/confirmatory results
purpose
- suggest a possible microorganism identity
- confirm the exact identity of a microorganism
accuracy
- not conclusive
- highly accurate/reliable
speed
- quick
- slow and lengthy
example
- a lactose-fermenting colony on macconkey agar could indicate e. coli
- biochemical testing to confirm it is e. coli
what is selective and differential media and what useful function do they serve?
media that inhibits the growth of some microorganisms while allowing for the growth of others. it is helpful because it selects for a specific group of bacteria
media that allows multiple organisms to grow but contains indicators that show differences between them. it is helpful because it can differentiate between species based on observable changes
what does the term enteric mean?
what does the prefix entero- mean?
what does the suffix -itis mean?
what is the meaning of enteritis and what are its signs/symptoms?
refers to the intestines, mostly the small intestine
intestine
inflammation of a body part
the inflammation of the small intestine, accompanied by symptoms/signs like abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting/nausea, etc
which organisms are lactose fermenters? which are non-lactose fermenters?
lactose fermenters include:
escherichia coli
enterobacter aerogenes
non-lactose fermenters include:
salmonella enterica
serratia marcescens
pseudomonas fluorescens
pseudomonas aeruginosa
which organisms don’t grow on macconkey or cna agar and why?
gram-positive organisms don’t grow on macconkey, and gram-negative organisms don’t grow on cna. this is because macconkey inhibits gram-positive growth and cna inhibits gram-negative growth
a carbohydrate fermentation broth tube that is yellow indicates the presence of
acid production
what type of substance is in both a carbohydrate fermentation broth tube and differential agar media that indicates a certain condition in the media?
phenol red
what is the name of the specific substance added to carbohydrate fermentation broth tubes and which turns yellow under acidic conditions?
phenol red
what is the function of the small, inverted durham tube in the larger carbohydrate fermentation broth tube?
its used to collect gas (if produced) during fermentation