Micro Lab Final questions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk contain the enzyme _____________ that destroys certain bacteria.
protein kinase
granzyme
lysozyme
adenylate cyclase
lysozyme
Which first-line defense molecules produced by the immune system kill pathogens, and pathogens rarely become resistant to them?
AMPs
tumor necrosis factors
holoenzymes
antibodies
AMPs
Which subcategory of first-line defenses does skin belong to?
molecular barriers
physical barriers
mechanical barriers
chemical barriers
physical barriers
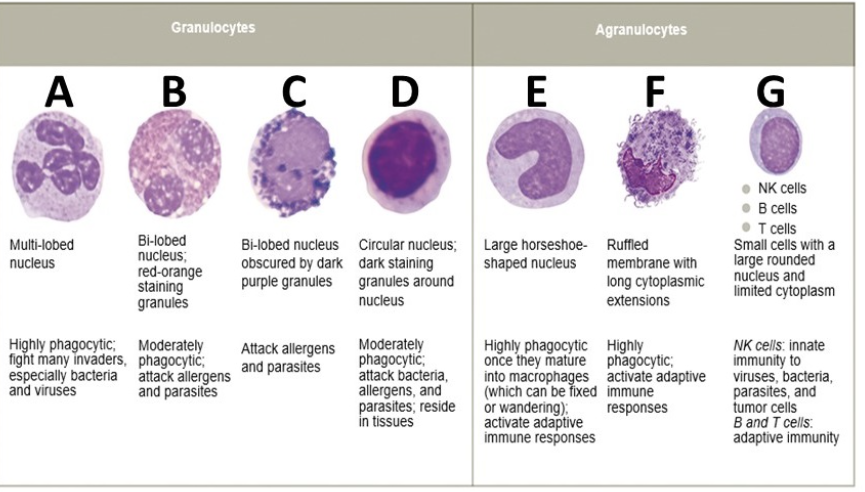
what is B
eosinophil
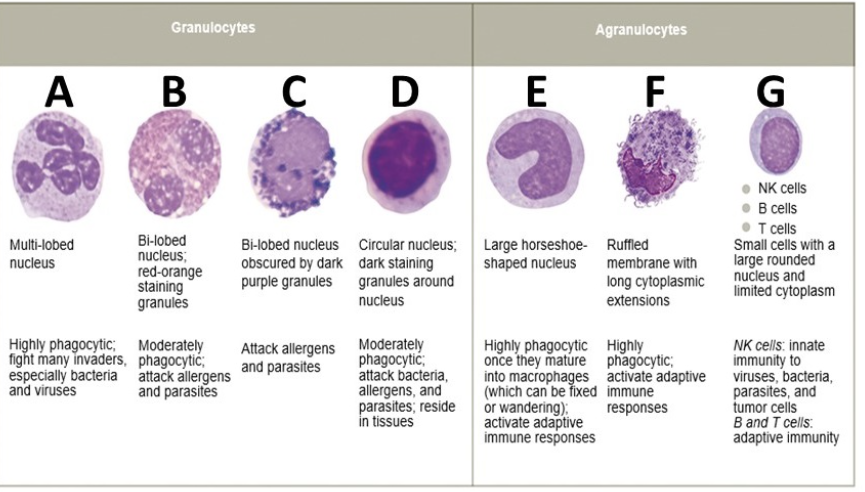
what is A
neutrophil
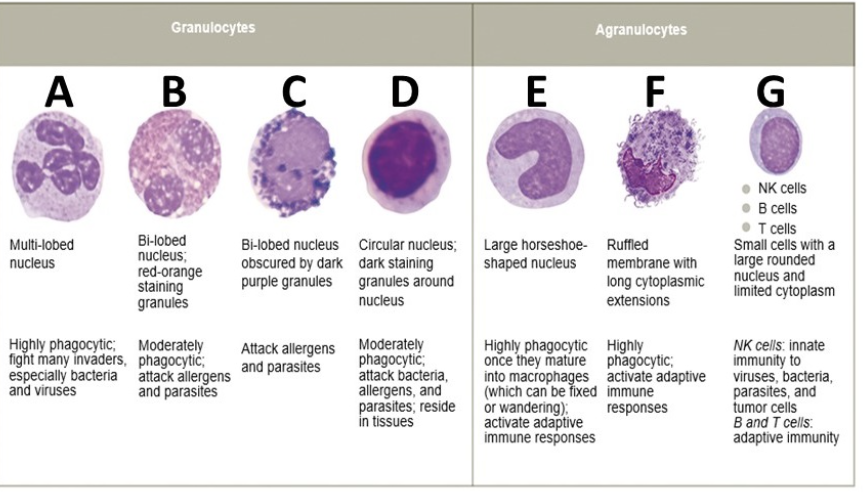
what is F
dendritic cell
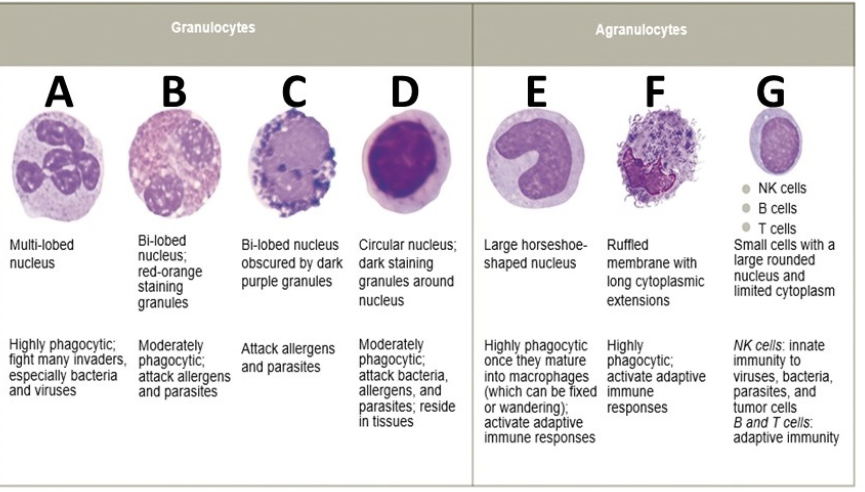
what is E
monocyte
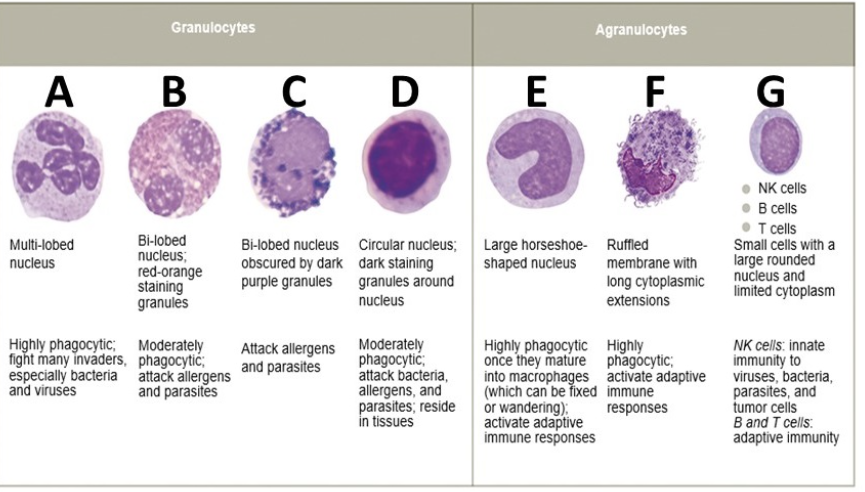
what is C
basophil
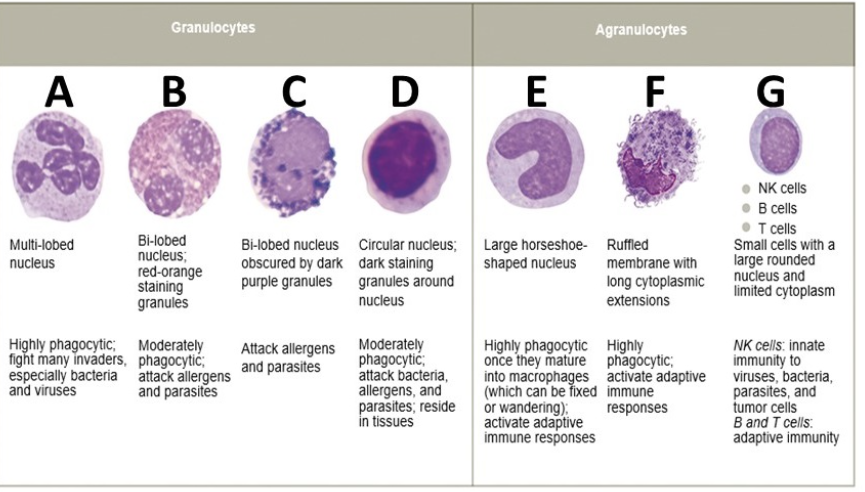
what is D
mast cell
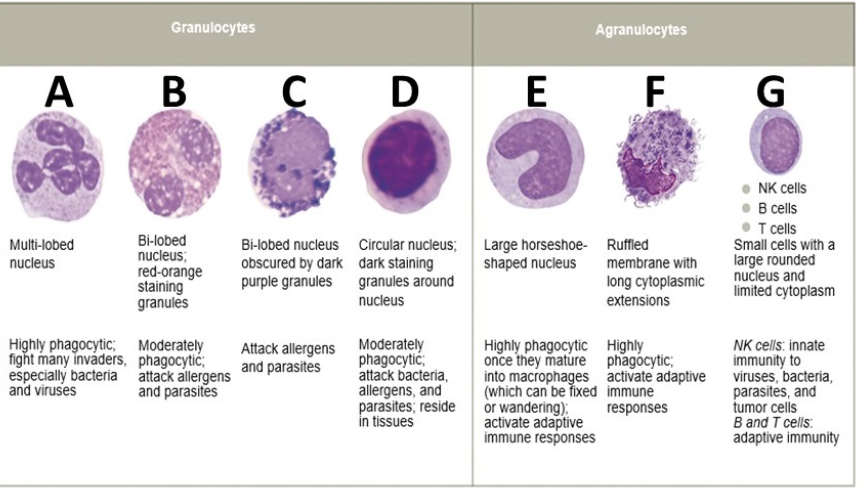
what is D
lymphocyte
Swollen ________ indicate that a foreign antigen is present, and leukocytes are rapidly multiplying to mount an immune response.
thymus tissue
lymph nodes
spleen tissue
bone marrow
lymph nodes
The thymus and bone marrow are considered _________ lymphoid tissue.
secondary
GALT
MALT
primary
primary
The majority of secondary lymphoid tissue is called ________, and includes Peyer’s patches, tonsils, and the appendix.
the spleen
MALT
bone marrow
lymph nodes
MALT
Which granulocyte when stained exhibits red-orange granules, is moderately phagocytic, and attacks allergens and parasites?
mast cells
eosinophils
basophils
neutrophils
eosinophils
Which granulocyte contains granules packed with histamine, that stain dark purple?
eosinophils
monocytes
neutrophils
basophils
basophils
Which agranulocyte has a large horseshoe-shaped nucleus, and matures into either fixed or wandering macrophages?
dendritic cells
mast cells
NK cells
monocytes
monocytes
Signaling proteins that support cell-to-cell communication and initiate and coordinate immune responses are called ___________. Examples of these signaling proteins are interleukins and interferons.
necrosis factors
pyrogens
cytokines
siderophores
cytokines
Which complement pathway has complement proteins that are directly activated by interacting with a pathogen?
traditional pathway
classical pathway
alternative pathway
lectin pathway
alternative pathway
Which of the following is NOT a hallmark sign of inflammation?
pain
redness
swelling
fever
fever
Fever-inducing agents released by certain microbes are called ___________.
adhesins
siderophores
pyrogens
lectins
pyrogens
______ cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity and ______ cells are involved in humoral immunity.
B; T
granulocyte/agranulocyte
T; B
agranulocyte/granulocyte
T;B
T cells can be classified by certain glycoproteins on their surface called clusters of differentiation (CD). T helper cells are classified as __________, and T cytotoxic are classified as __________.
CD8/CD4
CD4/ CD8
CD8/CD3
CD7/CD4
CD4/ CD8
What is the function of activated macrophages in cell-mediated immunity?
stimulates the production of IgE and IgM
enhances phagocytic activity
activates cells related to cell-mediated immunity (macrophages, Tc cells, NK cells)
recruits neutrophils and stimulates the production of antimicrobial proteins
enhances phagocytic activity
Once T or B cells are activated, they proliferate and differentiate into active immune cells and ___________ cells that protect the body from reinfection from the same pathogen.
regulatory
terminal
memory
post-immune
memory
T helper cells produce cytokines that signal B cells to produce plasma cells, and T ________ cells, that function to destroy infected cells, cancer cells, and transplanted tissues.
regulatory
necrotic
cytotoxic
stimulatory
cytotoxic
The T helper cell subclass that stimulates B cells to proliferate and differentiate is called ________.
TC
TH2
Treg
TH1
TH2
Which of the following is a function of antibodies?
increases phagocytosis
all answers are functions of antibodies
activation of complement
neutralization of antigens
all answers are functions of antibodies
Which antibody isotype can be monomeric or dimeric, and is the primary antibody found in breast milk?
IgA
IgM
IgG
IgD
IgA
Which antibody isotype can be monomeric or pentameric, and is produced early in infection?
IgE
IgM
IgG
IgA
IgM
Various mechanisms used by the host to defend against unwanted pathogens is called __________.
immunity
hygiene hypothesis
tolerance
immune theory
immunity
First-and second-line defenses are considered ___________.
cellular immunity
adaptive immunity
humoral immunity
innate immunity
innate immunity
Which of the following is not considered a part of innate immunity?
normal microbiota
phagocytes
cytotoxic T-cells
skin
cytotoxic T cells
Which of the following doesn't describe an action of first line-innate mechanical defenses?
trapping
rinsing
digesting
flushing
digesting
Which type of first-line innate defenses does stomach acid belong to?
physical barriers
chemical barriers
mechanical barriers
cellular barriers
chemical barriers
Which of the following is NOT a molecular second-line innate defense?
complement
iron-binding proteins
cytokines
lysozyme
lysozyme
Which of the following leukocytes is part of cellular second-line innate immunity?
plasma cells
T cells
B cells
neutrophils
neutrophils
Which type of cytokines interfere with viral replication in virus infected cells?
chemokines
interleukins
interferons
tumor necrosis factors
interferons
What is the innate immune function of ferritin in the blood?
binds free iron
recruits phagocytes
induces apoptosis
induces fever
binds free iron
Which of the following is not a complement pathway?
classical pathway
lectin pathway
primary pathway
alternative pathway
primary pathway
Which of the following in not an outcome of complement cascade activation?
fever
cytolysis
opsonization
inflammation
fever
What is the outcome when a MAC complex is formed in a cell?
cell proliferation
cell phagocytosis
cell lysis
cell differentiation
cell lysis
A molecule that stimulates an immune response is called __________.
an opsonin
a siderophore
an antigen
a pyrogen
an antigen
T cell and B cell receptors only recognize one type of ____________.
amino acid
complement protein
epitope
adaptogen
epitope
The cellular and humoral responses proceed through four stages of activation. Put the following stages in the order that they occur:
A) Antigen elimination and memory
B) Antigen presentation
C) Lymphocyte differentiation and proliferation
D) Lymphocyte activation
B,D,C,A