ATI Engage Fubdamentals Tissue integrity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:47 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Skin
largest organ system in the body accounting for 15% of total body weight
2
New cards
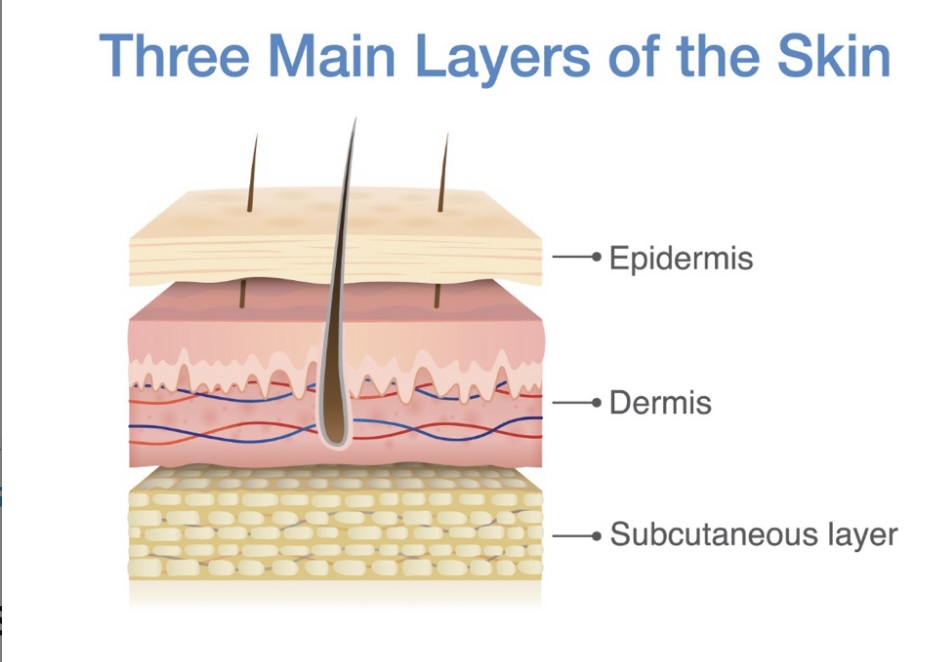
The skin contains what 3 layers?
\-epidermis
\-dermis
\-subcutaneous layer of adipose tissue
\-dermis
\-subcutaneous layer of adipose tissue
3
New cards
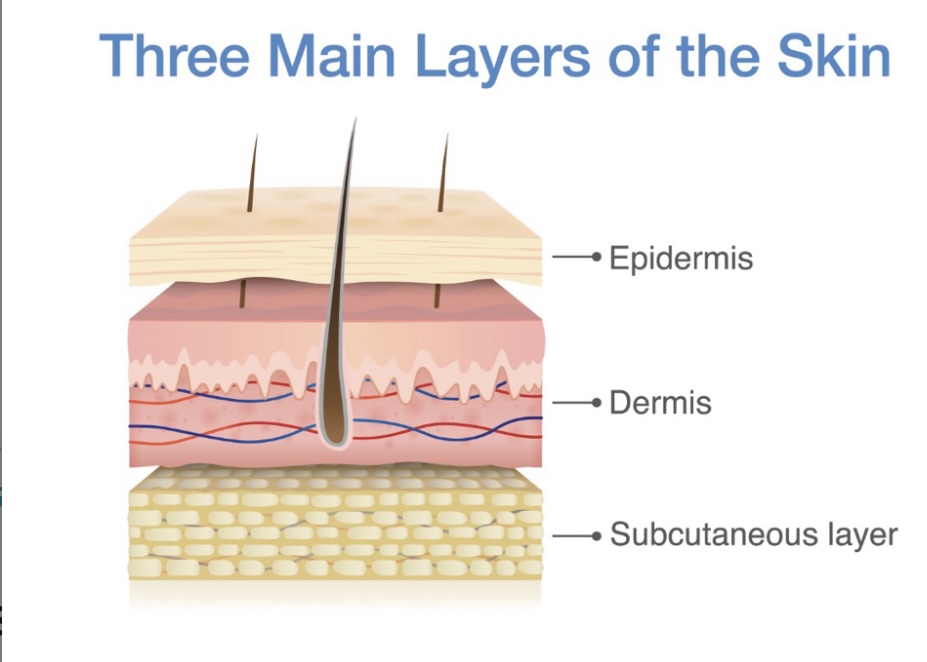
Epidermis
outermost layer of the skin, made of squamous epithelial cells, which provide a barrier against the external environment
4
New cards
kartinocytes
cells formed in the basal layer of the skin that function to protect the skin from external environment
5
New cards
Melanocytes
cells that are produced in the epidermis and produce melanin
6
New cards
Melanin
a pigment that determines the color fo the hair & skin
7
New cards
Merkel cells
receptor cells in the epidermis that are specialized for detection of light touch
8
New cards
Langerhans cells
cells found in the epidermis that play a role in cutaneous immune system reactions
9
New cards
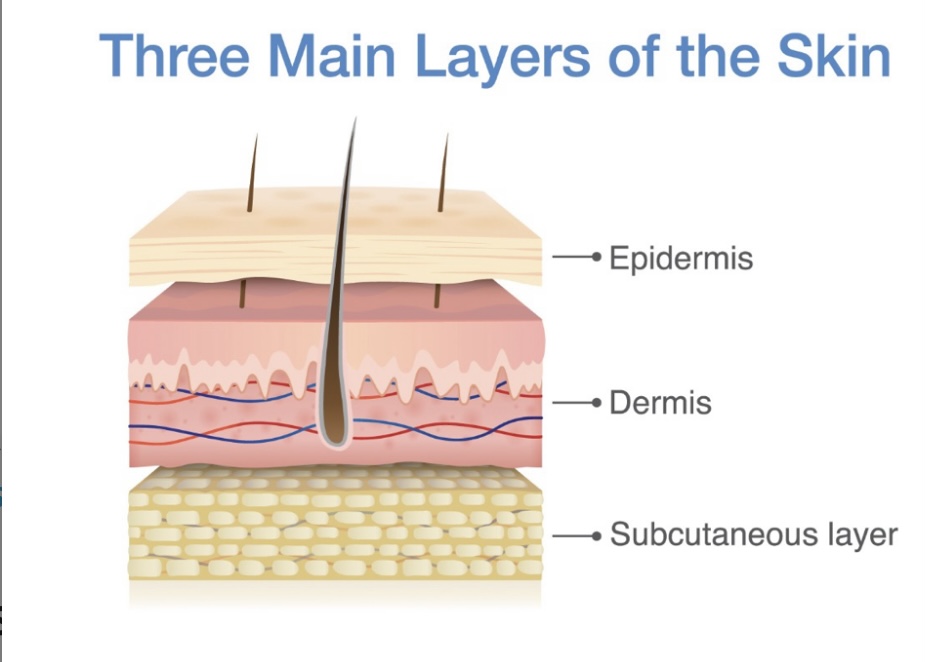
Dermis
Layer under the epidermis that is composed of connectiove tissue & provides strength & flexibility of the skin
10
New cards
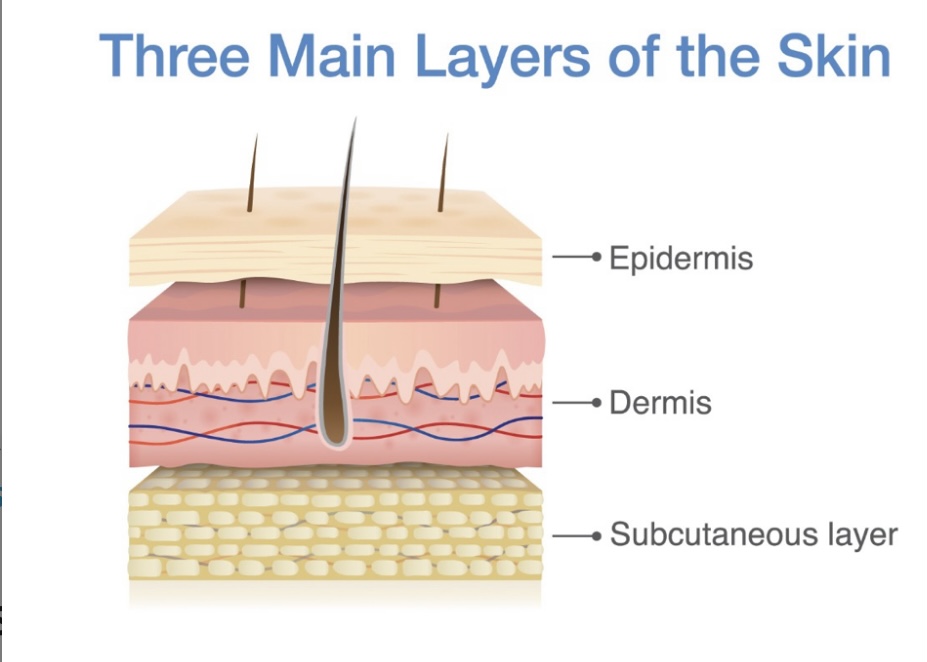
Subcutaneous tissue
found under the epidermis & dermis mostly composed of adipose tissue insulates the body, absorbs shock, and pads internal organs & structures
11
New cards
Maceration
an irritation of the epidermis caused by moisture
12
New cards
Dermatitis
red skin irritation that develops when the skin is exposed to irritants such as feces, urine, stoma effluent, & wound exudates (irritant dermatitis)
13
New cards
Skin tears
loss of the top skin layer caused by mechanical forces. Severity of skin tear defined bu the depth of the skin layer loss
14
New cards
Besides age what other conditions predispose clients to alterations in skin integrity?
Spina bifidia, cerebral palsy, chronic disease such as; liver failure, kidney disease, & cancer
15
New cards
Skin fragility
at-risk vulnerable skin
16
New cards
Pressure injuries
localized damage to the skin &/or the soft underlying tissue, which can be caused by prolonged contact with a firm surface that interferes with circulation to that area
17
New cards
Cellulitis
an infection of the superficial layers of skin
18
New cards
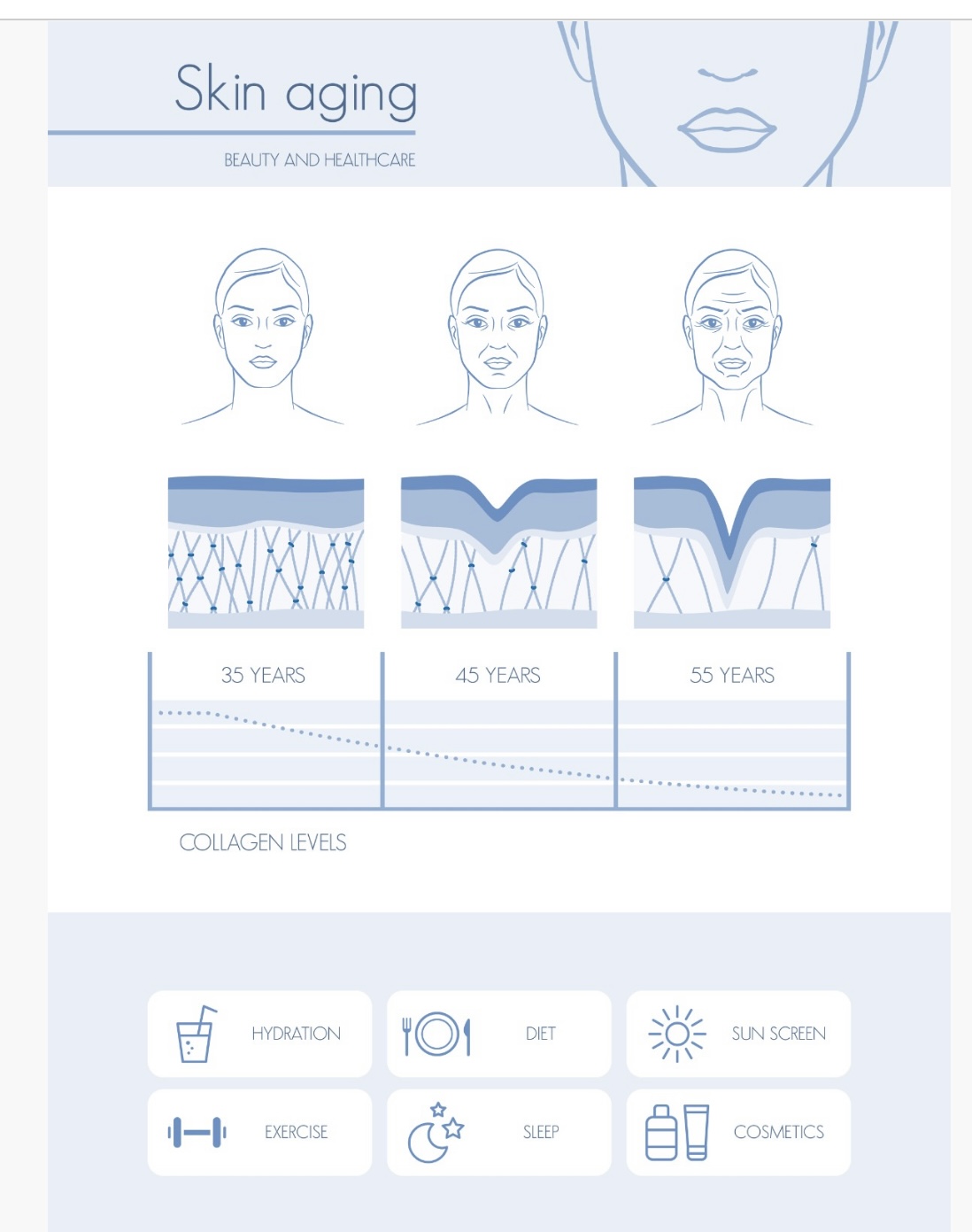
Skin aging diagram
\-hydration
\-exercise
\-diet
\-sleep
\-sun screen
\-cosmetics
\-exercise
\-diet
\-sleep
\-sun screen
\-cosmetics
19
New cards
Neonates and children skin changes & contributing factors
\-immature skin
\-prolonged duration of pressure
\-moisture/maceration
\-poor perfusion
\-prolonged duration of pressure
\-moisture/maceration
\-poor perfusion
20
New cards
Neonates & children skin problems
\-diaper rash
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
21
New cards
Older adults skin changes and contributing factors
Thinning for he skin resulting in decreased:
\-elasticity
\-subcutaneous tissue
\-blood supply
\-hydration
\-elasticity
\-subcutaneous tissue
\-blood supply
\-hydration
22
New cards
Older adults skin problems
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
\-itchy, dry, flaky skin
\-skin infections
\-pressure injuries
\-itchy, dry, flaky skin
\-skin infections
23
New cards
Clients who have decreased mobility/paralysis (e.g., spina bifida) skin changes & contributing factors
\-reduced blood circulation
\-alterations in thermoregulation
\-incontinence
\-loss of collagen
\-muscles atrophy
\-impaired sensation
\-alterations in thermoregulation
\-incontinence
\-loss of collagen
\-muscles atrophy
\-impaired sensation
24
New cards
Clients who have decreased mobility/paralysis skin issues
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
\-skin infection
\-incontinence-associated dermatitis
\-pressure injuries
\-skin infection
\-incontinence-associated dermatitis
25
New cards
Clients who are obese skin changes & contributing factors
\-decreased moisture
\-dry skin
\-maceration
\-elevated skin temperature
\-decreased blood & lymphatic flow
\-dry skin
\-maceration
\-elevated skin temperature
\-decreased blood & lymphatic flow
26
New cards
Clients who are obese skin issues
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
\-diabetic ulcers
\-0moisture lesions
\-skin-fold rashes
\-pressure injuries
\-diabetic ulcers
\-0moisture lesions
\-skin-fold rashes
27
New cards
Clients who have cancer skin changes and contributing factors
Radiation resulting in:
Inflammation
\-skin surface damage
\-decreased blood supply
Inflammation
\-skin surface damage
\-decreased blood supply
28
New cards
Clients who have skin cancer skin issues
\-pressure injuries
\-delayed wound healing
\-skin infections
\-radiation induced dermatitis
\-delayed wound healing
\-skin infections
\-radiation induced dermatitis
29
New cards
Clients who have chronic illnesses & other conditions skin changes and contributing factors
Skin changes due to:
\-hepatic diseases
\-renal diseases
\-cardiovascular diseases
\-malnutrition
\-stomas
\-psychological issues
\-hepatic diseases
\-renal diseases
\-cardiovascular diseases
\-malnutrition
\-stomas
\-psychological issues
30
New cards
Clients who have chronic illnesses and other conditions skin issues
\-skin tears
\-pressure injuries
\-infections
\-moisture associated lesions
\-pressure injuries
\-infections
\-moisture associated lesions
31
New cards
How can nurses decrease the risks of client’s developing skin breakdown
\-regular skin assessments
\-observation of environmental factors
\-diligent implementation of prevention measures
\-observation of environmental factors
\-diligent implementation of prevention measures
32
New cards
Erythema
Redness of the skin due to dilation of the blood vessels
33
New cards
Blanchanble erythema
An area of reddened skin that temporarily turns white or pale when light pressure is applied, then reddens when pressure is relieved
34
New cards
Nonblanchable erythema
Redness of the skin that does not go away when pressure is applied indicating striuctural damage has occurred to the small vessels supplying blood to the underlying skin and tissues
35
New cards
Wound
A disruption in the normal composition and performance of the skin and its underlying structures
36
New cards
Intentional wounds
Created during a surgical procedure
37
New cards
Unintentional wounds
Develop as a result of a traumatic injury, such as burn, punctures, or gunshot wounds
38
New cards
Lacerations
Any tearing of the skin, usually caused by blunt/sharp objects
39
New cards
Clean & clean contaminated wounds
Have minimal bacterial loads & are closed at the completion of the procedure
40
New cards
Contaminated & dirty wounds
Have higher bacterial loads that’s may interfere with healing, these wounds may be left open after the procedure and recquire long-term wound management for healing
41
New cards
Surgical wounds should have?
Intact, well-approximated edges
42
New cards
Would healing colors
\-incision red on days 1-4 (day 4 epithelial closure)
\-bright pink days 5-14 (edema progressively decreases by day 5) (days 9-14 sutures/staples removed usually)
\-pale pink 15days - 1year
\-scar tissue white/silver on fair skin
\-scar tissue early pigmented skin pale pink to darker than normal skin tone
\-bright pink days 5-14 (edema progressively decreases by day 5) (days 9-14 sutures/staples removed usually)
\-pale pink 15days - 1year
\-scar tissue white/silver on fair skin
\-scar tissue early pigmented skin pale pink to darker than normal skin tone
43
New cards
Exudate
Fluid secreted by the body during th inflammatory stage of healing and is made of plasma
44
New cards
Moisture-associated skin damage (MASD)
Form of dermatitis; a skin irritation that forms when the skin is exposed to the irritants like fecesm urine, stoma content, and wound exudates
45
New cards
Chronic wounds develop to which conditions?
\-chronic venous insufficiency
\-peripheral artery disease
\-diabetes mellitus
\-older clients/clients who smoke
\-malnourishment
\-immunosuppressed
\-immobilized
\-would infection
\-peripheral artery disease
\-diabetes mellitus
\-older clients/clients who smoke
\-malnourishment
\-immunosuppressed
\-immobilized
\-would infection
46
New cards
Venous ulcer
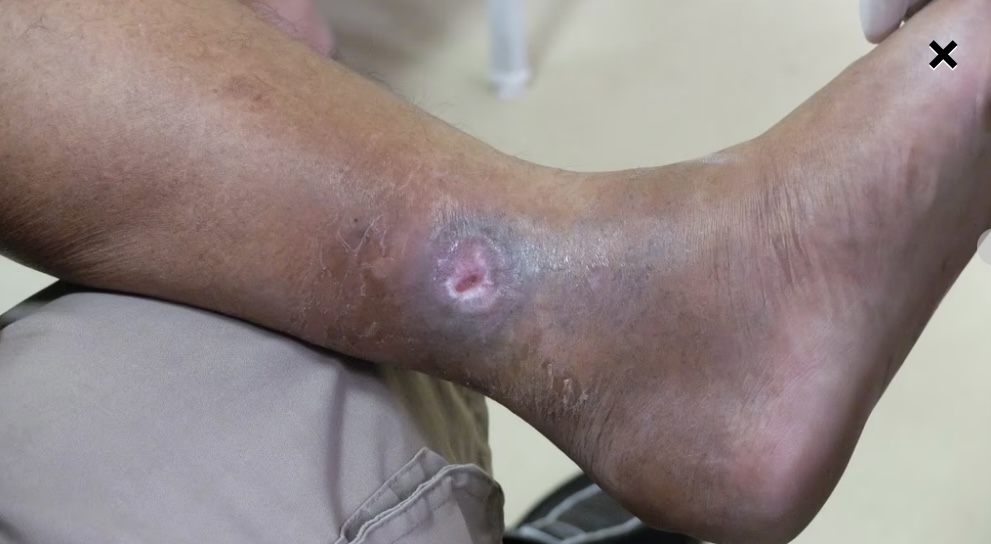
47
New cards
Neuropathic ulcer
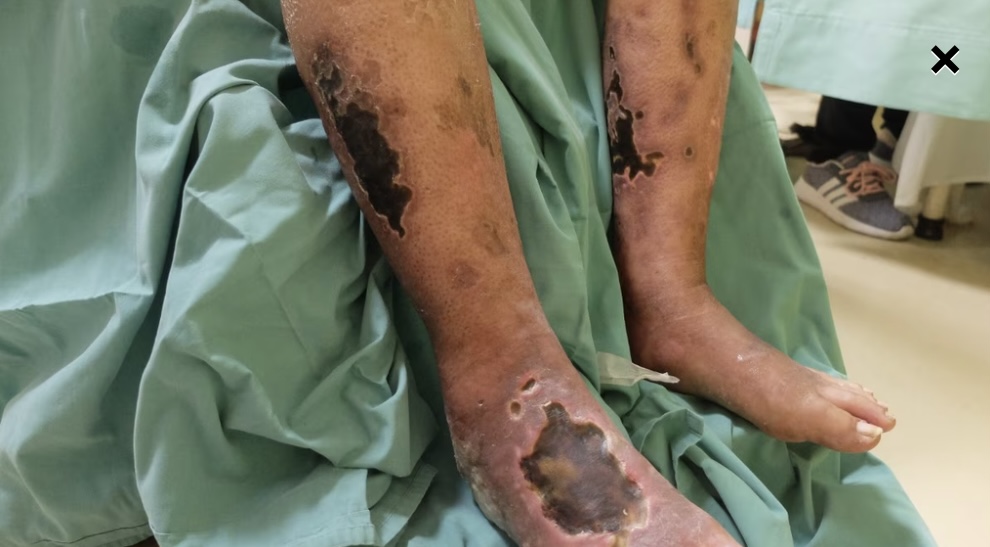
48
New cards
Serous
thin, watery wound drainage
49
New cards
Serosanguineous
thin, watery wound drainage mixed with blood
50
New cards
Sanguineous
bloody wound drainage
51
New cards
Purluent
green/yellow wound drainage
52
New cards
Nurses most commonly use the following methods to measure wound size:
\-tracing the wound circumference & calculating the wound surface area using a see-through film
\-measuring the length and width of the wound using a ruler
\-measuring the length and width of the wound using a ruler
53
New cards
Measurement of wound depth should be done with?
A sterile premoistened cotton tip applicator
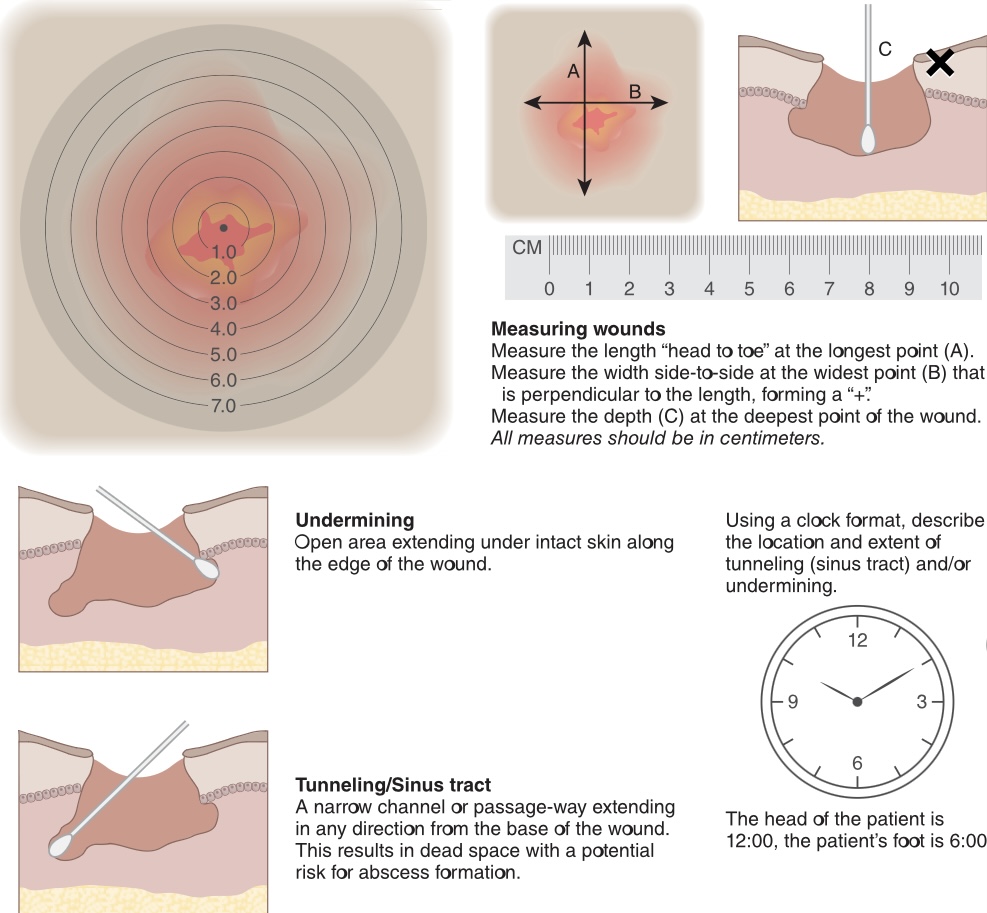
54
New cards
Tunneling
a narrow channel or passage way extending in any direction from the base of the wound
55
New cards
Pressure injuries develop due to?
Prolonged pressure over an area of skin/ due to a combination of pressure and shearing
56
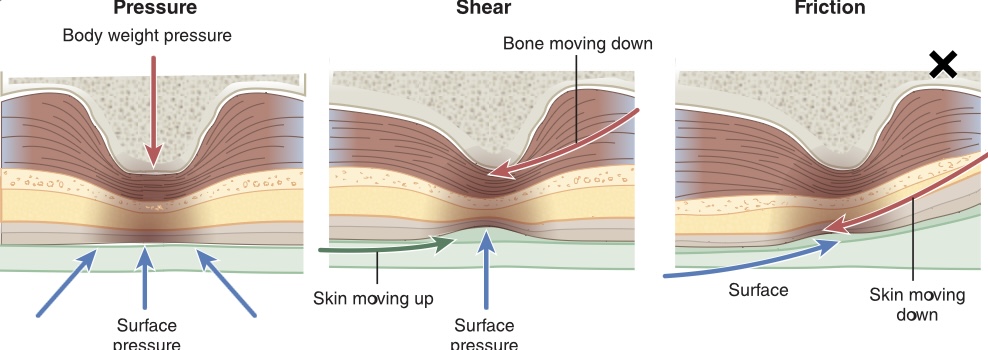
New cards
Shearing
a force parallel to the surface of the skin
57
New cards
What are the risk factors that predispose clients to pressure injuries?
\-immobility
\-malnutrition
\-reduced perfusion
\-altered sensation
\-decreased LOC
\-exposure to moisture
\-tearing
\-cuts
\-bruises
\-friction
\-malnutrition
\-reduced perfusion
\-altered sensation
\-decreased LOC
\-exposure to moisture
\-tearing
\-cuts
\-bruises
\-friction
58
New cards
Malnutrition
imbalance in a client’s intake, which can include deficiencies or excesses in nutrients, vitamins, or calories
59
New cards
Friction
the force created when two objects rub together
60
New cards
Each year in the United States approximately how many people due from complications of pressure injuries?
60,000
61
New cards
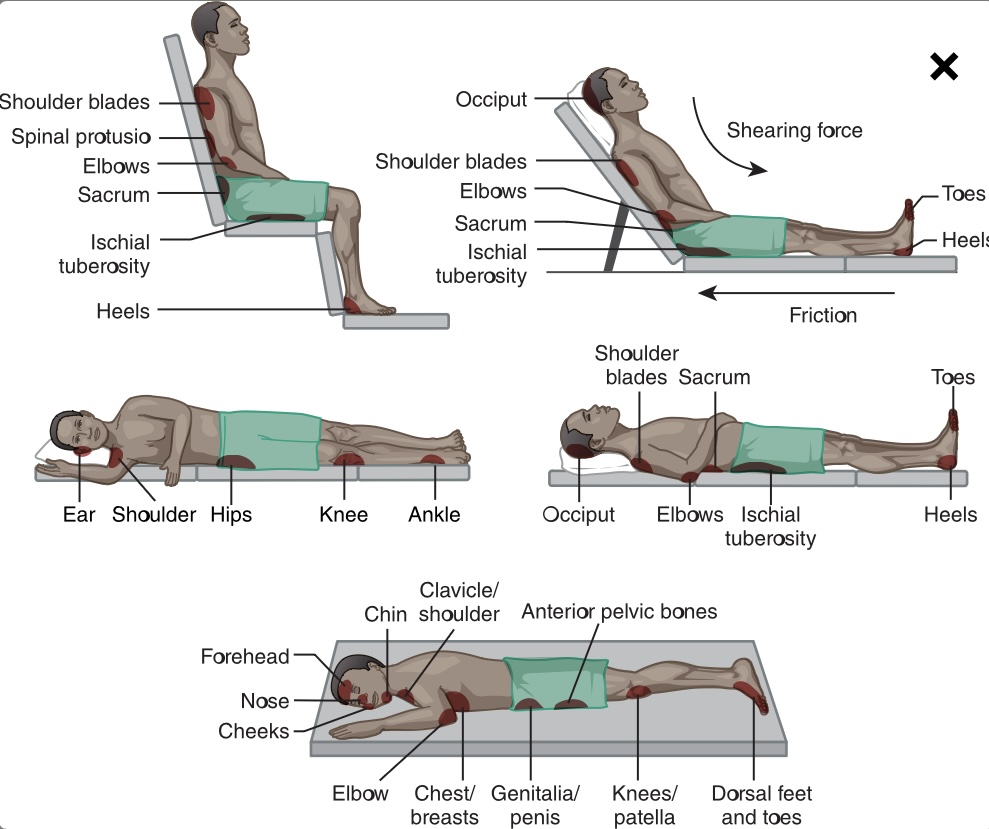
What areas are the moist susceptible to pressure injury formation?
Bony prominences
\-heels, toes, sacrum, hips, elbows, shoulders, and back of the head
\-heels, toes, sacrum, hips, elbows, shoulders, and back of the head
62
New cards
Risk assessments fort pressure injury development includes:
\-immobility
\-malnutrition
\-perfusion
\-sensory loss
\-malnutrition
\-perfusion
\-sensory loss
63
New cards
Immobility
one of the greatest factors contributing to the development of pressure injuries
64
New cards
malnutrition cause of pressure injury
malnutrition and low albumin levels place clients at a greater risk for developing pressure injuries
\-assessment of clients dietary intake and capacity it’s to maintain weight is one of the strongest nutritional measures for tissue integrity risk
\-assessment of clients dietary intake and capacity it’s to maintain weight is one of the strongest nutritional measures for tissue integrity risk
65
New cards
Hypoperfusion
inadequate supply of blood circulation, which results in low oxygen level sin tissues
66
New cards
Sensory loss
in clients with certain neurological conditions such as dementia can have altered sensation to pain putting them at risk for pressure injuries
67
New cards
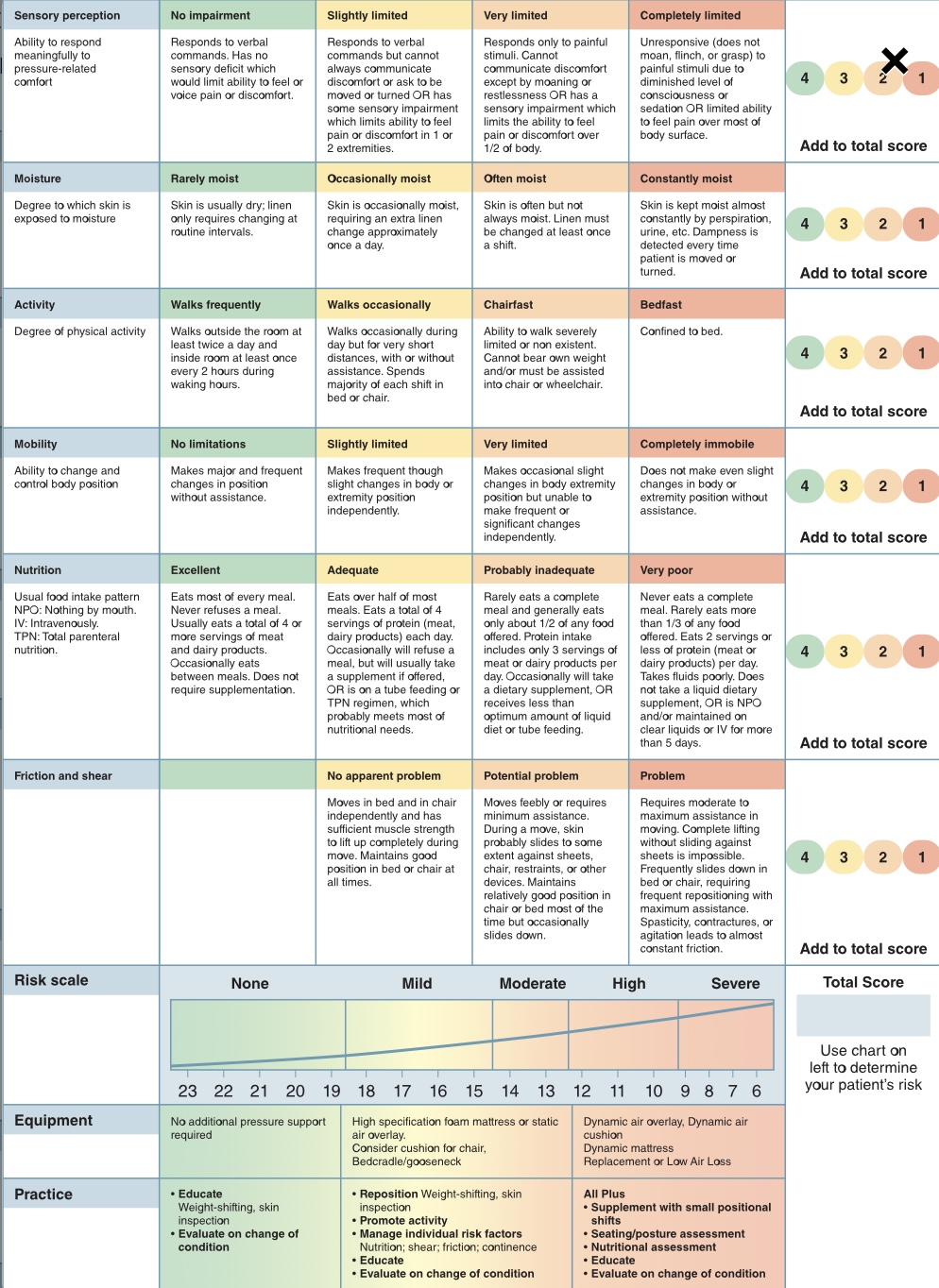
Braden scale
risk assessment tool for alterations in skin integrity
Categorized into 6 categories:
\-sensory perception
\-moisture
\-activity
\-mobility
\-nutrition
\-friction and shear
Categorized into 6 categories:
\-sensory perception
\-moisture
\-activity
\-mobility
\-nutrition
\-friction and shear
68
New cards
what is the lowest (worst outcome) score that can be received on a Braden scale?
6
69
New cards
What is the highest (best outcome) score that can be received on a Braden scale?
23
70
New cards
Undermining
an open area extending under the skin along the edge of the wound
71
New cards
Benchmarking
comparing results and outcomes to other sources of similarly retrieved data
72
New cards
Stage 1 pressure injury
\-skin is intact
\-non-blanchable edema present
\-non-blanchable edema present
73
New cards
Stage 2 pressure injury
\-partial-thickness skin loss
\-pink/red viable tissue in the wound bed
\-may also present as a ruptured serum-flies blister
\-pink/red viable tissue in the wound bed
\-may also present as a ruptured serum-flies blister
74
New cards
Stage 3 pressure injury
\-full-thickness skin loss with visible adipose tissue
\-wound edges may be rolled
\-granulation/new skin tissue may form on the surface of the wound
\
\-wound edges may be rolled
\-granulation/new skin tissue may form on the surface of the wound
\
75
New cards
Granulation tissue
new skin that forms on the surface of the wound
76
New cards
stage 4 pressure injury
\-full thickness skin and tissue loss
\-fascia, muscles, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and/or bone are visible
\-edges are rolled and undermining and tunneling may be present
\-dead tissue may also be seen
\-fascia, muscles, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and/or bone are visible
\-edges are rolled and undermining and tunneling may be present
\-dead tissue may also be seen
77
New cards
Unstageable pressure injury
\-obscured full thickness skin and tissue loss
\-covered with either slough, or eschar
\-covered with either slough, or eschar
78
New cards
Slough
yellow, stringy tissue found in the base of the wound
79
New cards
Eschar
hard nonviable black/brown tissue found in the wound bed
80
New cards
Deep tissue pressure injury
persistent nonblanchable tissue injury of the skin appearing deep red, maroon, or purple color
81
New cards
Device related pressure injury
occur as a result of prolonged pressure from devices worn by the client
\-MDRPI (oxygen masks, oxygen tubing, urinary catheters, cervical collars, and compression stockings)
\-MDRPI (oxygen masks, oxygen tubing, urinary catheters, cervical collars, and compression stockings)
82
New cards
Mucosal membrane pressure injury
Mucosal tissues: lining of respiratory tract, GI tract, genitourinary tract
Injury to a mucous membrane caused by the pressure related to the insertion or placement of a foreign device
Injury to a mucous membrane caused by the pressure related to the insertion or placement of a foreign device
83
New cards
Assessing pressure injuries in clients who have darker-pigmented skin
\-skin temp and moisture in the wounds may be the first indicator of a pressure injury
\-edema, hardened skin, localized pain
\-nurse should apply light pressure ands then observe for an area that is darker than the surrounding skin
\-skin can also appear taut, shiny, or indurated
\-edema, hardened skin, localized pain
\-nurse should apply light pressure ands then observe for an area that is darker than the surrounding skin
\-skin can also appear taut, shiny, or indurated
84
New cards
When documenting pressure injuries the nurse should include:
\-location
\-stage
\-size
\-description of the tissue
\-color of the wound bed
\-condition of surrounding tissue
\-appearance of wound edges
\-presence of undermining and tunneling
\-any foul odor present
\-wound drainage
\-pain at site
\-stage
\-size
\-description of the tissue
\-color of the wound bed
\-condition of surrounding tissue
\-appearance of wound edges
\-presence of undermining and tunneling
\-any foul odor present
\-wound drainage
\-pain at site
85
New cards
Debridement
process of surgically removing dead tissue and other debris (biofilm) that can cause infection
86
New cards
Wound irrigation
removes surface materials and decreases bacteria levels in the wound
\-most often 0.9% sodium chloride solution is used to irrigate wounds
\-most often 0.9% sodium chloride solution is used to irrigate wounds
87
New cards
Biological debridement
various enzymatic agents such as collagenase , papain (papaya extract) and bromelain (pineapple extract) can be applied to the wounds to clear dead tissue and debris
88
New cards
larvae therapy
larvae of green bottle fly and the Australian sheep blowfly secrete an enzyme that liquifies necrotic tissue
89
New cards
Sterile dressings
applied after surgery and are usually kept on the incision site for 24-48 hours
\-after 48 hrs wounds are managed using clean technique
\-after 48 hrs wounds are managed using clean technique
90
New cards
Open dressings
gauze bandages
\-after being moistened with 0.9% sodium chloride gauze dressings are used to pack wounds to assist with the debridement process
\-also called wet-to-dry dressing
\-after being moistened with 0.9% sodium chloride gauze dressings are used to pack wounds to assist with the debridement process
\-also called wet-to-dry dressing
91
New cards
semi-open dressings
\-3 layers
\-bottom layers comprises a layer of knit gauze infused with therapeutic ointments
\-middle layer contains padding and absorbent gauze followed by a final layer of adhesive
\-do not control drainage well and place client at risk for poor wound healing
\-bottom layers comprises a layer of knit gauze infused with therapeutic ointments
\-middle layer contains padding and absorbent gauze followed by a final layer of adhesive
\-do not control drainage well and place client at risk for poor wound healing
92
New cards
Films
advantages: include their ability to allow moisture to evaporate while still maintains a moist wound bed and the ability to woo oxygen to enter the wound wile decreasing the risk of micro-organism entrance into the wound
\-allows providers to visualize wound without removing dressing
\-not dressing of choice for wounds it’s significant exudate
\-allows providers to visualize wound without removing dressing
\-not dressing of choice for wounds it’s significant exudate
93
New cards
Hydrocolloid dressings
\-used for small abrasions, superficial burns, pressure injuries, and postoperative wounds
\-gel-like dressings occlude the wound maintain moist wound bed, bacteriostatic properties, and stimulate growth of granulation tissue
\-comfortable and produce less maceration
Disadvantages: potential fro contact dermatitis, could smelling yellow gelatinous film that develops as bacteria are trapped on the underside of the dressing
\-gel-like dressings occlude the wound maintain moist wound bed, bacteriostatic properties, and stimulate growth of granulation tissue
\-comfortable and produce less maceration
Disadvantages: potential fro contact dermatitis, could smelling yellow gelatinous film that develops as bacteria are trapped on the underside of the dressing
94
New cards
Alginate dressings
recommended for moderate to highly exudative wounds
\-provide hemostasis, high absorption abilities, can remain for several days, variety of forms (ribbon, pads, and beads)
Disadvantage: secondary dressing is needed to cover the alginate increasing cost
\-provide hemostasis, high absorption abilities, can remain for several days, variety of forms (ribbon, pads, and beads)
Disadvantage: secondary dressing is needed to cover the alginate increasing cost
95
New cards
Hydrofiber dressings
\-used for moderate and highly exudative wounds
\-provide high absorbency and can stay in the wound for several days
\-draw less fluid from the wounds edges resulting gin less maceration
\-provide high absorbency and can stay in the wound for several days
\-draw less fluid from the wounds edges resulting gin less maceration
96
New cards
Foams
used in wounds with mild to moderate exudate
\-requires more frequent dressing changes
\-may produce malodorous discharge
\-requires more frequent dressing changes
\-may produce malodorous discharge
97
New cards
Polymeric membranes
used in mildly exudative wounds
\-stimulate the growth of new epithelium and do not stick to the wound bed, resulting in less trauma to the new granulation tissue
\-stimulate the growth of new epithelium and do not stick to the wound bed, resulting in less trauma to the new granulation tissue
98
New cards
Hydrogels
Used in dry wounds for debridement of necrotized tissue and eschar
\-they can provide moisture to or draw moisture away from the wound depending on the needs
\-have soothing effect and cause little trauma
\-many require frequent changes
\-they can provide moisture to or draw moisture away from the wound depending on the needs
\-have soothing effect and cause little trauma
\-many require frequent changes
99
New cards
Staples
\-healing is faster with a stapled wound (7 to 14 days)
\-common complications are scarring and difficulty with removal
\-common complications are scarring and difficulty with removal
100
New cards
Sutures
made of synthetic materials such as nylon/polyester, or natural fibers such as silk, linen, or dried animal intestines
\-both synthetic and natural sutures can be absorbable/nonabsorbable
\
\-both synthetic and natural sutures can be absorbable/nonabsorbable
\