PSTAT 160A ichiba
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Given a random variable X, define the moment generating function
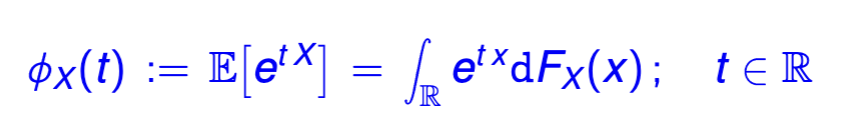
if X and Y are independent, how does the MGFX+Y(•) simplify?
MGFX(•) • MGFY(•)
similarly E(et(x+y)) = E(etx) • E(ety)
obtain the mgf by differentiating

what is the power/taylor series defined as?
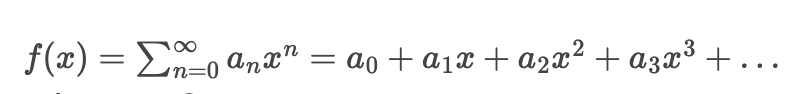
define the probability generating function
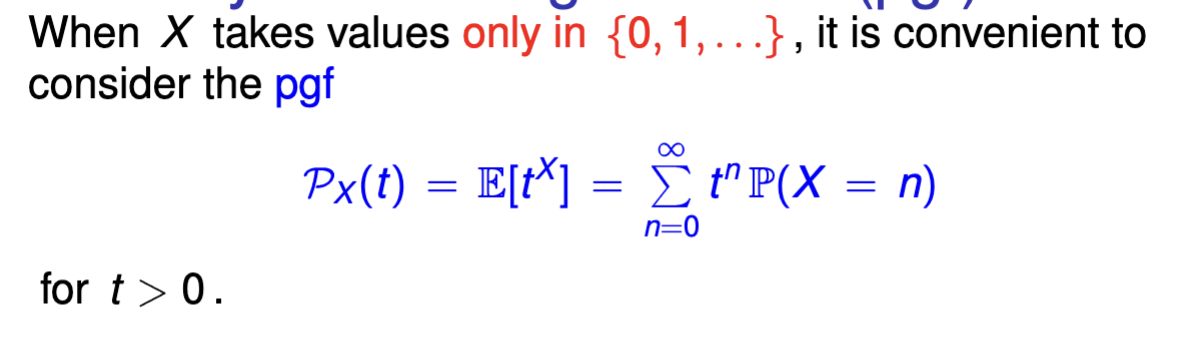
what is the formula for turning the PGF into a probability formula?
This process proves that the PGF and the probability distribution contain the exact same information. If PX(t) is identical to PY(t), then decoding them will produce the exact same set of probabilities. Therefore, X and Y must be identically distributed.
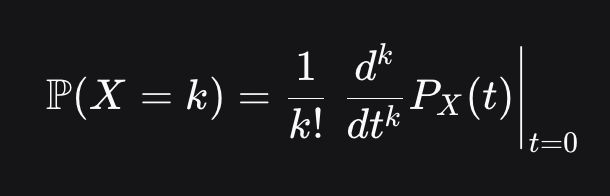
what is the reflection principle

when is a random walk transient?
when P(Sn = a infiinitely often in n) = 0
might visit “a” a few times but eventually it will leave and never return
returns to “a” a finite number of times
when is a random walk recurrent?
when P(Sn = a infinitely often in n) = 1
guaranteed to return to “a” over and over again forever
what is the formula for a symmetric random walk and the properties of symmetric random walk?
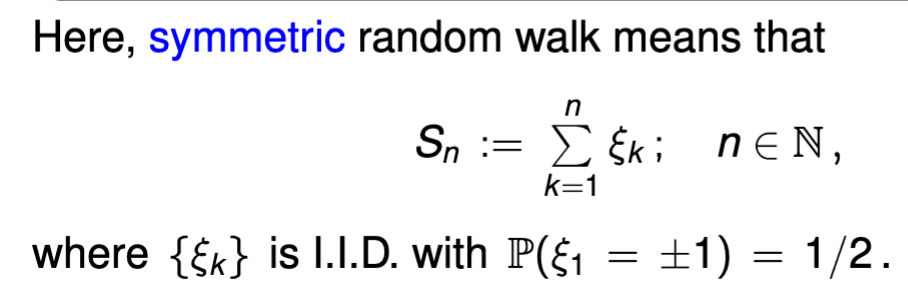
what is τ?
τ is a stopping time, a random time where the random walk decides to stop at time n and depends only on the info up to time n and not the future .
when does the reflection decide to reflect in a random sample walk?
at time τ
where does the sample walk decide to reflect?
at Mn = maxSl (the “y” value where the reflection starts and reflects over)
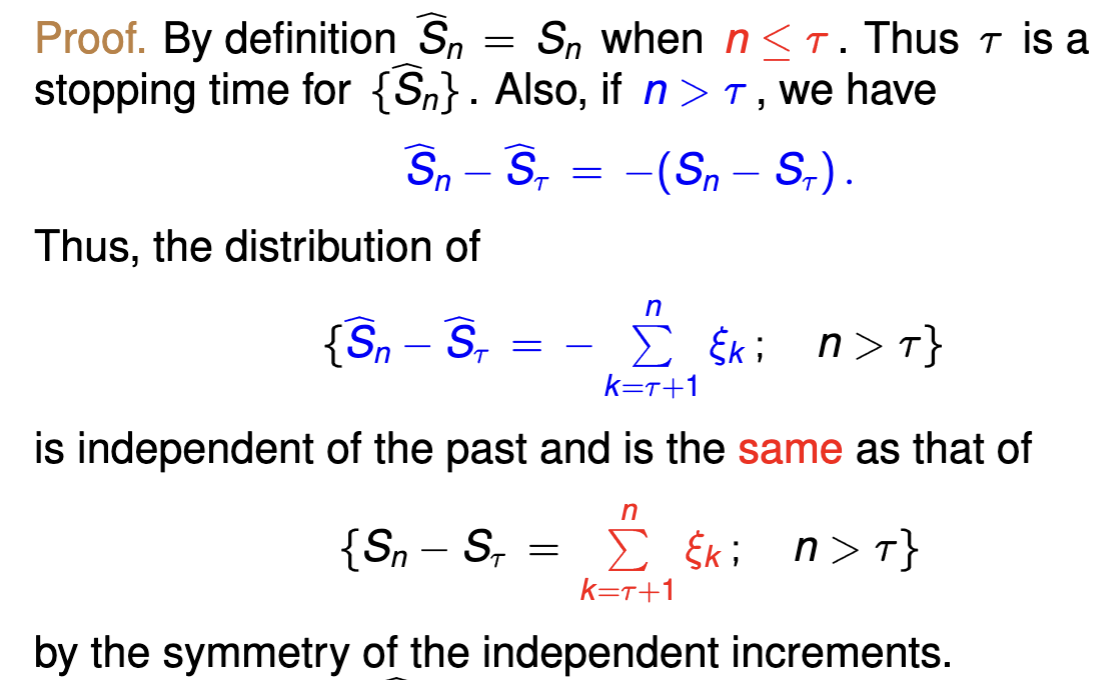
write the proof that states {^Sn} is the symmetric random walk:
what is the central limit theorem?
No matter what distribution you start with, if you take the average of enough independent samples, it will look like a normal distribution.
