A&P II- Unit 4
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Endocine & Exocrine System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Describe endocrine Glands
secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
Endocrine glands are apart of?
Both the endocrine system and other bodily systems
Describe exocrine Glands
Secretes enzymes directly into organs via ducts, bypass the bloodstream
Mammary Glands exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine
What hormones/secretions do the mammary glands have?
Prolactin
Mammary glands function
Stimulates milk to the body production
Sudoriferous glands exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine
What hormones/secretions do the sudoriferous glands have?
Sweat
Sudorifeous glands function
Secrete sweat to cool the body and eliminate waste
Sebaceous glands exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine
What hormones/secretions do the sebaceous glands have?
Secrete oil (sebum)
Sebaceous glands function?
Secrete oil (sebum) into hair follicles to lubricate skin
Salivary glands exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine
What hormones/secretions do the salivary have?
Saliva
Salivary glands function?
Produce saliva...digestive lubricant and helps to digest carbohydrates
What are the 6 individual saliva glands?
Parotid gland (x2)
Submandibular gland (x2)
Sublingual gland (x2)
Pancreas exocrine or endocrine?
Both endocrine & exocrine
What hormones/secretions does the pancreas have?
Insulin
glucagon
enzymes
What does the pancreas consist of?
-Head
-Body
-Tail
-Large central pancreatic duct leading to the small intestine
Pancreas exocrine function?
the production of pancreatic enzymes which aid in digestion
What percentage of the pancreas is exocrine?
~98%
What percentage of the pancreas is endocrine?
~2%
Pancreas endocrine function?
Regulates blood sugar levels
What are Islets of Langerhans?
Specialized cells throughout that make insulin
Liver exocrine or endocrine?
Exocrine
What hormones/secretions does the liver have?
Bile
Liver function?
Produce bile which emulsifies lipids from food ingested (breakdown fats)
Pituitary gland exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions does the pituitary gland have?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Melanocyte stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Antidiuretic hormone
Oxytocin
Prolactin
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
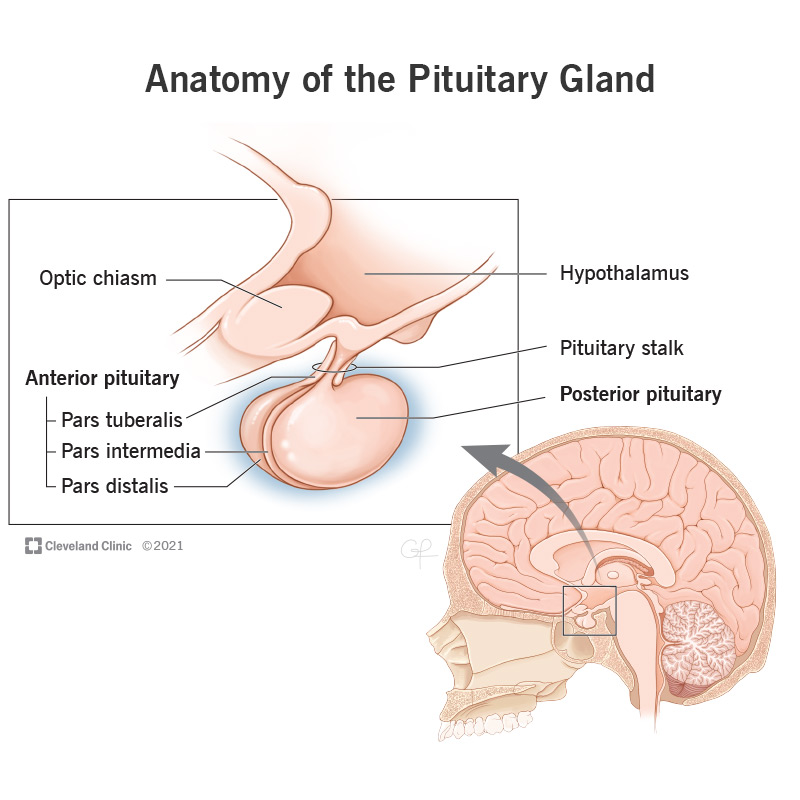
Pituitary gland function?
Controls all other endocrine glands of body
What is another name for the pituitary gland?
The master gland
Where is the pituitary gland located?
In the center of the skull beneath the brain
What does the pituitary gland consist of?
-Anterior lobe
-Posterior lobe
-Infundibulum (Stalk)
Pineal gland exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions does the pineal gland have?
Melatonin
Pineal gland function?
Small pea-sized gland that controls sleep cycles
Where is the pineal gland located?
Centrally located within the cranium, posterior to pituitary gland
Thyroid gland exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions do the thyroid gland have?
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Calcitonin
Thyroid gland function?
Promotes mental & physical development and maintains metabolism
Where is the Thyroid gland?
Located below the thyroid cartilage in the lower neck, about level of C5
Parathyroid glands exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions do the parathyroid gland have?
Parathyroid hormone
How many parathyroid glands do we have & where are they located?
4 small glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid
Parathyroid glands function?
Regulate calcium levels in blood
Adrenal (suprarenal) glands exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions do the adrenal glands have?
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
Corticosteroids
Adrenal (suprarenal) glands function?
Regulates vital signs
Regulates metabolism of proteins, glucose, lipids & electrolytes
Where are Adrenal glands located?
Located on the superior surface of each kidney (T11-T12)
What do the adrenal glands consist of?
The outer cortex and inner medulla
Gonads (testes and ovaries) exocrine or endocrine?
Endocrine
What hormones/secretions do the testes have?
Testosterone
What hormones/secretions do the ovaries have?
Estrogen
Progesterone
Hormones are?
The secretions of endocrine glands serve to activate certain tissues of the body or to increase its activity
What are the two types of hormones?
Steroids and peptides
What do steroids
-Enter into cell cytoplasm
-Bind to receptor molecules
-Enter nucleus -> create new proteins
Peptides
-Do NOT enter cell cytoplasm
-Bind to receptor molecules on cell membrane
-Cause chemical reactions to occur in cells (e.g. glycolysis)
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Pituitary gland; stimulates the thyroid to make its hormones.
*It is produced by the pituitary gland & acts on the thyroid*
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
Pituitary gland; stimulates skin to produce melanin
Growth Hormone (GH)
Pituitary gland; controls skeletal growth & development
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Pituitary gland; stimulates adrenal glands
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Pituitary gland; decreases urine output
Oxytocin
Pituitary gland; uterine contractions, emotional bonding
Prolactin
Pituitary gland; stimulates mammary glands (alveoli) to produce milk
Gonadotropic Hormones (GH)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) & Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Pituitary gland; stimulates ovaries/testes to make sex hormones
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothryinine (T3)
Thyroid; regulate energy metabolism & protein synthesis
The thyroid needs sufficient iodine intake to produce T4 & T3
Calcitonin
Thyroid; decreases the movement of calcium and phosphate minerals from bones to blood...acts to keep calcium & phosphates IN bones
Parathryoid Hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid; increases movement of calcium and phosphate minerals from bones to blood (opposite of calcitonin)...pulls minerals OUT of bones
Adrenaline (epinephrine) & Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
Adrenal glands; both increase heart rate & respiration and dilate the bronchial tree during stressful moments
Corticosteroids
Adrenal glands; regulate metabolism of proteins, glucose, lipids & electrolytes (sodium & potassium)...reduce inflammation by suppressing immune system
Cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
Insulin
Pancreas; decreases sugar levels in blood by accelerating glucose transport into cells and breaking glucose into glycogen
Glucagon
Pancreas; increases blood sugar by causing the liver to release more glucose in the bloodstream. (Opposite of insulin)
Diabetes is…
The reduced insulin production or reduced insulin effectiveness
Estrogen
Ovaries; development of secondary sex characteristics...increases endometrial lining of uterus during menstrual cycle
Progesterone
Ovaries; stimulates mammary glands during menstrual cycle
Testosterone
Testes; development of secondary sex characteristics and libido (sex drive)
Melatonin
Pineal; promotes sleep
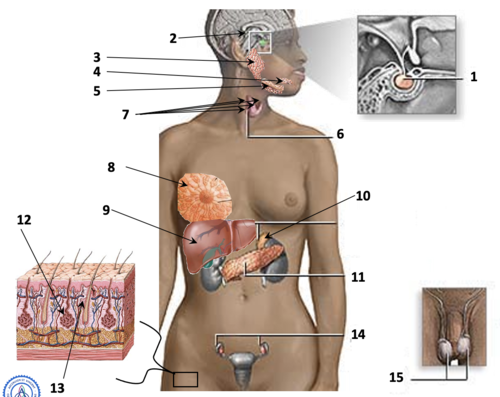
Label 1-15
Pituitary gland (endocrine)
Pineal gland (endocrine)
Parotid gland (exocrine)
Sublingual gland (exocrine)
Submandibular gland (exocrine)
Thyroid gland (endocrine)
Parathyroids (endocrine)
Mammary gland (exocrine)
Liver (exocrine)
Adrenal gland (endocrine)
Pancreas (both)
Sebaceous gland (exocrine)
Sudoriferous gland (exocrine)
Ovaries (endocrine)
Testes (endocrine)