Carbohydrates
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the process called when carbohydrates are broken down to CO₂?
Oxidation
Why are carbohydrates a principal energy source for cellular metabolism?
Because the oxidation of carbohydrates releases large amounts of energy.
What polymer of glucose forms the building blocks of wood and cotton?
Cellulose
What is a single carbohydrate molecule called?
A monosaccharide (simple sugar).
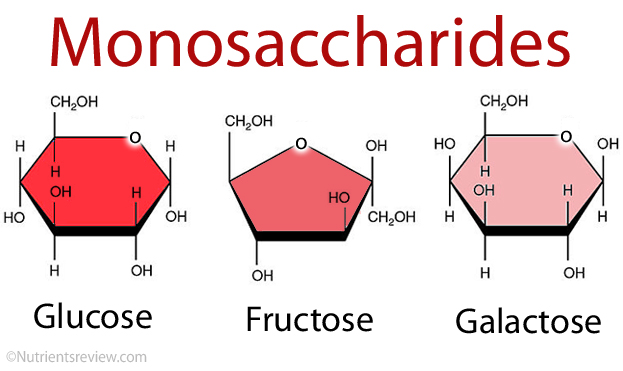
What is the general chemical formula for monosaccharides?
CₙH₂ₙOₙ.
Give examples of monosaccharides.

What forms when two monosaccharides join together?
A disaccharide.
Give examples of disaccharides.
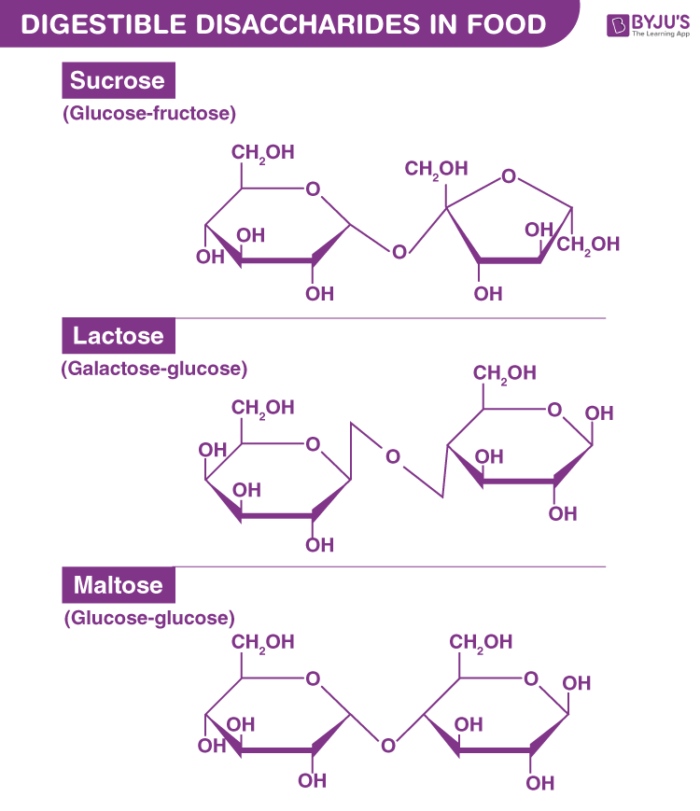
What monosaccharides is sucrose made of?
glucose + fructose
What monosaccharides is lactose made of?
glucose + galactose
What monosaccharides is maltose made of?
two glucose molecules
What is an oligosaccharide?
A carbohydrate composed of a few (typically 3-10) monosaccharides linked together.
What is a polysaccharide?
A carbohydrate composed of many monosaccharides bonded together.
What is a glycosidic linkage?
A covalent bond formed between two sugar molecules during a dehydration reaction (H2O leaves)

What type of reaction forms a glycosidic linkage?
A dehydration reaction that removes a molecule of water and requires enzymatic catalysis (increasing rate of chemical reaction by adding catalyst)

How are glycosidic linkages named?
Based on the specific carbon atoms involved in the bond and the α (alpha) or β (beta) configuration of the linkage.
What is the composition and linkage of sucrose?
Sucrose is composed of glucose and fructose with an α-1,2-glycosidic bond.
What is the composition and linkage of lactose?
Lactose is composed of galactose and glucose with a β-1,4-glycosidic bond.
What is the composition and linkage of maltose?
Maltose is composed of two glucose molecules with an α-1,4-glycosidic bond.
What is the composition and linkage of cellobiose?
Cellobiose is composed of two glucose molecules with a β-1,4-glycosidic bond
What is glycogen and its role?
Glycogen is an energy storage carbohydrate in animals, stored mainly in liver and muscle cells.
Describe the structure of glycogen.d
Composed of thousands of glucose units joined by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds with α-1,6 branches.
What is starch and its role?
Starch is the primary energy storage carbohydrate in plants, found in seeds, tubers, and roots.
Describe the structure of starch.
Composed of amylose (linear) and amylopectin (branched) with α-1,4 and α-1,6-glycosidic bonds.
What is cellulose and its role?
Cellulose is a structural component in plant cell walls, providing rigidity and strength.
pg 79