IMED1003 - Cholesterol Distribution (2)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Distribution
Sources
- Cholesterol absorbed from diet (enterocytes)
- Cholesterol is endogenously synthesised (hepatic, extrahepatic tissues)
- Distribution between tissues via bloodstream requires lipoproteins
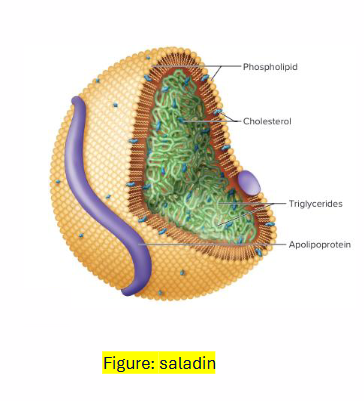
Lipoproteins: Structure
SURFACE (SHELL):
- Phospholipids
- Proteins: recognition by receptors, cofactors, enzymes
- Cholesterol
CORE:
- esterified lipids (TG, CE)
- Fat-soluble vitamins
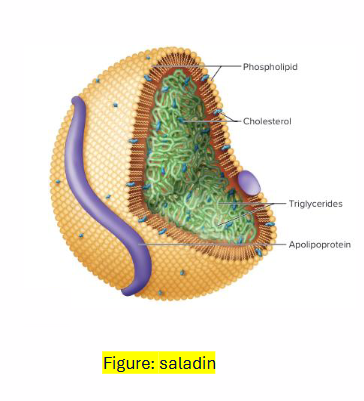
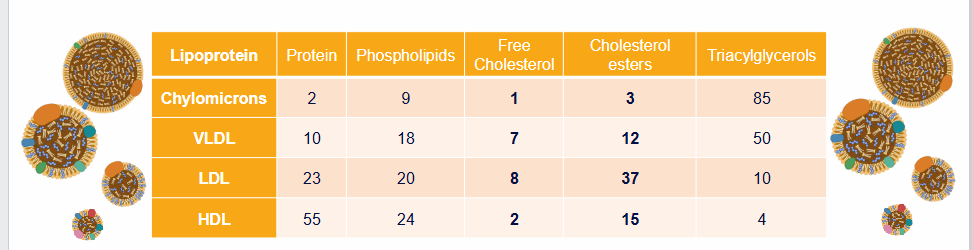
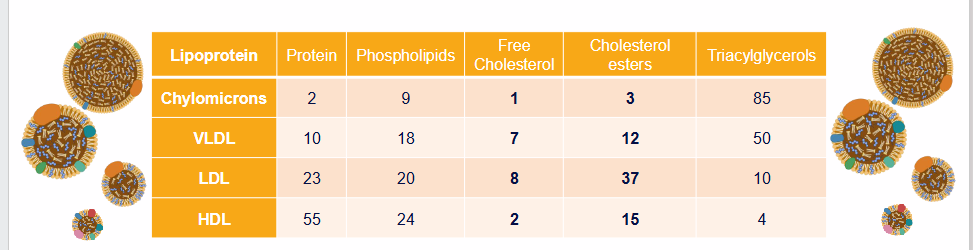
Lipoproteins vary in composition
- Surface (shell): different proteins, serve different functions
- Core: different composition of esterified lipids
- As lipoproteins circulate, contents is taken up by tissues
- This changes composition of lipoproteins, generates lipoprotein "remnants"
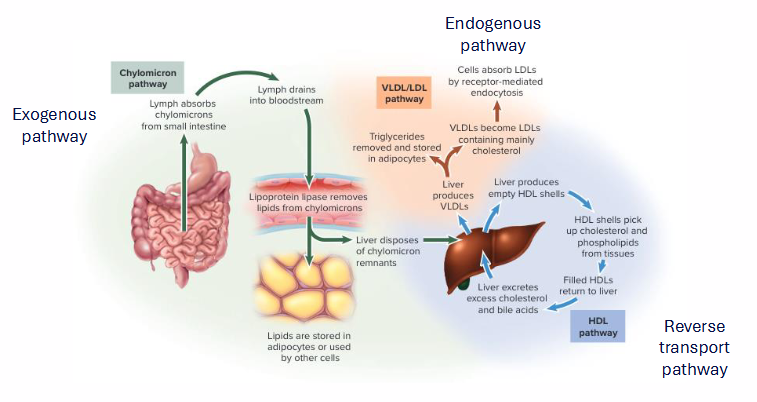
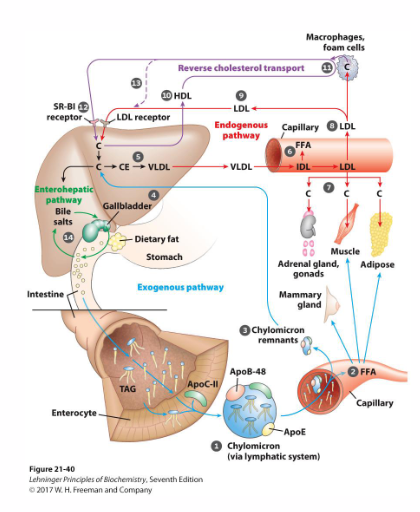
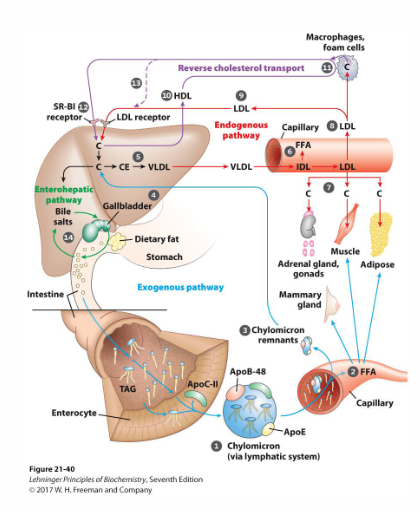
3 Pathways of Cholesterol Distribution (NAMING ONLY)
- Exogenous Pathway
- Endogenous Pathway
- Reverse Transport Pathway
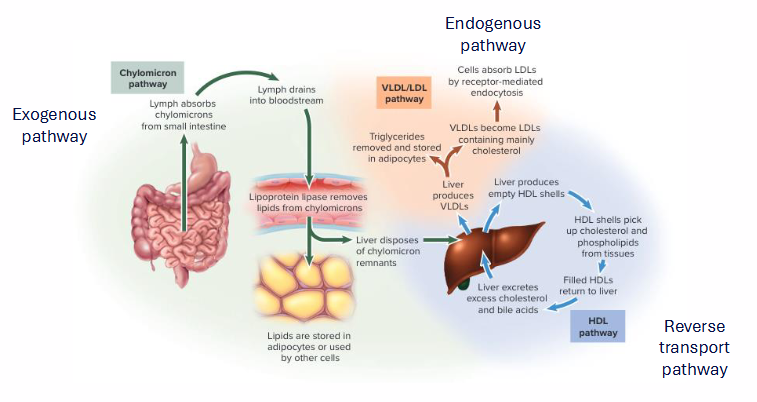
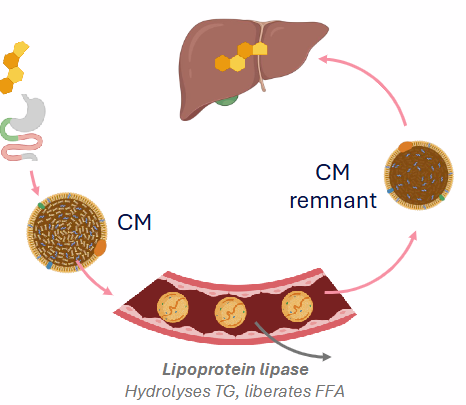
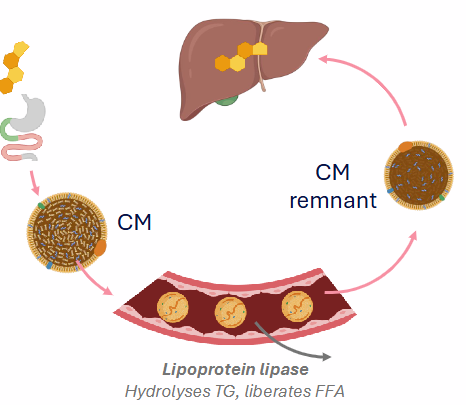
Exogenous Pathway (Cholesterol Distribution)
- enterocytes absorb cholesterol, secrete chylomicrons (85% TG)
- Chylomicrons transported through capillaries - TG depleted
- Lipoprotein lipase: Liberates FFA for use by peripheral tissues
- Chylomicron becomes chylomicron remnant (taken up by liver. The cholesterol from membrane and cholesteryl esters from core
- as the chylomicrons move through the bloodstream lipoprotein lipase triglycerides are depleted from the chylomicrons, liberates FFA
- CM remnant still has cholesterol in membrane and cholesteryl esters in core
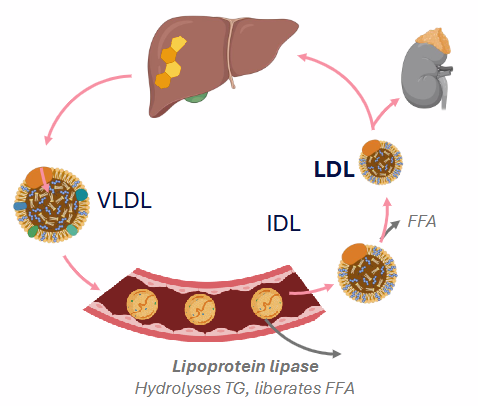
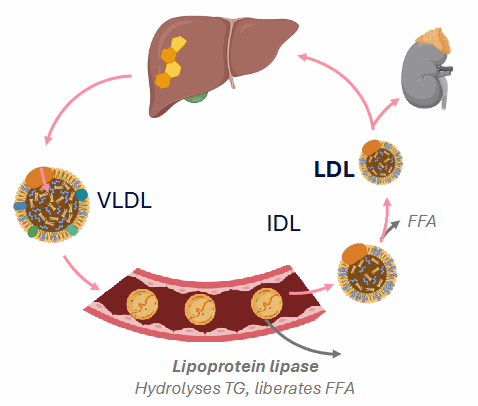
Endogenous Pathway (Cholesterol Distribution)
- liver synthesises cholesterol
- esterifies C as CE, packages CE into VLDL, secretes into bloodstream
- Lipoprotein lipase: liberate FFA from VLDL
- VLDL becomes LDL
- LDL is rich in free (8%) and esterified cholesterol (37%)
- LDL distributes cholesterol to peripheral tissues (adrenal glands, gonads, muscle, adipose)
- LDL absorbed by liver, and process repeats
- once the IDL is formed FFA are liberated again and LDL is formed (highest conc. of cholesterol)
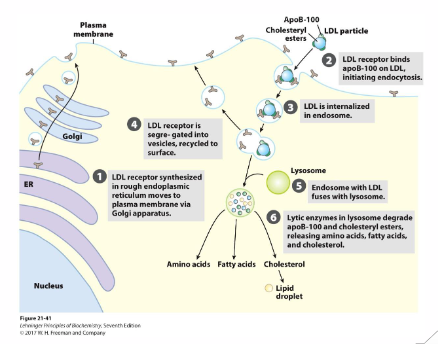
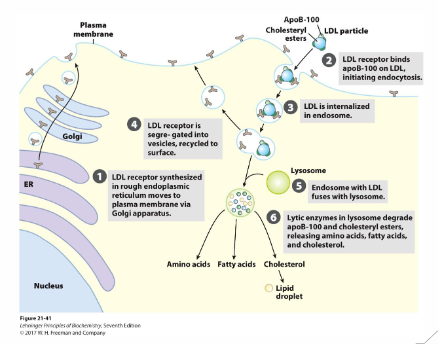
Regulation of cellular cholesterol concentrations: LDL receptor
- Cholesterol within LDL is absorbed by via the LDL receptor
- Regulation of LDL Receptor: high intracellular cholesterol levels, inhibit transcription LDLR gene, Decreased LDL receptor protein, Decreased cholesterol uptake
- Cells import cholesterol appropriate to requirements
.
- even hypothyroidism decreases activity of receptor
- detection of the LDL begins the receptor mediated endocytosis of LDL into the cell
- high intracellular cholesterol levels inhibits transcription LDLR gene, which means that there are less LDL recptor protein on membrane, hence decreased cholesterol uptake
![<p>Atherosclerosis: High [LDL] in bloodstream</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1d374a14-c239-4b29-a8d7-f64c74a72373.png)
Atherosclerosis: High [LDL] in bloodstream
- Atherosclerosis results in narrowing of blood vessels.
- this is a major cause of heart attack and stroke
- results from high plasma LDL concentrations
.
- hgih conc of LDL means that a plaque starts to form (which bulges and makes the blood vessel narrower)
- stroke or heart attack happens when this narrowing causes reduced blood flow to heart and brain
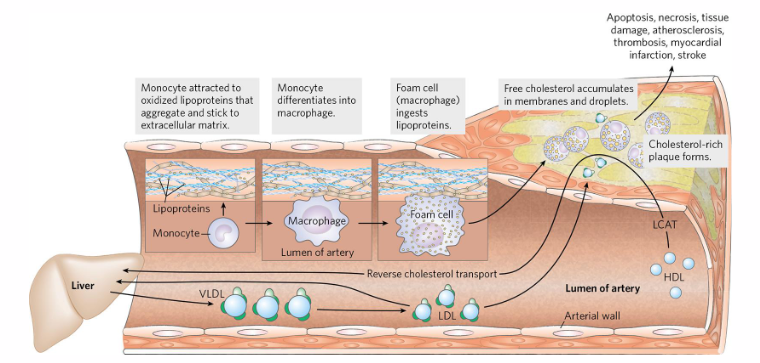
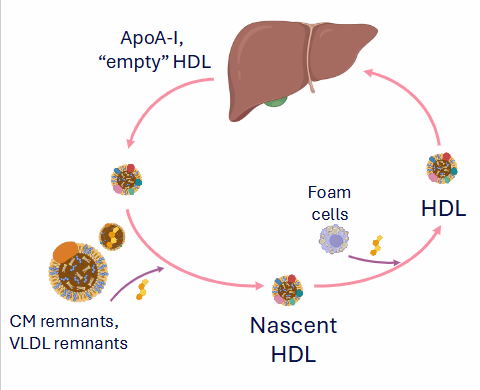
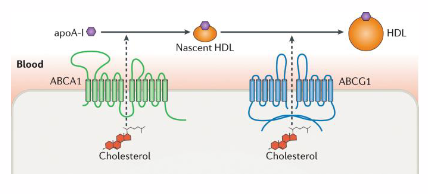
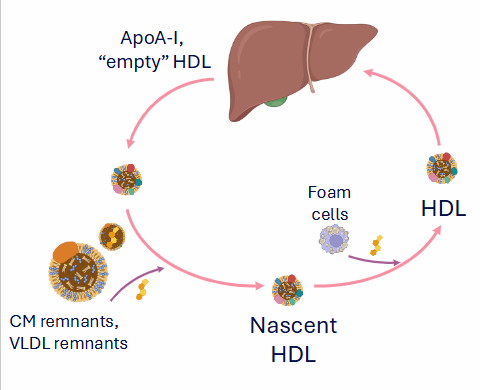
Reverse Cholesterol Transport
- Scavenges lipids in circulatory system
- HDL scavenges free cholesterol from: Extrahepatic tissues, remnant lipoproteins, foam cells growing atherosclerotic plaques
- HDL surface: Lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT): forms cholesteryl esters. the co-factor is ApoA-I
- HDL transports cholesterol back to the liver
.
- basically the liver secretes an empty HDL particle which scavenges free cholesterol from extrahepatic tissues etc.
- when empty HDL takes up cholesterol they become Nascent HDL
- this nascent HDL also scavenges cholesterol from Foam cells (this restricts growth of aterosclerotic plaque)
- HDL particle is escorted back to liver where it is absorbed
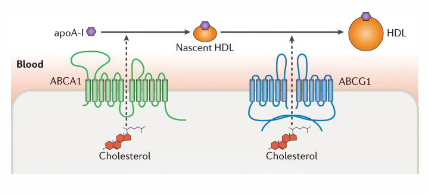
ABC Transporters
- export free cholesterol from cells
- ABC: ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters
- ABCA1: most cells
- ABCG1: macrophages, foam cells