Developmental Biology Laboratory LE1
1/295
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
296 Terms
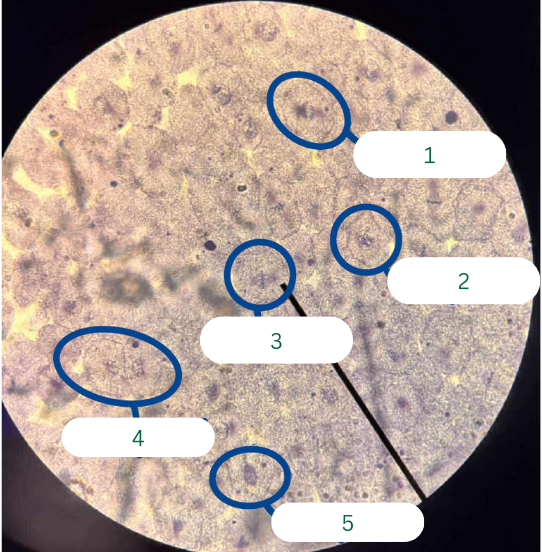
Anaphase
What phase of mitosis is in cell 1?
Prophase
What phase of mitosis is in cell 2?
Metaphase
What phase of mitosis is in cell 3?
Prophase
What phase of mitosis is in cell 4 (JUST ONE CELL)?
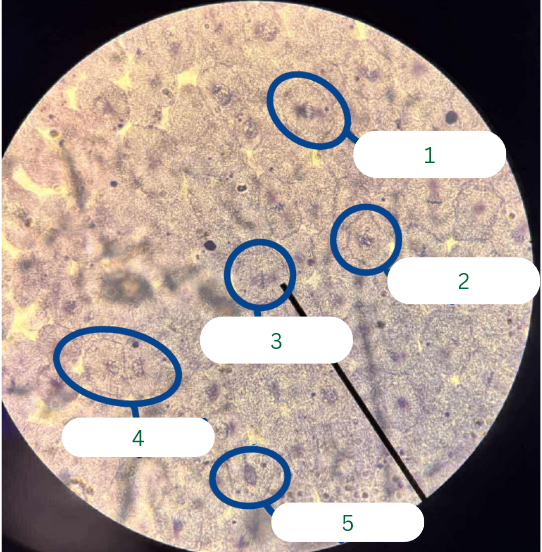
Prophase
What phase of mitosis is in cell 5?
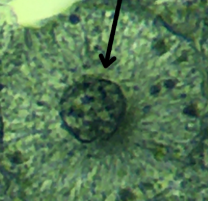
Interphase
What phase of mitosis is in this cell?
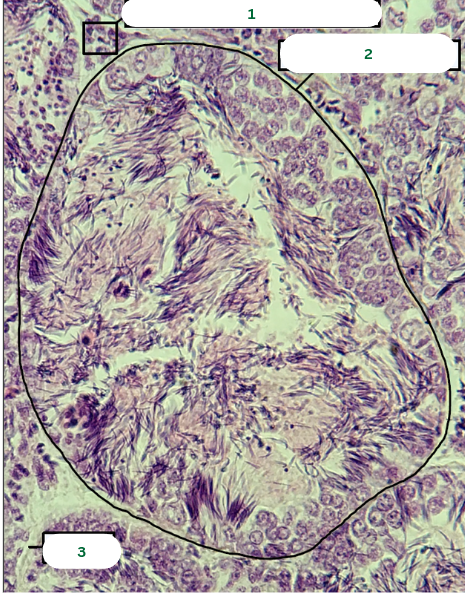
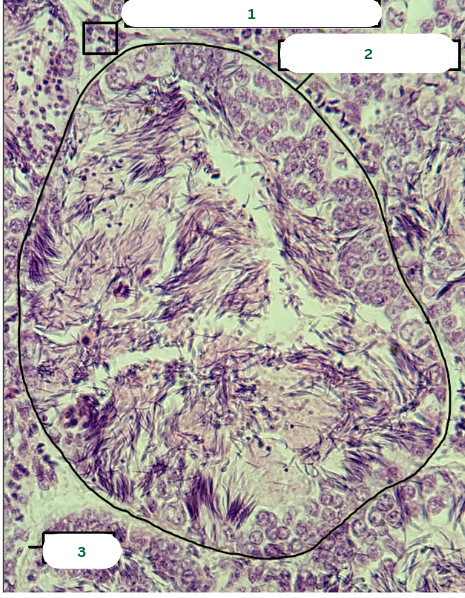
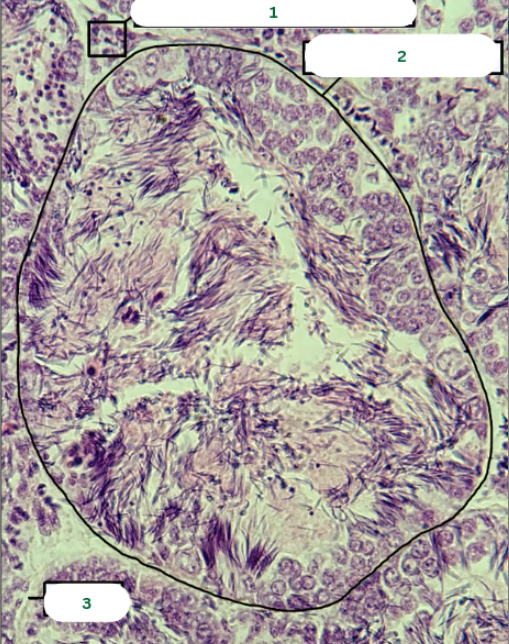
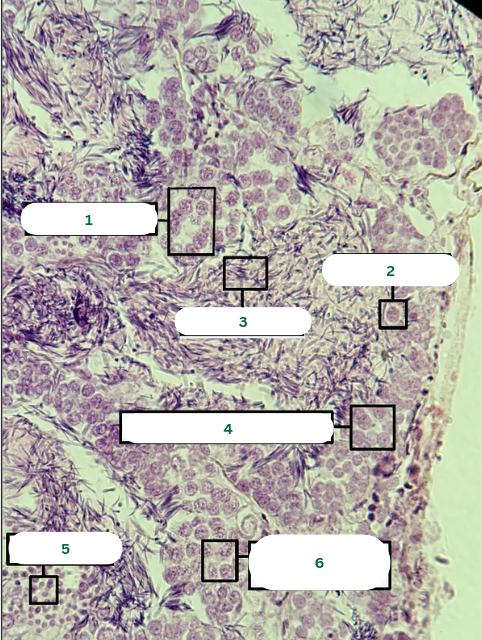
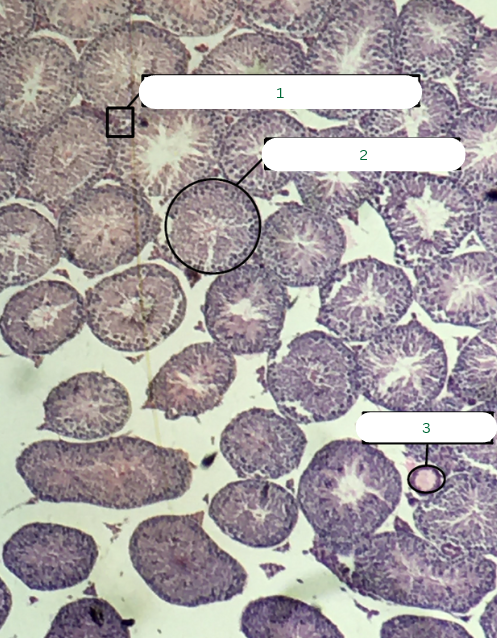
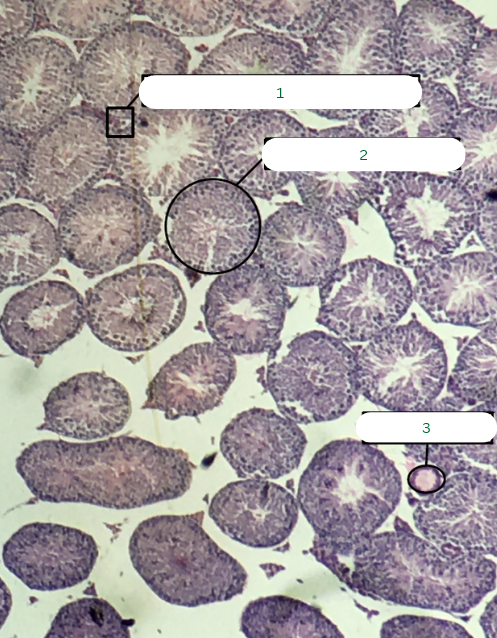
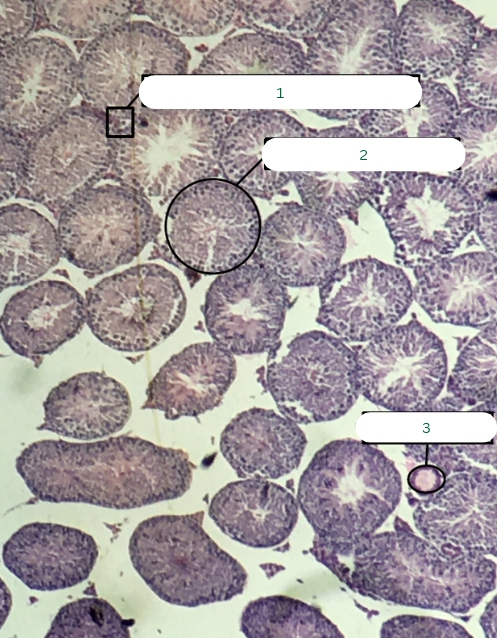
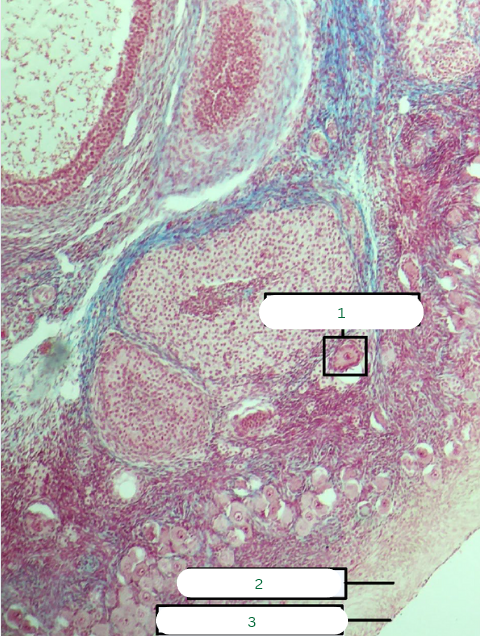
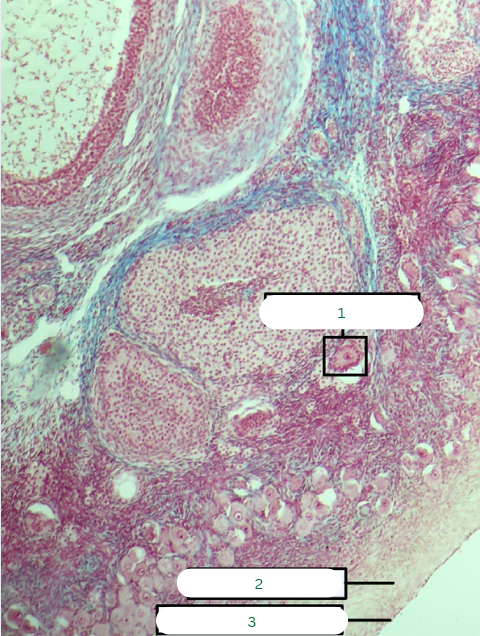
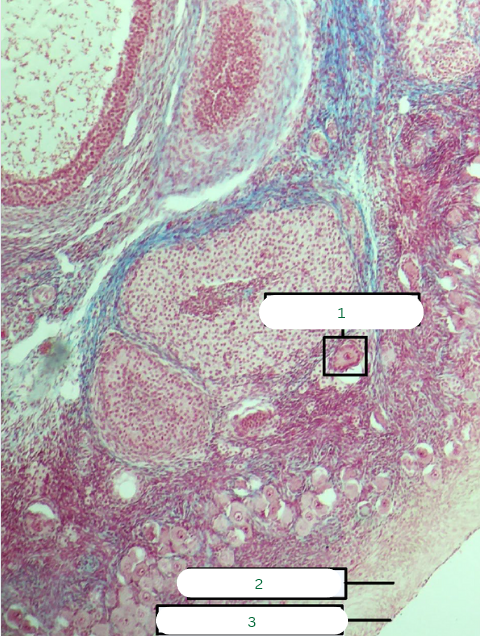
Frog’s Testis
What is the specimen in the photo?
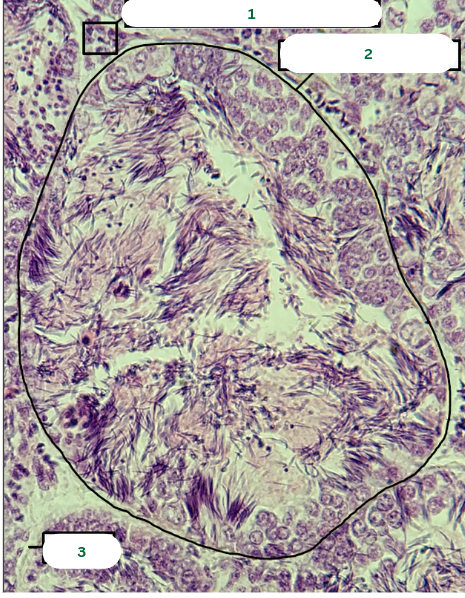
Frog’s Testis
What is the specimen in the photo?
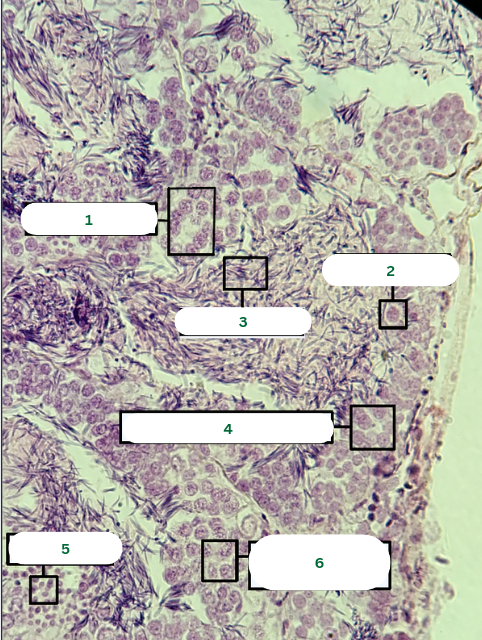
Interstitial Connective Tissue
What is the structure in 1?
Seminiferous Tubules
What is the structure in 2?
Septum
What is the structure in 3?
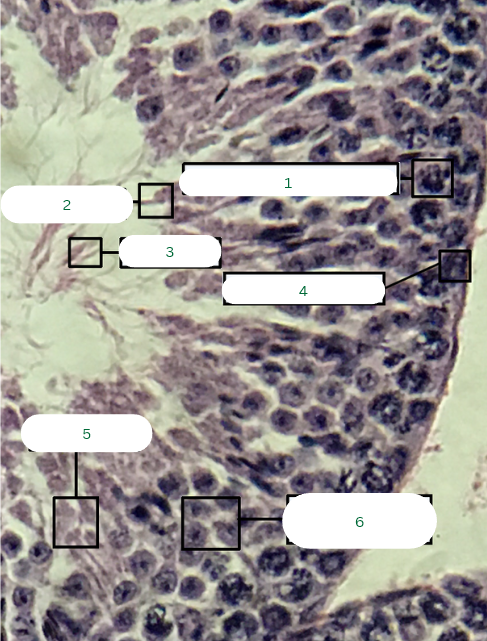
Spermatocyst
What is the structure in 1?
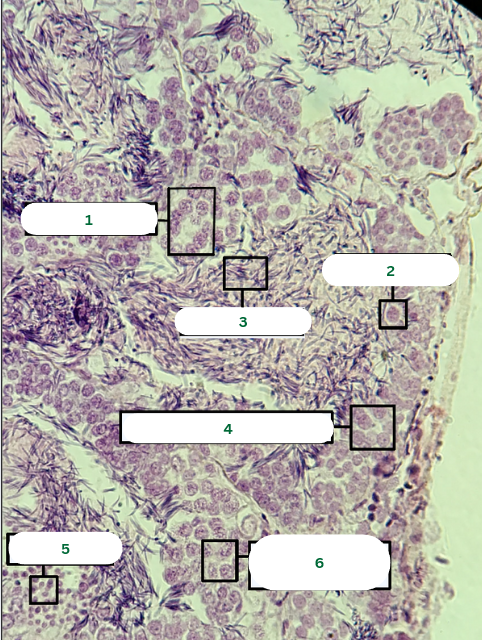
Sertoli Cell
What is the structure in 2?
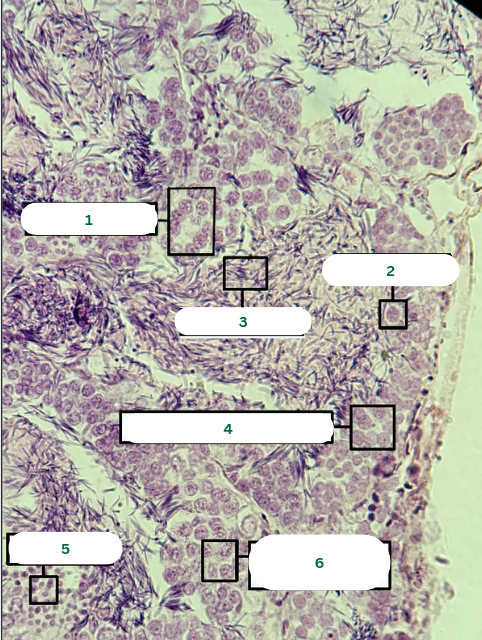
Spermatozoa
What is the structure in 3?
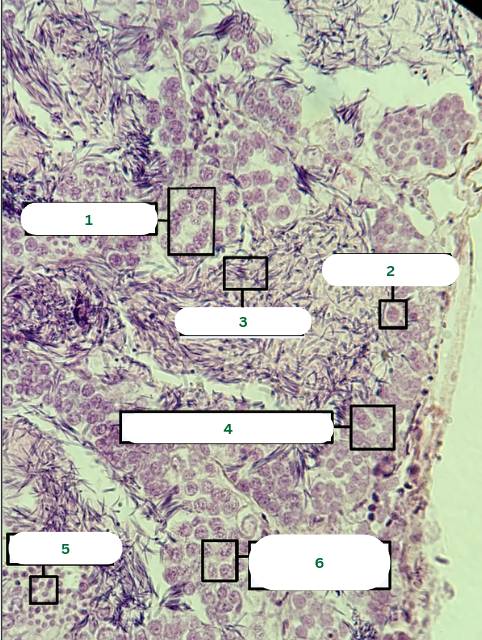
Primary Spermatocyte
What is the structure in 4?
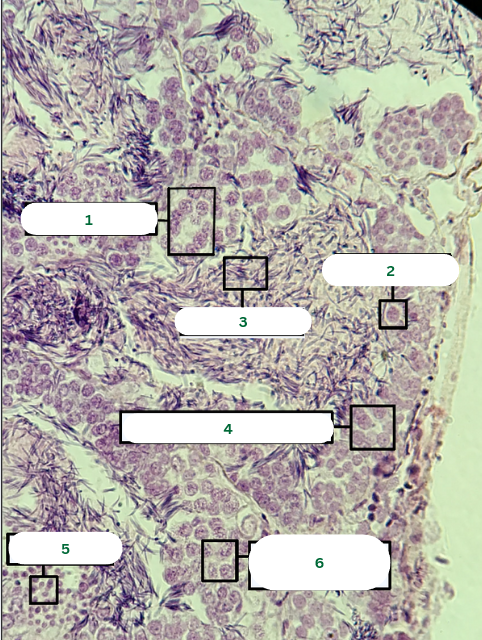
Spermatids
What is the structure in 5?
Primary Spermatocyte
What is the structure in 6?
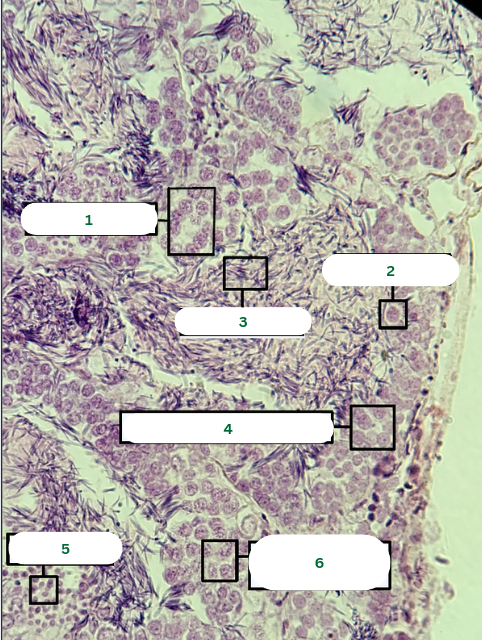
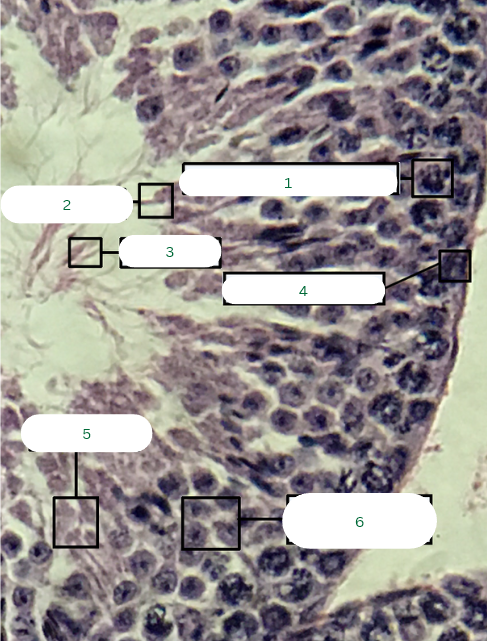
Mouse’s Testis
What is the specimen in the photo?
Mouse’s Testis
What is the specimen in the photo?
Interstitial Connective Tissue
What is the structure in 1?
Seminiferous Tubule
What is the structure in 2?
Blood Vessel
What is the structure in 3?
Primary Spermatocyte
What is the structure in 1?
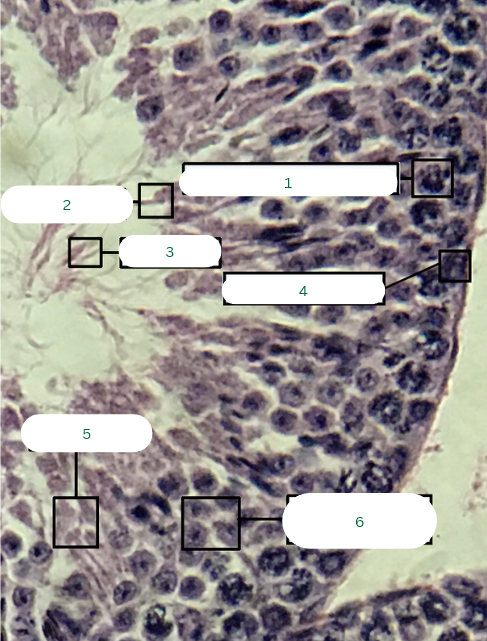
Sperm Head
What is the structure in 2?
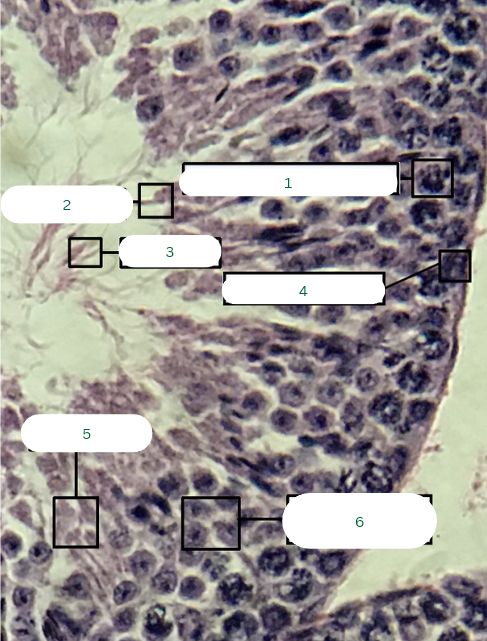
Sperm Tail
What is the structure in 3?
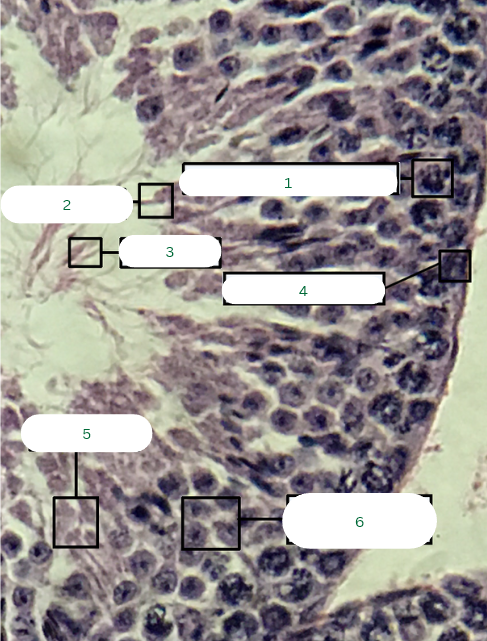
Spermatogonium
What is the structure in 4?
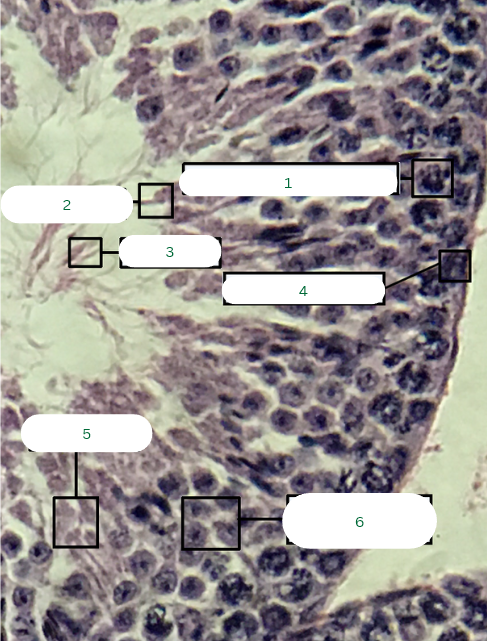
Spermatids
What is the structure in 5?
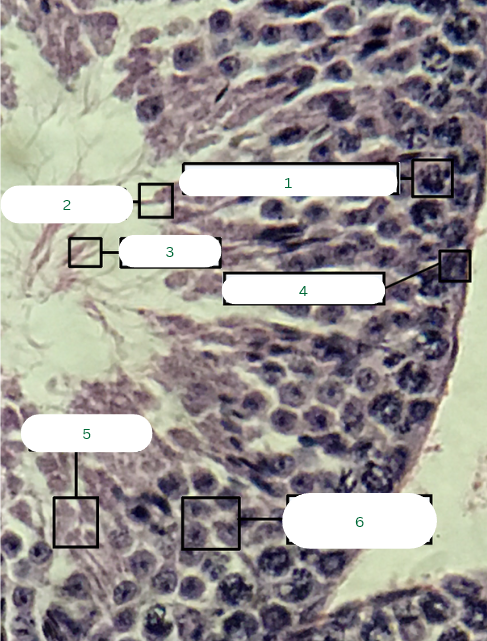
Secondary Spermatocytes
What is the structure in 6?
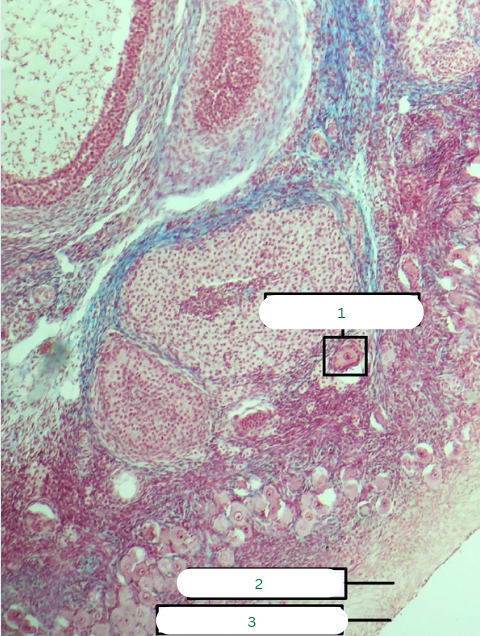
Frog’s Ovary
What is the specimen in the photo?
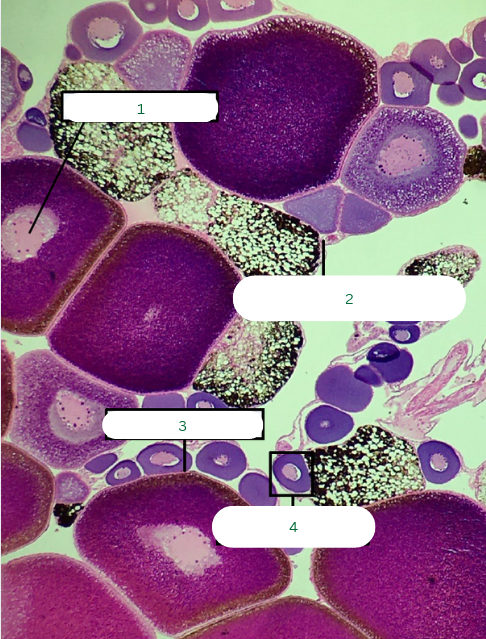
Germinal Vesicle
What is the structure in 1?
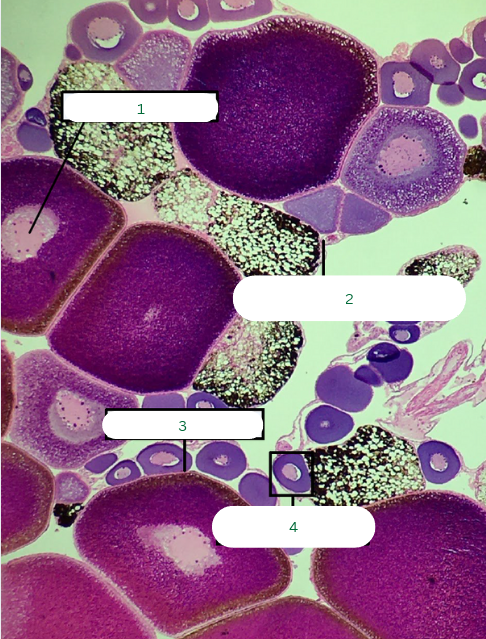
Theca Folliculi Interna
What is the structure in 2?
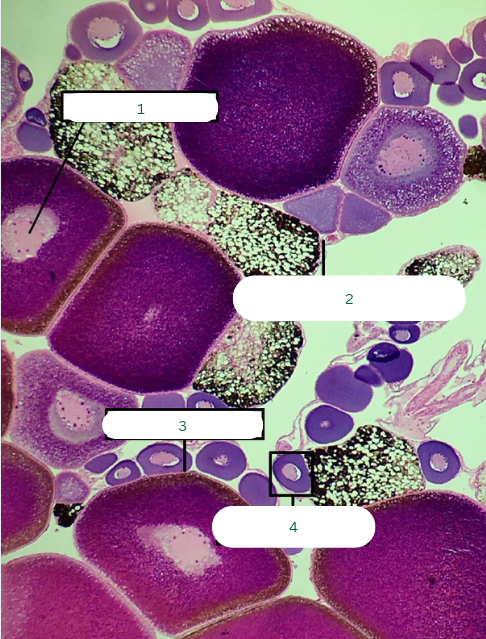
Follicular Cells
What is the structure in 3?
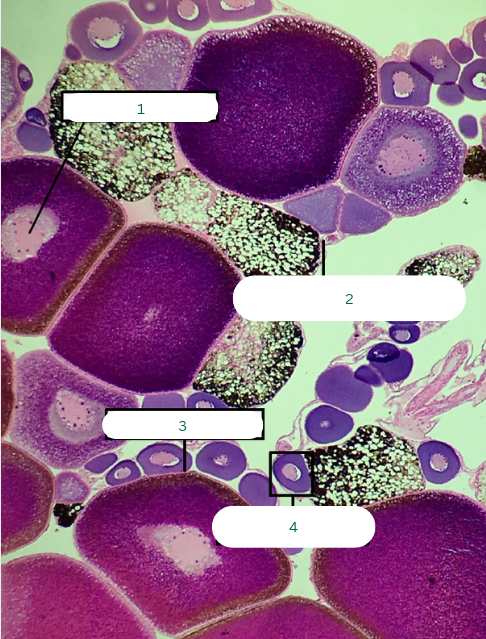
Primary Oocyte
What is the structure in 4?
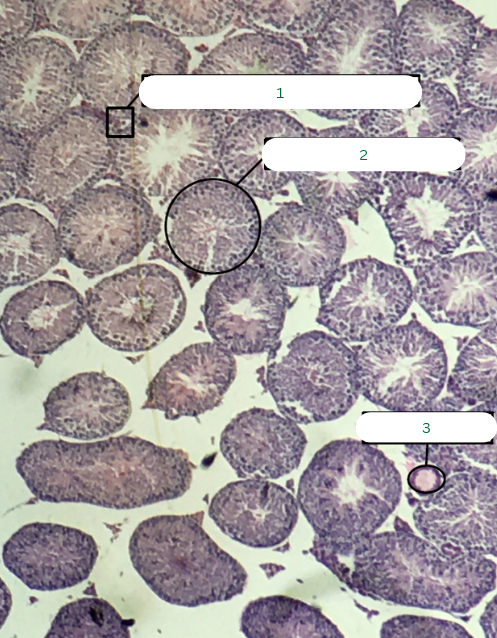
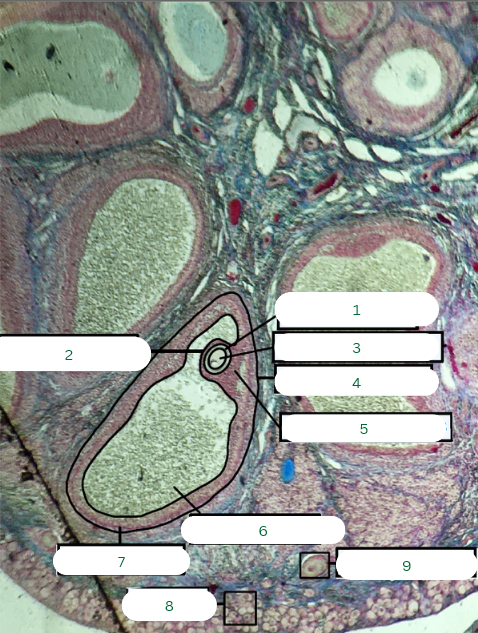
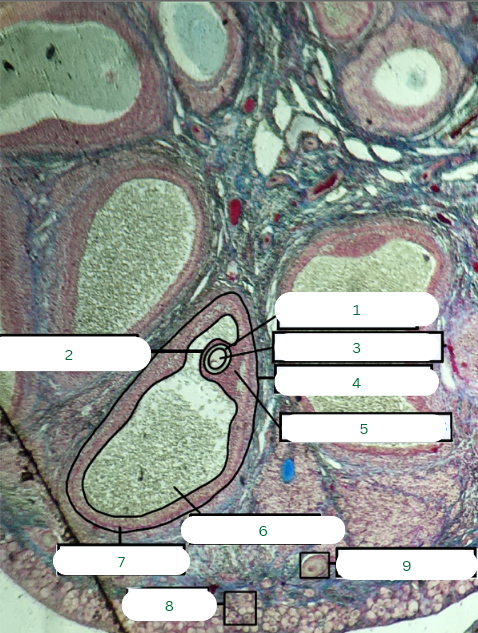
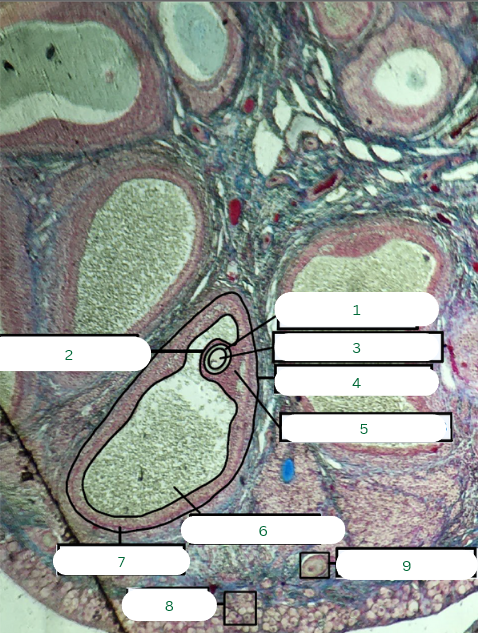
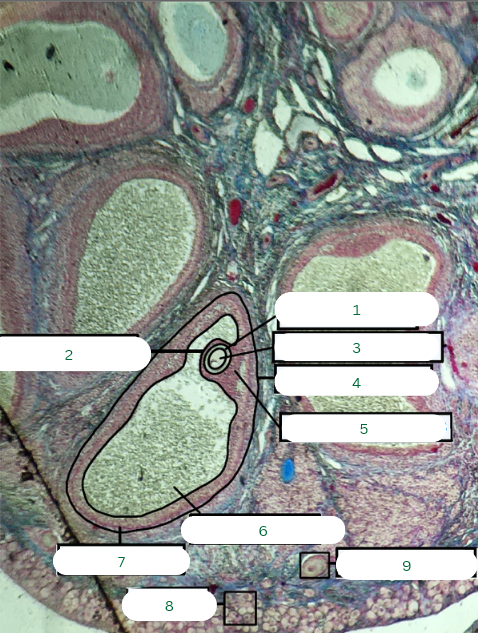
Cat’s Ovary
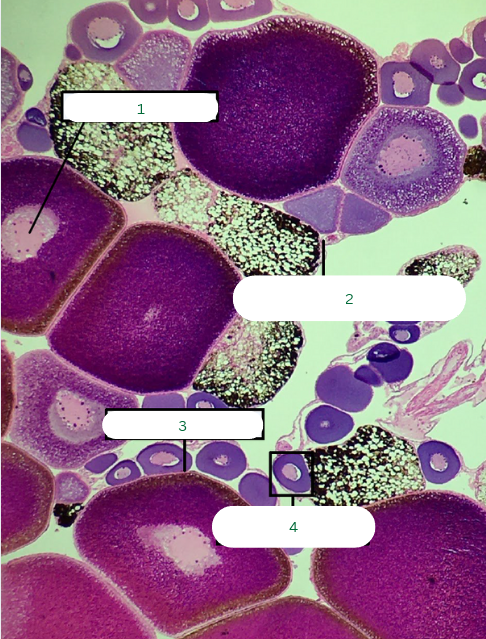
What is the specimen in the photo?
Cat’s Ovary
What is the specimen in the photo?
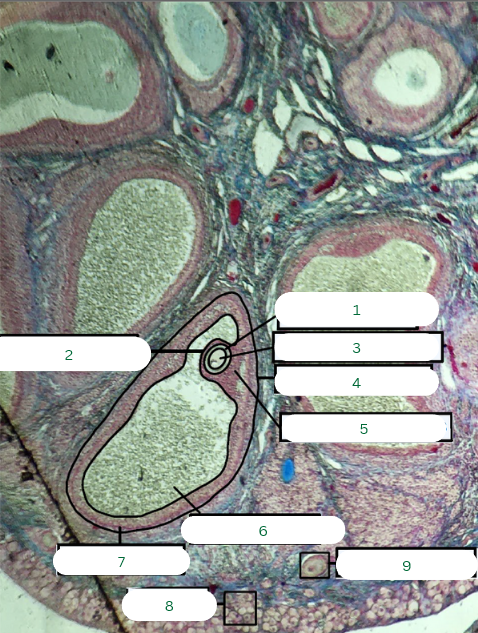
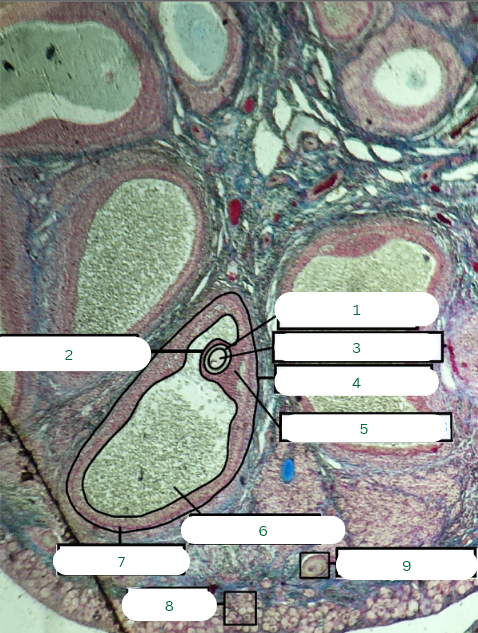
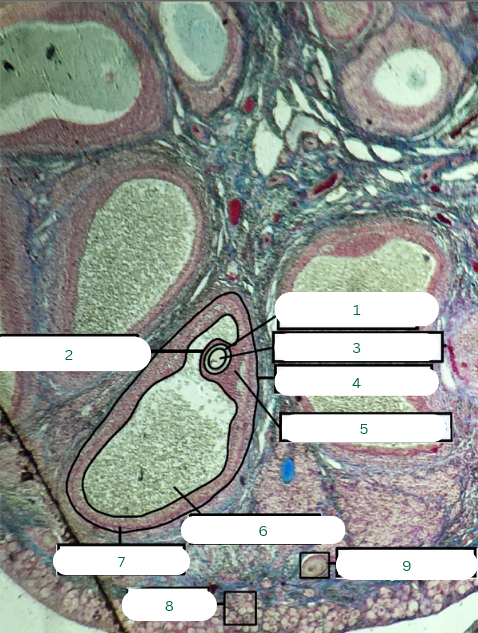
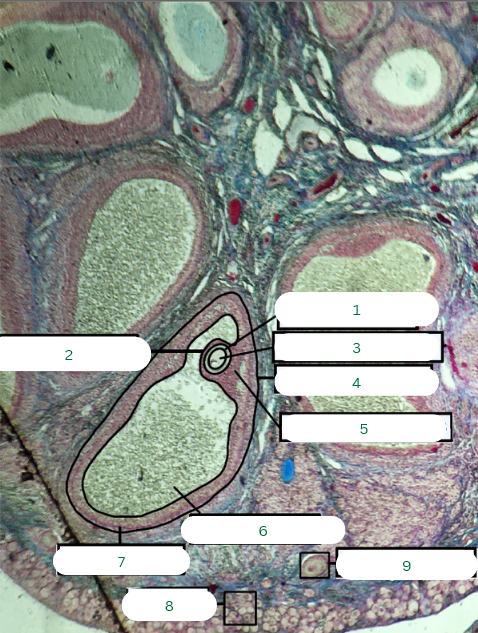
Primary Follicle
What is the structure in 1?
Tunica Albuginea
What is the structure in 2?
Germinal Epithelium
What is the structure in 3?
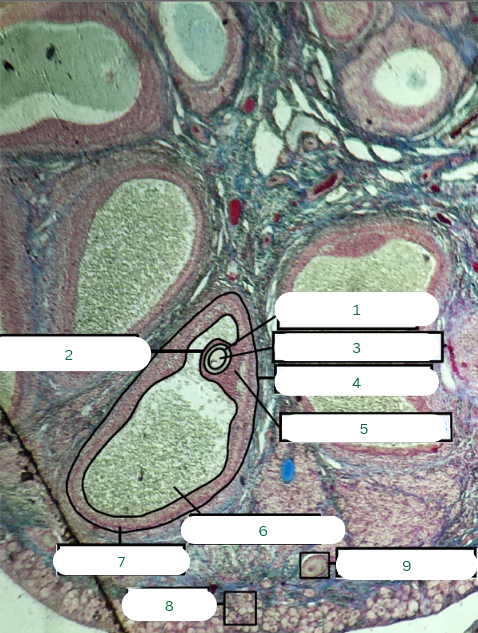
Zona Pellucida
What is the structure in 1?
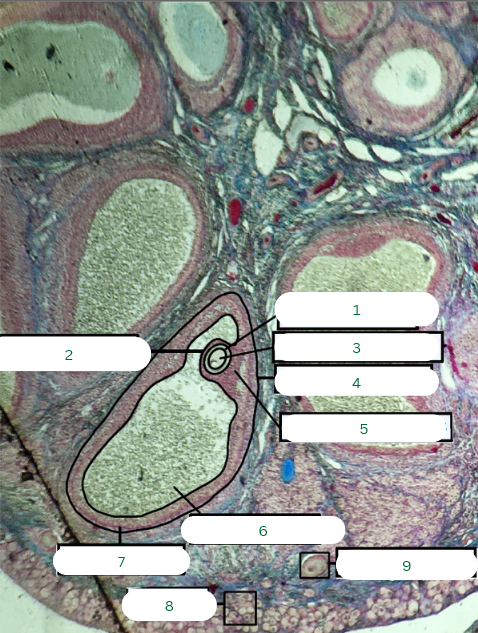
Corona Radiata
What is the structure in 2?
Secondary Oocyte
What is the structure in 3?
Tertiary Follicle
What is the structure in 4?
Cumulus Oophorus
What is the structure in 5?
Antrum or Cavity
What is the structure in 6?
Theca Interna
What is the structure in 7?
Oogonia
What is the structure in 8?
Primary Oocyte
What is the structure in 9?
G1 Phase
Part of cell cycle where cell growth occurs and metabolic activity is present.
S Phase
Part of cell cycle where DNA replicates/duplication of chromosomes.
G2 Phase
Part of cell cycle where cell prepares for division via duplication of centrosomes.
True
True or False:
Interphase is not a part of cell division.
Interphase
This is where the chrosomes are not yet condensed and appears as chromatin, the nuclear envelope and the nucleolus are still intact.
Karyokinesis
Major event in cell division where the nucleus divdes.
Cytokinesis
Major event in cell division where the cytoplasm divides.
Cleavage Furrow
During cytokinesis, this indentation forms in an animal cell.
Actin Microfilaments
What do you call the contractile ring that is responsible for the formation of the cleavage furrow in cytokinesis?
Cell Plate
During cytokinesis, this forms in a plant cell.
Syncytia
Not all cells complete cytokinesis, some may form multi-nucleated cytoplasm called?
Microtubules
Forms the mitotic spindle.
Responsible for chromosome movement during karyokinesis.
Microfilaments
Responsible for cytokinesis via cleavage furrow
Forms the contractile ring at the equatorial plane
Intermediate Filaments
Provides strucutural stability but is less directly involved in mitosis.
Prophase
What stage of mitosis is being described below?:
Chromosomes condense (supercoiling).
Nuclear envelope starts to disintegrate.
Centrosomes move to opposite poles, spindle fibers form.
Metaphase
What stage of mitosis is being described below?:
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (equatorial plane).
Centrosomes at opposite poles; spindle fibers attach to kinetochores.
Anaphase
What stage of mitosis is being described below?:
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Duplicated centrosomes clearly visible at poles.
Spindle fibers shorten, pulling chromatids apart.
Telophase
What stage of mitosis is being described below?:
Chromatids reach poles; nuclear envelope reforms.
Cleavage furrow forms
Results in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Meoisis I
Which part of meiosis is considered reductional?
Meoisis II
Which part of meiosis is considered equational?
Leptotene
Which substage of Meiosis I is described below?":
Chromosomes start condensing.
Chromosome ends attach to the nuclear envelope.
Zygotene
Which substage of Meiosis I is described below?":
Formation of the synaptonemal complex.
Homologous chromosomes pair up (synapsis).
Pachytene
Which substage of Meiosis I is described below?":
Crossing overoccurs at chiasmata.
Exchange of homologous chromosome segments
Diplotene
Which substage of Meiosis I is described below?":
Homologous chromosomes begin to separate but remain attached at chiasmata.
Diakinesis
Which substage of Meiosis I is described below?":
Final condensation of chromosomes.
Nuclear envelope breaks down.
seminiferous tubules of testes
Where does spermatogenesis occur?
Cleavage
Rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote that establish multicellularity.
Blastomeres
Products of cleaveage, they get smaller with each division, but overall embryo size does not increase.
maternal mRNA and Proteins
What controls cleavage of cells?
Blastulation
Formation of the blastulafrom the morula (solid ball of cells).
Blastula
hollow structure with a cavity inside
Morula
solid cluster of blastomeres (resembles mulberry fruit).
Blastocoel
Forms eccentrically
Surrounded by a layer of cells called the blastoderm.
Gastrulation
Morphogenetic movements that reorganize the blastula into a gastrula with 3 germ layers.
Ectoderm
This germ layer is the outer layer, will form skin & nervous system.
Mesoderm
This germ layer is the middle layer, will form muscles, skeleton, circulatory & urogenital systems.
Endoderm
This germ layer is the inner layer, will form gut lining and accessory glands like the liver, pancreas, thyroid, and other digestive glands.
Forebrain and Sense Organs
Neural tube begins forming regions of the forebrain.
Olfactory placodes → future smell organs.
Eye development: optic cup and lens primordium visible.
Pineal gland and epiphysis forming from the prosencephalon.
Midbrain and Pharyngeal Region
Nasal placodes and oral primordium appear.
Pituitary rudiment (from infundibulum and Rathke’s pouch).
Otic placode invaginates → forming otic vesicle(inner ear).
Pharyngeal pouches visible, precursors of gill structures.
Hindbrain and Notochord
Myelencephalon (hindbrain) develops → autonomic control.
appears as a midline rod supporting early body structure.
Cranial nerves (trigeminal, epipharyngeal placodes) are visible.
Thoracic/Abdominal Region
Somites forming → future skeletal muscle and vertebrae.
Heart rudiments (atrium, ventricle, pericardial cavity) visible.
Endoderm forms primitive gut tube.
Posterior Region
Spinal cord and spinal ganglia develop from neural tube.
Intestine visible but simple, straight tube.
Yolk-filled endodermal cells dominate posterior.
Tail bud and cloacal membrane form.
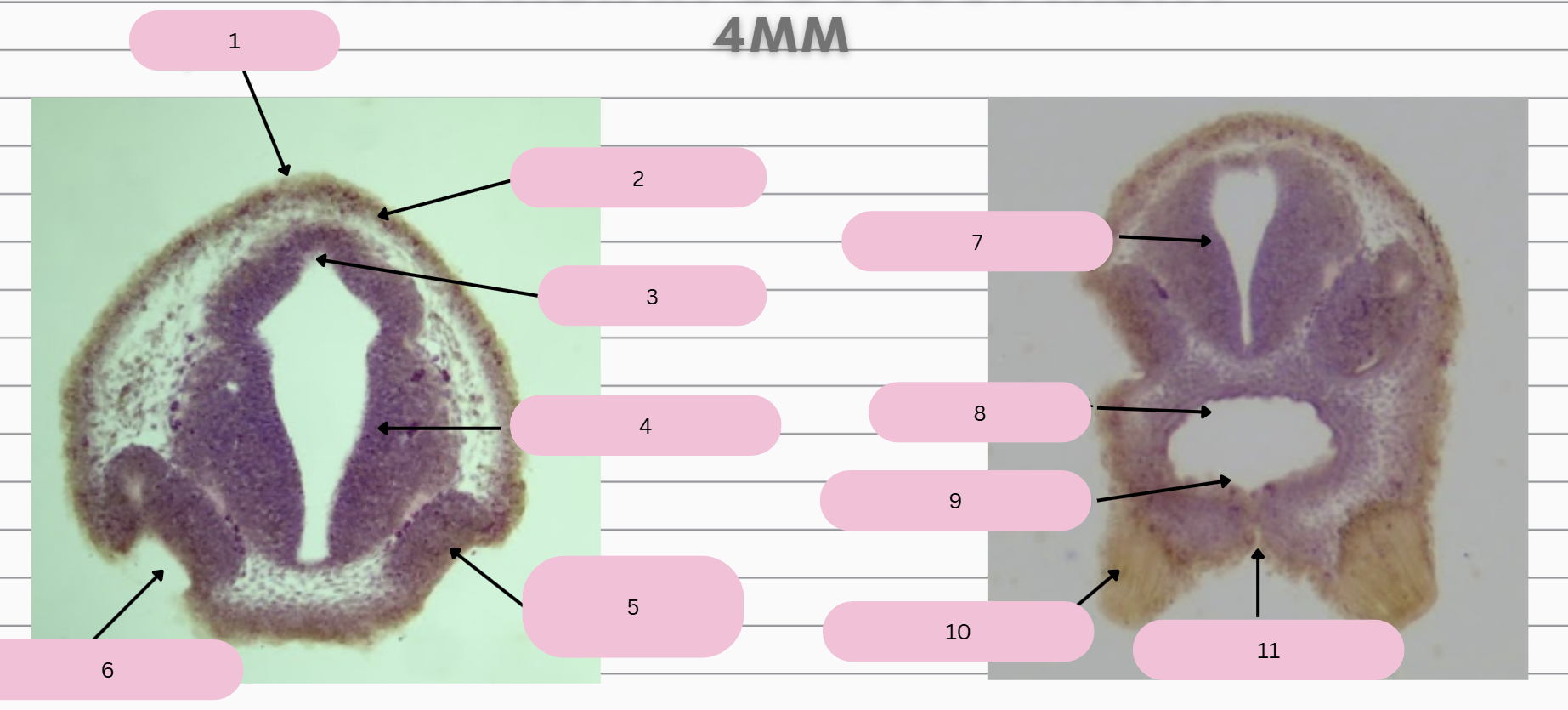
Epidermis
What structure is in 1?
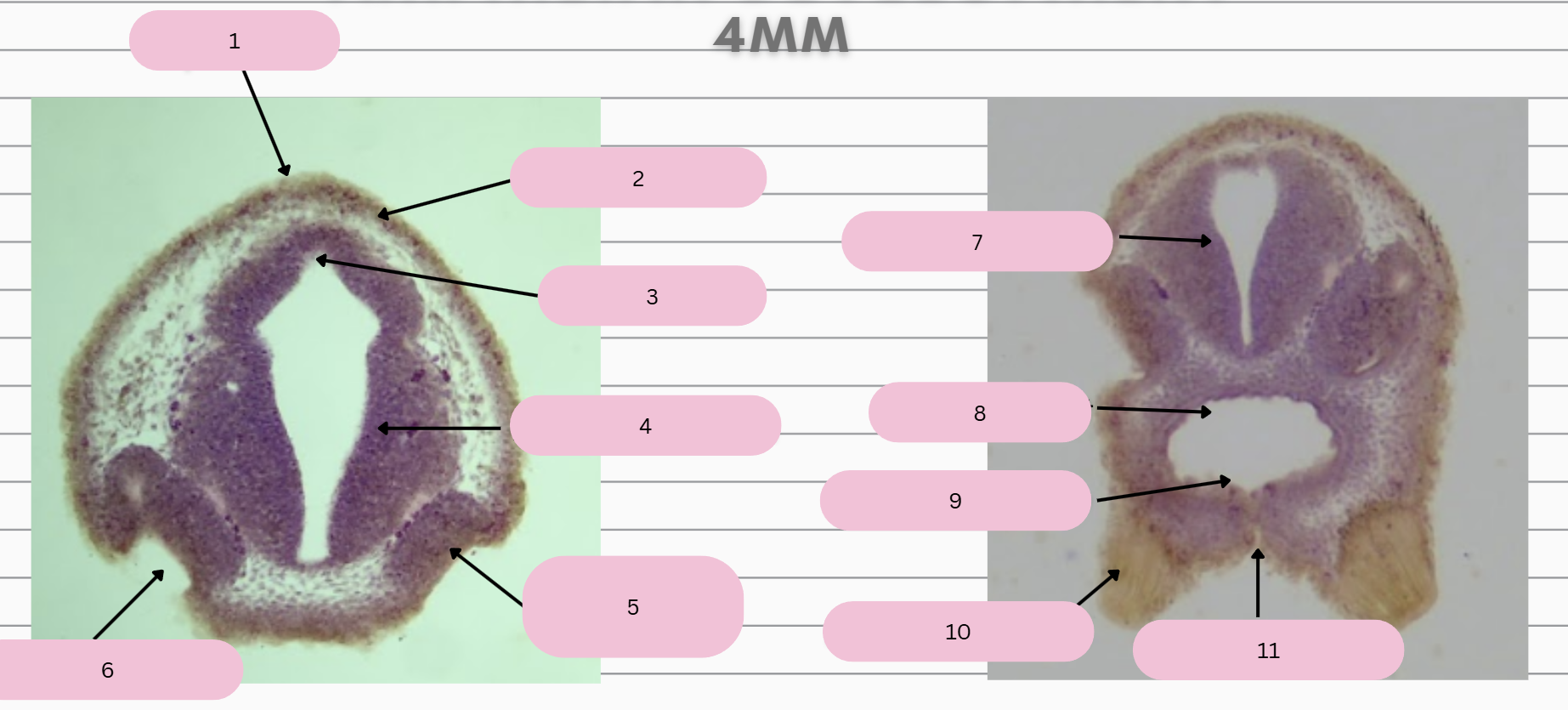
Skin Ectoderm
What structure is in 2?
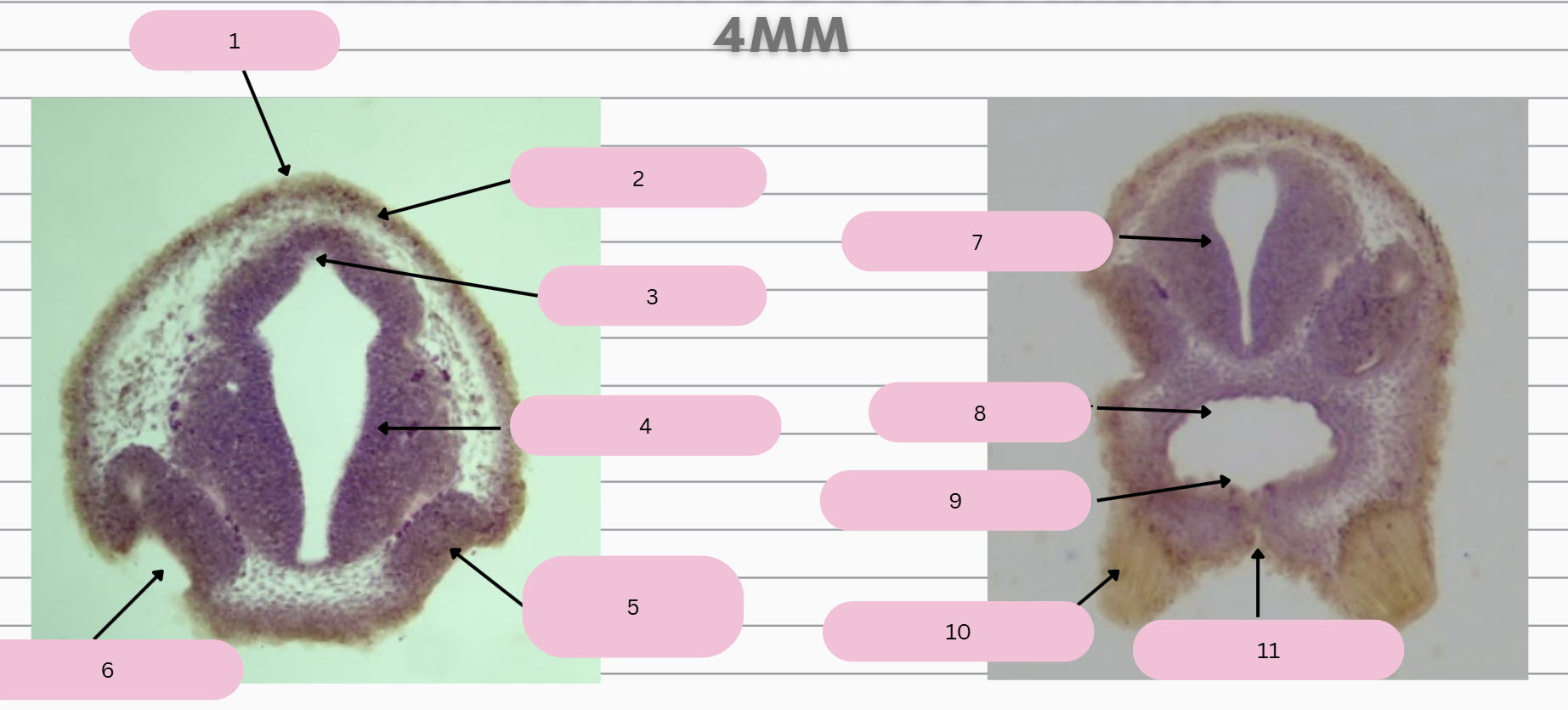
Pineal Gland
What structure is in 3?
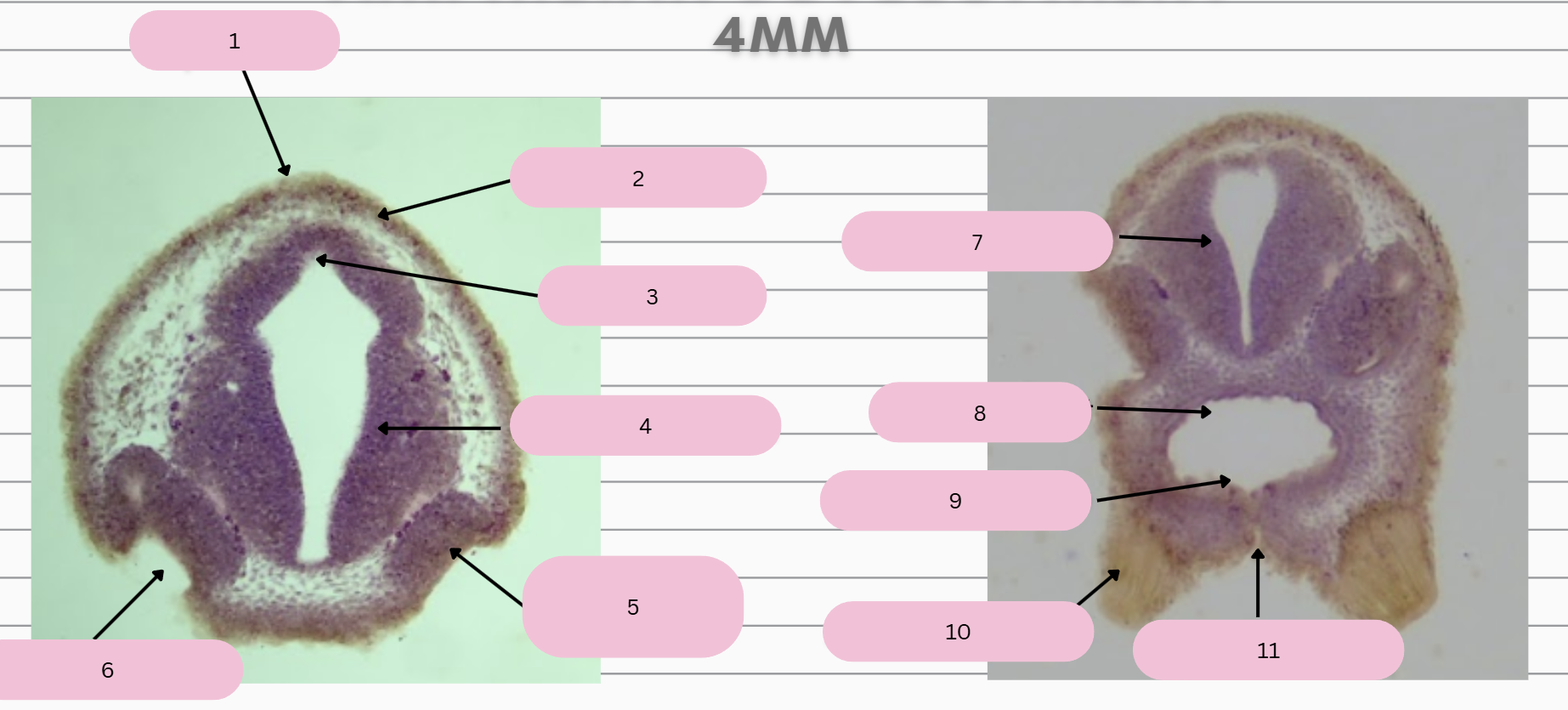
Prosencephalon
What structure is in 4?
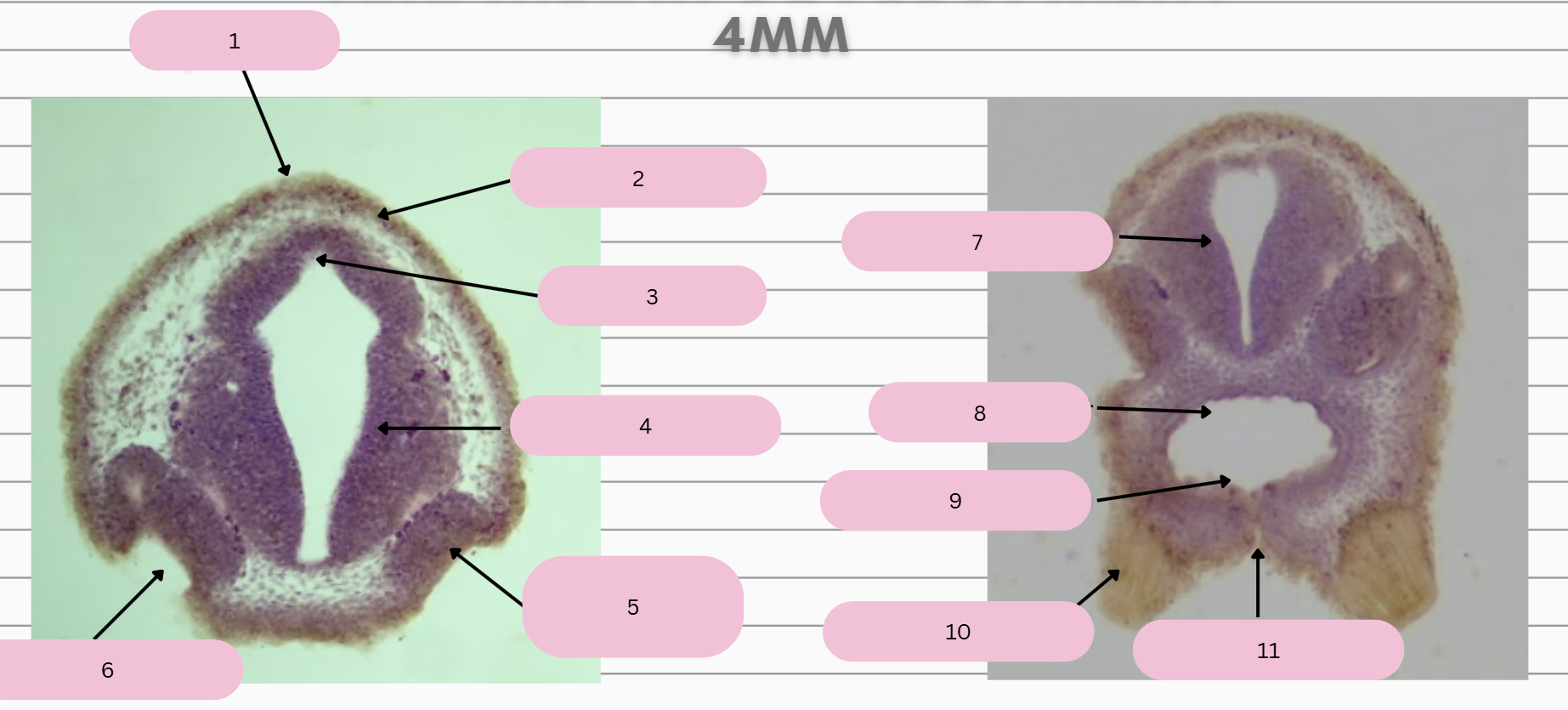
Olfactory Placode
What structure is in 5?
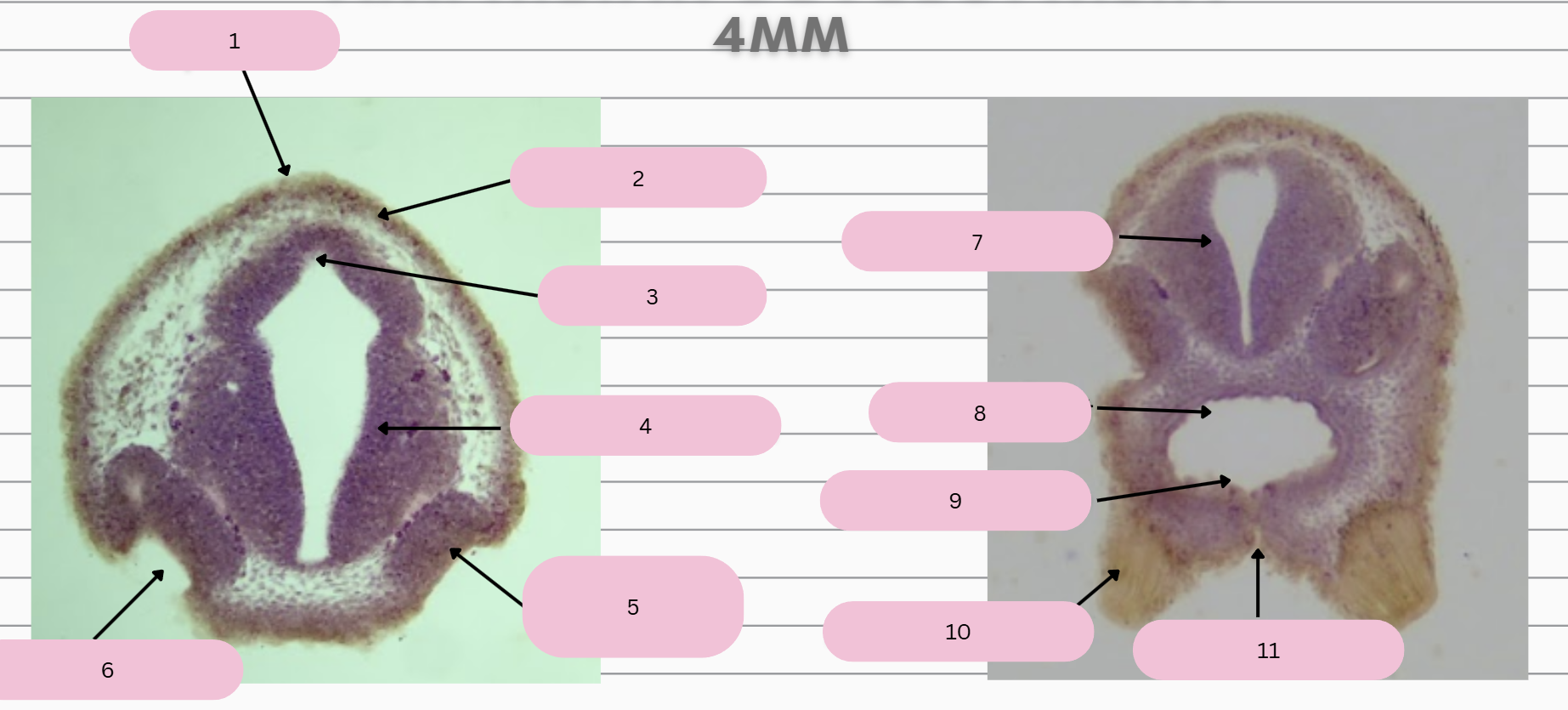
Olfactory Pit
What structure is in 6?
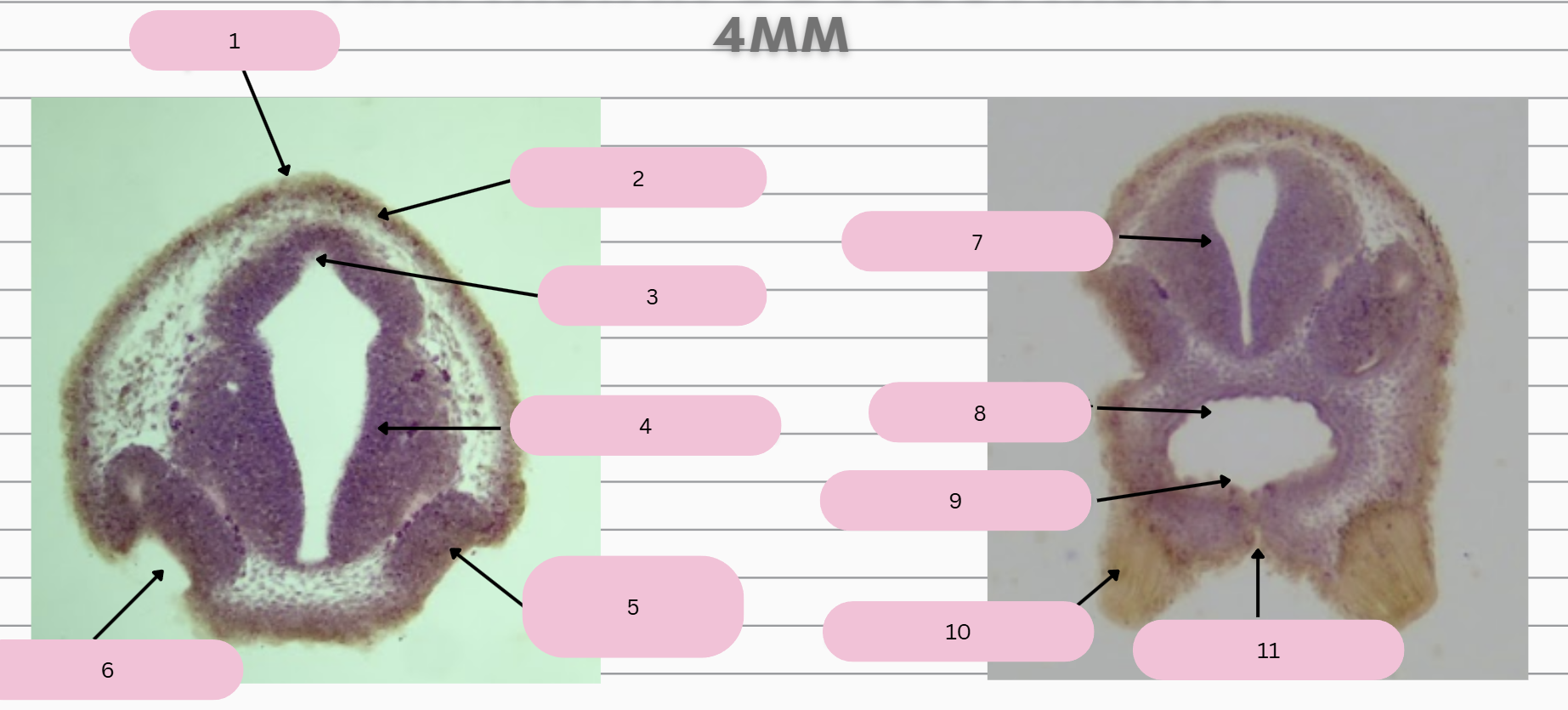
Prosencephalon
What structure is in 7?
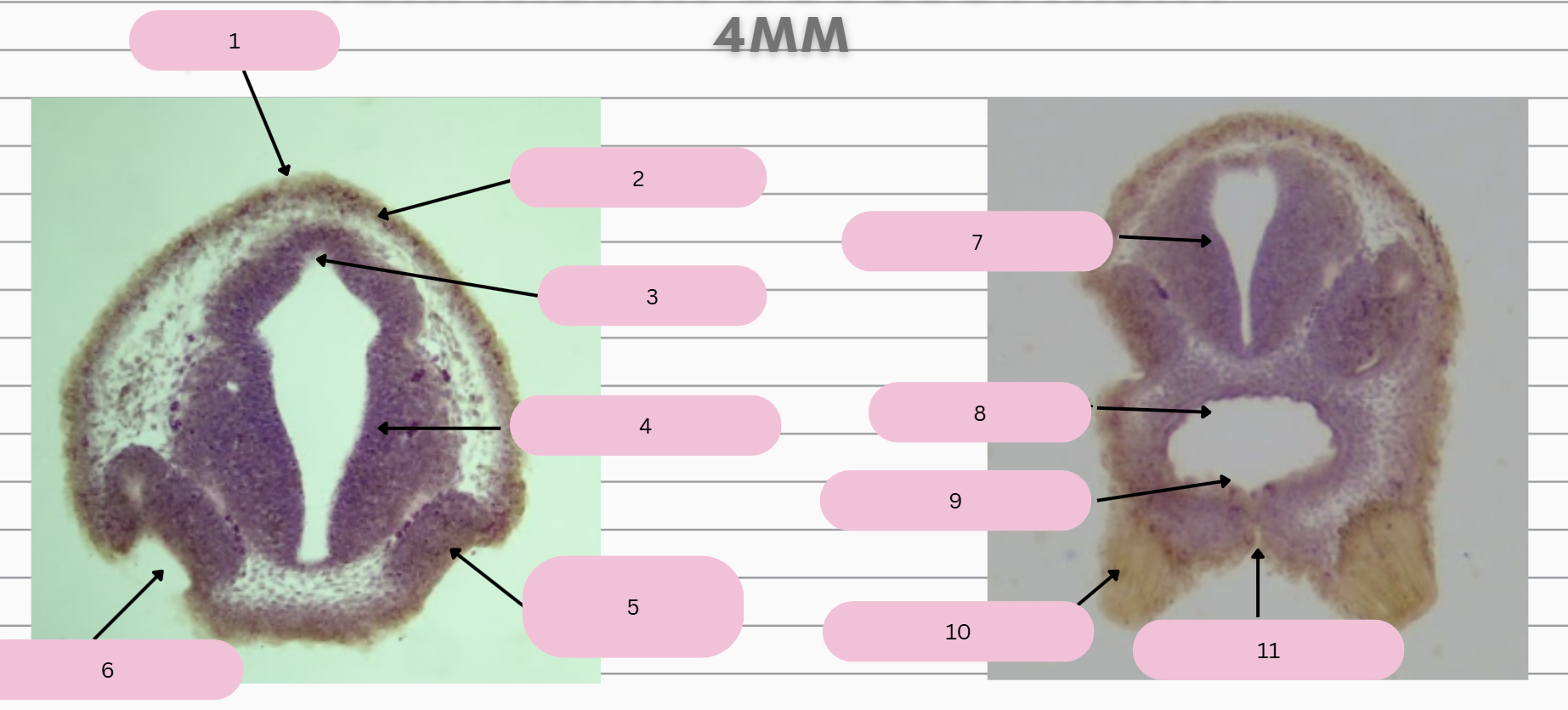
Foregut
What structure is in 8?
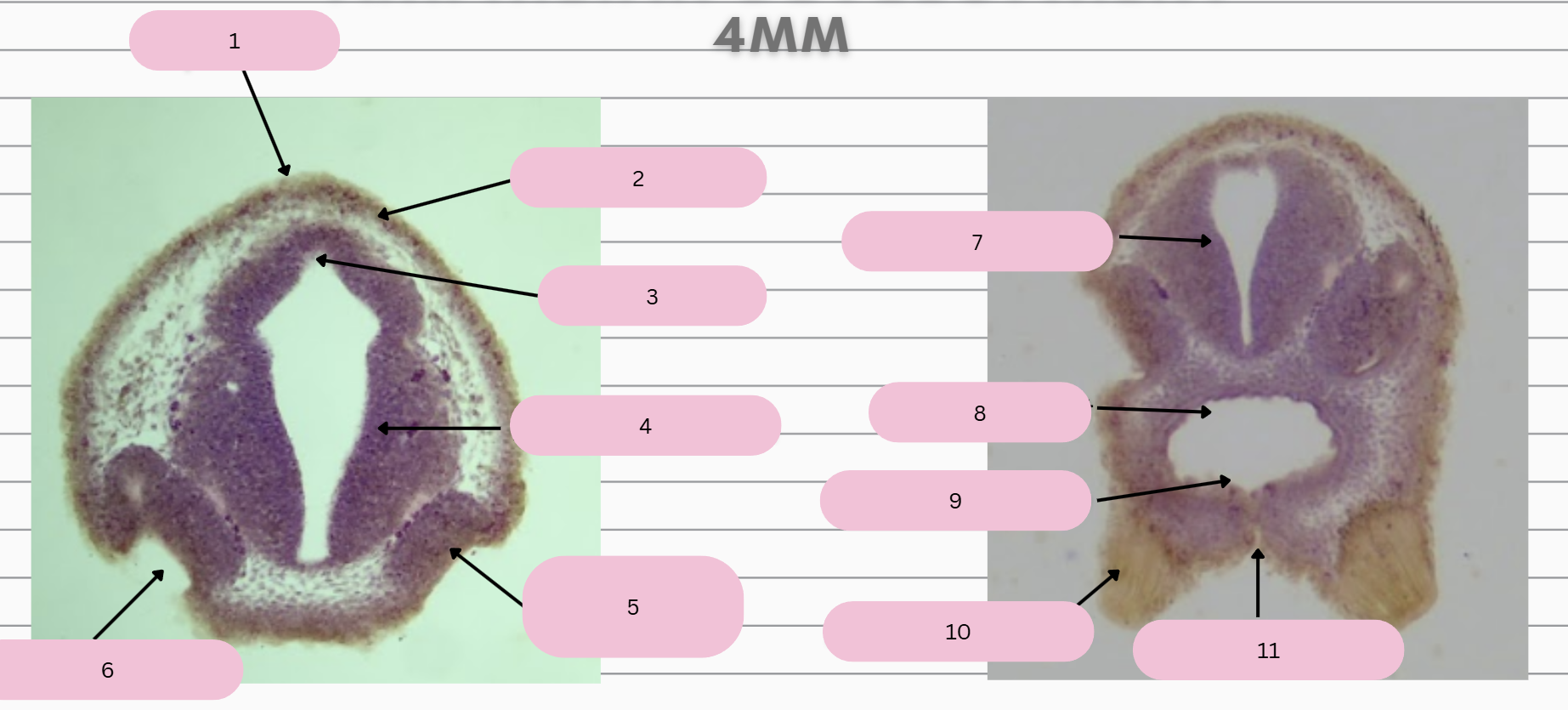
Oral Membrane
What structure is in 9?
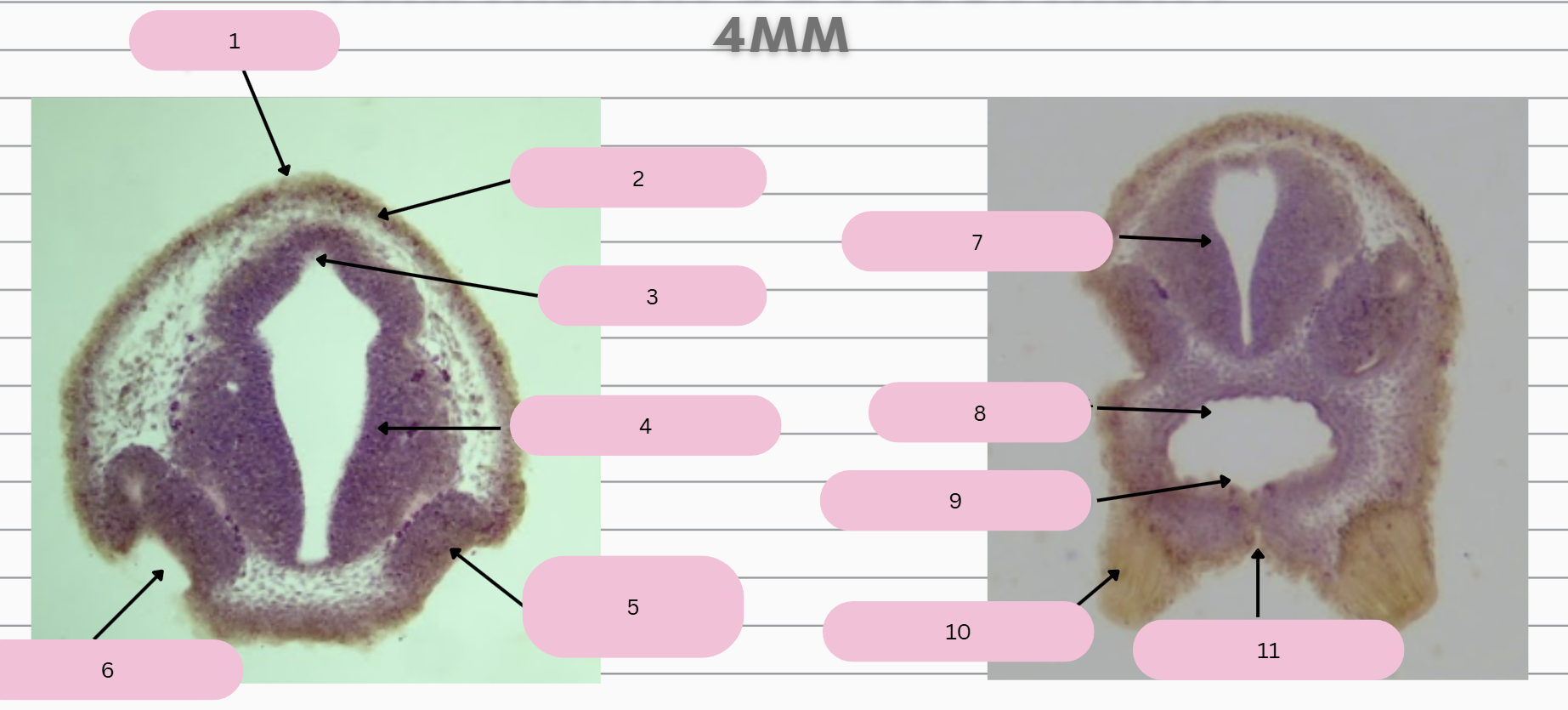
Adhesive Gland
What structure is in 10?
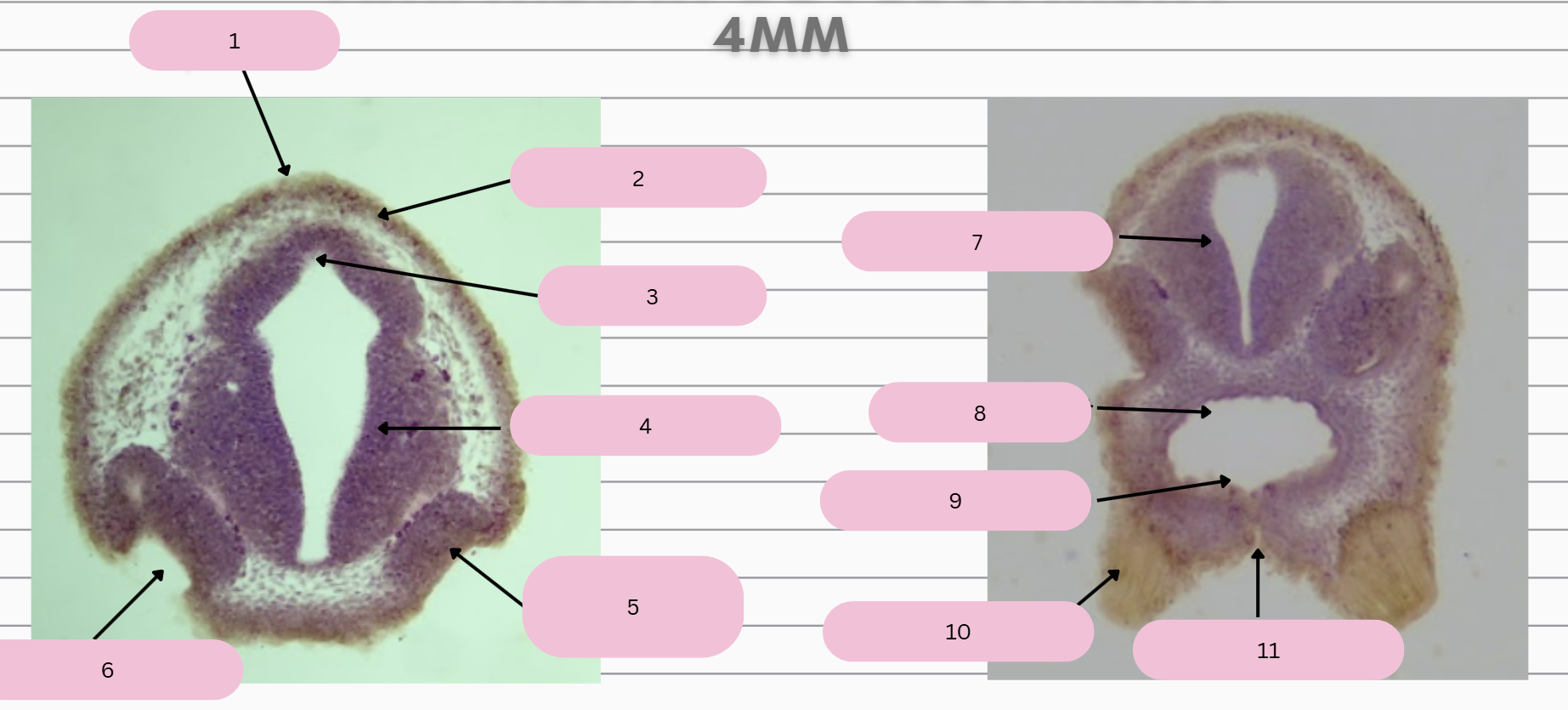
Stomodeum
What structure is in 11?