m370 final
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
three types of consumer products
development, design, and sale
core customer value
defines the basic problem-solving benefits that customers are seeking
actual product
includes the name, quality, communication, packaging design, and features
associated services (augmented prodcut)
ex amazon has no risk because you can return if you don’t like
include non physical aspects of product such as warranties financing product support and after sale service
product complexity
degree of difficulty involved in designing manufacturing selling and maintaining a product
arises from the number of components interdependencies among parts or functions and variety in configurations or versions of a product
product complexity core dilemma
should a firm simplify its product offerings and risk losing variety driven customers or embrace complexity and risk inefficiency and brand dilution
four steps a company must take when determining how complex to make their product
identify and compare product complexity sources
evaluate strategic trade-offs
customer perception
broader implications
ex of first step to determine how complex to make product (identify and compare product complexity sources)
apple: fewer models, standardized components, simple externally, minimal product variety but strong ecosystem lock in
samsung: wide range of skus and price points, frequence updates, compelx supply chains and overlapping features
step 2 example (evaluate strategic trade-offs)
apple: dependent on few skus, strong brand coherence, focused, lower operational complexity
samsung: faster iteration and feature adoption, broader market coverage, cannibalization, brand fragmentation
step 3 example (customer perception)
how do customers perceive apple and samsung differently
how does perceived simplicity influence brand equity
step 4 ex (understand broader implications)
complexity might increase coordination cost or hinder agility
simplicity might improve quality control and brand consistency
complexity might allow market segmentation and technological leader
types of consumer products
products and services used by people for their personal use
specialty, shopping, convenience, unsought
specialty product dimensions
high end, willing to make a special purchasing effort- few substitutes
brand loyalty: very high
price sensitivity: low
distribution: limited
purchase frequency: low
promotion strategy: image based, prestige, emotional
shopping product dimensions
consumer behavior: buyers compare options carefully before deciding
price sensitivity: moderate to high (consumers look for value)
purchase frequency: less frequent than convenient goods
distribution: selective
promotion: focused on information, benefits, and value comparison
buying motive: functional and emotional (balanced)
convenience product feautres
purchase frequency: high
consumer effort: low little planning or comparison
price leve: low
brand loyalty: moderate (brand switching is common)
distribution: intensive - available in many outlets
promotion focus: top of mind awareness, impulse buying triggers
unsought product features
consumer awareness: low
purchase motivation: problem driven not desire
marketing challenge: must create or remind consumers of need
promotion strategy: heavy personal selling, direct marketing, reminders
distribution: varies
product mix product lines and product items
mix: complete set of products the company makes
lines: categorize every product into lines (ex: energy drink, bottled water, etc)
items: individual items that fix under the umbrella lines
breadth
number of product lines in a product mix
depth
number of products within a product line
increase depth ex
ex: adding new ice cream flavors etc
decrease depth ex
p&g eliminates cannibalization by eliminating slow moving products and introduce new products that have potential
increase breadth ex
add new product lines to capture new or evolving markets (ex: coke adding alcohol product line)
decrease breadth ex
a firm drops its line due to changing market conditions or internal strategic priorities (loreal doesn’t have mousse anymore because it’s not as popular)
difference between a brand and product
product is item or service for sale, while brand is intangible identiy and reputation built in the mind of consumers
a company manufactures a product, but consumers through their perceptions and experiences create the brand
what makes a brand
brand name, urls, logos and symbols, characters, slogans, jingles/sounds
why is it important for a brand to have value
facilitate purchases
move consumers to loyalty
protect from comp or price comp
asset value
affect marketplace value with wholesale/retail
brand value vs brand equity
equity: qualitative measure of consumer perception (brand’s value in minds of consumers)
value: quantitative financial metric (financial worth of a brand name)
important considerations in creating and increasing brand equity
brand awareness
perceived value
brand associations
loyalty
brand extension vs line extension
brand: same brand name in diff product line
line: same brand name within same product line
cobranding
partnership w other brands
why do business create new products
stay competitive and drive growth in evolving marketplace.
how do new products create value for a business

how do new products create value for a customer

innovation segmentation
the category already exists: a completely new product that your business has never made or sold before to compete w others
the category doesnt exist: a completley new product innovation created and brought to the marketplace that doesn’t exist yet
already in market: they may be existing products that you have modified or improved
degree of innovation is based on the risk ( line extension, brand extension, and true innovation)

diffusion of innovation theory

diffusion of innovation curve
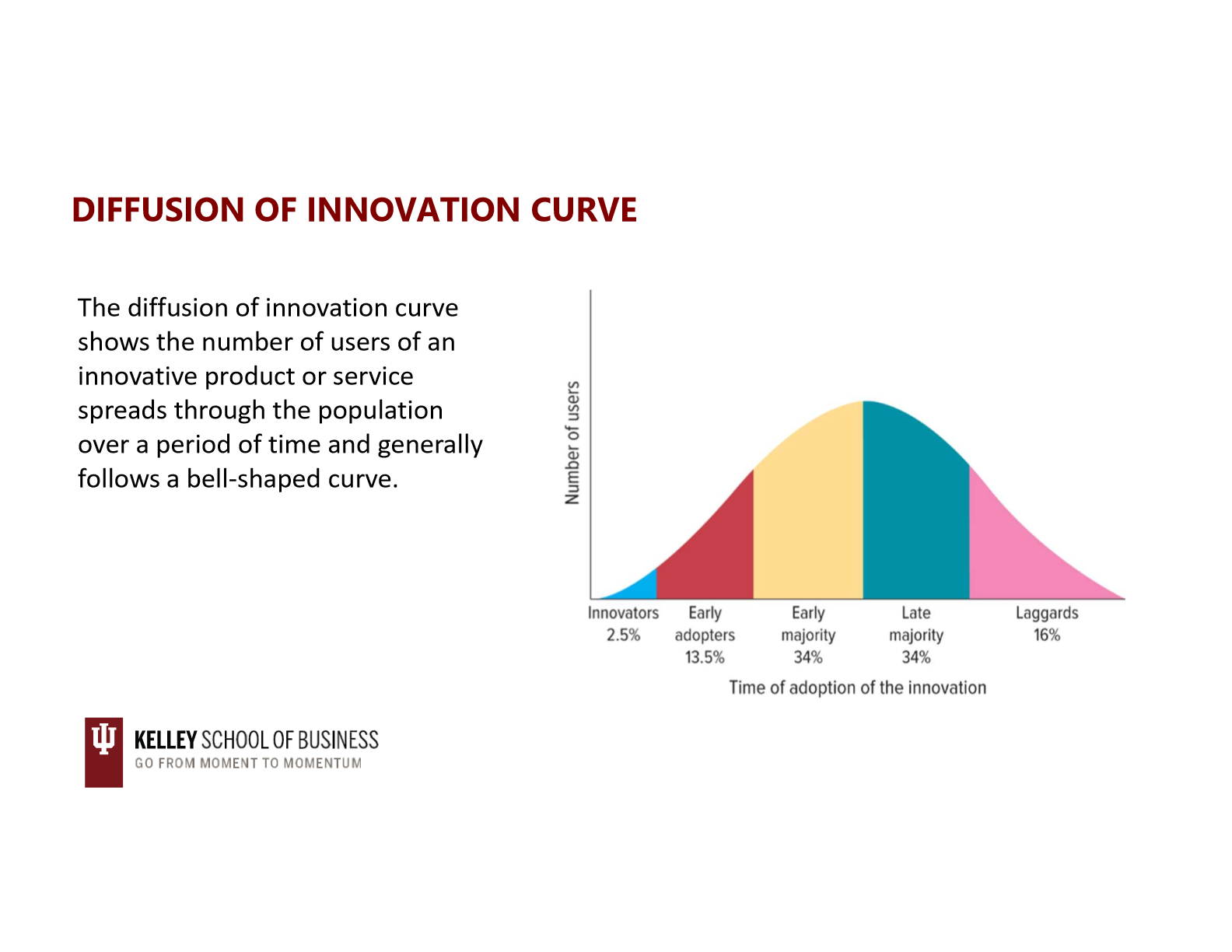
diffusion of innovation curve- innovators

diffusion of innovation curve- early adopters

diffusion of innovation curve- early majority

diffusion of innovation curve- late majority

diffusion of innovation curve- laggards
pro

proudct development process
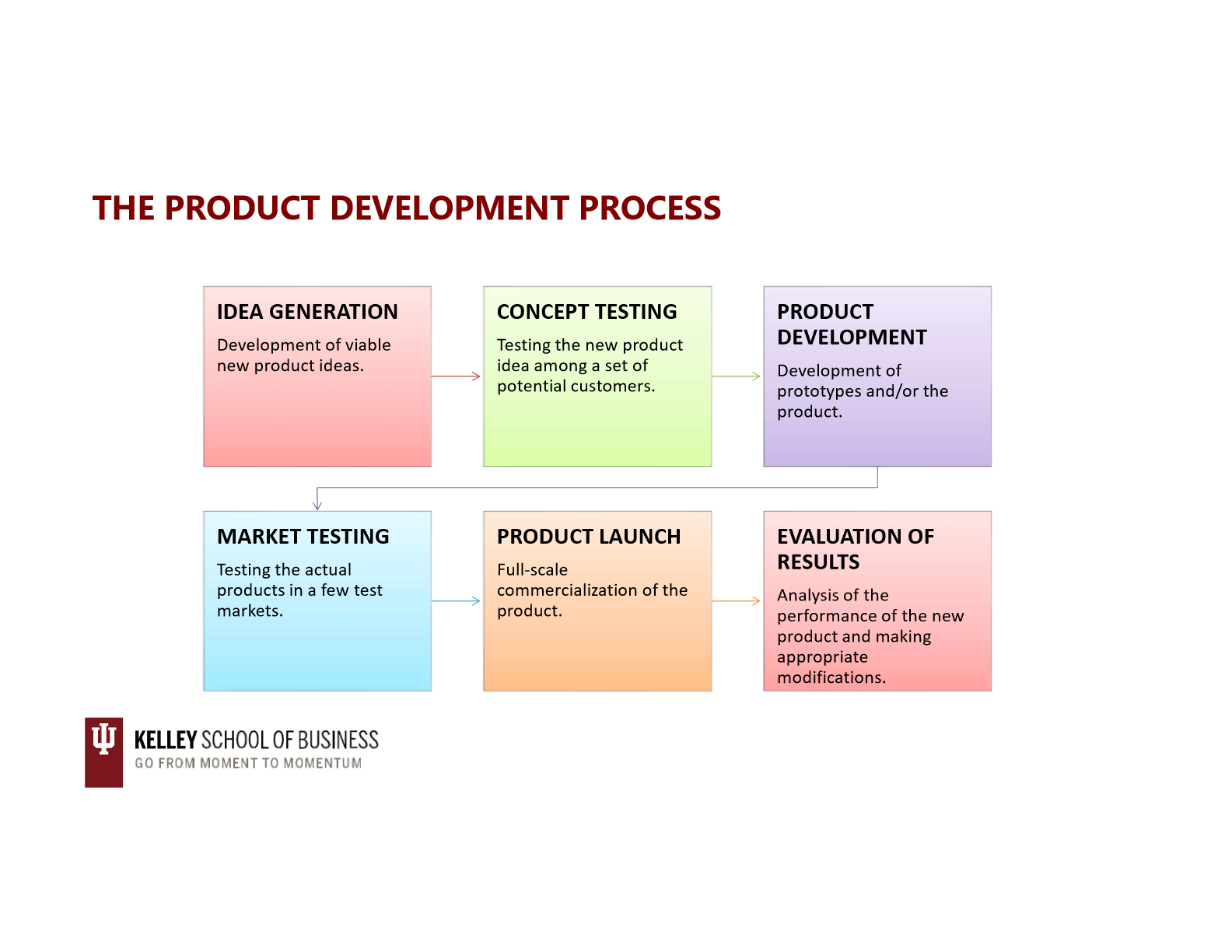
idea generation: sources of ideas
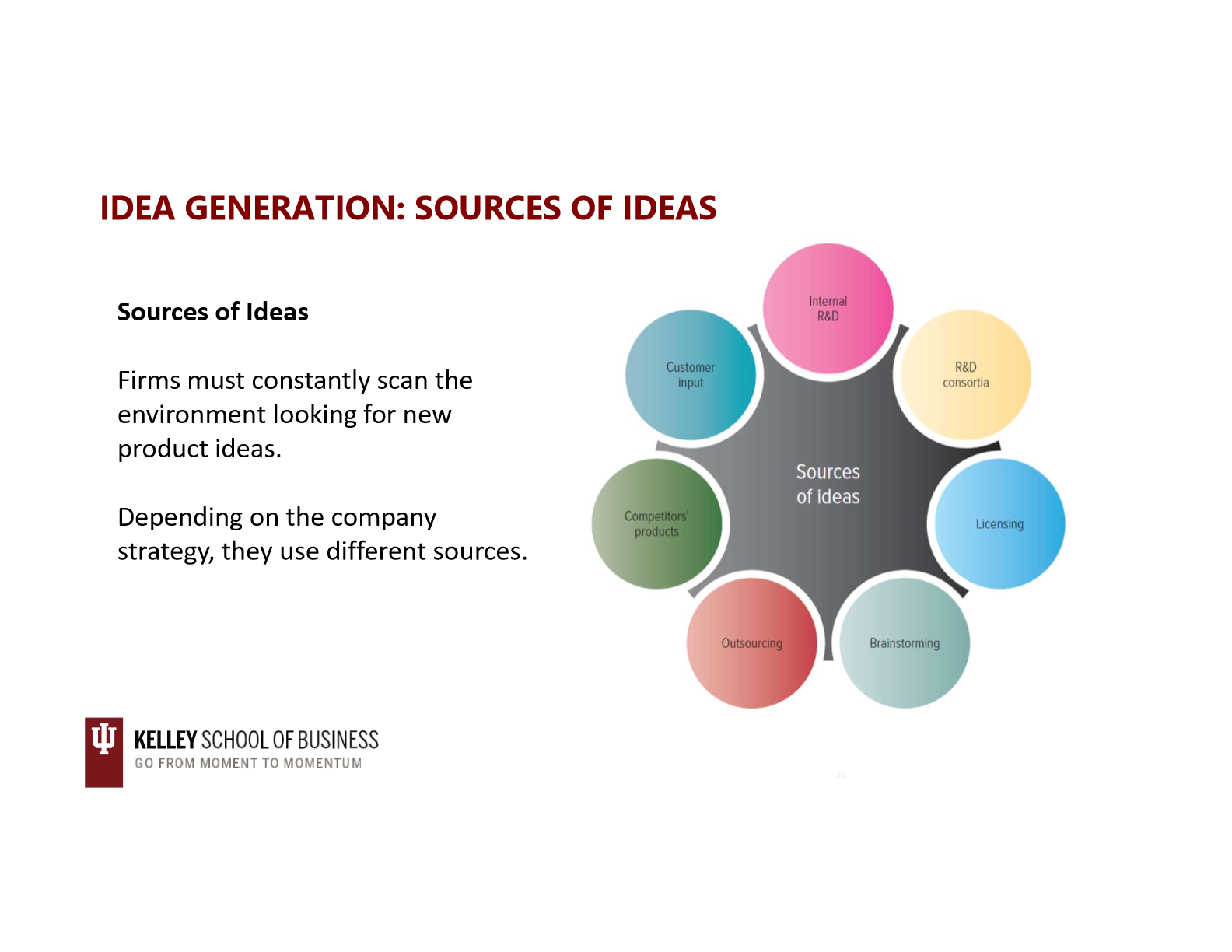
idea generation: internal r+d

idea generation: r+d consortia

idea generation: licensing

idea generation: brainstorming

idea generation: outsourcing
hiring an outside firm to help generate ideas and develop new products and services
idea generation: competitors products
products w patents or other proprietary protections cannot be copied so reverse engineered products must be substantively different from their source product
idea generation: consumer input

the product development process: concept testing

the product development process
at this stage, an engineering team develops a product prototype that is based on research findings from previous conecept testing steps
product development process (internal and external)
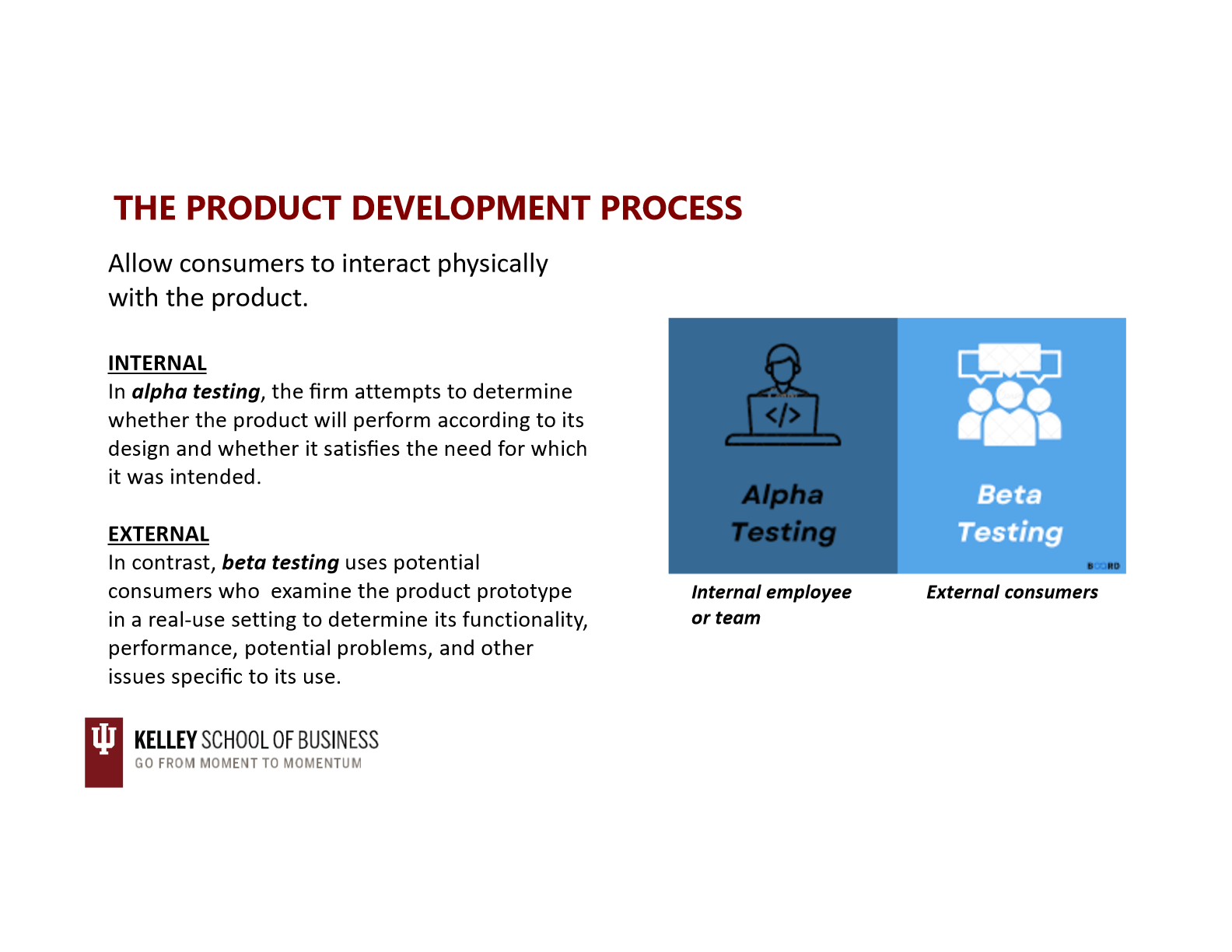
product development process: market testing
premarket tests:
customers exposed
customers surveryed
firms makes decision
test marketing (considerations: type of innovation, confidentiality)
mini product launch
more expensive
demand is estimated
the product development process: product launch
this step requires tremendous financial resources and extensive coordination of all aspects of the marketing mix. the firm confirms its target markets, decides how the product will be positioned, finalizes the remaining marketing mix variables, and determines the marketing budget. timing of the launch may be critical
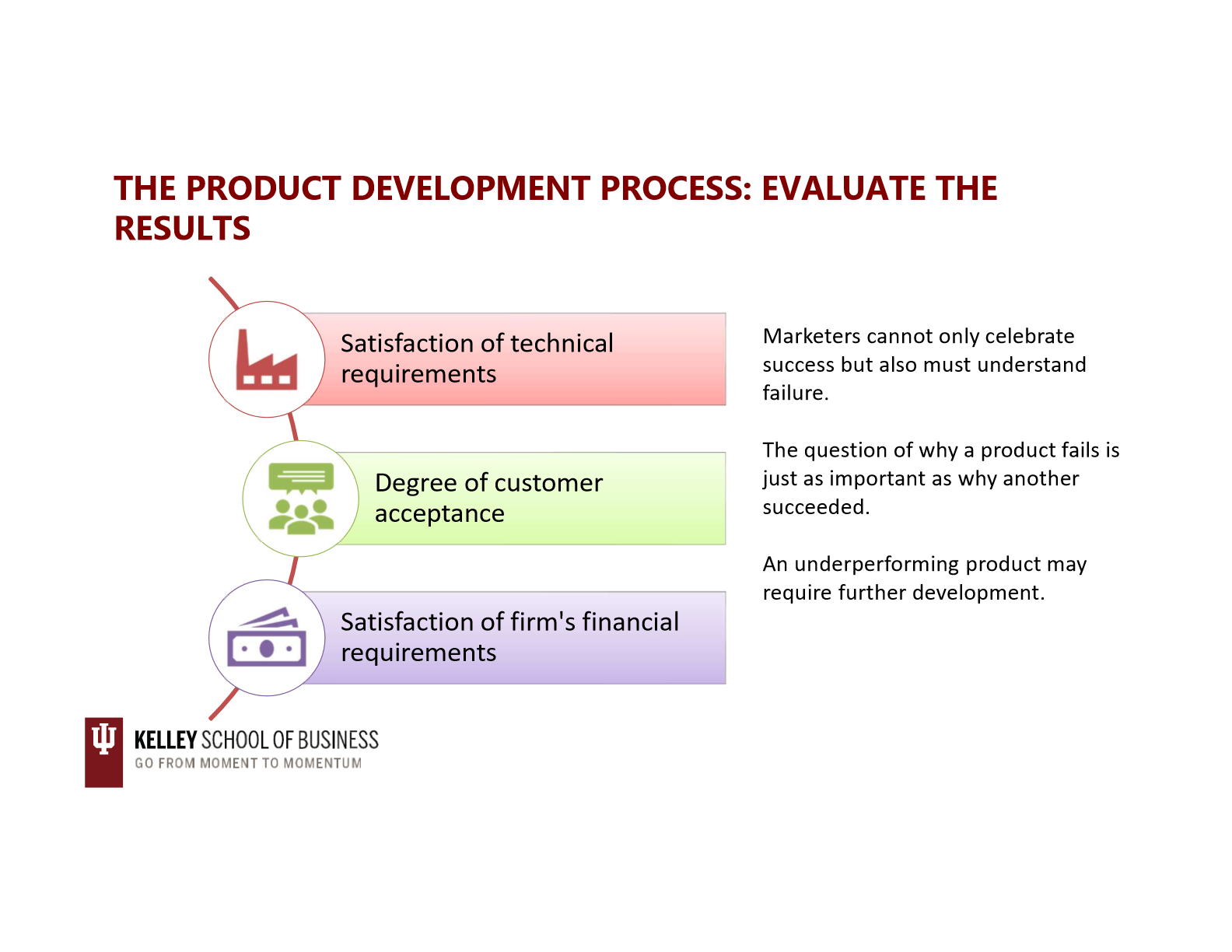
product development process: evaluate the results
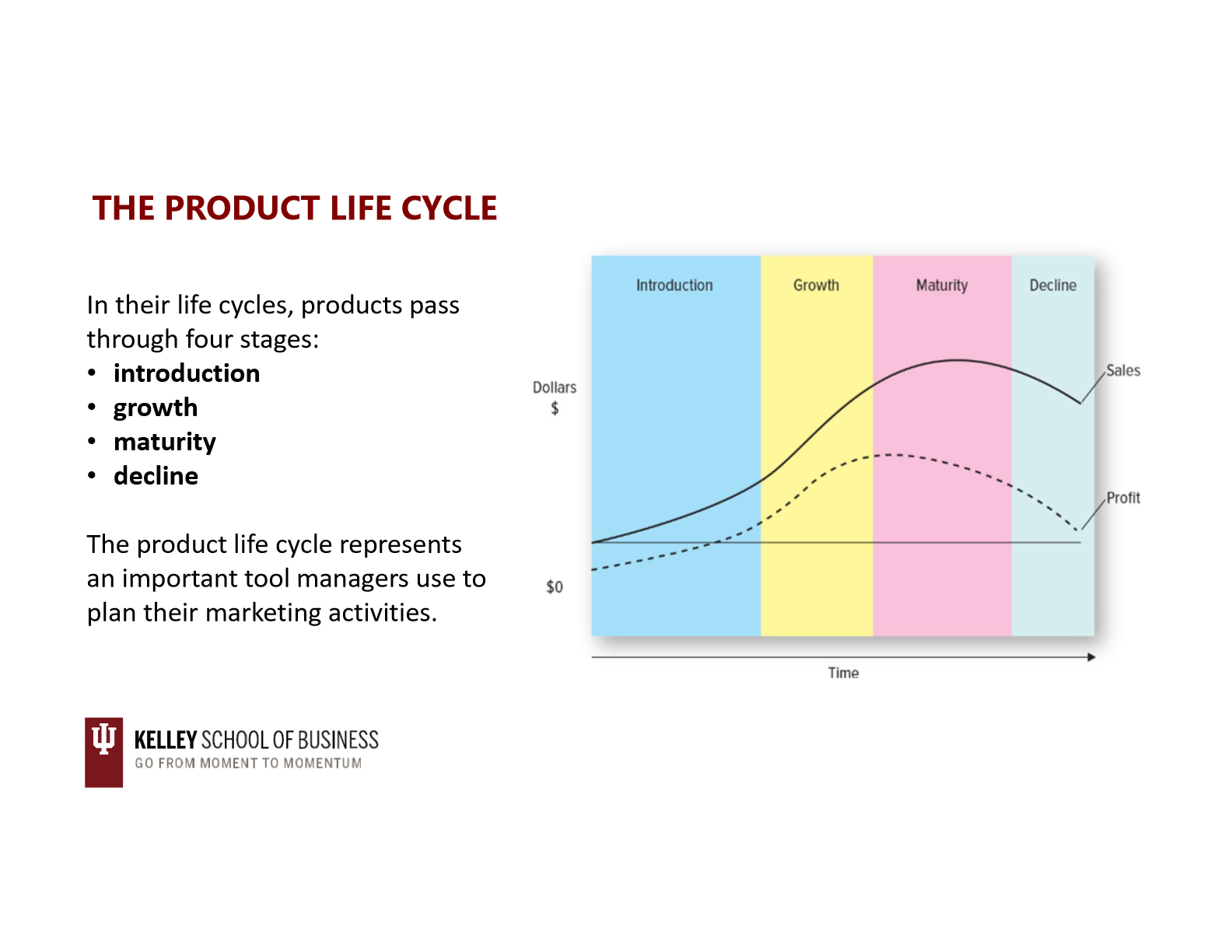
the product life cycle (4)
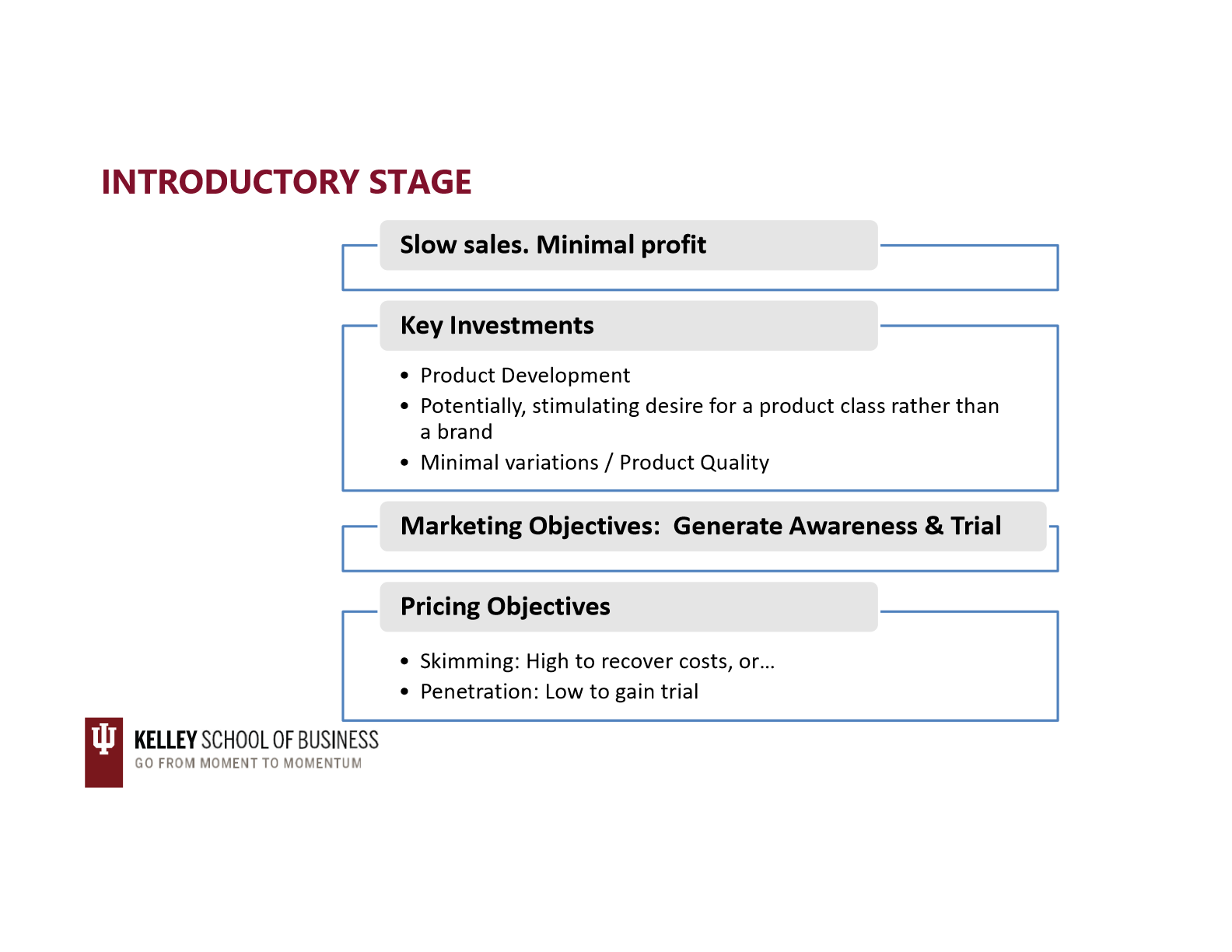
introductory stage
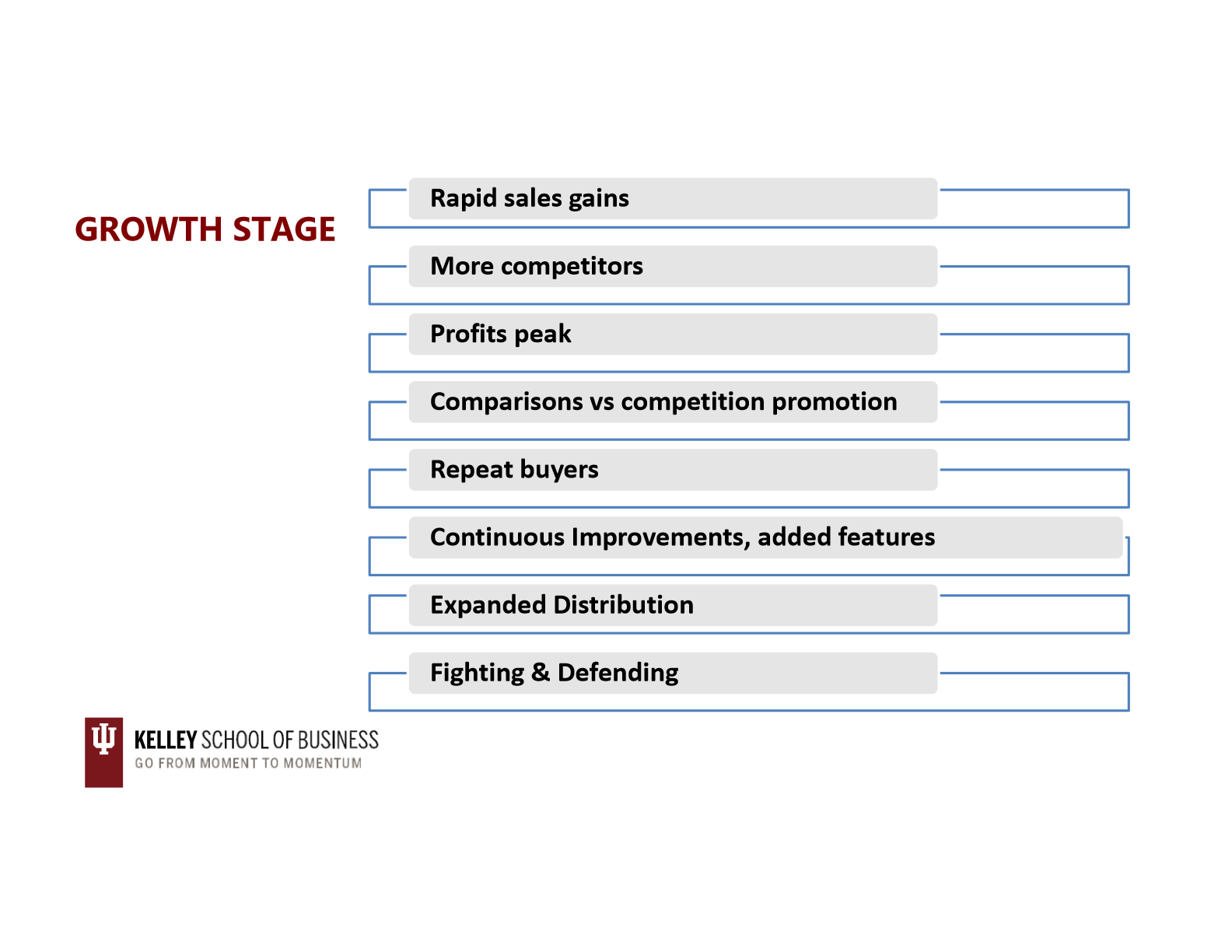
growth stage
marked by a growing number of product adopters, rapid growth in industry sales, and increased in the number of competitors and the number of available product versions. majority of new products fail at thsi point
the maturity stage

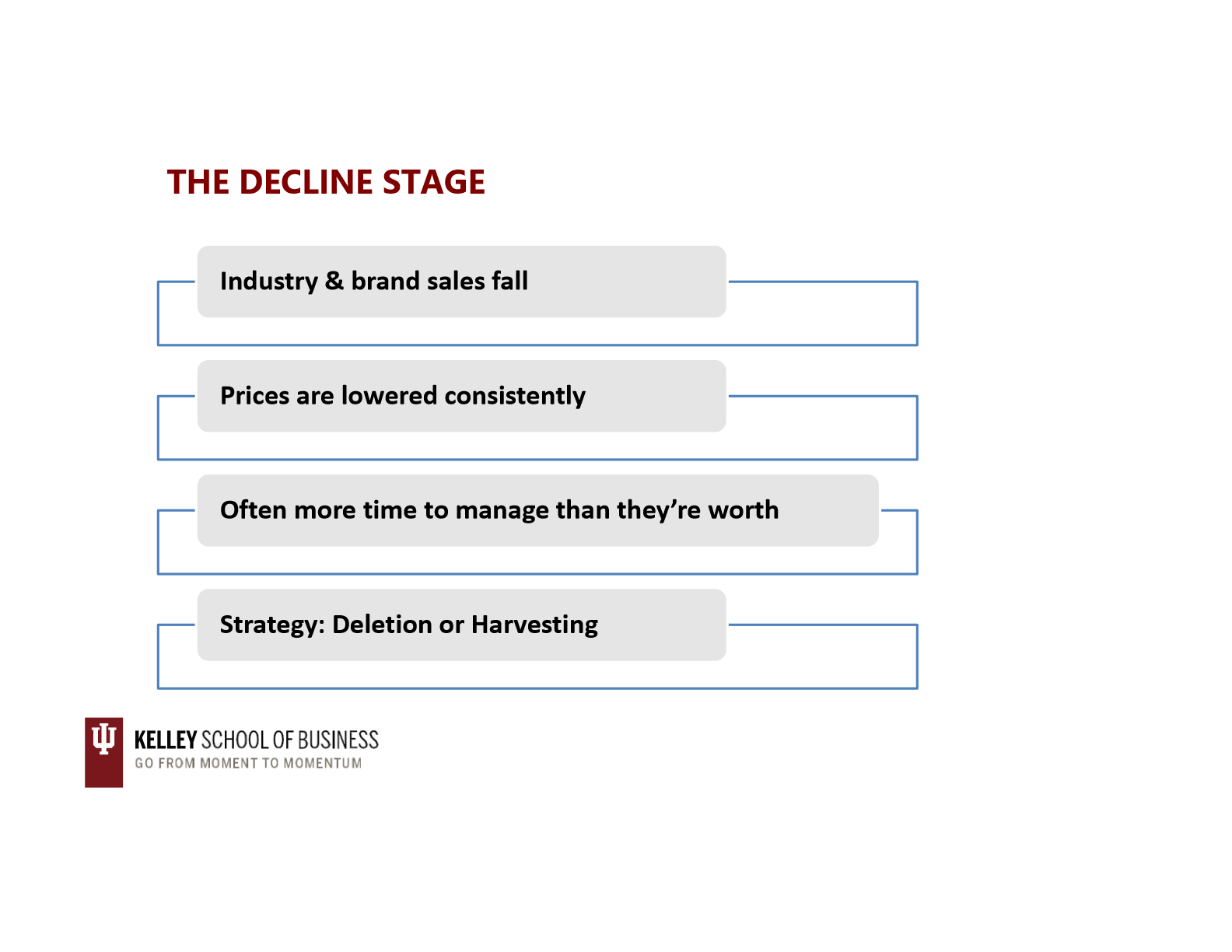
decline stage
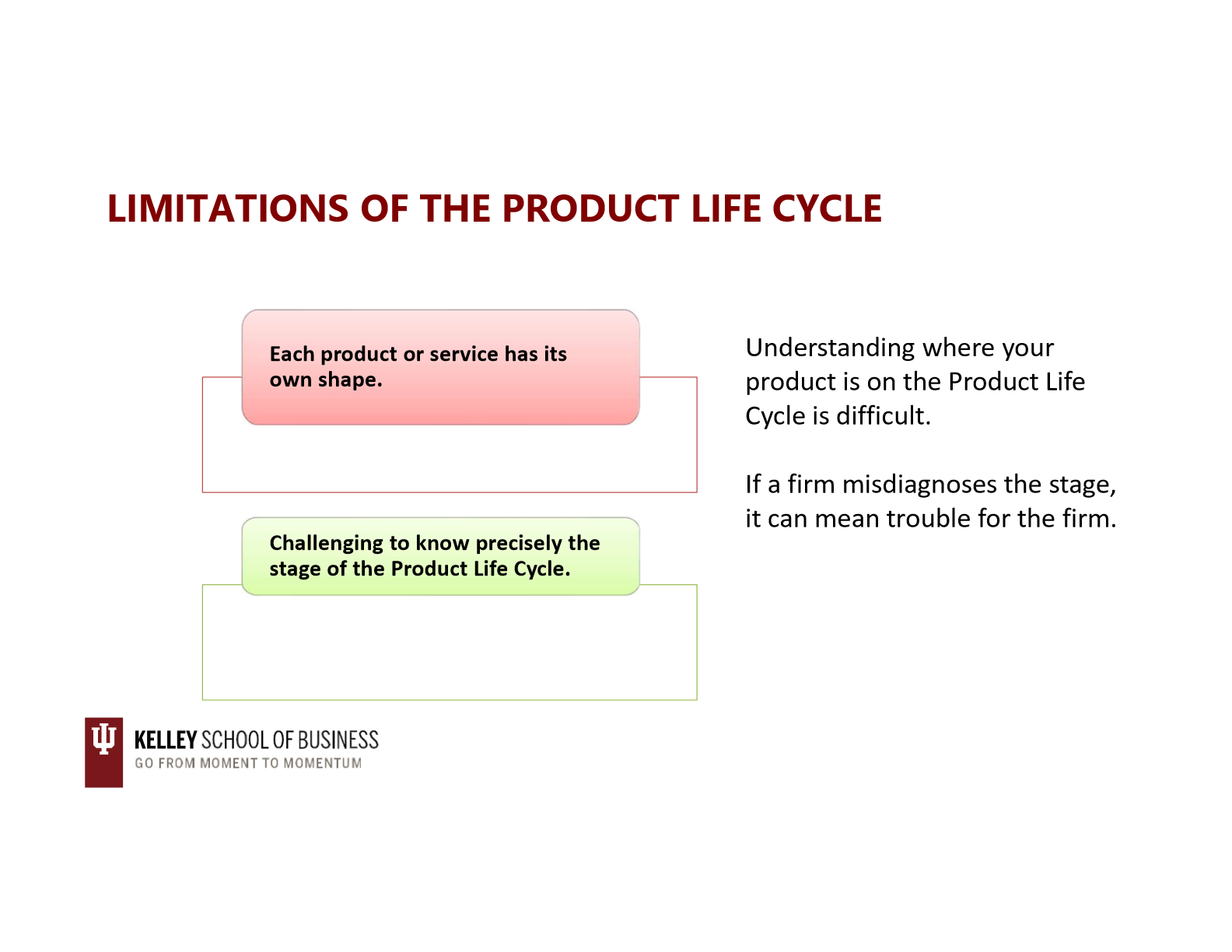
limitations of the product life cycle
5 questions that marketing answers

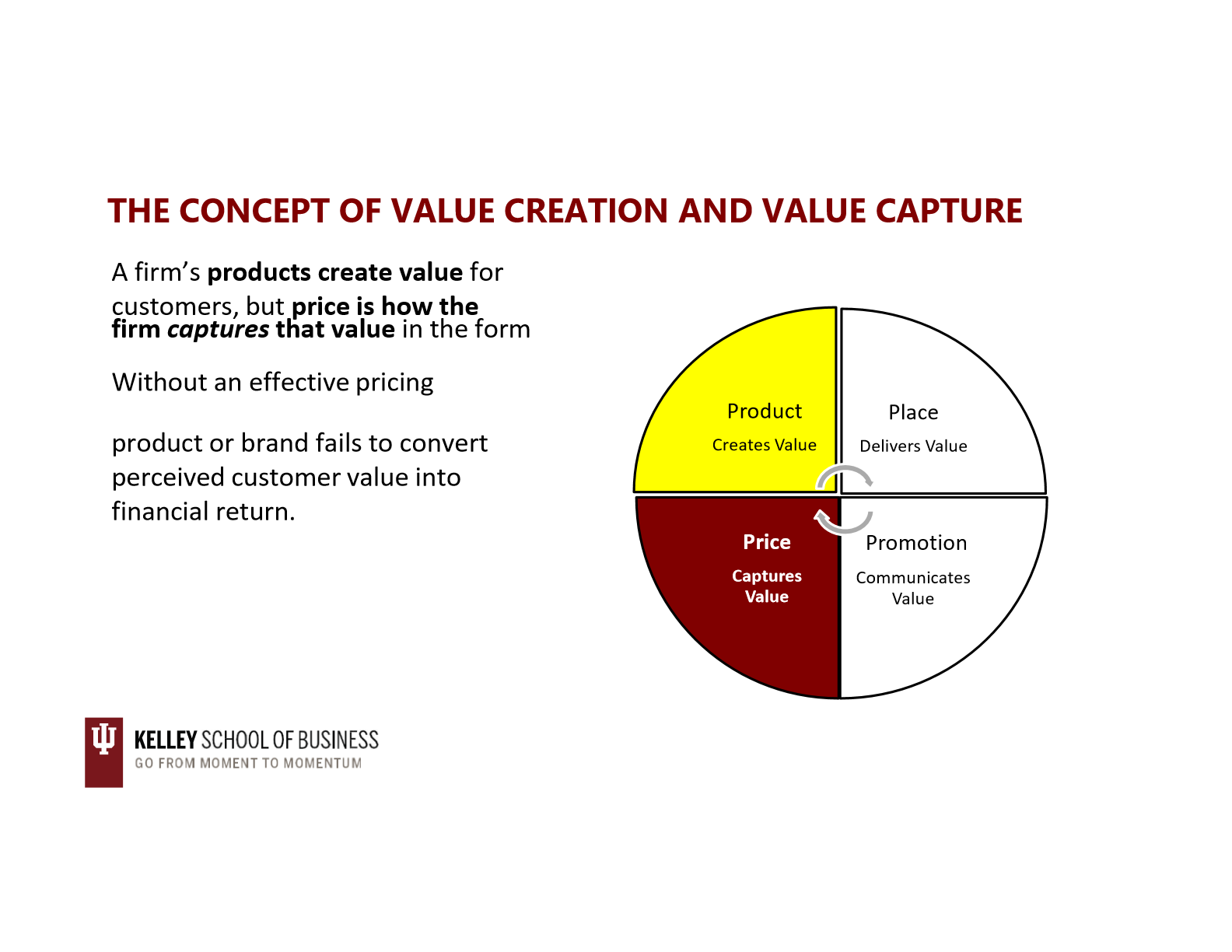
concept of value creation and value capture
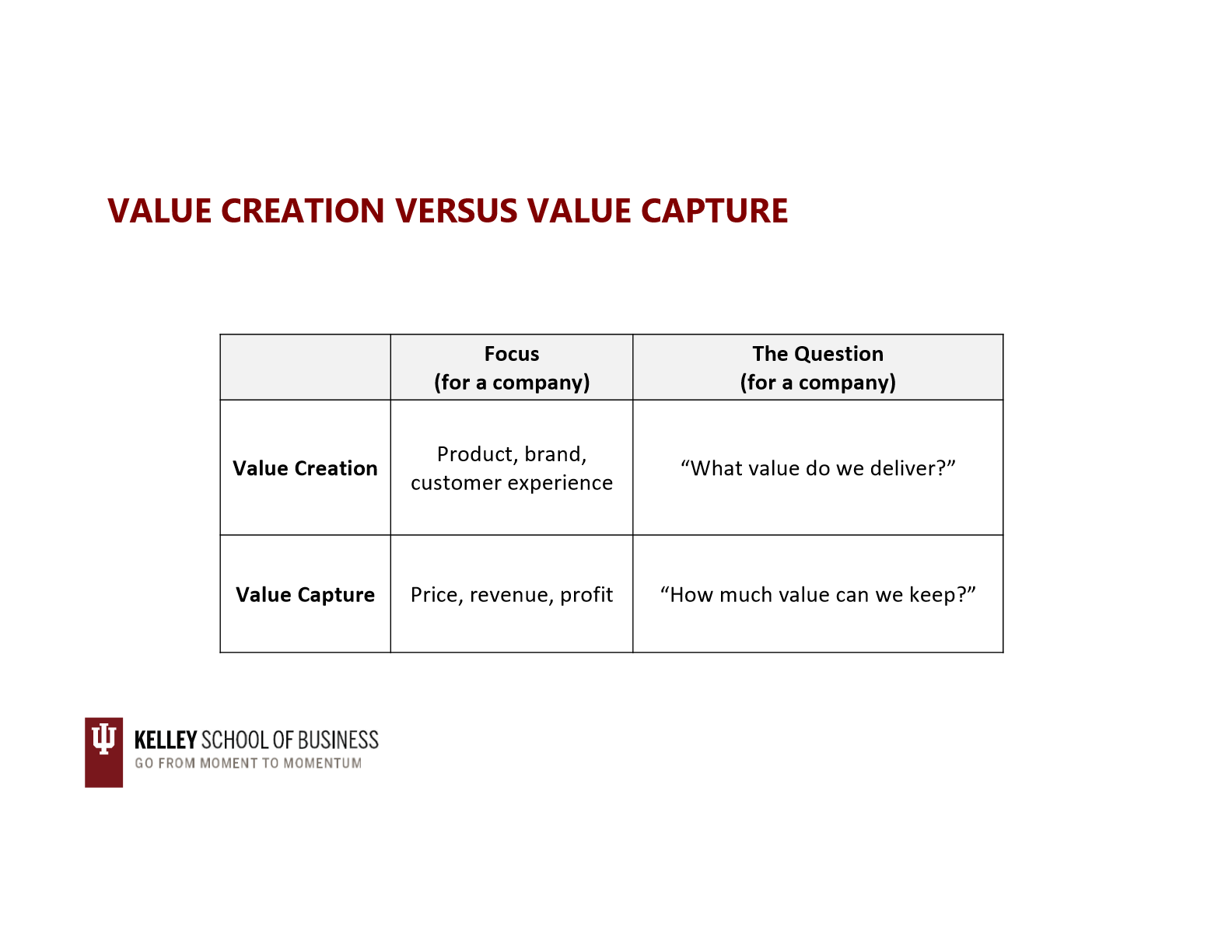
value creation vs value capture
the role of price for a company (1)
price links customer value to company value
customers express willingness to pay based on perceived benefits
companies translate that willingness into a price that covers cost + returns a profit
customer/producer surplus
a company can capture value when its price is less than a customer’s perceived value, but greater than a firm’s cost.
customer surplus= perceived value-price
producer surplus= price-cost
ex: if perceived value is $100 and cost is $60, a price of $80 gives: customer surp: $20 and producer surp; $20
role of price for a company (2)
price is the revenue driver
among the 4ps price is the only one that generates income, the others create costss
role of price for a company (3)
price signals quality and positioning
a premium price can reinforce a premium image
the price value relationship
key question comps must answer pos for the customer: do you get equal or more value than you give up in money
corporate internal considerations or why company’s set price a certain way (6 corp objects)

a targeted profit return objective:

a sales revenue objective:

a market share objective:

a unit sales objective:

a survival objective:

a responsibility objective:

pricing strategy or how company’s set price (4)

demand oriented: skimming
skimming: start high, end lower

demand oriented: penetration pricing
start lower, maintain or raise price.

penetration pricing

demand oriented: value based pricing

demand oriented: presitge pricing

demand oriented: yield management

yield managmenet ex
uber uses surge pricing during peak ride times
cost oriented: standard mark up

whys standard mark up used
retailers can’t accurately estimate demand for all their products, so demand can’t be basis for setting price
cost oriented: loss leader

cost oriented: cost plus

profit oriented: target profit

benefits of target profit pricing

profit oriented: target ROS

benefits of target return on sales pricing

profit oriented: target ROI

competition based: customary pricing

competition based: everyday low price (EDLP)
no fluctuation in pricing as an enticement to customers
competition based: high low pricing
multiple tiers of pricing
often controlled by the manufacturer
limited risk for the retailer
the psychology behind setting the final price

strategic questions you need to answer before lowering price
what’s the goal of the cut: volume, share, survival
how will competitors respond
will customers perceive lower price as lower value
can we maintain profitability at lower price
are there other non-price alternatives that we can implement instead