Lec 2 - Pathology of the Esophagus & Stomach
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
T/F: The majority of the esophagus does not have a serosal layer.
TRUE
What are the 2 routes of infection of the esophagus?
ingestion
penetration
What is achalasia?
esophageal motility disorder → failure of sphincters to relax
What is cricopharyngeal achalasia?
congential disorder of upper esophageal (cricopharyngeal) sphincter
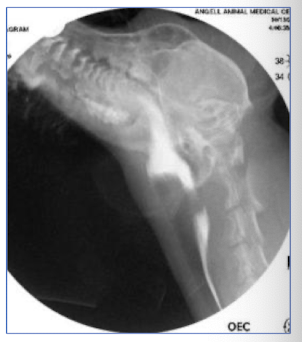
When are you most likely to see congential cricopharyngeal achalasia?
young, small breed dogs (terriers, cockers, mini poodles)
postweaning dysphagia (regurg of solid food, gagging, choking)
T/F: Acquired achalasia is fairly common.
FALSE - typically associated with abnormalilities in cricopharyngeal muscle (fibrosis, muscular hypertrophy or atrophy, myositis
What is megaesophagus and what does it result in?
dilation of the esophagus → insufficient, absent, or uncoordinated peristalsis
What 3 things cause megaesophagus?
innervation/denervation disorders
partial physical obstruction/ stenosis
idopathic
When is megaesophagus usually suspected clinically?
regurgitation after ingestion of solid food → malnutrition, rhinitis & aspiration pneumonia
What is regurgitation?
contents of the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus are expelled
What happens during regurgitation?
gagging, coughing, NO ABDOMINAL EFFORT
What does regurgitation look like?
food undigested ± covered with mucus
often tubular
What is vomiting?
contents of the stomach & upper intestine are forcefully ejected
What happens during vomiting?
ptyalism, nervous behavior, borborygmi, ABDOMINAL EFFORT, heaving retching
What does vomit look like?
food may contain bile, usually digested
What are the 2 forms of congenital megaesophagus?
persistent right 4th aortic arch
congenital idiopathic megaesophagus
A persistent right fourth aortic arch is formed by what structures?
vascular ring of aorta, pulmonary artery, & ductus arteriosus
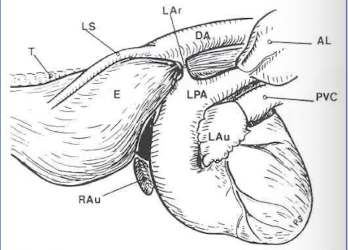
Dilation of the esophagus due to a persisent right fourth aortic arch occurs ________ to the heart.
cranial
What breeds are genetically predisposed to a persisten right fourth aortic arch?
GSD, Irish Setters, German Pinscher, Boston Terrier, Greyhounds
T/F: A persistent right fourth aortic arch may be incomplete & diagnosed before 1 year of age.
FALSE - may be diagnosed after one year of age
What is thought to be responsible for congenital idiopathic megaesophagus?
idiopathic denervation
Which breeds are associated with congenital idiopathic megaesophagus?
Great Danes, Irish Setters, Mini Schnuazers, Labs
Can megaesophagus be acquired? Is this common?
yes
no
What is the major form of acquired megaesophagus?
esophageal achalasia → failure of relaxation of the distal esophageal (cardic) sphincter
Dilation of the esophagus secondary to esophageal achalasia occurs _________ to the stomach.
cranial
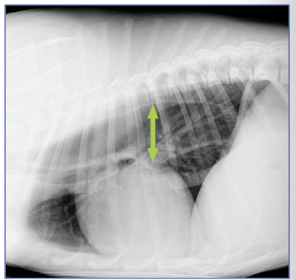
What are the 5 main causes of esophageal achalasia?
idopathic → GSD, Goldens, Irish Setters
secondary to polymyositis or inflammation
myasthenia gravis → NM Ach receptors
hypothyroidism
lead & thallium toxicity
What are the 2 main causes of esophagitis?
gastric reflux → anesthesia, chronic vomiting
viral esophagitis → erosive/ulcerative, feline calicivirus
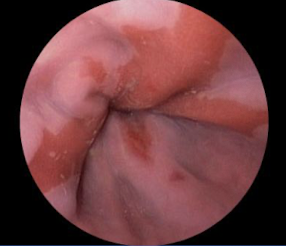
Inflammation and ulceration of the esophagus may lead to _______.
strictures
most common 2o to anesthesia
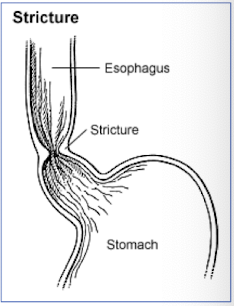
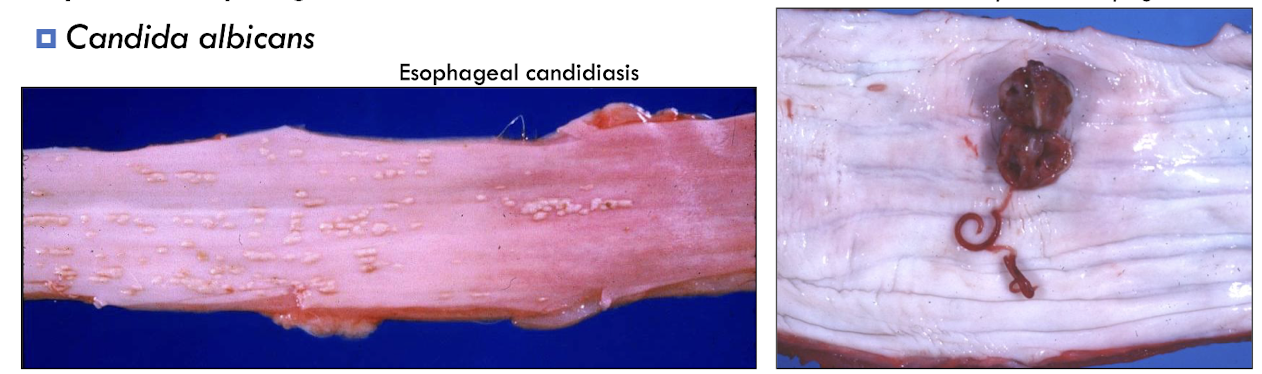
What are 2 less common causes of esophagitis?
parasites → Spirocerca lupi form cystic granuloma
fungal → Candida albicans (thrush)
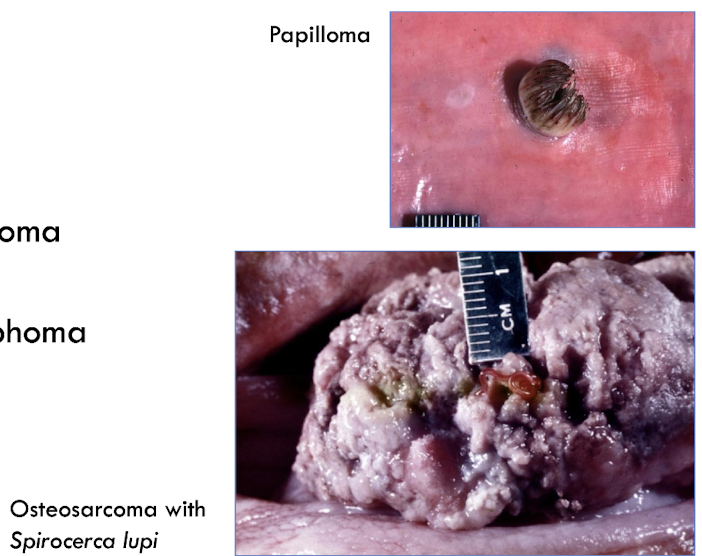
What are the 4 main neoplasms that can affect the esophagus?
papillomas
squamous cell carcinoma (very rare)
fibroma, fibrosarcoma, osteosarcoma (Spirocerca lupi)
leiomyoma/sarcoma, lymphoma (rare)
What are 2 causes of gastric dilation?
young puppies after overeating
source of distending gas (aerophagia), fluid, or food → obstruction of cardia & pylorus
What types of dogs are at risk of developing GDV?
large, deep chested breeds (Danes, St. Bernards, Irish Setters, Wolfhounds, etc)
What is the “formula” of events that leads to a GDV?
lax gastrohepatic ligament + overfeeding, postprandial exercise + other predisposing factors
The stomach rotates ________ on the __________ axis when view from the _______ surface.
clockwise
ventrodorsal
ventral
Rotation of the stomach during a GDV is about _______ degrees.
180-360
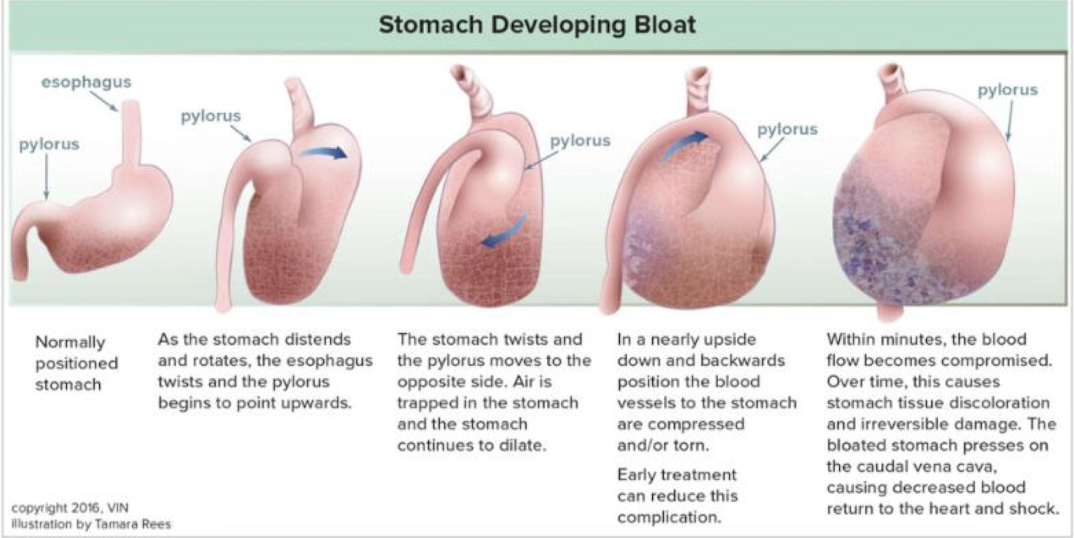
What other organs can be affected by a GDV?
twisted esophagus
vascular compression → HYPOXIA
What are the chain of events following an unresolved GDV?
gastric hypoxia, acid-base imbalance, antiperistaltic waves → atony, cardiovascular ischemia, arrythmia, shock
pancreatic ischemia → myocardial depressant factor → cardiovascular collapse → DEATH
Gastritis is associated clinically with what signs?
vomiting, dehyrdation, metabolic acidosis
What are the 2 main causes of gastritis?
dietary indiscretion
generalized gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases (food allergies, idiopathic IBD)
What types of pathogens can lead to gastritis?
Bacterial → Heliobacter spp maybe
Fungal → Histoplasma capsulatum, Pythium insidiosum
Parasitic → T. canis, Physaloptera spp, Gnathostoma, Cylicospirura felineus, Ollulanus tricupsis (cats)
Idopathic → scirrhous eosinophilic gastritis of dogs and cats
T/F: Chronic gastric ulcers have fibrosis/ regeneration.
TRUE
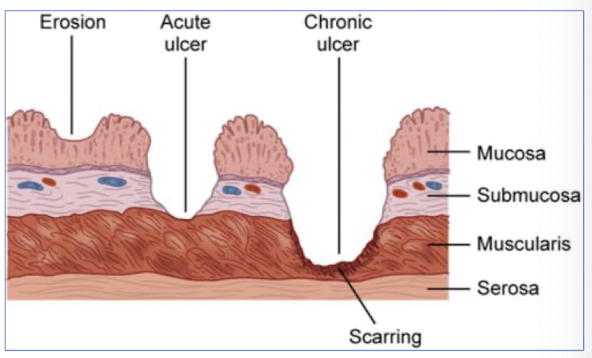
What clinical signs are associated with stomach ulcers?
vomiting (hematemesis), inappetence, abdominal pain, anemia, melena
What are some causes of gastric ulcers seen in small animals?
local disturbances in mucosal epithelial barrier, gastric acidity (hypersecretion), blood flow
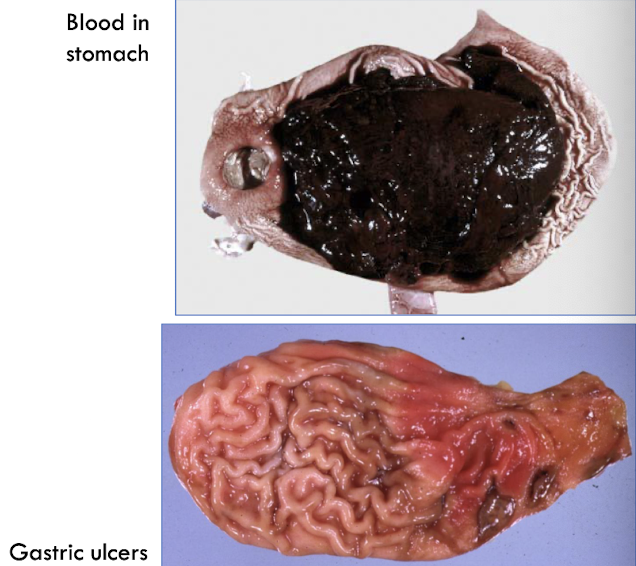
What are some specific causes of gastric ulcers?
steroids & NSAIDs, Helicobacter spp. (unclear), 2o to mast cell tumors (histamine release), gastrin secreting tumors (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome), idopathic
Uremic gastropathy is also known as ___________.
uremic gastritis
Uremic gastropathy is secondary to what disease?
chronic renal disease
can also see mineralization w 2o renal hyperparathyroidism
Uremic gastropathy is characterized by what?
mineralization of the glands, vessels (endothelium), & lamina propria of the gastric mucosa w/ thrombosis, hemorrhage, necrosis ± ulceration
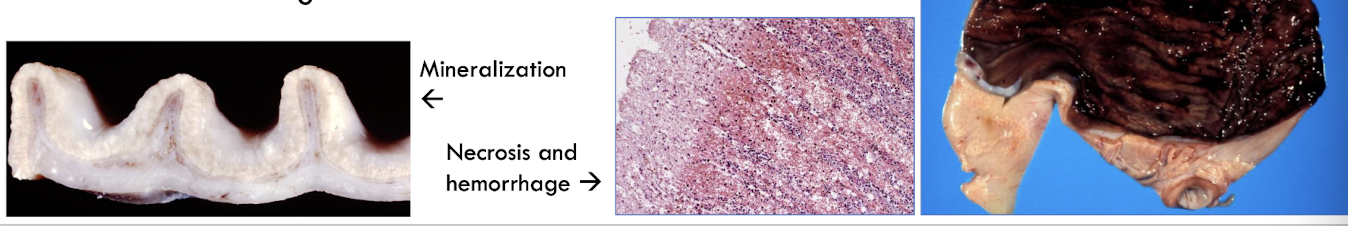
What clinical signs are associated with uremic gastropathy?
hemorrhage → hematemesis & melena