PSY3310 Lecture Notes on Prenatal Development and Early Cognition
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the PSY3310 lecture notes on prenatal development, perception, cognition, and findings from related journal articles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What provides a cushion for the developing embryo/fetus and also helps with temperature regulation?
Amnion/Amniotic sac/Amniotic Fluid
During what period of prenatal development do most miscarriages occur?
During the period of the embryo
What are three factors that impact the effects of teratogens?
Dose, Time of exposure (age), Genetic Predispositions/Heredity
What period of prenatal development is characterized by cell differentiation?
Embryonic Period
Which sense is the least developed at birth?
Vision
Why are reflexes important in infants?
They can assess health, help survival, and prepare for voluntary control.
What is depth perception linked to in infants?
Motor skill development.
Which part of the brain is involved in controlling motor actions?
Basal ganglia or parietal cortex.
At what age do infants first realize the A-not-B error?
Around coordination of Secondary Circular reactions.
What cognitive development approach believes children have innate capabilities?
Core Knowledge Theorists.
What is the example of accommodation when a child learns a new schema?
When a child sees a tomato and calls it an 'apple' but learns it is different from an apple.
During which substage of the sensorimotor period do infants first repeat interesting effects in their surroundings?
Secondary circular reactions (ages 4-8 months).
What does HPA axis represent?
Hypothalamus-Pituitary gland-Adrenal axis.
What was the key finding in Journal Article #3?
Emotion regulation at ages 3-5 mediates the relationship between early attachment security and later social interaction in preadolescence.
What conceptual framework was used in Journal Article #3?
Eisenberg’s conceptual framework.
What statistical design was used to test hypothesis in Journal Article #3?
Mediation model.
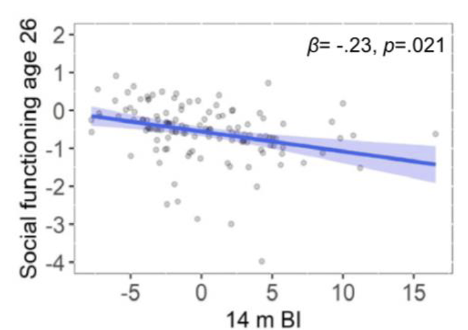
What do the figures in the journal article indicate about behavior inhibition and social functioning?
Higher scores in behavior inhibition at 14 months lead to lower levels of social functioning at 26 years.
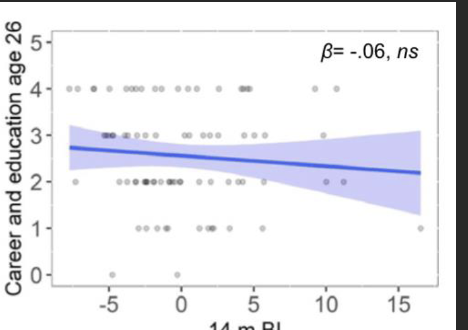
What does the non-significant finding in the journal article indicate?
It cannot be interpreted.
condition in which the spinal cord is not fully encased in the spinal column's protective covering
spina bifida
fetal death that occurs late in pregnancy when survival outside womb would normally have been possible
stillbirth
process in which neurons move to locations throughout the brain to become part of specialized functioning units
migration
delivery in which the fetus emerges feet first or buttocks first rather than head first
breech delivery
process in early brain development in which neurons multiply at a staggering rate
proliferation
method of holding a young infant skin-to-skin on a parent's chest; often used with premature babies
kangaroo care
condition arising when bits of tissue lining the uterus grow outside the uterus
endometriosis
any disease, drug, or other environmental agent that can harm a developing fetus
teratogen
death of a sleeping baby because of respiratory system failure; linked to maternal smoking
sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
assessment to determine a newborn's heart rate, respiration, color, muscle tone, and reflexes immediately after birth
Apgar test
outermost membrane that becomes attached to the uterine lining to gather nourishment for the embryo
chorion
watertight membrane that surrounds the developing embryo, regulating its temperature and cushioning it against injuries
amnion
couple's inability to get pregnant after a year of trying to do so
infertility
sphere of cells the zygote forms by rapid cell division while moving through the fallopian tube
blastocyst
point when a fetus may survive outside the uterus; occurs around the 24th prenatal week
age of viability
substance that aids breathing by preventing the air sacs of the lungs from sticking together
surfactant
procedure in which the baby is removed via incision made in the mother's abdomen and uterus
cesarean section
loss of a pregnancy before survival of the baby outside the womb is possible
miscarriage
group of symptoms commonly observed in the offspring of mothers who drink liquor heavily during pregnancy
fetal alcohol syndrome
mass when born of less than 2500 grams, associated with increased risk of developmental problems
low birth weight
organ that provides for nourishment of the unborn child and elimination of its metabolic wastes
placenta
defined stage in an organism's development when it is particularly sensitive to certain environmental influences
critical period
episode of extreme sadness and exhaustion lasting months in a woman who has just given birth
postpartum depression
condition in which the main portion of the brain above the brain stem develops improperly
anencephaly
process through which the prenatal environment affects the genetic unfolding of the embryo/fetus
fetal programming
individual who lives to be 100 years of age
centenarian
slower and less-dramatic male counterpart of menopause, characterized by decreasing levels of testosterone
andropause
hormone involved in regulating a woman's menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for a pregnancy
progesterone
combination of risk factors that can lead to heart disease
metabolic syndrome
hormone that stimulates childhood physical growth and the adolescent growth spurt
growth hormone
specialization of the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex of the brain
lateralization
period of biological change that results in an individual's attaining sexual maturity
puberty
unlearned and automatic response to a stimulus
reflex
Werner's principle that development proceeds from global and undifferentiated states toward differentiated and integrated response patterns
orthogenetic principle
inherited digestive problem in which gluten triggers an immune response that damages a person's small intestine
Celiac disease
male's first ejaculation
spermarche
phenomenon whereby children who experienced growth deficits grow rapidly and resume their genetically programmed growth trajectory
catch-up growth
female's first menstrual period
menarche
removal of unnecessary connections between neurons in response to experience
synaptic pruning
use of estrogen and progestin to compensate for loss of natural regulatory substances from menopause
Hormone replacement therapy
organ that secretes chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream
endocrine gland
female hormone responsible for the development of the breasts, female sex organs, and secondary sex characteristics
estrogen
process of generating new neurons across the life span
neurogenesis
principle that growth proceeds from the center of the body to the extremities
proximodistal principle
“master gland” at the base of the brain that regulates other glands and produces growth hormone
pituitary gland
defect present at birth that is caused by genetic factors, prenatal events, or both
congenital malformation
nerve cell
neuron
degenerative brain disease with symptoms of memory loss, poor impulse control, depression, and eventually dementia
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
growth of connections between neurons
synaptogenesis
ending of a woman's menstrual periods and reproductive capacity around age 51
menopause
postformal operational thought in which knowledge depends on context and the subjective perspective of the knower
relativistic thinking
concept that people's abilities vary depending on the context
developmental range
deliberation fixed on end states rather than on changes that transform one state into another
static thought
ability to conceptualize processes of change from one state to another
transformational thought
phenomenon that involves confusing one's own thoughts with the thoughts of a hypothesized gathering for behavior
imaginary audience
cognitive structure or organized pattern of action or thought used to deal with experiences
schema
verbal communication for the self, commonly used by preschoolers to guide their activities
private speech
friend invented by a child in the preoperational stage who has developed capacity for symbolic thought
imaginary companion
concept that new knowledge is created through changes in neural structures in response to experience
neuroconstructivism theory
process of modifying existing schemes to incorporate or adapt to new experiences
called accommodation.
phenomenon in which obvious features of a situation have disproportionate influence on perceptions of young children
perceptual salience
person's inborn tendency to adjust to the demands of the environment
adaptation
ability to focus on two or more dimensions of a problem at one time
decentration
phenomenon that involves thinking that oneself and one's thoughts and feelings are unique
personal fable
logical operation allowing a person to mentally order a set of stimuli along a quantifiable dimension
seriation
proposed stages of cognitive development that lie beyond formal operations
postformal thought
tendency to seek and interpret new information that confirms our existing beliefs about something
confirmation bias
ability to use words, images, or actions to represent or stand for objects and experiences
symbolic capacity
problem solving in which a person starts with general ideas and traces to their specific implications
hypothetical- deductive reasoning
tendency to focus on only one aspect of a problem when multiple aspects are relevant
centration
understanding that items continue to exist when they are no longer detectable to the senses
object permanence
ability to negate an action by mentally performing the opposite action
reversibility
tendency of infants to search for an object where they last found it versus its new hiding place
A- not- B error
during Piaget's sensorimotor period, infant's experimenting with actions to find new ways to solve problems
tertiary circular reaction
during Piaget's sensorimotor period, infant's repetition of interesting actions on objects
secondary circular reaction