BLG401 EXAM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Last updated 6:19 AM on 4/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
**Scientific method**
* empirical method for acquiring knowledge
* careful observation + skepticism about what is observed
* used by all critical thinkers
* eg. natural scientists, engineers, economists, social scientists, investigative journalists, lawyers, judges
* careful observation + skepticism about what is observed
* used by all critical thinkers
* eg. natural scientists, engineers, economists, social scientists, investigative journalists, lawyers, judges
2
New cards
**Ecotoxicology**
* **1969**: first defined by Rene Truhart
* combines **ecology** + **toxicology** (multidisciplinary)
* **Ecotoxicology: study of the fate and effect of toxic agents on individuals, populations, and ecosystems**
* assesses impact of **stressors**
* **Stressors**: chemicals, thermal waste, habitat destruction, invaders
* combines **ecology** + **toxicology** (multidisciplinary)
* **Ecotoxicology: study of the fate and effect of toxic agents on individuals, populations, and ecosystems**
* assesses impact of **stressors**
* **Stressors**: chemicals, thermal waste, habitat destruction, invaders
3
New cards
**Disciplines of Ecotoxicology (10)**
1. Biochemistry
2. Hydrology
3. Organic chemistry
4. Microbiology
5. Geology
6. Sedimentology
7. Physiology
8. Immunology
9. Molecular genetics
10. Geography
4
New cards
**The Great Lakes + Rivers**
**H.O.M.E.S**
**Great Lakes:** Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior
\
**Rivers:** St. Marys, St. Clair, Detroit River, Niagara River, St. Lawrence River
**Great Lakes:** Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior
\
**Rivers:** St. Marys, St. Clair, Detroit River, Niagara River, St. Lawrence River
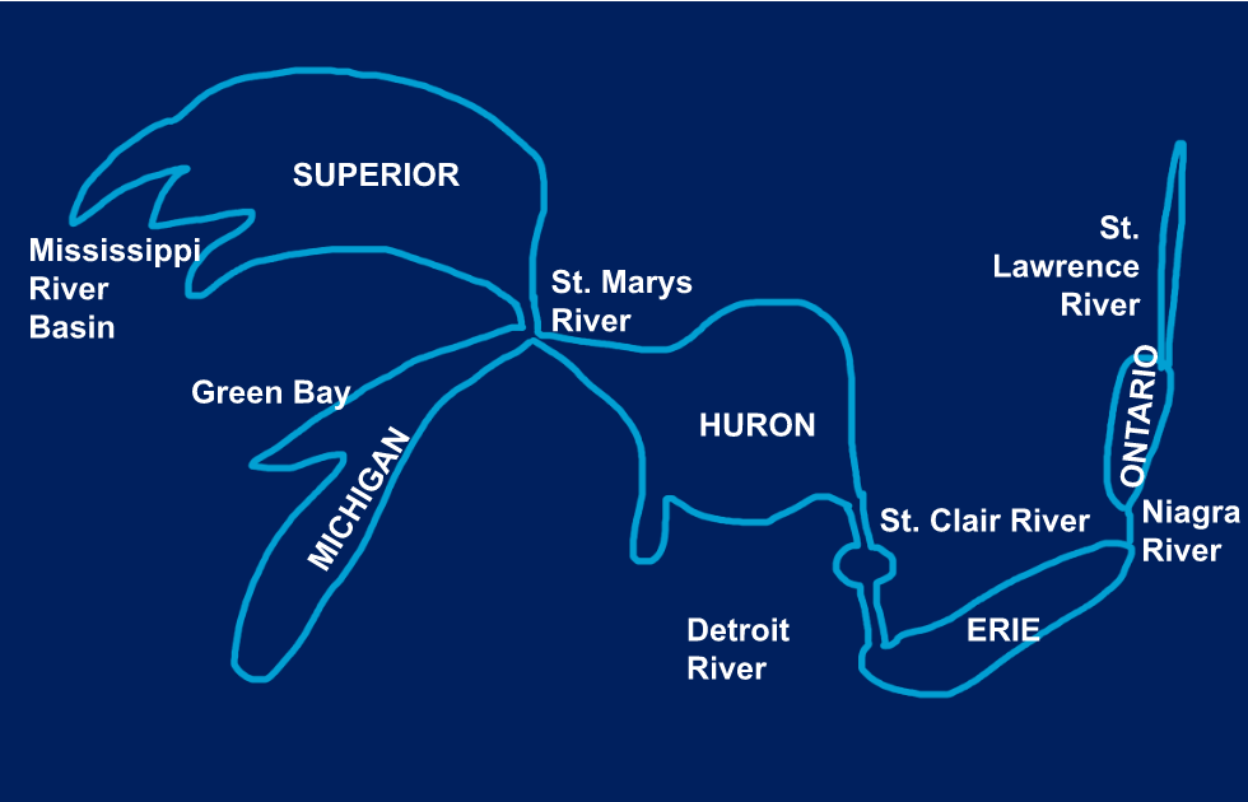
5
New cards
**What contaminants leave the terrestrial landscape (urban + agricultural) during extreme weather events and enter receiving bodies of water? (9)**
Rainwater + snow brings down:
* farm waste (manure with antibiotics + steroids)
* pesticides + fertilizers from farmland + golf courses
* oil + lead + platinum + other metals from cars
* asphaltenes (oil, bitumen)
* sewage overflow
* road salt runoff
* polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
* polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
* warm water slugs
* farm waste (manure with antibiotics + steroids)
* pesticides + fertilizers from farmland + golf courses
* oil + lead + platinum + other metals from cars
* asphaltenes (oil, bitumen)
* sewage overflow
* road salt runoff
* polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
* polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
* warm water slugs
6
New cards
**What is a Wetland?**
area of land that is permanently or seasonally underwater
7
New cards
**Wetland ecological functions (10)**
1. protection from floods + tsunamis, droughts (slows down water flow)
2. absorbs/sequesters carbon dioxide through photosynthesis:
* using atmospheric inorganic carbon CO₂ to produce sugar, turns inorganic carbon into organic carbon (carbon fixing)
3. prevents loss of land/shoreline erosion
4. produces fertile sediment (peat)
5. provides habitats + supports biodiversity
6. wetland plants pull contaminants in from water
7. harvests dead stock/macrophytes → uses for biofuels
8. slows down water and replenishes lakes + groundwater (soft + mushy sediment allows water to replace ground water through water retention)
9. shelters for larval organisms
10. pollinator source during blooming seasons
8
New cards
**What are Macrophytes?**
* multicellular, primary producers (autotrophs)
* emergent + submerged large plants
* emergent + submerged large plants
9
New cards
**Macrophyte functions (5)**
1. protect larval fish + other aquatic organisms
2. provide O₂
3. food for fish + wildlife
4. CO₂ sequestration
5. capture terrestrial pollutants: N, P
10
New cards
**What are Periphyton?**
Periphyton means ‘on plants’
* composed of: algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes, detritus, protozoa
* attached to macrophytes + other substrates
* composed of: algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes, detritus, protozoa
* attached to macrophytes + other substrates
11
New cards
**Periphyton functions (3)**
1. absorbs contaminants
2. important food source for invertebrates, small fish, larval amphibians
3. water quality indicator
12
New cards
**What are Plankton?**
* unicellular + multicellular
* microscopic to small macroscopic community
* suspended in open water
* subject to wind + currents → cannot propel themselves forward
* microscopic to small macroscopic community
* suspended in open water
* subject to wind + currents → cannot propel themselves forward
13
New cards
**Plankton function**
critical food source
14
New cards
**Phytoplankton**
* autotrophic component of plankton community
* prokaryotic, eukaryotic
* prokaryotic, eukaryotic
15
New cards
**Bacterioplankton**
* bacterial component of the plankton community
* both primary producers + primary consumers
* biogeochemical cycling: C, N, organic matter
* both primary producers + primary consumers
* biogeochemical cycling: C, N, organic matter
16
New cards
**Zooplankton**
* animal component of the planktonic community
* heterotrophic
* resource for consumers on higher trophic levels
* heterotrophic
* resource for consumers on higher trophic levels
17
New cards
**Mycoplankton**
* deals with fungi (mycorrhiza + hyphae)
* saprotrophic
* saprotrophic
18
New cards
**Virioplankton**
any planktonic, free-swimming virus
19
New cards
**What is Benthos? What does it include?**
__*community*__ found in sediment
\
**Includes:**
* insect larvae
* small crustaceans
* larval fish
* worms
* microbial consortium
\
**Includes:**
* insect larvae
* small crustaceans
* larval fish
* worms
* microbial consortium
20
New cards
**Great Lakes Problems (1870s to 1980s)**
**1870s**: **Degraded water quality**
* drinking water intake pipes built beyond city discharge zones due to excess raw sewage dumping by settlers– massive raw sewage causing water borne disease (cholera, typhoid fever, dysentery)
\
**1940’s: World War II**
* urban centers around Great Lakes needed to produce chemicals, rubber, steel, nuclear weapons, pesticides for war → polluted water
\
**1950s + 1960s**: **Profligate urban + rural pollution**
* atmospheric pollutants, waste water
\
**1960s**: **Massive algal blooms**
* “lake erie dying” caused by nutrient runoff from farmers’ fields, sewage input
* fertilizers (containing N+P) caused runoff into Lake Erie (from heavy rainfall) causing massive algal blooms
* algae dies off → falls to the bottom → phosphobacteria degrades it → bacteria needs O₂ during respiration → decreased O₂ in water → lifeforms die
* algae dies, falls to bottom + ice layer forms in winter → restricts O₂ for fish → once ice melts fish are dead
\
**1970s to 1980s**: **Fish tumours, imposex, physiological abnormalities in fish-eating birds**
* Causes: DDT, PCBs, Mirex, Hg (mercury), Pb (lead)
* drinking water intake pipes built beyond city discharge zones due to excess raw sewage dumping by settlers– massive raw sewage causing water borne disease (cholera, typhoid fever, dysentery)
\
**1940’s: World War II**
* urban centers around Great Lakes needed to produce chemicals, rubber, steel, nuclear weapons, pesticides for war → polluted water
\
**1950s + 1960s**: **Profligate urban + rural pollution**
* atmospheric pollutants, waste water
\
**1960s**: **Massive algal blooms**
* “lake erie dying” caused by nutrient runoff from farmers’ fields, sewage input
* fertilizers (containing N+P) caused runoff into Lake Erie (from heavy rainfall) causing massive algal blooms
* algae dies off → falls to the bottom → phosphobacteria degrades it → bacteria needs O₂ during respiration → decreased O₂ in water → lifeforms die
* algae dies, falls to bottom + ice layer forms in winter → restricts O₂ for fish → once ice melts fish are dead
\
**1970s to 1980s**: **Fish tumours, imposex, physiological abnormalities in fish-eating birds**
* Causes: DDT, PCBs, Mirex, Hg (mercury), Pb (lead)
21
New cards
**International Joint Commission: who are they? -- detail their restoration strategies (staring in 1909 through 1950s + ‘60s)**
**1909**: **International Joint Commission**:
* **Independent, binational** (Canada + America)
* 3 experts from each country
* The Boundary Waters Treaty: to prevent + resolve disputes over use of waters shared by Canada + US
\
**1918**: **First IJC report**: “*chaotic, perilous, disgraceful* water pollution” in many parts of the Great Lakes
\
**1954**: **Great Lakes Fisheries Commission**: protect fisheries → lamprey eel
\
**1964**: **IJC recommends reduction of P in STPs** to **reduce** **eutrophication**
\
**1965**: **IJC asks Canada to set up Experimental Lakes Area in NW Ontario**
* area for study of impacts of various factors affecting water quality
* **Independent, binational** (Canada + America)
* 3 experts from each country
* The Boundary Waters Treaty: to prevent + resolve disputes over use of waters shared by Canada + US
\
**1918**: **First IJC report**: “*chaotic, perilous, disgraceful* water pollution” in many parts of the Great Lakes
\
**1954**: **Great Lakes Fisheries Commission**: protect fisheries → lamprey eel
\
**1964**: **IJC recommends reduction of P in STPs** to **reduce** **eutrophication**
\
**1965**: **IJC asks Canada to set up Experimental Lakes Area in NW Ontario**
* area for study of impacts of various factors affecting water quality
22
New cards
**Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement (1972, 1978, 1987, 2012, 2019)**
**1972**: **Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement** between US + Canada
* most powerful agreement ever made
* limit P inputs to reduce algal blooms
* rapid improvement in lake Erie algae (1970s - 1980s)
* detergent industries forced to remove P from products
\
**1978**: **Agreement revised**
* new focus: toxic substances
\
**1987**: **Agreement revised**
* *Remedial Action Plans* (RAPs) for Areas of Concern (AoC)
* AoC: nearshore + harbours
\
**2012**: **Agreement revised**: **Great Lakes State report** every **3 years** – public consultation regarding report, public invited to ask questions
\
**2019**: **Henry Lickers** brought in as one of the 6 members (Haudenosaunee member/indigenous expert)
* most powerful agreement ever made
* limit P inputs to reduce algal blooms
* rapid improvement in lake Erie algae (1970s - 1980s)
* detergent industries forced to remove P from products
\
**1978**: **Agreement revised**
* new focus: toxic substances
\
**1987**: **Agreement revised**
* *Remedial Action Plans* (RAPs) for Areas of Concern (AoC)
* AoC: nearshore + harbours
\
**2012**: **Agreement revised**: **Great Lakes State report** every **3 years** – public consultation regarding report, public invited to ask questions
\
**2019**: **Henry Lickers** brought in as one of the 6 members (Haudenosaunee member/indigenous expert)
23
New cards
**Four Obama initiatives of 2010**
1. Combating invasive species (Asian carp, zebra mussels, sea lamprey)
2. Promoting nearshore health (harbours)
3. Restoring wetlands
4. Tracking progress + working with strategic partners (having American scientists and engineers go outside of America and go globally to other countries to see what worked elsewhere)
24
New cards
**Canada Centers for Inland Waters (CCIW) in 1968: what is it? what is their mission?**
* **1968**: Creation of **CCIW (Canada Centers for Inland Waters)**
\
* Natural scientists, engineers, social scientists, behavioural psychologists, journalists, economists → many experts + critical thinkers around the table
\
* **Not like-minded** except in agreeing to a **collective vision**: many disagreements (not like-minded), but always came back to the table (collective vision)
\
* *Collectively* helped the “environmental movement” + created engaged + educated “voting public” who voted in politicians that implemented deep environmental reforms at all levels
\
* Natural scientists, engineers, social scientists, behavioural psychologists, journalists, economists → many experts + critical thinkers around the table
\
* **Not like-minded** except in agreeing to a **collective vision**: many disagreements (not like-minded), but always came back to the table (collective vision)
\
* *Collectively* helped the “environmental movement” + created engaged + educated “voting public” who voted in politicians that implemented deep environmental reforms at all levels
25
New cards
**US Environmental Protection Agency** (**USEPA): what is it? what is its mission?**
**Dec 1970**: **USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) formed**
* agency of US federal government
* most powerful environmental protection agency formed
* **mission**: protect human health *and* the environment
* environmental assessment, research, and education
* maintains environmental laws in consultation with state, tribal, local governments
* works with industries, all levels of government, pollution prevention programs, energy conservation efforts
* **1972: Clean Water Act**
* **1976: Toxic Substances Control Act**
* **2002: Safe Drinking Water Act**
* has huge teeth: has environmental LAWS that are illegal to break
* agency of US federal government
* most powerful environmental protection agency formed
* **mission**: protect human health *and* the environment
* environmental assessment, research, and education
* maintains environmental laws in consultation with state, tribal, local governments
* works with industries, all levels of government, pollution prevention programs, energy conservation efforts
* **1972: Clean Water Act**
* **1976: Toxic Substances Control Act**
* **2002: Safe Drinking Water Act**
* has huge teeth: has environmental LAWS that are illegal to break
26
New cards
**Global environmental issues from 1945 to 1970 (two paradigms)**
**Opening Paradigm:** *Solution to pollution is dilution*
**Closing paradigm:** What you throw away will come back to hurt you
**Closing paradigm:** What you throw away will come back to hurt you
27
New cards
**Context of global environmental issues from 1945 to 1970 (6)**
**Huge reach of radioactive atmospheric contaminants:**
* bombing of Nagasaki + Hiroshima, explosion at Kyshtym, fire at plutonium processing plant in England, Chernobyl, Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
\
**Indiscriminant use of anthropogenic contaminants: Clear Lake California**
\
**Traditional pollution as “overnight killer”: London’s Great Smog**
\
**Heavy metal biomagnification: Minamata Bay**
\
**Beginning of desertification in Africa**
\
**Beginning of great loss of Amazonia**
* bombing of Nagasaki + Hiroshima, explosion at Kyshtym, fire at plutonium processing plant in England, Chernobyl, Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
\
**Indiscriminant use of anthropogenic contaminants: Clear Lake California**
\
**Traditional pollution as “overnight killer”: London’s Great Smog**
\
**Heavy metal biomagnification: Minamata Bay**
\
**Beginning of desertification in Africa**
\
**Beginning of great loss of Amazonia**
28
New cards
**Huge reach of radioactive atmospheric contaminants**
**1945: Testing of nuclear weapons at Alamogordo, New Mexico** **→ Nagasaki + Hiroshima**
\
**1957: Explosion at Soviet military plant (Kyshtym)** → released radioactive material → 63% agricultural land; 137Cs, 90Sr → level 6
\
**1957: Fire at plutonium processing plant in England** → released radioactive iodine (131I) → level 5
\
**1986: Chernobyl**
\
**2011: Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster**
\
__Radioactive isotopes: radioactive iodine (131I), strontium (90Sr), cesium (137Cs):__
\
131I: conc. in thyroid → cancer
* Iodine for thyroid hormones; thyroid gland runs all of metabolism (metabolism runs immune function), heart rate + growth in children
\
137 Cs: analogue of K+
* electrolytic balance: Na+/K+ pump
* muscle contraction
* nerve impulse transmission
\
90Sr: analogue of Ca2+ → brittle bones; bone cancer
* atmospheric deposition –> lands on crops → eaten by cows → cows eaten by humans
\
**1957: Explosion at Soviet military plant (Kyshtym)** → released radioactive material → 63% agricultural land; 137Cs, 90Sr → level 6
\
**1957: Fire at plutonium processing plant in England** → released radioactive iodine (131I) → level 5
\
**1986: Chernobyl**
\
**2011: Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster**
\
__Radioactive isotopes: radioactive iodine (131I), strontium (90Sr), cesium (137Cs):__
\
131I: conc. in thyroid → cancer
* Iodine for thyroid hormones; thyroid gland runs all of metabolism (metabolism runs immune function), heart rate + growth in children
\
137 Cs: analogue of K+
* electrolytic balance: Na+/K+ pump
* muscle contraction
* nerve impulse transmission
\
90Sr: analogue of Ca2+ → brittle bones; bone cancer
* atmospheric deposition –> lands on crops → eaten by cows → cows eaten by humans
29
New cards
**Indiscriminant use of anthropogenic contaminants: Clear Lake California**
**1949: 40K gallons DDT sprayed in Clear Lake California to control** __**non-biting**__ **midge,** ***Chaoborus astictopus***
* first demonstration of biomagnification
* biomagnification: chemical levels exponentially increase through food chain
* DDT developed prior to WW2 (insecticide: returning men brought back variety of insects (ie. lice + mosquitoes)
* sprayed on returning men + crops + virtually everywhere (agricultural + domestic insecticide)
* known that midge was NON BITING (not a vector)
* larvi swam up from sediment → remained for 48 hours → died thereafter → bothered beach goers
\
**1954: 50% stronger dose of DDT put into water**
* Western Grebe washing up dead on shore
* Eggshell thinning + reproductive impairment
\
**1957**: **More DDT dumped**
* DDT started to bioaccumulate within lower aquatic levels
* bioaccumulation: accumulation of chemical conc. in organism over time due to constant exposure from multiple sources (water, food, sediment)
* first demonstration of biomagnification
* biomagnification: chemical levels exponentially increase through food chain
* DDT developed prior to WW2 (insecticide: returning men brought back variety of insects (ie. lice + mosquitoes)
* sprayed on returning men + crops + virtually everywhere (agricultural + domestic insecticide)
* known that midge was NON BITING (not a vector)
* larvi swam up from sediment → remained for 48 hours → died thereafter → bothered beach goers
\
**1954: 50% stronger dose of DDT put into water**
* Western Grebe washing up dead on shore
* Eggshell thinning + reproductive impairment
\
**1957**: **More DDT dumped**
* DDT started to bioaccumulate within lower aquatic levels
* bioaccumulation: accumulation of chemical conc. in organism over time due to constant exposure from multiple sources (water, food, sediment)
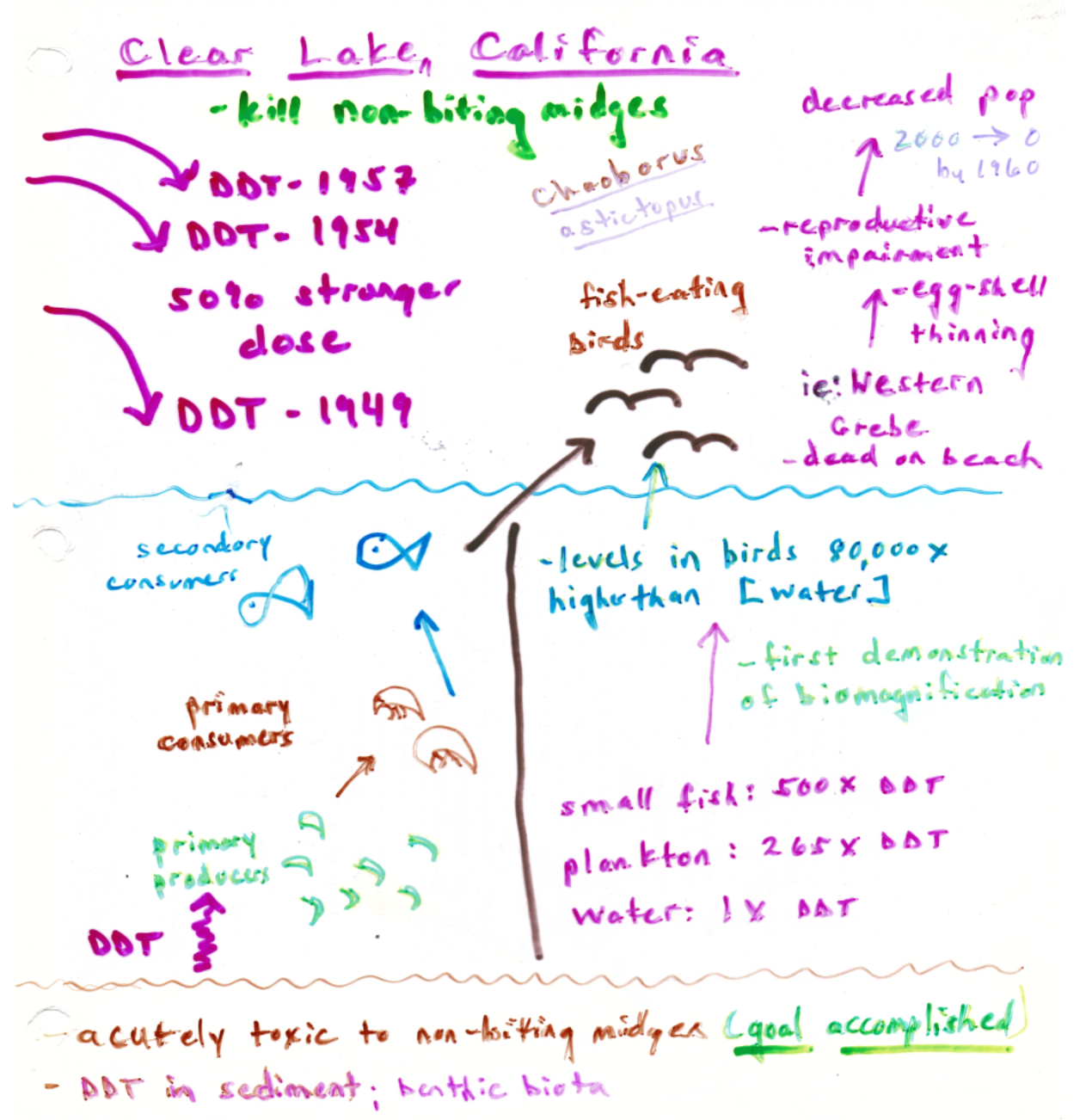
30
New cards
**Traditional pollution as “overnight killer”: Great Smog of London**
**1952: Great Smog of London:** Result of burning low-quality, high sulphur coal
* pollutants: particulates, SOx, NOx, CO, O₃, CH₄: deposit in lungs
* reasons for death:
* respiratory failure: hypoxia, broncho-pneumonia, mechanical obstruction from pus accumulation
* Particulates in lungs causes production of mucus, affecting gas exchange (CO₂ + O₂) → can’t breathe → suffocation
* **Clean Air Act, 1956: domestic fires banned**
* pollutants: particulates, SOx, NOx, CO, O₃, CH₄: deposit in lungs
* reasons for death:
* respiratory failure: hypoxia, broncho-pneumonia, mechanical obstruction from pus accumulation
* Particulates in lungs causes production of mucus, affecting gas exchange (CO₂ + O₂) → can’t breathe → suffocation
* **Clean Air Act, 1956: domestic fires banned**
31
New cards
**Heavy metal biomagnification: Minamata Bay**
**1950s**: Organic mercury in Minamata Bay, Japan poisons hundreds
\
Chisso factory wastewater contaminated with high mercury concentrations dumped into Minimata Bay → biomagnification of organic mercury in food chain → citizens consumed fish → become poisoned with “Minamata Disease”
\
**Result: Ataxia**: lack of coordination of muscle movements
* gross lack of co-ordination of muscle movements
* insanity, paralysis, death
* chromosome breakage
* birth defects
* can be congenital
* pathological irritation
\
Chisso factory wastewater contaminated with high mercury concentrations dumped into Minimata Bay → biomagnification of organic mercury in food chain → citizens consumed fish → become poisoned with “Minamata Disease”
\
**Result: Ataxia**: lack of coordination of muscle movements
* gross lack of co-ordination of muscle movements
* insanity, paralysis, death
* chromosome breakage
* birth defects
* can be congenital
* pathological irritation
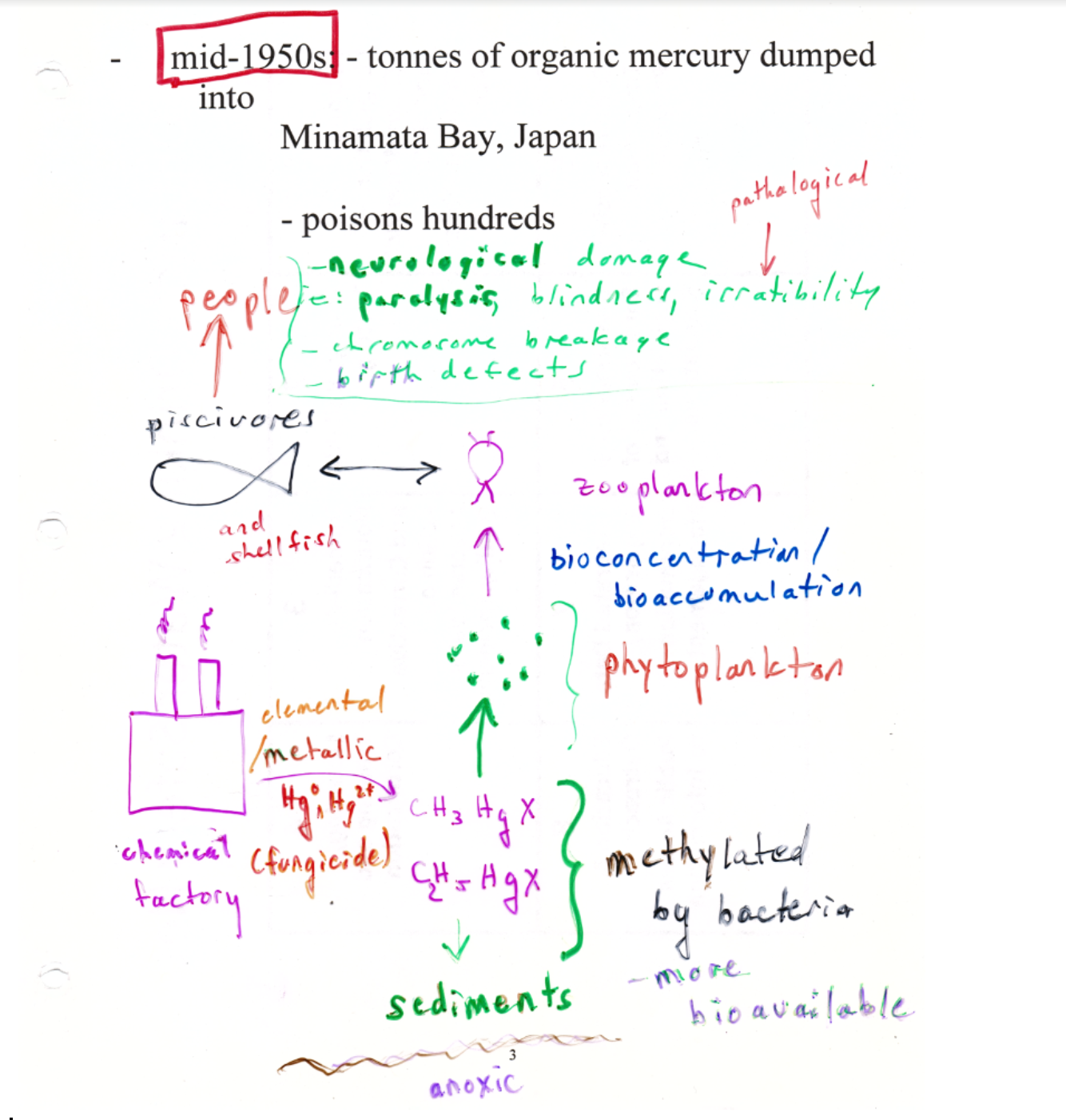
32
New cards
**Beginning of desertification in Africa**
* large herbivores (elephants, giraffes, water buffalo, rhinos, wildebeast, zebras) travel in packs → do not eat past soil → move onto another spot of botanical oasis → rain → vegetation grows back
\
* unsound farming practices: patches of devegetation from large herbivores being penned → not able to graze → eat past soil + destroy roots + new vegetation growth
\
* drought caused by climate change – aquifers being exploited
\
* unsound farming practices: patches of devegetation from large herbivores being penned → not able to graze → eat past soil + destroy roots + new vegetation growth
\
* drought caused by climate change – aquifers being exploited
33
New cards
**Beginning of great loss of Amazonia**
* due to fires + over-farming
* largest land use: grow cattle
* what is lost from loss of amazonia: biodiversity + rain → desertification
* largest land use: grow cattle
* what is lost from loss of amazonia: biodiversity + rain → desertification
34
New cards
**Rachel Carson: her life history, what was accomplished**
Born: May 27, 1907
* Earned degree in Zoology at Johns Hopkins University
* Intended to continue for a doctorate, but following her fathers death, had to help out her family instead
* **Marine biologist**
* US Fish and Wildlife: analyzed fish field data
* Saw effects of *DDT*
* **Started writing** ***Silent Spring***
\
**1962:** ***Silent Spring*** **published** **informing the voting public**: **draws public attention to global environmental problems**
**1962**: **Rachel Carson publishes Silent Spring** → educated voting public
* Rachel Carson + key vocal citizen scientists started environmental movement
* Solutions started to be implemented
* Formation of environmental *collectives*
* Environmental movement + collectives + academic and government expertise = progress
* Chemical industry tried to discredit her; intense vitriol
* **Vindicated her book**
* **Died of breast cancer**
\
**1971**: **Voting Public** **continued education** – **Dr Seuss publishes The Lorax** → reaches children
* Lorax for children
* Silent Spring for adults
* Earned degree in Zoology at Johns Hopkins University
* Intended to continue for a doctorate, but following her fathers death, had to help out her family instead
* **Marine biologist**
* US Fish and Wildlife: analyzed fish field data
* Saw effects of *DDT*
* **Started writing** ***Silent Spring***
\
**1962:** ***Silent Spring*** **published** **informing the voting public**: **draws public attention to global environmental problems**
**1962**: **Rachel Carson publishes Silent Spring** → educated voting public
* Rachel Carson + key vocal citizen scientists started environmental movement
* Solutions started to be implemented
* Formation of environmental *collectives*
* Environmental movement + collectives + academic and government expertise = progress
* Chemical industry tried to discredit her; intense vitriol
* **Vindicated her book**
* **Died of breast cancer**
\
**1971**: **Voting Public** **continued education** – **Dr Seuss publishes The Lorax** → reaches children
* Lorax for children
* Silent Spring for adults
35
New cards
**Greater specifics on Great Lakes pollution: 1960s: 8 major problems**
1. **LAKE ERIE EUTROPHICATION**
* massive algal blooms: “Lake Erie dying” caused by nutrient runoff from farmers’ fields (*non-point source*), sewage treatment plant input (*point source*)
* GLWQA: only **point source P solved**: **STPs**
\
2. **ACID RAIN**
* **Area of Concern (AoC): Detroit River**
* Iron ore smelted to remove rock that Fe is encapsulated in → low grade coal used as heat generator – NOx + SOx released → acid rain
\
3. **BACTERIAL + ORGANIC CONTAMINATION + HEAVY METALS**
* excessive nutrient inputs from STPs (point source) + farms (nonpoint source)
\- P, N, organic matter
\- **DDT, dieldrin, PCBs, mercury, arsenic, lead, cadmium**
**- water borne diseases: Typhus, Cholera, Diphtheria**
\
4. **OIL POLLUTION**
* **Area of Concern (AoC): Detroit River: 1969:** Cuyahoga River, Cleveland, caught fire
\
5. **ACID SEEPS: Industrial and mining practices: acid mine drainage (AMD)**
* Pyrite exposed to O₂ → water seeps into mine → sulfuric acid forms → dissolves metal from rocks → water drains out of mine → metals fall into stream water → aquatic animals + plants killed by drainage
\
6. **THERMAL WASTE: Thermal wastes from coolant waters of nuclear plants**
* Uranium fuel rods become hot → cooling water brought from Great Lakes to prevent meltdown → put into exchanger → cools fuel rods → warm water sent to cooling towers → warm “cooling water” returned to the lake → disrupts cold water fisheries
* warm water returned to cold water source → warm water removes O₂ from water
\
7. **SEDIMENTATION + SHORE EROSION**
* erosion → sedimentation goes into water → prevents photosynthesis (blocks sunlight) → fish eggs suffocated by the sedimentation)
* particulate matter in water column → blocks sunlight → primary producers impacted→ periphyton killed
\
8. **INVASIVE SPECIES**
* lamprey eel → by 1950s destroyed lake trout fishery
36
New cards
**1970s Major US Antipollution legislation: more detail of USEPA + Acts**
\
**Dec 1970**: **U.S. Environmental Protection Agency**
* enforces national standards under variety of environmental laws or *acts*
* works with industry, all levels of government
* consults with state, tribal, local governments
* conducts environmental assessment, research, education
* regulates chemicals + protects *human* health
* safeguards *natural environment*, including air, water, land
* employs: engineers, scientists, legal, public policy, financial, information technologists, etc.
\
**Safe Drinking Water Act, Clean Water Act, Toxic Substances Control Act**
**Dec 1970**: **U.S. Environmental Protection Agency**
* enforces national standards under variety of environmental laws or *acts*
* works with industry, all levels of government
* consults with state, tribal, local governments
* conducts environmental assessment, research, education
* regulates chemicals + protects *human* health
* safeguards *natural environment*, including air, water, land
* employs: engineers, scientists, legal, public policy, financial, information technologists, etc.
\
**Safe Drinking Water Act, Clean Water Act, Toxic Substances Control Act**
37
New cards
**Safe Drinking Water Act**
* federal law to ensure safe drinking water for the public
* USEPA sets standards for all states, localities, water suppliers
* applies to every public water system in the US
* does not apply to private wells or bottled water (FDA regulates bottled water)
* set limits for Pb in delivery systems
* USEPA sets standards for all states, localities, water suppliers
* applies to every public water system in the US
* does not apply to private wells or bottled water (FDA regulates bottled water)
* set limits for Pb in delivery systems
38
New cards
**Clean Water Act**
**1948: Water Pollution Control Act (WPCA)**
**1972: Clean Water Act**
* built upon the WPCA
* most influential US environmental law
* federal law controlling water pollution
* restore, maintain chemical, biological, physical integrity of nation’s waters by preventing point and nonpoint source pollution
* healthy source water = healthy drinking water
**1972: Clean Water Act**
* built upon the WPCA
* most influential US environmental law
* federal law controlling water pollution
* restore, maintain chemical, biological, physical integrity of nation’s waters by preventing point and nonpoint source pollution
* healthy source water = healthy drinking water
39
New cards
**Toxic Substances Control Act**
**1976: Toxic Substances Control Act**
* regulates introduction of new or already-existing chemicals
* focused on PCBs, Pb, Hg, radon
* regulates introduction of new or already-existing chemicals
* focused on PCBs, Pb, Hg, radon
40
New cards
**Great Lakes problems TODAY (7)**
1. **Intense increasing urbanization**: results in concentrated pollution stressors
\
2. **Selling water**: huge amounts of water taken + transported transported, never to be returned
\
3. **Altering water regimes**: Mid-West (massive crop producers + exporters) eyeing Great Lakes for agriculture
\
4. **Persistent pollutants in water + sediment:**
* Legacy (ie. PCBs, mercury)
* Emerging (PPCPs, endocrine disruptors, etc)
* Microplastics
\
5. **Loss of wetlands, aquatic habitat**
* Lack of filtration of incoming pollutants
* Lack of aquatic nurseries
* Increasing shoreline erosion
\
6. **Continued invasion of exotic species:** Asian carp, Zebra Mussels, Sea Lamprey
* lamprey eel destroyed lake trout fishery
* parasitic in the Great Lakes → have no predators
* got into Great Lakes from incoming ocean vessels containing sea lampreys on cargo
* Asian carp invasion: introduced into the US to control algae, weed, and parasite growth in aquatic farms
* escaped and invaded through Chicago diversion → diverts water from Lake Michigan watershed into Upper Mississippi River basin
\
7. **Climate change: Lake Erie “dead zone”**
* Intense, frequent thunderstorms → farm soil runoff, phosphorous
* M*icrocystis aeruginosa* from zebra mussels *→* mussels digest everything except *Microcystis →* expelled covered in fecal pellet → produces algal toxins
* O₂ free zones → dead fish
41
New cards
**Great Lakes potential solutions (4)**
1. **Ryerson Urban Water: 2 diagrams**
2. **Wastewater treatment polishing**
3. **Vari green roof**
4. **Citizen scientists**
42
New cards
**Ryerson Urban Water (RUW)**
**2010: Ryerson Urban Water (RUW)**
* a collective who, with municipalities, industry, other water centers, will find solutions to solve unhealthy urban water cycles
\
**SUSTAINING HEALTHY URBAN WATERSHEDS**
**APPLIED RESEARCH (SENP)**
* Social + economic sciences
* Engineering
* Natural sciences
* Policy + regulations
\
↑Innovation/commercialization ↓
\
**EDUCATION (GPGP)**
* Government, industry training/apprenticeships
* Public, NGOs, journalists
* Graduate + undergraduate
* Primary + secondary schools
\
↑Innovation/commercialization ↓
\
**THINK TANK (IDTD)**
* Information repository
* Discussion forum
* Trend analysis
* Decision support
* a collective who, with municipalities, industry, other water centers, will find solutions to solve unhealthy urban water cycles
\
**SUSTAINING HEALTHY URBAN WATERSHEDS**
**APPLIED RESEARCH (SENP)**
* Social + economic sciences
* Engineering
* Natural sciences
* Policy + regulations
\
↑Innovation/commercialization ↓
\
**EDUCATION (GPGP)**
* Government, industry training/apprenticeships
* Public, NGOs, journalists
* Graduate + undergraduate
* Primary + secondary schools
\
↑Innovation/commercialization ↓
\
**THINK TANK (IDTD)**
* Information repository
* Discussion forum
* Trend analysis
* Decision support
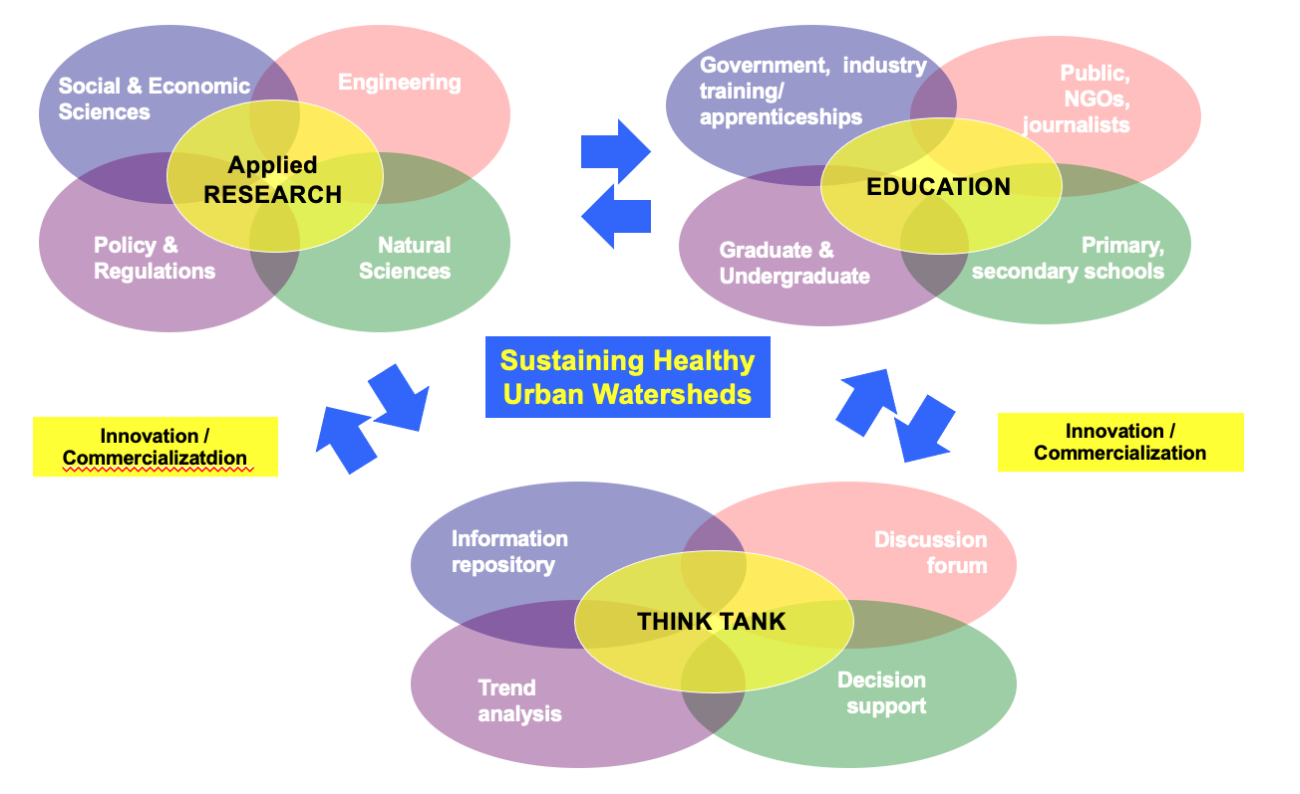
43
New cards
**Wastewater Polishing for Reuse**
* wastewater treatment for industrial + domestic wastes **at source by engineered wetlands**
\
__**how it works:**__
engineered wetland → degrade organic contaminants coming from slaughterhouse wastewater (containing blood, bacteria, potential pathogens, bone, meat, antibiotics, steroids, particulates from gristle, meat, bone) or from source (shower water) → goes through polishing process → reused for industry (eg. cleaning floors) and domestic (eg. toilet flushing) purposes
\
__**how it works:**__
engineered wetland → degrade organic contaminants coming from slaughterhouse wastewater (containing blood, bacteria, potential pathogens, bone, meat, antibiotics, steroids, particulates from gristle, meat, bone) or from source (shower water) → goes through polishing process → reused for industry (eg. cleaning floors) and domestic (eg. toilet flushing) purposes
44
New cards
**Ryerson Vari Engineering Building Rooftop Garden**
* **green and blue roof advantages:**
* grabs + holds water from extreme water events
* helps with insulation
* has a local hydrological event (helps keep humidity in place)
\
* **Ryerson Urban Farm: student-run initiative**
* fresh, organic, local produce: campus kitchens, Ryerson Farmers Market, community food banks
* grabs + holds water from extreme water events
* helps with insulation
* has a local hydrological event (helps keep humidity in place)
\
* **Ryerson Urban Farm: student-run initiative**
* fresh, organic, local produce: campus kitchens, Ryerson Farmers Market, community food banks
45
New cards
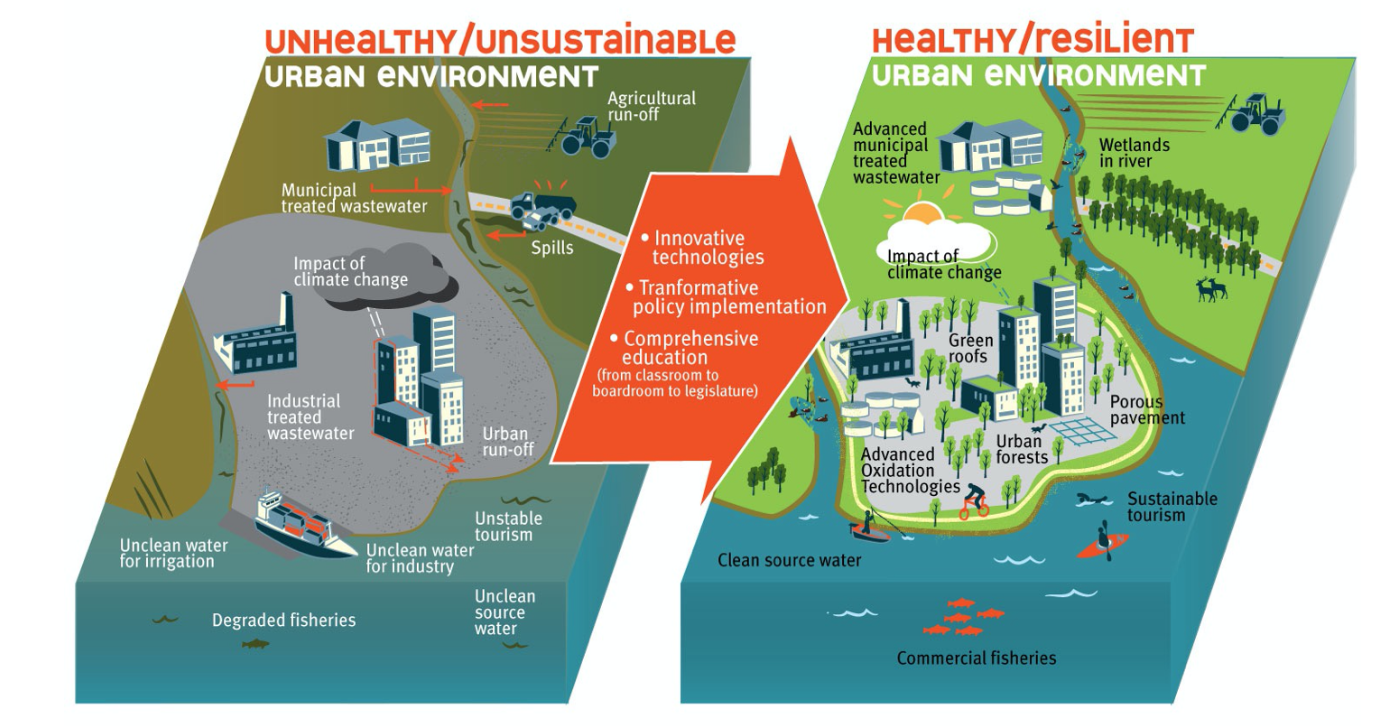
**Kai’s Diagram**
**Urban environment:**
**UNHEALTHY/UNSUSTAINABLE**
* Municipal treated wastewater
* Agricultural runoff + spills
* Impact of climate change
* Industrial treated wastewater (dumped rather than treated at source)
* Urban runoff
* Unclean water for irrigation + industry
* Unclean source water
* Degraded fisheries
* Unstable tourism
\
**Implemented:**
* Innovative technologies
* Transformative policies
* Comprehensive education
\
**HEALTHY/RESILIENT**
* Advanced municipal treated wastewater
* Wetlands along rivers
* Green roofs
* Urban forests
* Advanced oxidation technologies
* Porous pavement
* Clean source water
* Commercial fisheries
* Sustainable tourism
**UNHEALTHY/UNSUSTAINABLE**
* Municipal treated wastewater
* Agricultural runoff + spills
* Impact of climate change
* Industrial treated wastewater (dumped rather than treated at source)
* Urban runoff
* Unclean water for irrigation + industry
* Unclean source water
* Degraded fisheries
* Unstable tourism
\
**Implemented:**
* Innovative technologies
* Transformative policies
* Comprehensive education
\
**HEALTHY/RESILIENT**
* Advanced municipal treated wastewater
* Wetlands along rivers
* Green roofs
* Urban forests
* Advanced oxidation technologies
* Porous pavement
* Clean source water
* Commercial fisheries
* Sustainable tourism
46
New cards
**Citizen Scientists**
**Traditionally:**
* naturalists
* anglers
* conservationists
* birders
\
**Today:**
* collaboration between professional scientists and general public
* volunteer generated data
* written observations, apps (iNaturalist)
* naturalists
* anglers
* conservationists
* birders
\
**Today:**
* collaboration between professional scientists and general public
* volunteer generated data
* written observations, apps (iNaturalist)
47
New cards
**Endocrine disruptors: definition**
**Endocrine disruptors: human made or naturally occurring**
* Fit into hormone receptor to activate/block endocrine pathway
* **Cause disruption**
* if estrogenic: mimic effects of estrogen
* if antiestrogenic: blocks estrogen receptor
* if androgenic: mimics effects of androgen
* if antiandrogenic: blocks androgen receptor
\
**Normal**: hormone → binds to receptor → normal hormone response
**Activate/mimic**: hormone mimic → unwanted cellular response
**Block**: hormone blocker blocks incoming hormones → blocks cellular response
* Fit into hormone receptor to activate/block endocrine pathway
* **Cause disruption**
* if estrogenic: mimic effects of estrogen
* if antiestrogenic: blocks estrogen receptor
* if androgenic: mimics effects of androgen
* if antiandrogenic: blocks androgen receptor
\
**Normal**: hormone → binds to receptor → normal hormone response
**Activate/mimic**: hormone mimic → unwanted cellular response
**Block**: hormone blocker blocks incoming hormones → blocks cellular response
48
New cards
**Historical cases of endocrine disruption (5)**
**1970s: Botswana, Africa**: Insecticide Endosulfan → tsetse flies (vector for Trypanosomiasis, “sleeping sickness”)
\
**1970s: Thames River, England:** anglers catch intersex roach *Rutilus rutilus* in River Lea + 1980s: River Lea, England: female yolk protein **vitellogenin** found in male rainbow trout
\
**1970s + 80s: North America: reproductive problems in fish eating birds**
\
**1990s: Worldwide: Decline in amphibians**
\
**1940-1960s: American women given diethylstilbestrol (DES) to prevent miscarriages**
\
**1970s: Thames River, England:** anglers catch intersex roach *Rutilus rutilus* in River Lea + 1980s: River Lea, England: female yolk protein **vitellogenin** found in male rainbow trout
\
**1970s + 80s: North America: reproductive problems in fish eating birds**
\
**1990s: Worldwide: Decline in amphibians**
\
**1940-1960s: American women given diethylstilbestrol (DES) to prevent miscarriages**
49
New cards
**1970s: Botswana, Africa**: **Insecticide** **Endosulfan for Tsetse Fly**
**1970s: Botswana, Africa**: Insecticide Endosulfan sprayed to control tsetse flies (vector for Trypanosomiasis, “sleeping sickness”) → landed on soil → ran off into receiving waters → *Tilapia rendalli* stop reproducing
\
**Why:**
* mature males develop elaborate body patterns + colouration → wards off competition + stakes out territory + attracts females → Endosulfan *changed* male body patterns → interrupted *nesting behaviour* of males + mating strategies → no offspring
\
**Why:**
* mature males develop elaborate body patterns + colouration → wards off competition + stakes out territory + attracts females → Endosulfan *changed* male body patterns → interrupted *nesting behaviour* of males + mating strategies → no offspring
50
New cards
**1970s: River Lea**
**1970s: Thames River, England: anglers catch intersex roach** ***Rutilus rutilus*** **in River Lea**
* downstream of sewage treatment plant effluent
\
**1980s: River Lea, England: Female yolk protein vitellogenin found in male rainbow trout**
* males have estrogen receptors in liver – normally not induced bc males don’t have estrogen
* exogenous forms of estrogen binds to male estrogen receptors → vitellogenin in males
* reason: chemicals from STP
* downstream of sewage treatment plant effluent
\
**1980s: River Lea, England: Female yolk protein vitellogenin found in male rainbow trout**
* males have estrogen receptors in liver – normally not induced bc males don’t have estrogen
* exogenous forms of estrogen binds to male estrogen receptors → vitellogenin in males
* reason: chemicals from STP
51
New cards
**1970s, 1980s: North America: reproductive problems in fish eating birds**
**1970s, 1980s: North America: reproductive problems in fish eating birds**
* changes in reproductive organs in Great Lakes fish → decreased reproduction
* reproductive problems in fish-eating birds:
* non-mating behaviour
* high embryonic death
* non-caring of offspring
* crossed beaks
* brain asymmetries
* egg-shell thinning
* changes in reproductive organs in Great Lakes fish → decreased reproduction
* reproductive problems in fish-eating birds:
* non-mating behaviour
* high embryonic death
* non-caring of offspring
* crossed beaks
* brain asymmetries
* egg-shell thinning
52
New cards
**1990s: Worldwide: Decline in amphibians**
**1990s: Worldwide: Decline in amphibians**
hypothesis: thyroid gland produces thyroxine → induces metamorphosis from tadpole to adult
* hormone mimic → excess thyroxine → tadpole becomes adult too early
* hormone blocker → thyroxine lack → tadpole does not become adult
**3 factors**: habitat destruction, fungal infestation, endocrine disruptors
hypothesis: thyroid gland produces thyroxine → induces metamorphosis from tadpole to adult
* hormone mimic → excess thyroxine → tadpole becomes adult too early
* hormone blocker → thyroxine lack → tadpole does not become adult
**3 factors**: habitat destruction, fungal infestation, endocrine disruptors
53
New cards
**1940-1960s: American women given diethylstilbestrol (DES) to prevent miscarriages**
**1940-1960s: American women given diethylstilbestrol (DES) to prevent miscarriages**
* DES = synthetic estrogen
* double blind test showed no benefit
\
**1970: Observed connection between DES mothers and adult daughters + sons with reproductive abnormalities**
* early uterine cancers, infertility; clear-cell carcinoma of vagina + cervix
* DES mothers increased risk of breast cancer
* DES sons increased reproductive organ abnormalities: early testicular cancer, undescended testicles
\
**1971: DES banned**
* DES grandchildren: reproductive + oncological issues → DES mother gametes impacted by DES in the grandmother
* transgenerational effects
* DES = synthetic estrogen
* double blind test showed no benefit
\
**1970: Observed connection between DES mothers and adult daughters + sons with reproductive abnormalities**
* early uterine cancers, infertility; clear-cell carcinoma of vagina + cervix
* DES mothers increased risk of breast cancer
* DES sons increased reproductive organ abnormalities: early testicular cancer, undescended testicles
\
**1971: DES banned**
* DES grandchildren: reproductive + oncological issues → DES mother gametes impacted by DES in the grandmother
* transgenerational effects
54
New cards
**Dr. McCarthy’s Research at Ryerson: research questions + culprits**
**Do STP (municipal) and pulp mill (industrial) effluents cause observable endocrine disruption in aquatic organisms?**
\
**Ashbridges Bay STP: endocrine-modifying chemicals?**
\
**Pulp and Paper Mill: androgen mimics causing masculinization in female fish?**
\
**Ashbridges Bay STP: endocrine-modifying chemicals?**
\
**Pulp and Paper Mill: androgen mimics causing masculinization in female fish?**
55
New cards
**Dr. McCarthy’s Research at Ryerson: organism**
**Organism:** ***Gambusia affinis*** **(mosquitofish)**
* class: osteichthyes: bony fish
* 3 - 5 cm
* sexually dimorphic
* surface-feeder on insects, organic debris
* male gonopodium: deposits sperm near female anal pore → fertilization
* class: osteichthyes: bony fish
* 3 - 5 cm
* sexually dimorphic
* surface-feeder on insects, organic debris
* male gonopodium: deposits sperm near female anal pore → fertilization
56
New cards
**Dr. McCarthy’s Research at Ryerson: set up**
* 2 cells per aquaria
* 4 female fish per cell
* STP effluent
* Pulp mill effluent
* 4 replicate aquaria
* reference
* 4 female fish per cell
* STP effluent
* Pulp mill effluent
* 4 replicate aquaria
* reference
57
New cards
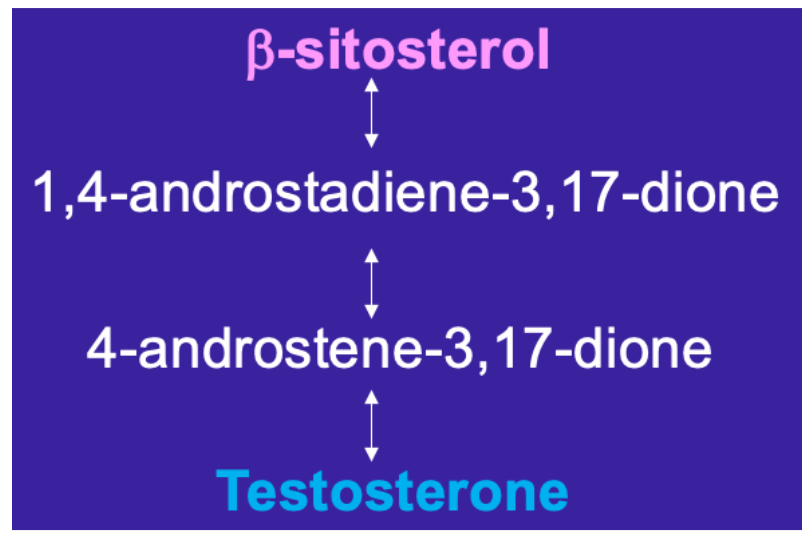
**Dr. McCarthy’s Research at Ryerson: result + conclusion + culprit**
**Result:** masculinization of female → growing gonapodium from anal fin
\
**Conclusion:** chemicals present having androgenic effect in both pulp mill + STP effluents
\
**Question:** which chemical(s)?
\
**Culprit: biodegradation of β-sitosterol by** ***Mycobacterium smegmatis***
* degraded β-sitosterol by *Mycobacterium smegmatis* → testosterone
* female mosquitofish exposed to __only__ β-sitosterol → no masculinization
* females exposed to β-sitosterol __*and*__ *Mycobacterium smegmatis →* masculinization after two weeks
\
**Conclusion:** chemicals present having androgenic effect in both pulp mill + STP effluents
\
**Question:** which chemical(s)?
\
**Culprit: biodegradation of β-sitosterol by** ***Mycobacterium smegmatis***
* degraded β-sitosterol by *Mycobacterium smegmatis* → testosterone
* female mosquitofish exposed to __only__ β-sitosterol → no masculinization
* females exposed to β-sitosterol __*and*__ *Mycobacterium smegmatis →* masculinization after two weeks
58
New cards
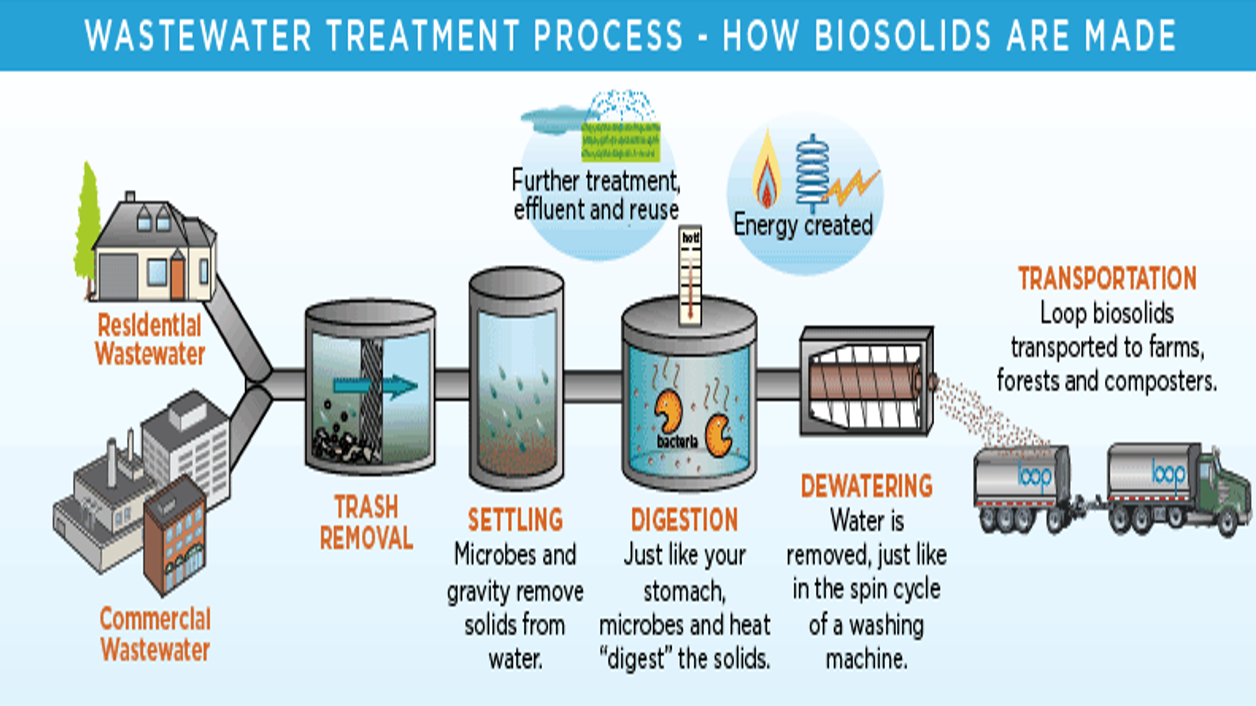
**Biosolids: how STPs work**
wastewater passed through screening equipment for object removal → grit removal → primary setting: settled material removed → aeration/activated sludge: pollutants consumed through biological degradation → secondary setting → filtration by disc filters → ultraviolet disinfection → aeration to bring dissolved O₂ up to permit level → sludge disposal
59
New cards
**How biosolids are made**
residential + commercial wastewater → trash removal → settling: microbes + gravity remove solids from water → digestion: microbes and heat digest solids → dewatering: water is removed → transportation: biosolids transported to farms + forests + composters
60
New cards
**Land-application of biosolids: advantages and disadvantages**
**advantages – human feces:**
1. source of nutrients to plants + organisms in soil: C, P, N, K
2. improves soil texture + structure
3. reduces water runoff → increased filtration
4. improved water - holding capability of soil
5. reduces energy - expensive production of commercial fertilizer
\
**disadvantages:**
* organic contaminants + heavy metals + pathogens
* may contain: drugs, phytosterols, microplastics
* soil compaction
* potential negative impact on groundwater + receiving water quality
* potential toxicity to terrestrial + aquatic organisms
1. source of nutrients to plants + organisms in soil: C, P, N, K
2. improves soil texture + structure
3. reduces water runoff → increased filtration
4. improved water - holding capability of soil
5. reduces energy - expensive production of commercial fertilizer
\
**disadvantages:**
* organic contaminants + heavy metals + pathogens
* may contain: drugs, phytosterols, microplastics
* soil compaction
* potential negative impact on groundwater + receiving water quality
* potential toxicity to terrestrial + aquatic organisms
61
New cards
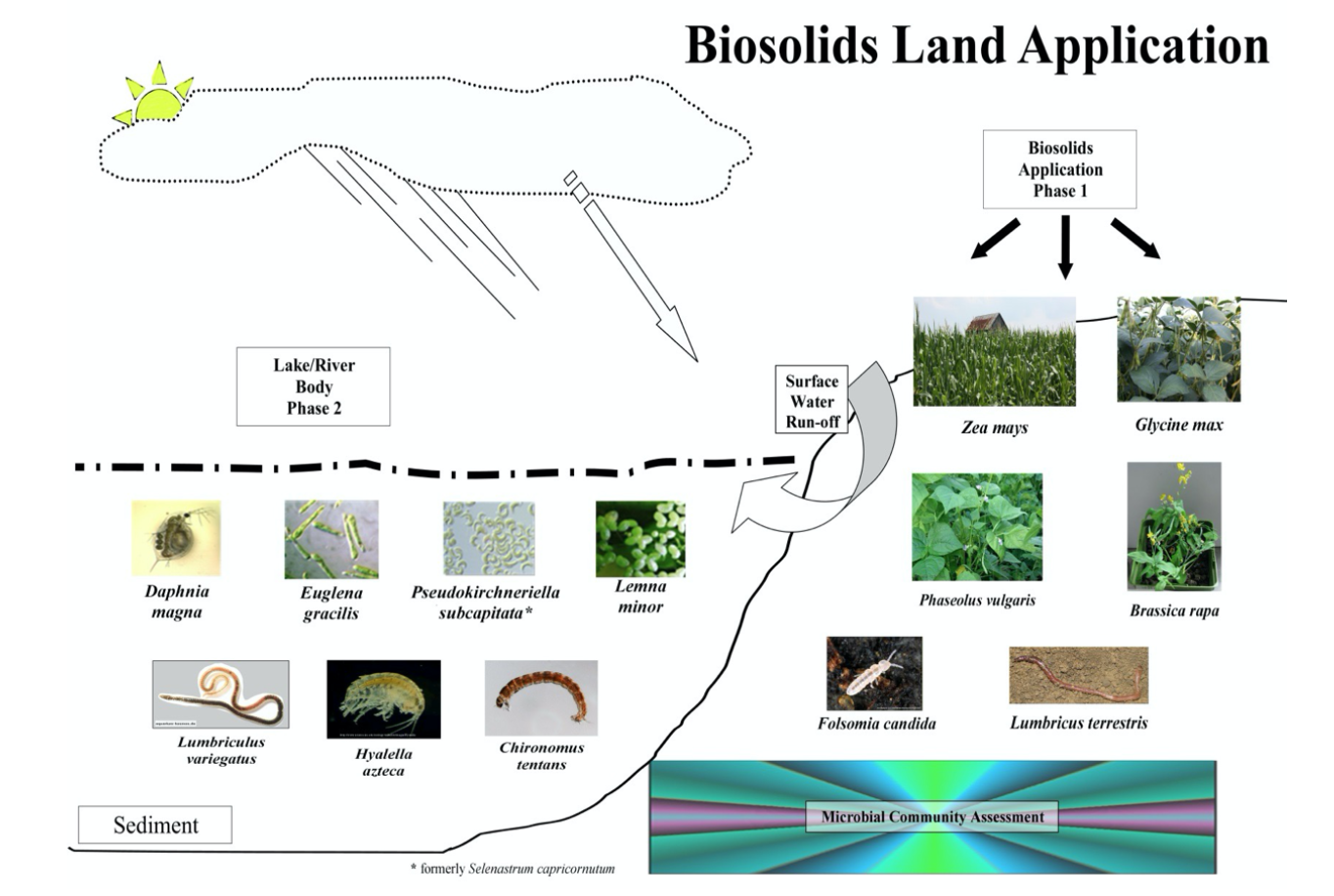
**How to assess potential impact of biosolids on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems**
**Phase I: Biosolids Application:**
* Plants: Zea mays + Glycine max + Phaseolus vulgaris + Brassica rapa
* Microbial community: Folsomia candida + Lumbricus terrestris → surface water runoff→
\
**Phase II: Lake/River Body**:
* Daphnia magna + Euglena gracilis + Raphidocelis subcapitata + Lemna minor + Lumbriculus variegatus + Hyalla azteca + Chironomus tentans
* Plants: Zea mays + Glycine max + Phaseolus vulgaris + Brassica rapa
* Microbial community: Folsomia candida + Lumbricus terrestris → surface water runoff→
\
**Phase II: Lake/River Body**:
* Daphnia magna + Euglena gracilis + Raphidocelis subcapitata + Lemna minor + Lumbriculus variegatus + Hyalla azteca + Chironomus tentans
62
New cards
**Lumbricus terrestris (microbial - terrestrial)**
* detritivorous
* hermaphroditic
* increase soil fertility: turns organic matter into humus (fertile soil)
* keystone species
* bioassay endpoints: mortality, growth, reproduction
* hermaphroditic
* increase soil fertility: turns organic matter into humus (fertile soil)
* keystone species
* bioassay endpoints: mortality, growth, reproduction
63
New cards
**Brassica rapa + Zea mays (plants - terrestrial)**
* short lifecycle
* multi-generation testing
* acute (short term) / chronic (long term)
\
**Zea mays - Corn**
* bioassay endpoints: percent + time-to-germination, plant height, number of leaves + length, time-to-flowering, # of seeds + fruit, final total biomass
* multi-generation testing
* acute (short term) / chronic (long term)
\
**Zea mays - Corn**
* bioassay endpoints: percent + time-to-germination, plant height, number of leaves + length, time-to-flowering, # of seeds + fruit, final total biomass
64
New cards
**Folsomia candida**: **Springtails (microbial - terrestrial)**
* detritivores
* standard soil test organism; government protocol (pesticides)
* consume plant-root pathogens
* easily cultured
* avoidance tests; reproductive tests
* standard soil test organism; government protocol (pesticides)
* consume plant-root pathogens
* easily cultured
* avoidance tests; reproductive tests
65
New cards
**Bio-criteria used for Sustainable Water Monitoring**
* sub-acute: biochemical, behavioural
* acute (short term): lethality
* chronic (long term): growth
* reproductive assessment: # of offspring
* multi-generational: health + reproductive potential of offspring
* acute (short term): lethality
* chronic (long term): growth
* reproductive assessment: # of offspring
* multi-generational: health + reproductive potential of offspring
66
New cards
**Raphidocelis subcapitata (aquatic)**
* single-celled, chlorophyte
* planktonic, autotrophs
* assess acute, chronic, reproductive toxicity
* whitens + straightens out when stressed
* planktonic, autotrophs
* assess acute, chronic, reproductive toxicity
* whitens + straightens out when stressed
67
New cards
**Hyalella azteca (aquatic)**
* amphipod, crustacea
* no carapace (no protection against contaminants)
* shredders + grazers
* scavenging omnivores
* benthic/swimmers (when stressed, produce very strange swimming behaviours)
* acute/chronic
* no carapace (no protection against contaminants)
* shredders + grazers
* scavenging omnivores
* benthic/swimmers (when stressed, produce very strange swimming behaviours)
* acute/chronic
68
New cards
**Chironomus tentans (aquatic)**
* larval insects: non-biting midges
* sensitive to pesticides
* monitor:
* swimming undulations
* ventilation
* avoidance responses
* sensitive to pesticides
* monitor:
* swimming undulations
* ventilation
* avoidance responses
69
New cards
**Lumbriculus variegatus (aquatic)**
* benthic annelid
* found in freshwater ponds, rivers, lakes
* feeds on microorganisms, organic material
* important food for larval fish
* rapid asexual reproduction
* bioassay endpoints: lethality, reproductive impairment
* found in freshwater ponds, rivers, lakes
* feeds on microorganisms, organic material
* important food for larval fish
* rapid asexual reproduction
* bioassay endpoints: lethality, reproductive impairment
70
New cards
**Daphnia magna (aquatic)**
* water flea: saltatory swimming behaviour
* crustacea
* fresh waters, planktonic
* grazers, filter feeder, consume phytoplankton
* important larval fish food source
\
**Bioassay endpoints:**
* lethality
* growth reduction
* reproductive impairment
* stress swimming behaviour
* crustacea
* fresh waters, planktonic
* grazers, filter feeder, consume phytoplankton
* important larval fish food source
\
**Bioassay endpoints:**
* lethality
* growth reduction
* reproductive impairment
* stress swimming behaviour
71
New cards
**Major Classes of Contaminants (5)**
1. **Organic compounds:**
* Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
* Organochlorine insecticides
* Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
* Dioxins and furans
* Polynuclear (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
\
2. **Inorganic gases:**
* Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
* Nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulphur dioxide (SO₂)
\
3. **Excessive nutrients:**
* O₂ demanding compounds
* nitrogen, phosphorus
\
4. **Heavy metals:**
* Arsenic (As)
* Cadmium (Cd)
* Mercury (Hg)
* Lead (Pb)
\
5. **Radionuclides**
72
New cards
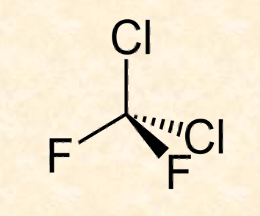
**Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) - organic compound**
* haloalkane
* very stable; nonreactive; nontoxic (in traditional bioassays)
* survive in atmosphere > 120 years: enough time to reach stratosphere
\
**Uses:**
* refrigeration, foam production
* flame retardant
* aerosol propellants
\
**Problem:**
* ozone depletion in stratosphere → protective O₃ gone → uv radiation hits Earth → uv rays damage DNA → causes thymine dimers → distorted DNA; improper function
* very stable; nonreactive; nontoxic (in traditional bioassays)
* survive in atmosphere > 120 years: enough time to reach stratosphere
\
**Uses:**
* refrigeration, foam production
* flame retardant
* aerosol propellants
\
**Problem:**
* ozone depletion in stratosphere → protective O₃ gone → uv radiation hits Earth → uv rays damage DNA → causes thymine dimers → distorted DNA; improper function
73
New cards
**Organoinsecticides - organic compound**
* bioaccumulate in food web; very lipophilic: adipose tissue, cell membranes
* neurotoxin: Na+ channels stay open → repetitive firing of action potential → death
* alternative insecticide: dieldrin → linked to Parkinsons, breast cancer
* neurotoxin: Na+ channels stay open → repetitive firing of action potential → death
* alternative insecticide: dieldrin → linked to Parkinsons, breast cancer
74
New cards
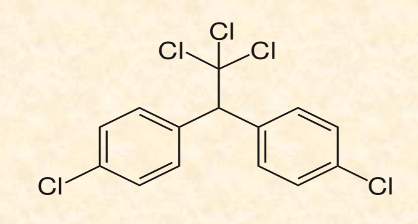
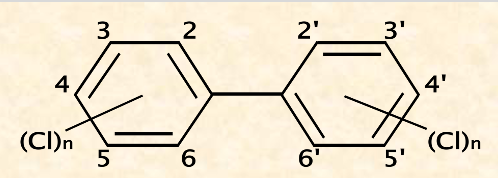
**Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) - organic compound**
* 209 congeners (related chemicals)
* very stable, not easily biodegraded, low flammability
\
**Uses:**
* industrial lubricants
* heat conductors in transformers plasticizers
\
**Problem:**
* PCBs = definite carcinogens in humans
* binds strongly to soil → very toxic + persistent, not easily biodegraded
* higher chlorination → higher lipophilicity → bioaccumulate up food webs
* transplacental transference to fetus: transferred to breastmilk → developmental learning in fetus → implicated in learning disabilities
* very stable, not easily biodegraded, low flammability
\
**Uses:**
* industrial lubricants
* heat conductors in transformers plasticizers
\
**Problem:**
* PCBs = definite carcinogens in humans
* binds strongly to soil → very toxic + persistent, not easily biodegraded
* higher chlorination → higher lipophilicity → bioaccumulate up food webs
* transplacental transference to fetus: transferred to breastmilk → developmental learning in fetus → implicated in learning disabilities
75
New cards
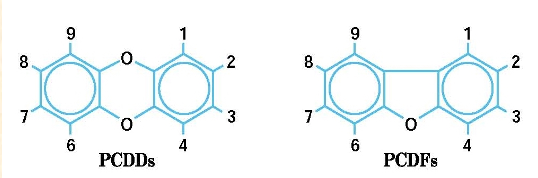
**Dioxins and furans furans (polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzo-p-furans) - organic compound**
**Sources:**
* incomplete combustion of PCBs; or photolytic degradation of PCBs
* organochlorine manufacturing byproducts: herbicides (Agent Orange), wood preservatives, PCBs
* 75 congeners
* toxicity depends on number, position of Cl
\
**Problem:**
* extremely toxic: known teratogen + mutagen, highly-suspected carcinogen
* extremely lipophilic → climbs food chain
* humans exposed in diet (fish, meat, dairy), cigarette smoke
* chronic exposure to low doses: liver malfunction
* mothers pass significant amount to children: placental transference, breast milk
* incomplete combustion of PCBs; or photolytic degradation of PCBs
* organochlorine manufacturing byproducts: herbicides (Agent Orange), wood preservatives, PCBs
* 75 congeners
* toxicity depends on number, position of Cl
\
**Problem:**
* extremely toxic: known teratogen + mutagen, highly-suspected carcinogen
* extremely lipophilic → climbs food chain
* humans exposed in diet (fish, meat, dairy), cigarette smoke
* chronic exposure to low doses: liver malfunction
* mothers pass significant amount to children: placental transference, breast milk
76
New cards
**Polynuclear (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) - organic compound**
**Sources:**
* natural crude oil, coal deposits, creosote
* incomplete burning: wood, coal, petroleum products, bbqing meat
* oil spills
* roofing tar; asphalt
* atmospheric pollutants: emissions from cars, steel smelters
* forest fires
\
**Problem:**
* toxicity: b(a)p – highly carcinogenic:
* DNA adducts: DNA replication errors → fused aromatic rings break open: bind to DNA
* historically: B(a)P implicated in chimney sweeps cancers
* lipophilic; binds to soil; aquatic sediments
* natural crude oil, coal deposits, creosote
* incomplete burning: wood, coal, petroleum products, bbqing meat
* oil spills
* roofing tar; asphalt
* atmospheric pollutants: emissions from cars, steel smelters
* forest fires
\
**Problem:**
* toxicity: b(a)p – highly carcinogenic:
* DNA adducts: DNA replication errors → fused aromatic rings break open: bind to DNA
* historically: B(a)P implicated in chimney sweeps cancers
* lipophilic; binds to soil; aquatic sediments

77
New cards
**Carbon dioxide (CO₂) - inorganic gas**
**Sources:**
* combustion: **fossil fuels**: cars, industry: airlines-
* burning of wood, dung, traditional heating
* controlled crop burns
* deforestation → stored carbon is released into the atmosphere again as **CO₂**
\
**Problem:**
* linked to global warming
* combustion: **fossil fuels**: cars, industry: airlines-
* burning of wood, dung, traditional heating
* controlled crop burns
* deforestation → stored carbon is released into the atmosphere again as **CO₂**
\
**Problem:**
* linked to global warming
78
New cards
**Nitrogen oxides (NOx) + sulphur dioxide (SO₂) - inorganic gas**
**Sources:**
* combustion: cars, coal power plants, airplanes
\
**Problem:**
* produce low pH precipitation: ***acid rain***
* combustion: cars, coal power plants, airplanes
\
**Problem:**
* produce low pH precipitation: ***acid rain***
79
New cards
**Oxygen-demanding compounds - excessive nutrients**
**carbon** materials with high **biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)**
* provide food for bacteria; uses up O₂
* leads to fish death → zooplankton death
* BOD level = measurement of organic pollution
* provide food for bacteria; uses up O₂
* leads to fish death → zooplankton death
* BOD level = measurement of organic pollution
80
New cards
**Nitrogen, phosphorus - excessive nutrients**
* excessive nutrients in water = unlimited plant growth → eutrophication
* changes structure, function of communities
* EXCESSIVE amounts of nutrients in waste water + in systems → depletion of O₂
* changes structure, function of communities
* EXCESSIVE amounts of nutrients in waste water + in systems → depletion of O₂
81
New cards
**Arsenic (As) - heavy metal**
**Group-A carcinogen**
\
**Uses:**
* alloy with Pb provides strength: car batteries, ammunition (bullets)
* pesticides: pressure-treated wood
\
**Problems:**
* As₂O₃: absorbed through lungs, intestines
* coagulates proteins
* binds to protein thiols; denatures 2°, 3 ° structure structure
* loss of biological activity
* inhibits production of ATP during Citric Acid Cycle (immediate death)
\
**Uses:**
* alloy with Pb provides strength: car batteries, ammunition (bullets)
* pesticides: pressure-treated wood
\
**Problems:**
* As₂O₃: absorbed through lungs, intestines
* coagulates proteins
* binds to protein thiols; denatures 2°, 3 ° structure structure
* loss of biological activity
* inhibits production of ATP during Citric Acid Cycle (immediate death)
82
New cards
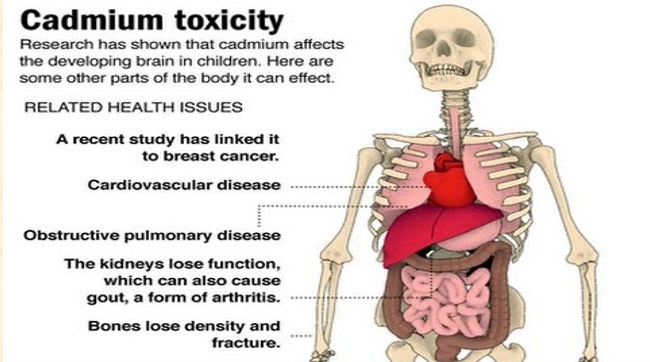
**Cadmium (Cd) - heavy metal**
**Uses:**
* metal alloys; paint pigments,
* batteries, plastic stabilizers
* anticorrosion in aircraft
* Q-LED displays: TVs
* high levels in cigarettes; tobacco plants accumulate Cd from soil
\
**Problem:**
* toxic, carcinogenic: causes bone disease, kidney damage, lung cell death
* metal alloys; paint pigments,
* batteries, plastic stabilizers
* anticorrosion in aircraft
* Q-LED displays: TVs
* high levels in cigarettes; tobacco plants accumulate Cd from soil
\
**Problem:**
* toxic, carcinogenic: causes bone disease, kidney damage, lung cell death
83
New cards
**Mercury (Hg) - heavy metal**
**Sources:**
* coal-burning power plants
* volcanic activity
\
**Uses:**
* electronics: good electricity conductor
* dental amalgams
* dams: expose HG in waterlogged land
* soaps, cosmetics
\
**Problem:**
* very toxic: brain tremours, kidney failure
* coal-burning power plants
* volcanic activity
\
**Uses:**
* electronics: good electricity conductor
* dental amalgams
* dams: expose HG in waterlogged land
* soaps, cosmetics
\
**Problem:**
* very toxic: brain tremours, kidney failure
84
New cards
**Lead (Pb) - heavy metal**
**Uses:**
* gasoline, batteries, piping, ammunition, paint
\
**Problem:**
* neurological dysfunction
* inhibition of synthesis of hemoglobin; binds to sulfhydral groups on enzymes
* accumulates in soft tissue, bones; destroys myelin sheath in neurons
* no lower level of Pb that has no effect on cognition in children
* gasoline, batteries, piping, ammunition, paint
\
**Problem:**
* neurological dysfunction
* inhibition of synthesis of hemoglobin; binds to sulfhydral groups on enzymes
* accumulates in soft tissue, bones; destroys myelin sheath in neurons
* no lower level of Pb that has no effect on cognition in children
85
New cards
**Radionuclides**
**Uses:**
* nuclear weapons production/testing
* energy production
* medical research
\
**Problem:**
* toxic, carcinogenic → lung cancer
* bonds broken in macromolecules
* bone marrow destroyed; conc. of RBCs destroyed
* nuclear weapons production/testing
* energy production
* medical research
\
**Problem:**
* toxic, carcinogenic → lung cancer
* bonds broken in macromolecules
* bone marrow destroyed; conc. of RBCs destroyed
86
New cards
**Top down: fate of contaminants case study 1: Florida everglades pre-1928: terrestrial compartment (Florida)**
**Florida Everglades:**
* temperate, tropical
* very slow-moving sheet of water
* heavy rains floods banks of:
* Kissimmee River
* Lake Okeechobee
* temperate, tropical
* very slow-moving sheet of water
* heavy rains floods banks of:
* Kissimmee River
* Lake Okeechobee
87
New cards
**Top down: fate of contaminants case study 1: Florida everglades pre-1928: aquatic compartment (Florida Bay)**
***Florida Bay/Florida Keys***:
* mangrove forests; marine nursery
* vast expanse of sawgrass wetlands (wet sedge)
* small islands of trees on limestone ridges
* during winter season: grassy plain is dry: lightning-strike fires sweep across plain → burn plant stocks down to wet soil → nutrients return to wet soil; roots unaffected → rich peat soil
* during rainy season: sea of sawgrass covered with 1m water: rapid plant growth
* drifts south from Lake to Florida Bay
* freshwater meets saltwater: estuarine ecosystem
* haven for all kinds of animals
* shelters: turtle grass, sea grass
* gator holes: alligators form holes in limestone depressions by clearing wet soil with feet + snout → conserve enough water during winter drought → keep fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds alive → then, rainy season starts → cycle begins again
* mangrove forests; marine nursery
* vast expanse of sawgrass wetlands (wet sedge)
* small islands of trees on limestone ridges
* during winter season: grassy plain is dry: lightning-strike fires sweep across plain → burn plant stocks down to wet soil → nutrients return to wet soil; roots unaffected → rich peat soil
* during rainy season: sea of sawgrass covered with 1m water: rapid plant growth
* drifts south from Lake to Florida Bay
* freshwater meets saltwater: estuarine ecosystem
* haven for all kinds of animals
* shelters: turtle grass, sea grass
* gator holes: alligators form holes in limestone depressions by clearing wet soil with feet + snout → conserve enough water during winter drought → keep fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds alive → then, rainy season starts → cycle begins again
88
New cards
**Mangrove forests ecological functions (8)**
* prevent erosion into sea
* barrier from tsunamis
* sequester CO₂
* filter runoff
* provide habitat
* protect land against flooding
* improve water quality
* support fisheries + recreational resources
* barrier from tsunamis
* sequester CO₂
* filter runoff
* provide habitat
* protect land against flooding
* improve water quality
* support fisheries + recreational resources
89
New cards
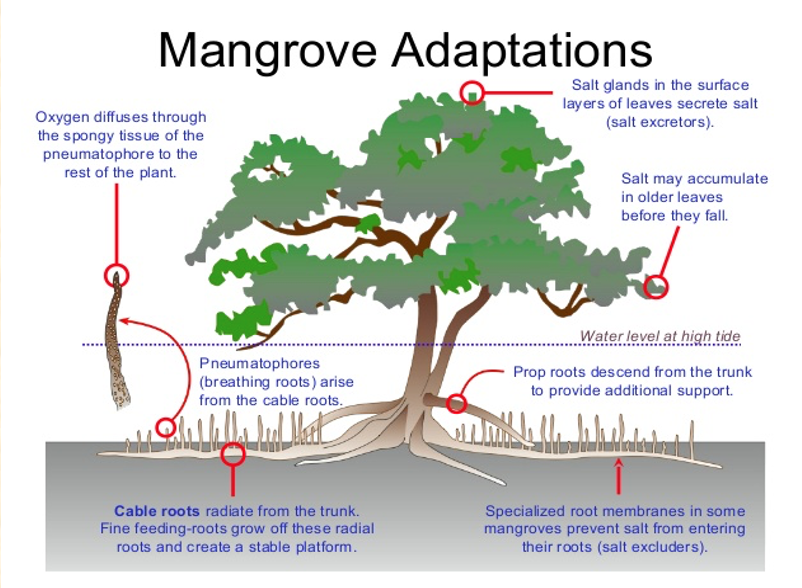
**Mangrove adaptions (to live in salty water)**
* salt glands in surface layers of leaves excretes salt (salt excreters)
* salt may accumulate in older leaves before they fall
* O₂ diffuses through spongy tissue of pneumatophore to rest of plant
* pneumatophores (breathing roots) arise from cable roots
* prop roots descend from trunk to provide additional support
* cable roots radiate from trunk; fine feeding-roots grow off radial roots + create stable platform
* specialized root membranes in some mangroves prevent salt from entering their roots (salt excluders)
* salt may accumulate in older leaves before they fall
* O₂ diffuses through spongy tissue of pneumatophore to rest of plant
* pneumatophores (breathing roots) arise from cable roots
* prop roots descend from trunk to provide additional support
* cable roots radiate from trunk; fine feeding-roots grow off radial roots + create stable platform
* specialized root membranes in some mangroves prevent salt from entering their roots (salt excluders)
90
New cards
**Florida everglades post-1928: problems**
**1928: Category 5 hurricane**
* storm surge on Lake Okeechobee
* 1800 people died
* Congress: prevent future tragedies:
* army corps of engineers (federal): built 40 ft high Hoover Dike along eastern + southern side of lake
* stopped flooding by building canals to Atlantic Ocean
* reduced Lake from recharging Everglades
* extended drought in 1930s: Everglades became dustbowl
* drying of soil and roots: lightning strike fires burned right down below soil → further dried out land
* Canals built by Everglades Drainage District: *State, Municipal*
* aquifers drained, excess freshwater all dumped into ocean (wasted)
* canals, levees, pump stations diverted excess fresh water to Atlantic Ocean
* much drier land: converted to farmland: sugarcane, pesticides
* fertilizers, pesticides ended up in rest of Everglades
* phosphorous in cattails: growth of non-native cattails → overran native sawgrass
* urban growth: 1950s: grew 4x faster than rest of nation
* nursery for amphibians, reptiles, birds, fish gone
* storm surge on Lake Okeechobee
* 1800 people died
* Congress: prevent future tragedies:
* army corps of engineers (federal): built 40 ft high Hoover Dike along eastern + southern side of lake
* stopped flooding by building canals to Atlantic Ocean
* reduced Lake from recharging Everglades
* extended drought in 1930s: Everglades became dustbowl
* drying of soil and roots: lightning strike fires burned right down below soil → further dried out land
* Canals built by Everglades Drainage District: *State, Municipal*
* aquifers drained, excess freshwater all dumped into ocean (wasted)
* canals, levees, pump stations diverted excess fresh water to Atlantic Ocean
* much drier land: converted to farmland: sugarcane, pesticides
* fertilizers, pesticides ended up in rest of Everglades
* phosphorous in cattails: growth of non-native cattails → overran native sawgrass
* urban growth: 1950s: grew 4x faster than rest of nation
* nursery for amphibians, reptiles, birds, fish gone
91
New cards
**Florida Bay post-1928 + today**
* estuary __**not recharged**__ from Everglades freshwater runoff
* became more salty
* cyanobacteria blooms huge
* use up O₂ → covers spawning beds
* seagrass declines
* mangrove forests removed for coastal condos
* no nurseries for fish, birds, shellfish
* reduced economy: tourism, commercial fisheries declined
\
**Today:**
* Everglades half original size
* bird population down 90%
* home to 50 endangered/threatened species
* exotic pets dumped (eg. pythons)
* became more salty
* cyanobacteria blooms huge
* use up O₂ → covers spawning beds
* seagrass declines
* mangrove forests removed for coastal condos
* no nurseries for fish, birds, shellfish
* reduced economy: tourism, commercial fisheries declined
\
**Today:**
* Everglades half original size
* bird population down 90%
* home to 50 endangered/threatened species
* exotic pets dumped (eg. pythons)
92
New cards
**2 major problems in Florida everglades + overview**
1. too little water recharging Everglades
2. any recharge = polluted
\
* overarching causative agent: the stopping of the water
\
* what is the toxic agent?
* removing floodwaters/water diversion
93
New cards
**Partial restoration of Florida everglades in 1996**
\
* farmers forced to clean up **P** runoff
* agricultural land bought: turned into marshes
* more recharge
* filter agricultural runoff before reaching Everglades
* Army Corps of Engineers re-engineer canals, levees
* more natural flow of water
* stop freshwater flowing to Atlantic Ocean
* farmers forced to clean up **P** runoff
* agricultural land bought: turned into marshes
* more recharge
* filter agricultural runoff before reaching Everglades
* Army Corps of Engineers re-engineer canals, levees
* more natural flow of water
* stop freshwater flowing to Atlantic Ocean
94
New cards
**Top down: fate of contaminants case study 2: acid rain**
**Definition:** caused by emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide
* any precipitation more acidic than natural rain: any pH* spreads over thousands of kms: long-range atmospheric transport
\
**Effects:**
* destroys terrestrial plants → leeches out nutrients, mobilizes metals → plaques out on plant roots → cannot take up water, O₂, nutrients
* impacts soil microorganisms
* impacts soil macroinvertebrates → breaks own calcium carbonate in exoskeletons
* pollutes water sources
* impacts aquatic organisms
* indirectly impacts crop production → more fertilizer must be used bc acid rain leeches out nutrients
\
\
* any precipitation more acidic than natural rain: any pH
\
**Effects:**
* destroys terrestrial plants → leeches out nutrients, mobilizes metals → plaques out on plant roots → cannot take up water, O₂, nutrients
* impacts soil microorganisms
* impacts soil macroinvertebrates → breaks own calcium carbonate in exoskeletons
* pollutes water sources
* impacts aquatic organisms
* indirectly impacts crop production → more fertilizer must be used bc acid rain leeches out nutrients
\
\
95
New cards
**Two (2) acid rain sources**
**Sources:** anthropogenic (human made)
\
1. **burning fossil fuels**:
* coal: ***electric power generation*** → SO₂
* gasoline: internal combustion engine → NOx
* coal: smelting metals → SOx
\
2. **burning rainforests: burning of 4 macromolecules:**
* SO₂: proteins - amino acid cysteine + disulfide bridges
* NOx: nitrogenous bases in DNA
\
1. **burning fossil fuels**:
* coal: ***electric power generation*** → SO₂
* gasoline: internal combustion engine → NOx
* coal: smelting metals → SOx
\
2. **burning rainforests: burning of 4 macromolecules:**
* SO₂: proteins - amino acid cysteine + disulfide bridges
* NOx: nitrogenous bases in DNA
96
New cards
**History of acid rain**
* loss of salmon in Scandinavian lakes in 1940s
* 1970s: rain in southern Michigan: pH 3.9
* U.S. record low: Wheeling, West Virginia: pH 1.4 → open-face coal mining
* coal dust goes into air, sulphur in dust combines with water in air → acid raid
* acid rain in southeastern Canada: Pierre Trudeau shows president Reagan in Quebec dead fish + forests + effects of coal burning and acid rain
* clean air act: scrubbers added to coal burning stacks
* flue-gas desulfurizer (scrubber) removes CO₂ before it goes into the atmosphere
* 1970s: rain in southern Michigan: pH 3.9
* U.S. record low: Wheeling, West Virginia: pH 1.4 → open-face coal mining
* coal dust goes into air, sulphur in dust combines with water in air → acid raid
* acid rain in southeastern Canada: Pierre Trudeau shows president Reagan in Quebec dead fish + forests + effects of coal burning and acid rain
* clean air act: scrubbers added to coal burning stacks
* flue-gas desulfurizer (scrubber) removes CO₂ before it goes into the atmosphere
97
New cards
**Experimental Lakes Area (ELA): Lake 223 - Schindler et. al**
* go into environment, add stressor, document findings, tell voting public the problem
* air masses from US causing high deposition of sulphate in Canadian lakes
* proposed deliberate lake acidification
* primarily look at phytoplankton + invertebrates
* literature research: threshold for damage to fish: pH5
* acid rain concern in Alberta: funding for lake 223 from Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Project
* spent 2 years gathering baseline date on lakes
* air masses from US causing high deposition of sulphate in Canadian lakes
* proposed deliberate lake acidification
* primarily look at phytoplankton + invertebrates
* literature research: threshold for damage to fish: pH5
* acid rain concern in Alberta: funding for lake 223 from Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Project
* spent 2 years gathering baseline date on lakes
98
New cards
**ELA: Lake 223: abiotic and biotic baseline in 2 lakes (223 + reference)**
abiotic baseline:
* baseline pH
* water levels
* conductivity (ions on minerals that are present)
* temperature
* O₂ levels
* N and P present
\
biotic baseline:
* invertebrates in sediment and water column
* fish
* phytoplankton
* amphibians
* plants (macrophytes in particular)
* baseline pH
* water levels
* conductivity (ions on minerals that are present)
* temperature
* O₂ levels
* N and P present
\
biotic baseline:
* invertebrates in sediment and water column
* fish
* phytoplankton
* amphibians
* plants (macrophytes in particular)
99
New cards
**ELA: Lake 223:** **8 years of treatment + impacts - 1976 to 1983**
* 1976: starts adding H₂SO₄ (aq): __terrestrial,__ __aquatic__ changes in __**abiotic**__ + __**biotic**__ factors compared to **reference lake**
* 1977: pH 6.1:
* primary producers impacted
* brown algae decreased
* single-species green algae increased
* algal biodiversity decreased
* 1978: pH 5.9:
* opossum shrimp: mysids decrease
* chironomids: larval midges heavy emergence
* fathead minnow fail to reproduce
* 1979: pH 5.6
* thick mats of green algae: mougeotia → O₂ levels decline
* crawfish exoskeletons affected: chitin + calcium carbonate degradation
* crawfish egg masses decrease
* fathead minnows decline → lake trout starve
* algal production + midge emergence high
* 1980: pH 5.6:
* primary producers: acidophillic diatoms: low quality food, hard to digest
* primary consumers: no edible rotifers → copepods go extinct
* starvation
* crawfish infested with parasites
* crawfish egg masses infected with fungus
* no successful crawfish reproduction: keystone aquatic food web organism
* 1981: pH 5.0:
* no successful lake trout reproduction
* starving, compromised immune systems
* inedible rotifers increase
* decreased edible zooplankton
* crawfish populations decline
* fish eating birds affected (no food)
* 1982: pH 5.1
* lake trout spawning sites covered with mougeotia
* thick algal mats smother fish eggs
* block sunlight for submerged macrophyte growth
* 1983: pH 5.1:
* algal populations: inedible
* lake trout = in bad shape → white sucker
* crawfish, mayflies absent
* 1977: pH 6.1:
* primary producers impacted
* brown algae decreased
* single-species green algae increased
* algal biodiversity decreased
* 1978: pH 5.9:
* opossum shrimp: mysids decrease
* chironomids: larval midges heavy emergence
* fathead minnow fail to reproduce
* 1979: pH 5.6
* thick mats of green algae: mougeotia → O₂ levels decline
* crawfish exoskeletons affected: chitin + calcium carbonate degradation
* crawfish egg masses decrease
* fathead minnows decline → lake trout starve
* algal production + midge emergence high
* 1980: pH 5.6:
* primary producers: acidophillic diatoms: low quality food, hard to digest
* primary consumers: no edible rotifers → copepods go extinct
* starvation
* crawfish infested with parasites
* crawfish egg masses infected with fungus
* no successful crawfish reproduction: keystone aquatic food web organism
* 1981: pH 5.0:
* no successful lake trout reproduction
* starving, compromised immune systems
* inedible rotifers increase
* decreased edible zooplankton
* crawfish populations decline
* fish eating birds affected (no food)
* 1982: pH 5.1
* lake trout spawning sites covered with mougeotia
* thick algal mats smother fish eggs
* block sunlight for submerged macrophyte growth
* 1983: pH 5.1:
* algal populations: inedible
* lake trout = in bad shape → white sucker
* crawfish, mayflies absent
100
New cards
**ELA: Lake 223:** **overall impacts (4) + conclusion**
1. **disturbance in normal ionic balance**
* crawfish exoskeleton not form
* some zooplankton species stop reproducing
\
2. **changes in species composition**
* less bacteria
* more fungi; more competition
* more fungal diseases
* more fungi covering spawning beds, egg masses
* less desirable phytoplankton species
* less O₂
* disrupt food chain by replacing edible with inedible
\
3. **soluble heavy metals in soil → leach into water**
\
4. **terrestrial impacts**
* pH changes kill biota: plants, animals, soil microbiota
* leach nutrients from soil: infertility
* heavy metal release from soil: leach into aquatic system
\
**Conclusion:** one stressor; huge community changes