Life science - Semester 1
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
The 4 spheres
Biosphere
Lithosphere
Atmosphere
hydrosphere
Biosphere
is made up of the parts of the earth where life exists all ecosystems.
Lithosphere
Solid outer part of the earth, is made up of the brittle upper portion of the mantel and the crust.
Atmosphere
Is made up of layers of gases surrounding a planet or other celestial body.
hydrosphere
Total water on the planet, includes ice, all water in the air on the ground, and underground.
Biotic factor
living components within an ecosystem that influence other organisms or the environment.
Abiotic
non-living components of an ecosystem that can influence living organisms and environment
Biosphere: Levels of organisation
biosphere → biome → ecosystem → community → population → species
8 major terrestrial biomes
Tropical rain forests, savannahs, subtropical deserts, chaparral, temperate grasslands, temperate forests, boreal forests, and artic tundra.
+ marine biome and freshwater biome
Food webs/food chains
food webs→ demonstrate across whole ecosystems and shows the biodiversity of an environment
food chains → show flow of energy
Photosythsis + equation
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
(Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen + water)
Hydrothermal vents and thermal environments
create chemical energy in inorganic chemicals, released by the vents. allows organisms to survive in those ecosystem s
Transfer of energy
every transfer Some energy is lost as heat energy that cannot be used as a source of energy for living. Only 10% of the energy transfers to the next trophic levels for next transfer
Trophic levels
First Trophic Level: Autotrophs. (the producers),
Second Trophic Level: Primary Consumers.
Third Trophic Level: Secondary Consumers.
Fourth Trophic Level: Tertiary Consumers.
Fifth Trophic Level: Apex Consumers.
Autotrophs, Consumers, Detritivores, and Decomposers
3 types of ecological pyramids + define purpose
are graphical representations of the relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem.
Numbers - how many producers/consumers are within each trophic level?
Biomass - the biomass (dehydrated mass) present shows relationships between biomass and trophic levels
Energy - shows available energy at each trophic level. (only 10% transfers)
Biodiversity
full range of different living things in a particular area or region; it can be described at various levels.
range of different species
genetic diversity
diversity of ecosystems present in larger area
Crucial for health and resilience of ecosystem, provides a variety of species with unique traits, enabling ecosystems to adapt to environmental changes
What high biodiversity enhances
ecosystem stability, making them resistant to disease, invasive species and climate fluctuations
Species richness
number of species within a given area
Species abundance/evenness
number of individuals within each particular species (also known as species eveness)
SDI
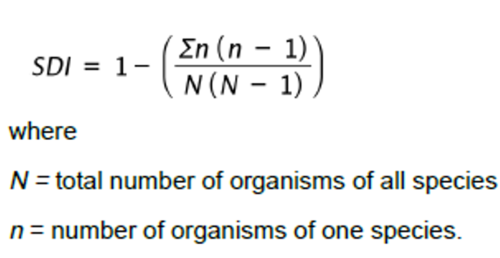
Ecosystem stabliity
closely linked with biodiversity not clear what level of biodiversity is required to guard against ecosystem disfunction.
Species loss
past certain point is likely to be detrimental to the functioning of the ecosystem and its ability to resist change.
Keystone species
significant influence on ecological communities which have a pivotal role in ecosystem function and ecosystem stability
Threats to biodiversity
habitat loss
climate change
pollution
over exploitation of species
invasive species
Species diversity
takes into account both the number of species present and evenness of each species measured by SDI
what is an ecological relationships + examples
Ecological relationships describe the interactions between and among organisms within their environment
symbiotic relationship
Living together with another organism in close association. mutualism, commensalism , paratism
Intraspecific vs interspecific
Interspecific - between different species
Intraspecific - between members of the same species
autotrophs, heterotrophs, and detrivore carnivores, omnivores
Autotrophs/ producers they are able to make their own food from raw materials and energy
Heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels in a food chain, a sequence of organisms that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms.
Detrivore an animal which feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus.
Carnivore is an organism that mostly eats meat, or the flesh of animals.
An omnivore is an organism that eats plants and animals.
Herbivore only eat plants
Competition
is the struggle between organisms for the same environmental resources, eg. food, nesting sites and mates.
role of decomposers in an ecosystem and cycling matter
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a critical role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter. This process recycles nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plants, which are the primary producers. thus maintaining flow of energy and the cycling of matter, ensuring ecosystem stability and productivity.
Predation + examples
involves one organism eating another
Commensalisim
one organism is benifited and the other is unharmed
eg. barnacles on a whale
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit from the association. eg. nitrogen fixing bacteria on legume nodules
Parasitism
The parasite benefits at the expense of the host eg. heartworms in dog
Amensalism
but in this association among organisms of two different species, one is destroyed or inhibited, and the other remains unaffected
Abiotic factors in Water
Water pH
Light
Temp
Turbidity
Oxygen levels
Abiotic factors in Soil
Soil texture/ moisture
Soil nutrient
Temp
pH Levels
Atmosphere
and levels
Troposphere
stratosphere
mesosphere
ionosphere
Thermosphere
exosphere
“Todays smalls moments. Tomorrows epic”
Trophosphere
the lowest layer of the earth atmosphere, - were most weather occurs
Stratosphere
Very drak layer of atmosphere, very little waters vapour, therefore few clouds
ozone layer
Mesosphere
coldest layer
Thermosphere
experience extremely high temps due to the apsorption of solar radiation
Exosphere
outer most layer
Earths climate
the atmosphere play a crucial role roel regulating the earth’s climate, influencing temperature, pressure, and weather patterns.
Cliamte change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns.
Sporadic evens leading to climate change and why
Volcanic eruption -
cooling - ash and sulfare aerosols
warming - large volumes co2, increase greenhouse warming
Plate tectonics and climate change
-alter ocean currents
-more glaciers over land
-also move plates to create more volcanic activity.
what is Nitrogen cycle
a nutrient that cells need to make proteins, amino acids and DNA important for plant growth and chlorophyll which helps absorbs sunlight
Stages of nitrogen cycle
Fixation -coverts nitrogen in the air to ammonium, which is biologically available
Nitrification - bacteria change ammonium to nitrates to be absorbed by plants
Assimilation: - Plant absorb nitrates by the roots
Ammonification - decomposers change nitrogen into ammonium to re-enter the cycle
denitrification - nitrogen in the soil gets back into the air
link earths spheres and carbon and nitrogen cycle
Earth's spheres are interconnected in the carbon and nitrogen cycles. The atmosphere exchanges CO2 and nitrogen with living organisms. The biosphere involves plants and animals that cycle these elements through photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition. The lithosphere stores carbon and nitrogen in rocks and soils, releasing them through natural processes and human activities. The hydrosphere absorbs CO2 and cycles nitrogen through marine ecosystems. These interactions sustain life and regulate environmental processes.
Impact of excess nitrogen
due to human activity
-burning fossil fuels
-clearing forestlands and greenland’s
-fertilizer
not all fertilizer is absorbed by plant some stay
and get carried into aquatic systems via rain
nitrogen on waterways lead to over growth in algae
which blocks sunlight-reaching organisms
What is Carbon cycle + Three types
the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the spheres
atmospheric carbon cycle
terrestrial carbon cycle
oceanic carbon cycle
Binomial nomenclature
scientific name 2 words
Genus name and Species name
Stages carbon cycle
Co2 gas moves from the atmosphere to the body through photosynthetic and cellular respiration
CO2 moves back from to the atmosphere when the organims die and decompose
carbon enters the geosphere when the remains of the organism are trapped under the sediment layers
carbon can also enter the atmosphere through bushfires and volcanic activity
Amospherical carbon cycle
CO2 leavess atmosphere- photosynthies
CO2 dissolves into bodies of water - forming carbonic acid
carbonic acid absorbed into rocks
Terrestrial carbon cylcle
Included organic carbon in all organisms+ in soil
included in organic carbon
autotrophs extract CO2 from air covert into organic carbon
heterotrophs receive carbon
return to air through respiration
Oceanic carbon cycle
dissolved CO2 converted to carbonate
converted by organisms into organic carbon - photosynthesis
exchanged through food chain
surface layer dissolved organic carbon - exchanges rapidly with atmosphere
deep layer holds dissolved inorganic carbon
carbon sequestration
CO2 captured from atmosphere and stored in nature helps mitigate climate change by reducing amount of CO2 available
Charateristics of a living thing
MRS GREN C
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion
Nutrition
Cells
living organisms can exist only if there is:
Energy
liquid water
the chemical buildings blocks required for life
stable environmental conditions
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles.
have no true nucleus,
their genetic material is found a region called the nuclear area
UNIcelluar organisms
like bacteria
Eukaryotes
having their genetic material contained within nuclear membrane
more complex celluar organism and have internal membranes - called organelles
eg. fungi, protistans, animal and plant cells
Fungal cell vs plant cells
plants are autotrophic (make own energy) and fungi is heterotopic (must take in energy)
both are eukaryotic
both have cell walls are stationary and typically multinuclear
Protists
unicellular organisms
classified under kingdom of Protista as eukaryotes
some contain cell wall
can be autotrophic, heterotrophic, parasitotic or saprotrophic
exhibits sexual and asexual reproduction
Cell size
Classification
placing living things in groups based on their internal structure and functional characteristics
order the hierarchy
Domain → kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → Genus → species
taxonomy
the science of grouping living things based on like characteristics
Types of kingdoms
Monera, Protista, Fungi, plantae, animalia
rocky shores
species closer to high tide mark are often best at being exposed to air and sunlight without drying out but worst at avoiding predation and worst at spending time under water for long periods of time
these physical and ecological pressures led to distinct zones in the community
Adaptaion + name the 3 types
A biological mechanism by which an organism adjusts to new environments to changes in current eviroment
Structural adaptation, physiological adaptation, behavioural adaptation
Structural adaptation
features on an organism body that helps it survive or reporduce
Physiological adaptation
an internal body processes to maintain homeostasis for an organism to survive in the environment which it exists
Behavioural adaptation
Something an animal does usually i response to some type of external stimulus in order to survive
Phyla’s
Abiotic factors and intertidal zones.+
effect on organisms