Fungi
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Fungi grow as filaments called what?
hyphae
What is a mass of hyphae?
mycelium
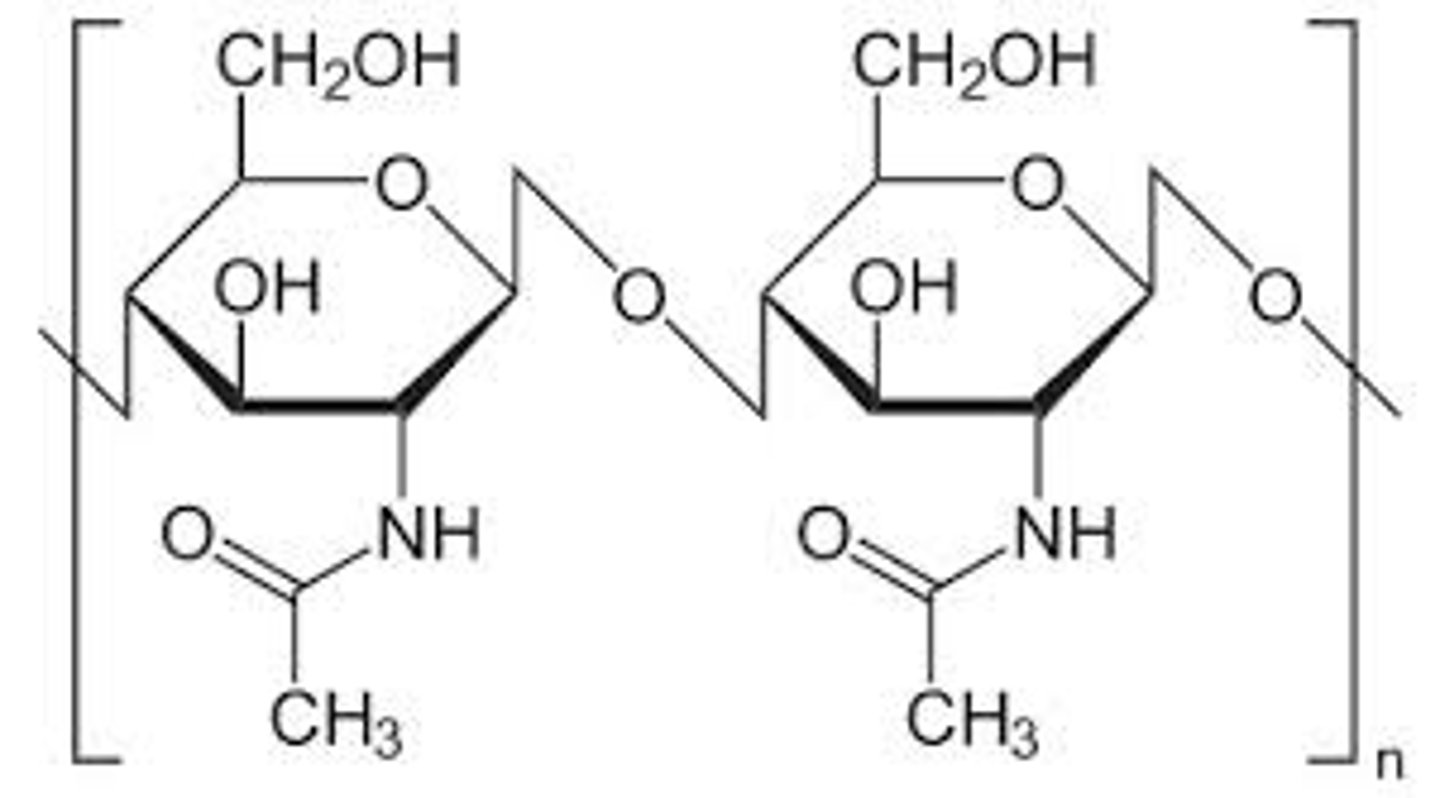
What substance composes fungal cell walls?
chitin
(Note: N-containing polysaccharide)
What structures divide fungal filaments into compartments containing a single nucleus?
septum
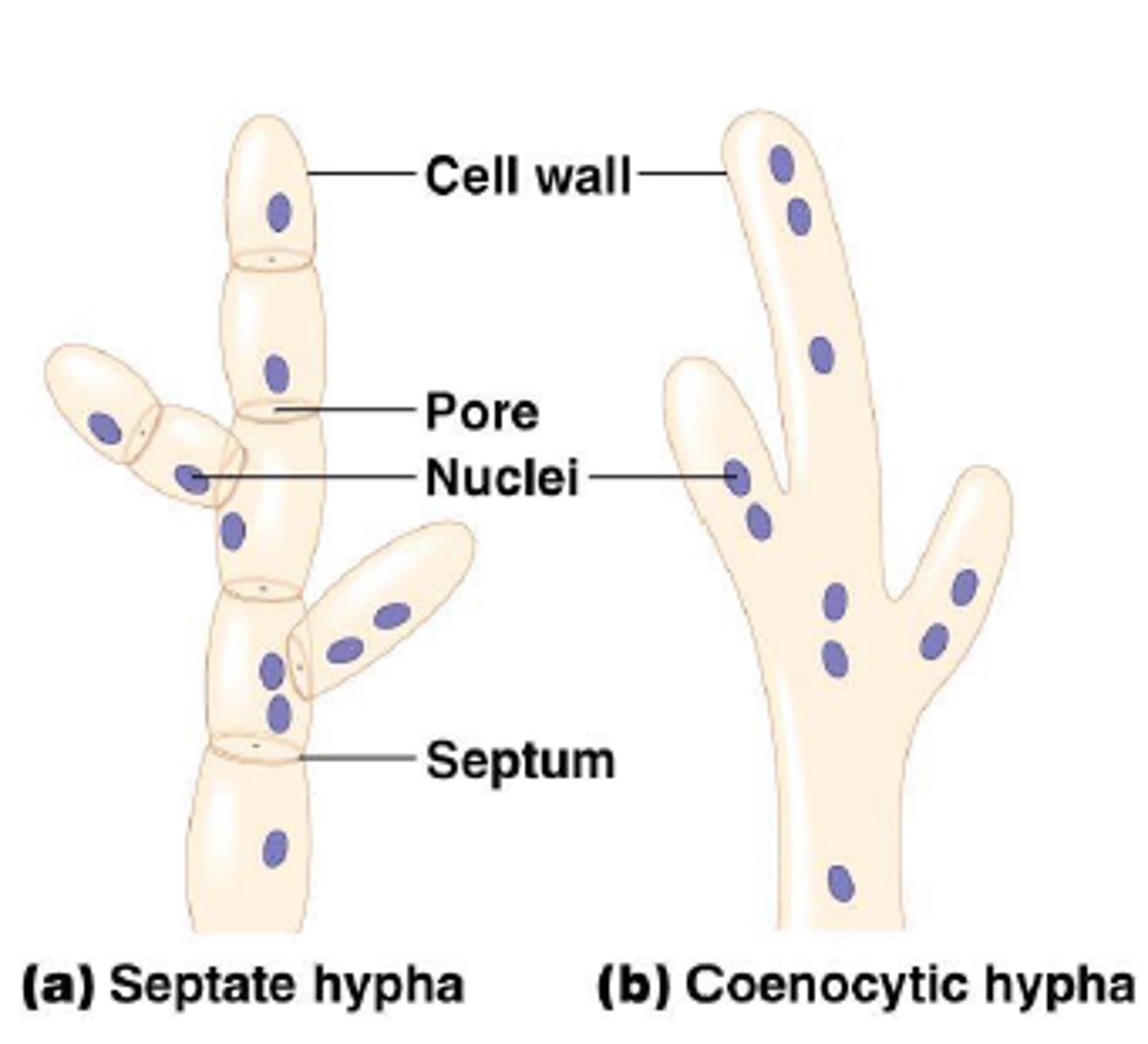
Fungi without septa are coenocytic, which means what?
they are multi-nucleate
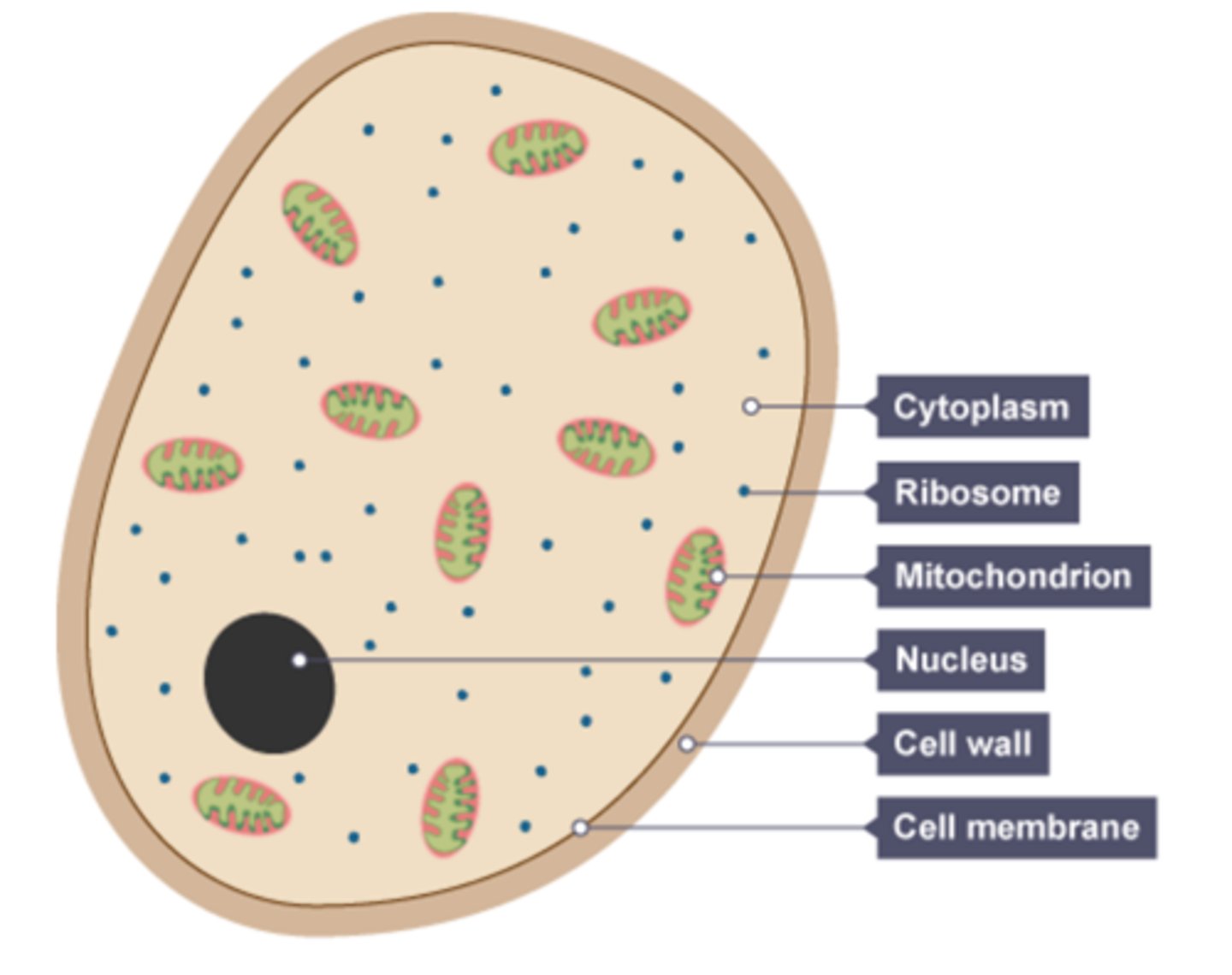
Which cell type composes fungi?
eukaryotic
How do fungi obtain energy?
heterotrophism
(Note: they secrete digestive enzymes and then absorb the products of digestion)
How do fungi reproduce?
sexually or asexually
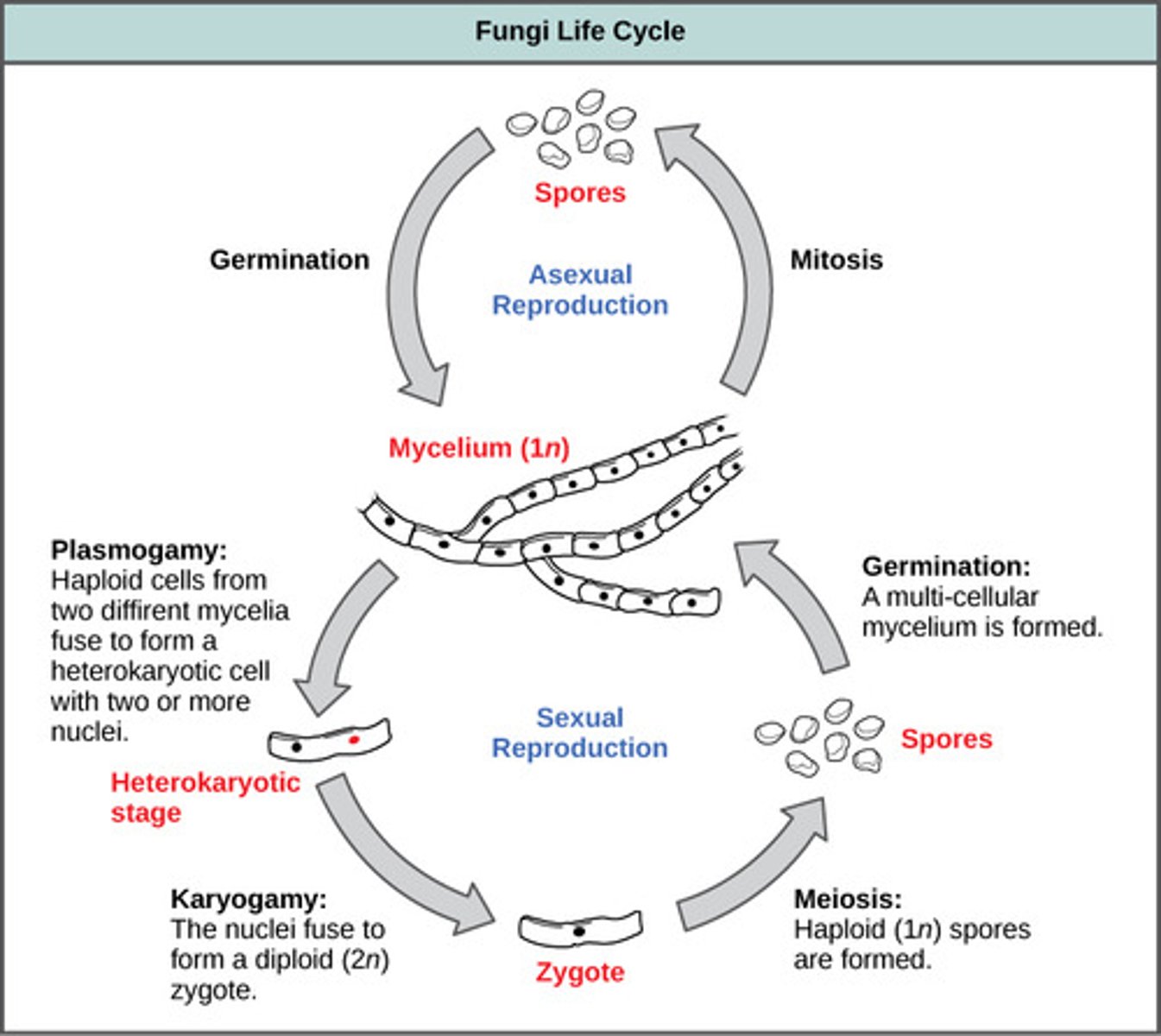
Which stage generally predominates the life cycle of most fungi?
haploid
(Note: have the
ability to alternate
diploid/haploid stages)
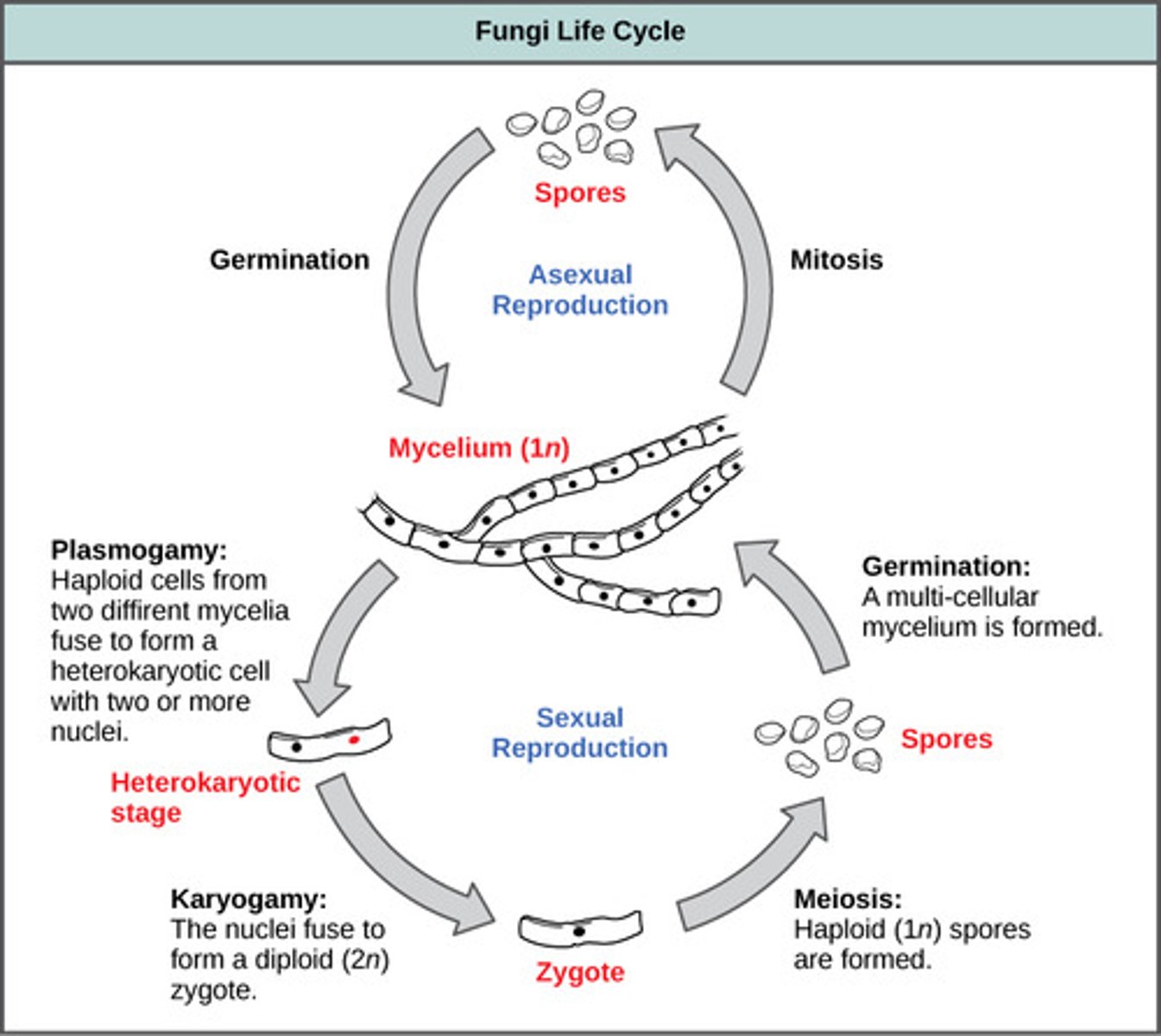
How motile are fungi?
generally immotile

Are fungal cells more similar to human or bacterial cells?
human
How are fungi generally classified?
based on type of sexual spores they produce
If there is no sexual phase in a fungus, what is it called?
imperfect fungi
What is a broad class of unicellular fungi?
yeast
What is the main purpose of fungi?
decomposition of biological waste
Which fungi have hyphae called haustoria that can penetrate the host?
parasitic fungi
Fungi are primarily haploid but form what structures for sexual reproduction?
temporary diploid structures
What is the fusing of cytoplasm of cells from two different fungal strains to produce a single cell without fusing of the nuclei?
plasmogamy
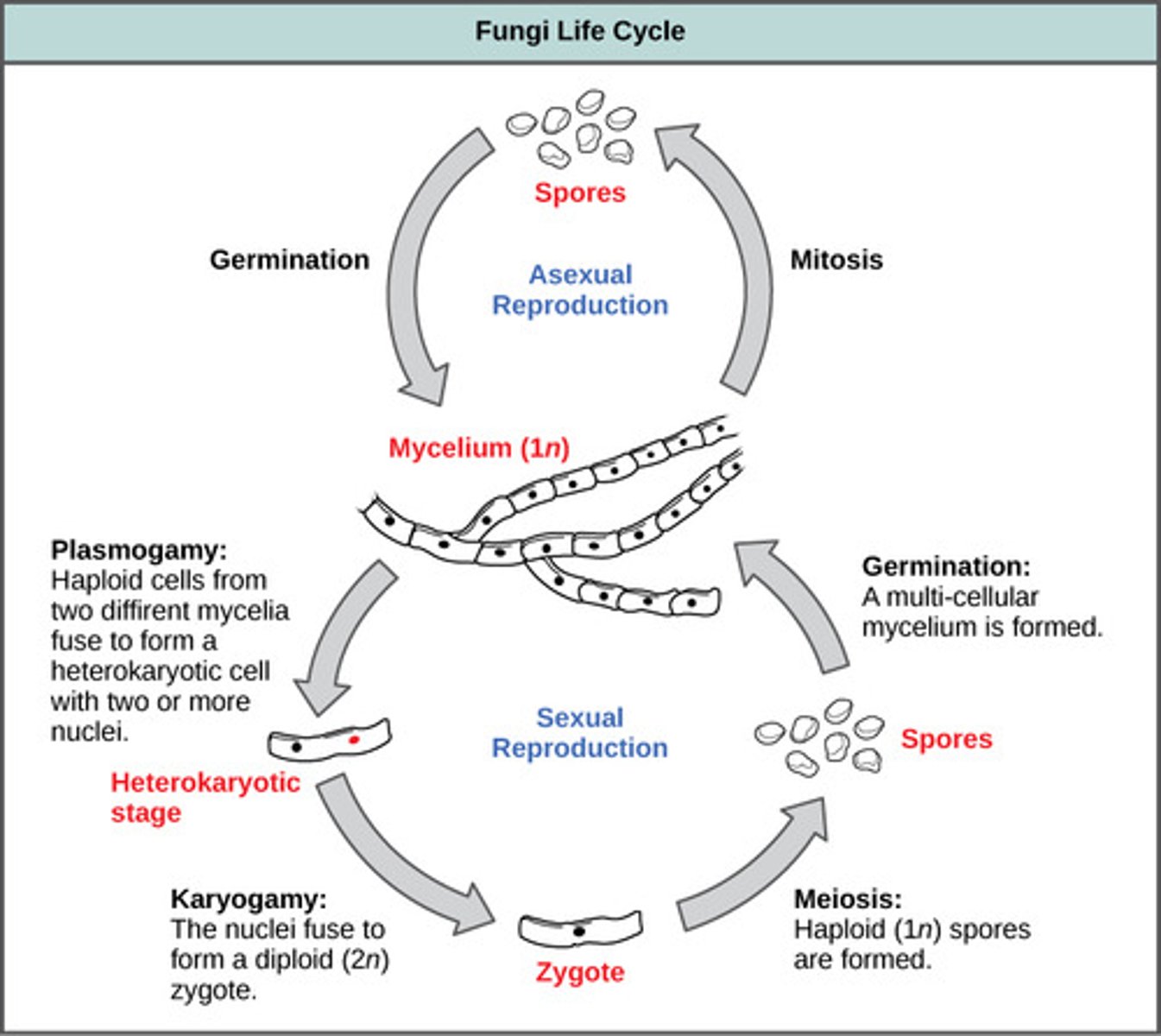
In plasmogamy, the resulting cell has a pair of which type of nuclei?
haploid nuclei
(Note: one from each strain)
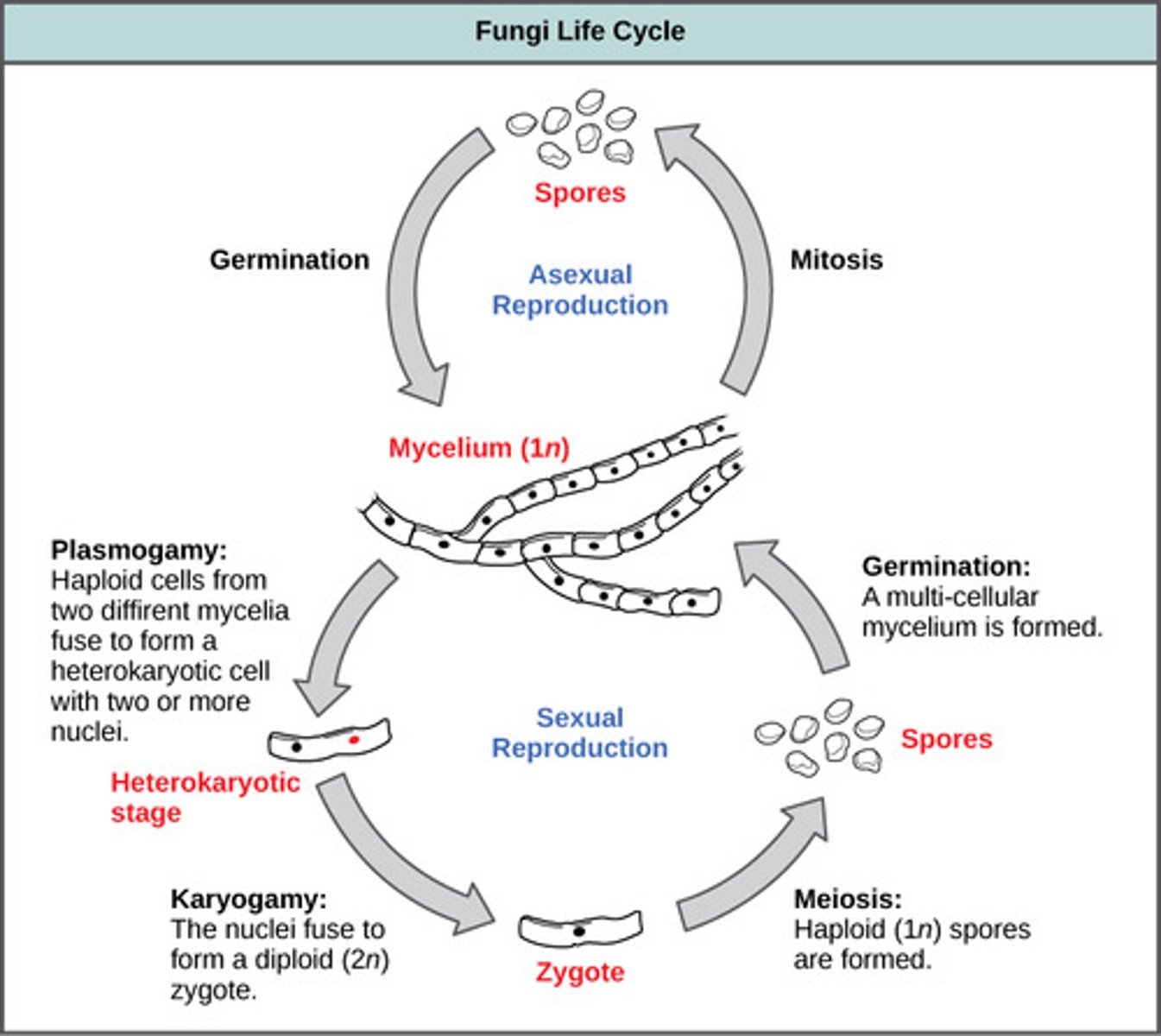
In plasmogamy, what is the fused organism called?
dikaryon
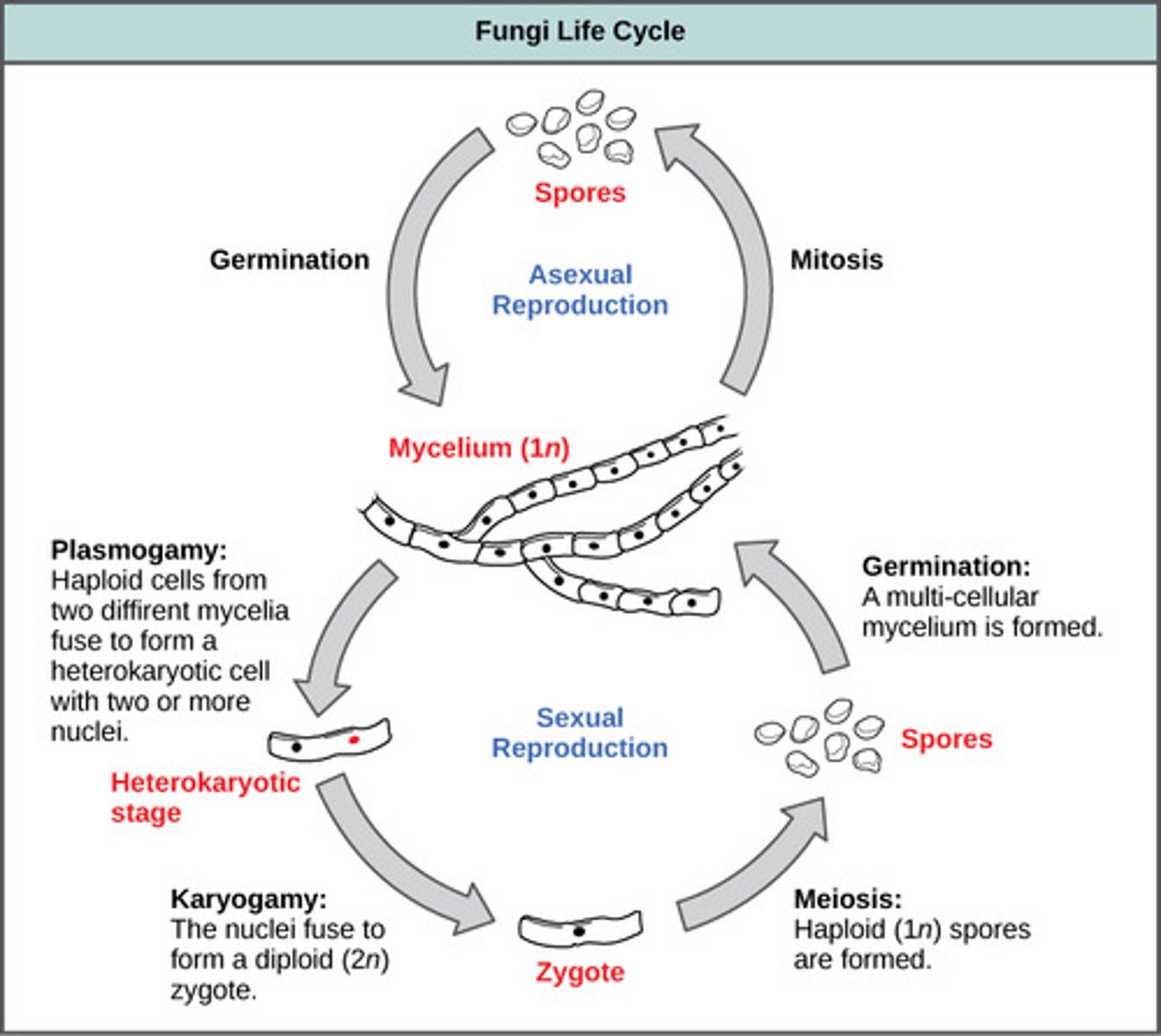
What is the fusing of two haploid nuclei of a dikaryon to form a single diploid nucleus?
karyogamy
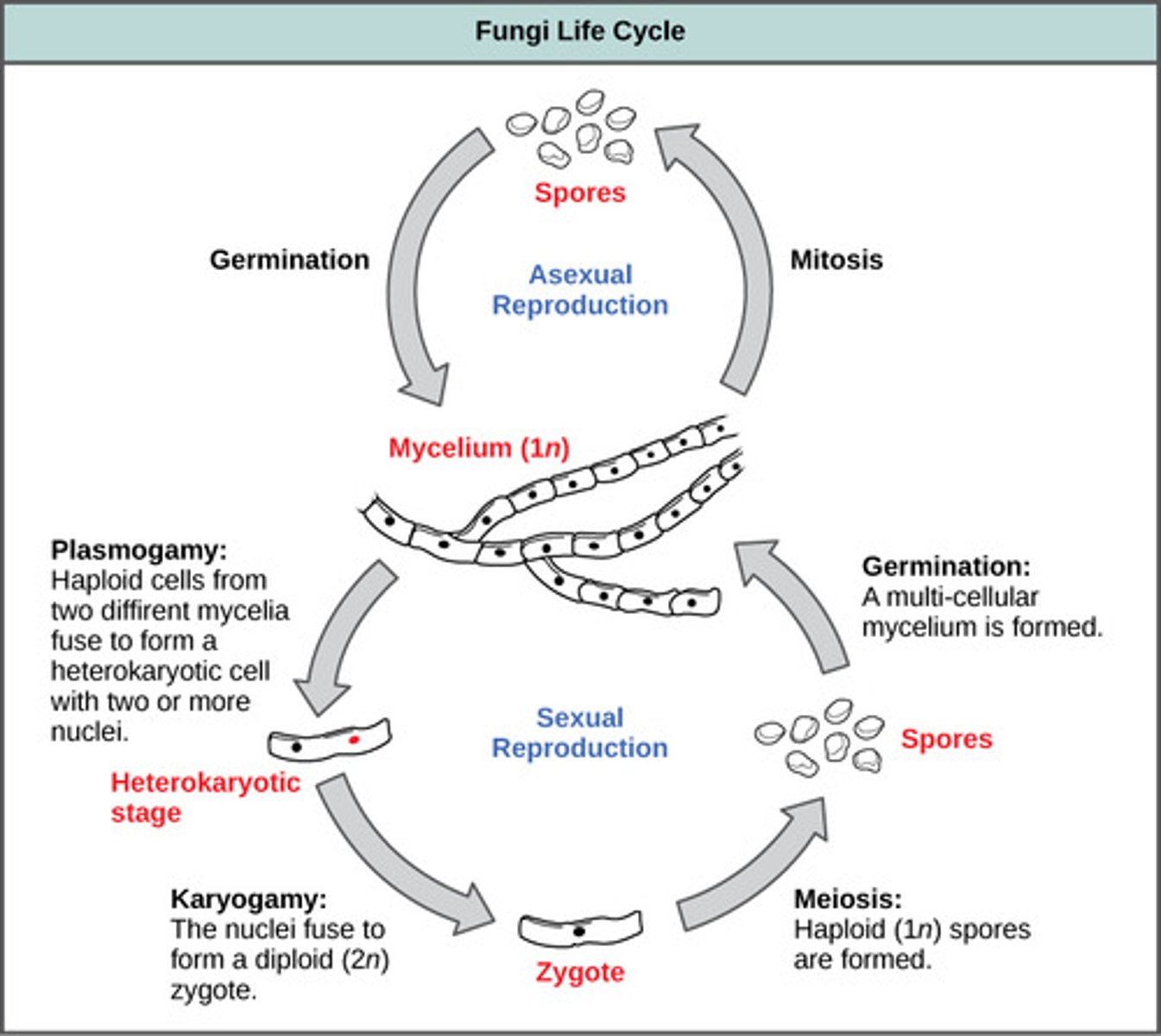
Meiosis of a diploid fungus restores what condition?
haploid condition
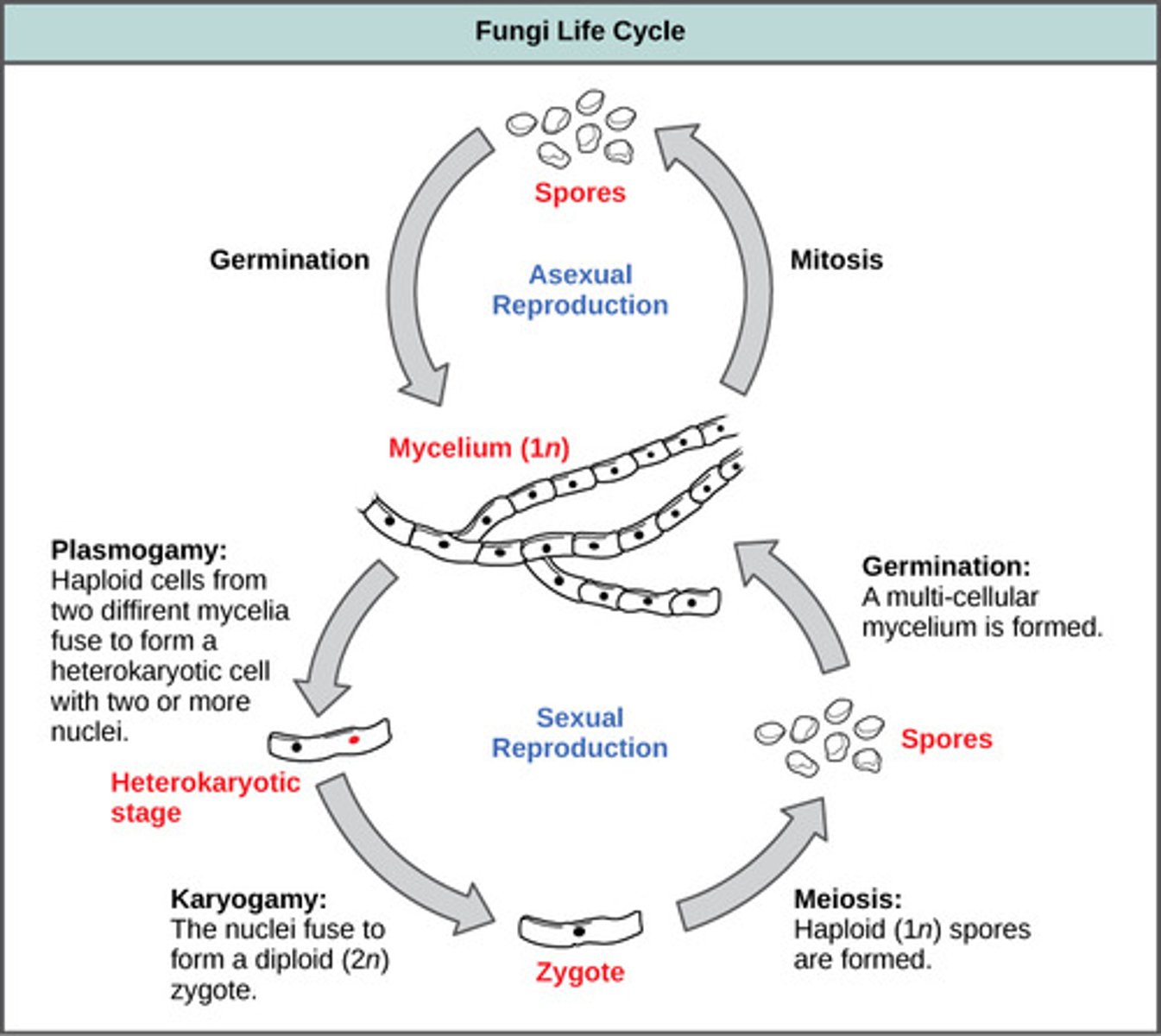
In fungal sexual reproduction, meiotic daughter cells develop into haploid spores which germinate into what structures?
haploid hyphae
(Note: only one
fungal strain -
allows continuation
of life cycle)
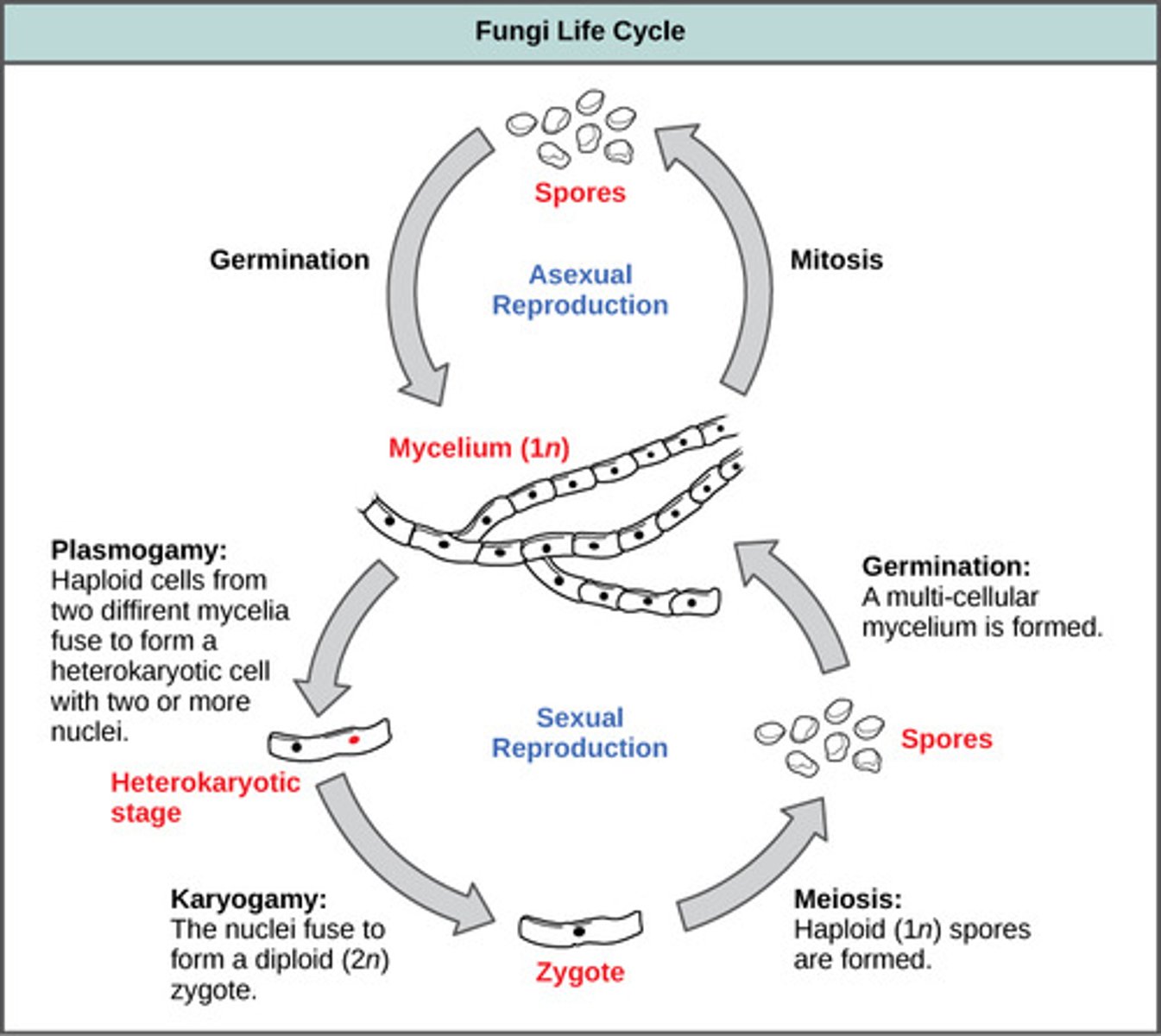
What are the methods of fungal asexual reproduction?
1. fragmentation
2. budding
3. asexual spores
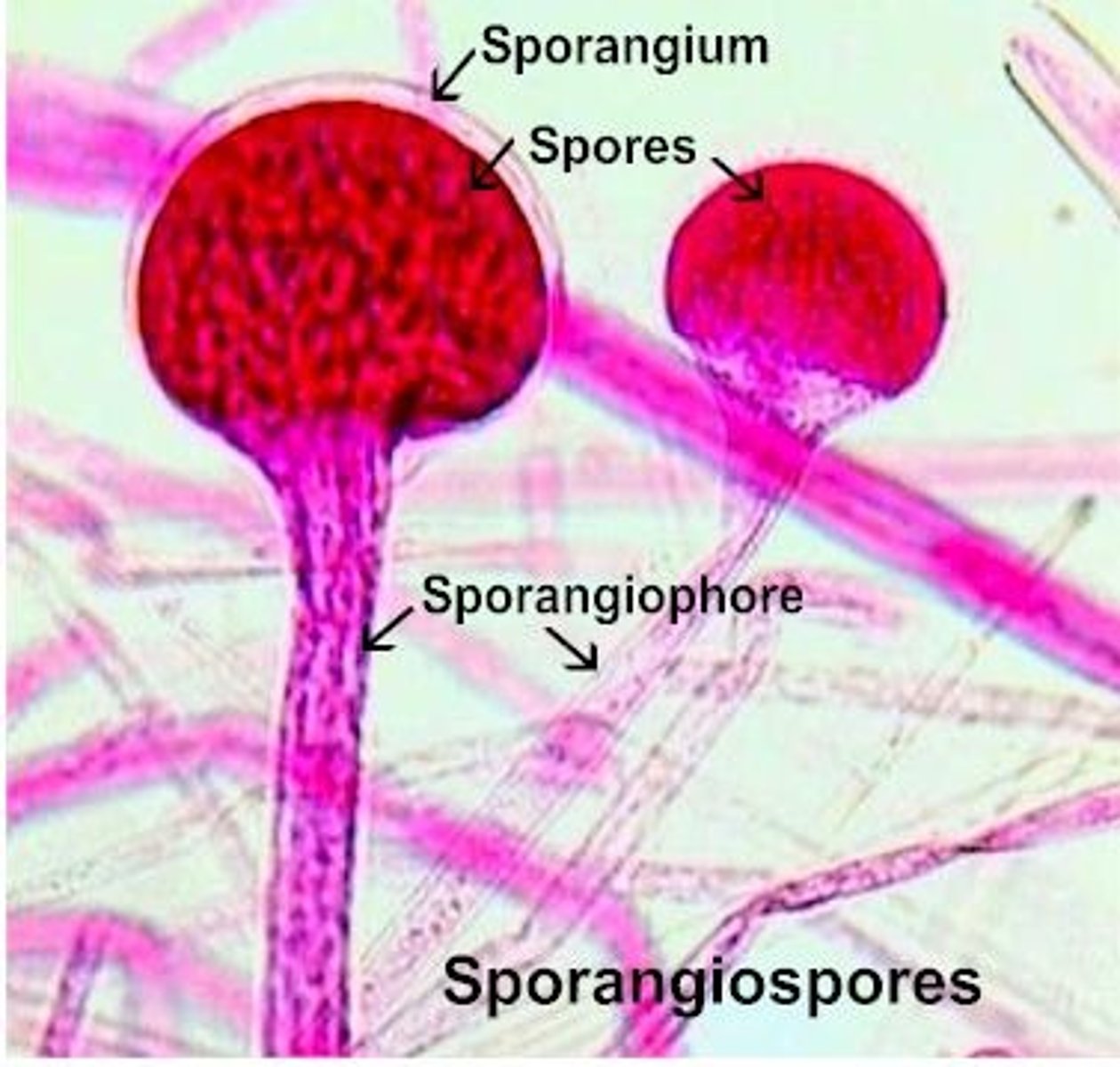
What are asexual spores produced in sac-like capsules called sporangia?
sporangiospores
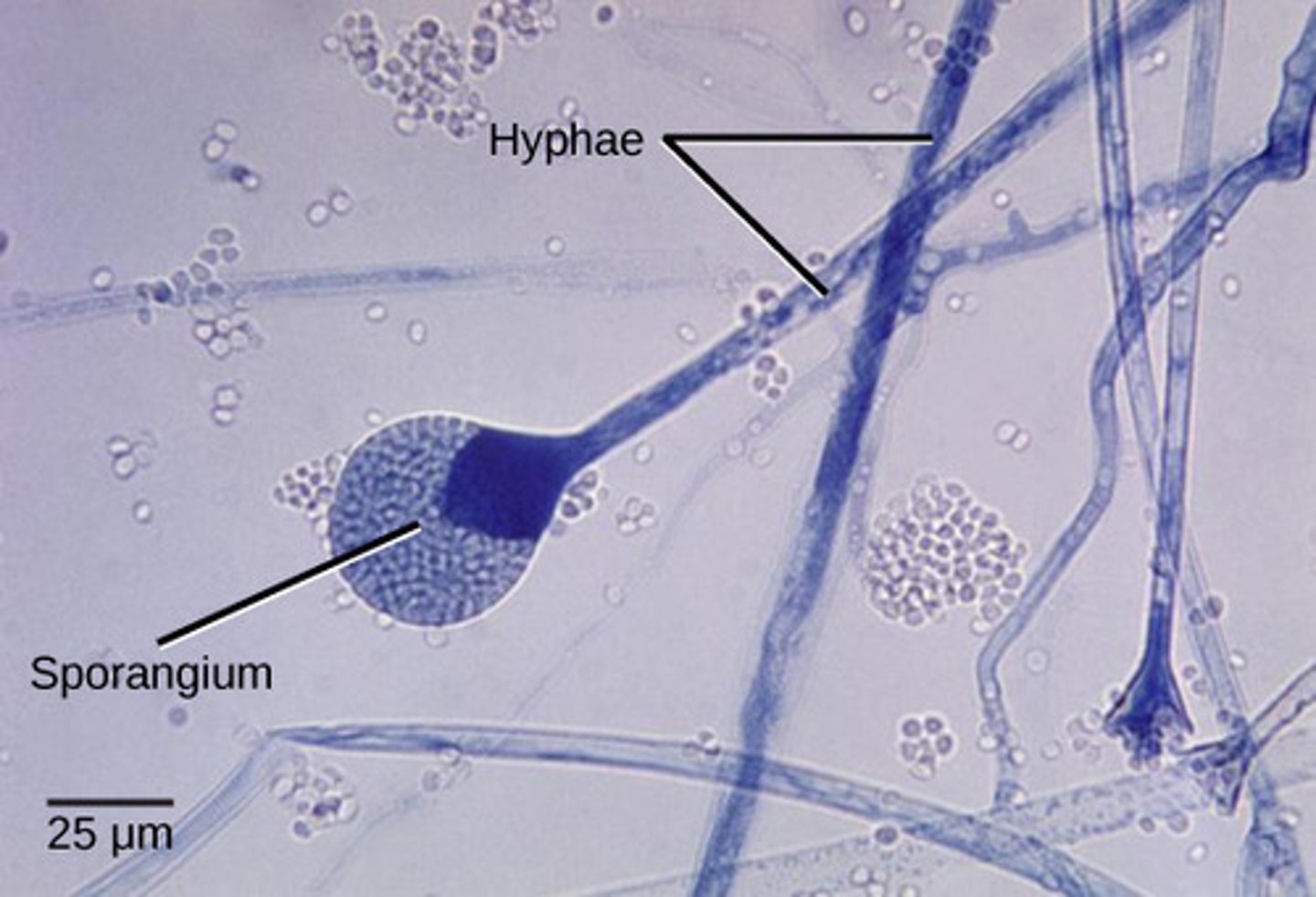
Sporangia develop on stalks called what?
sporangiophores
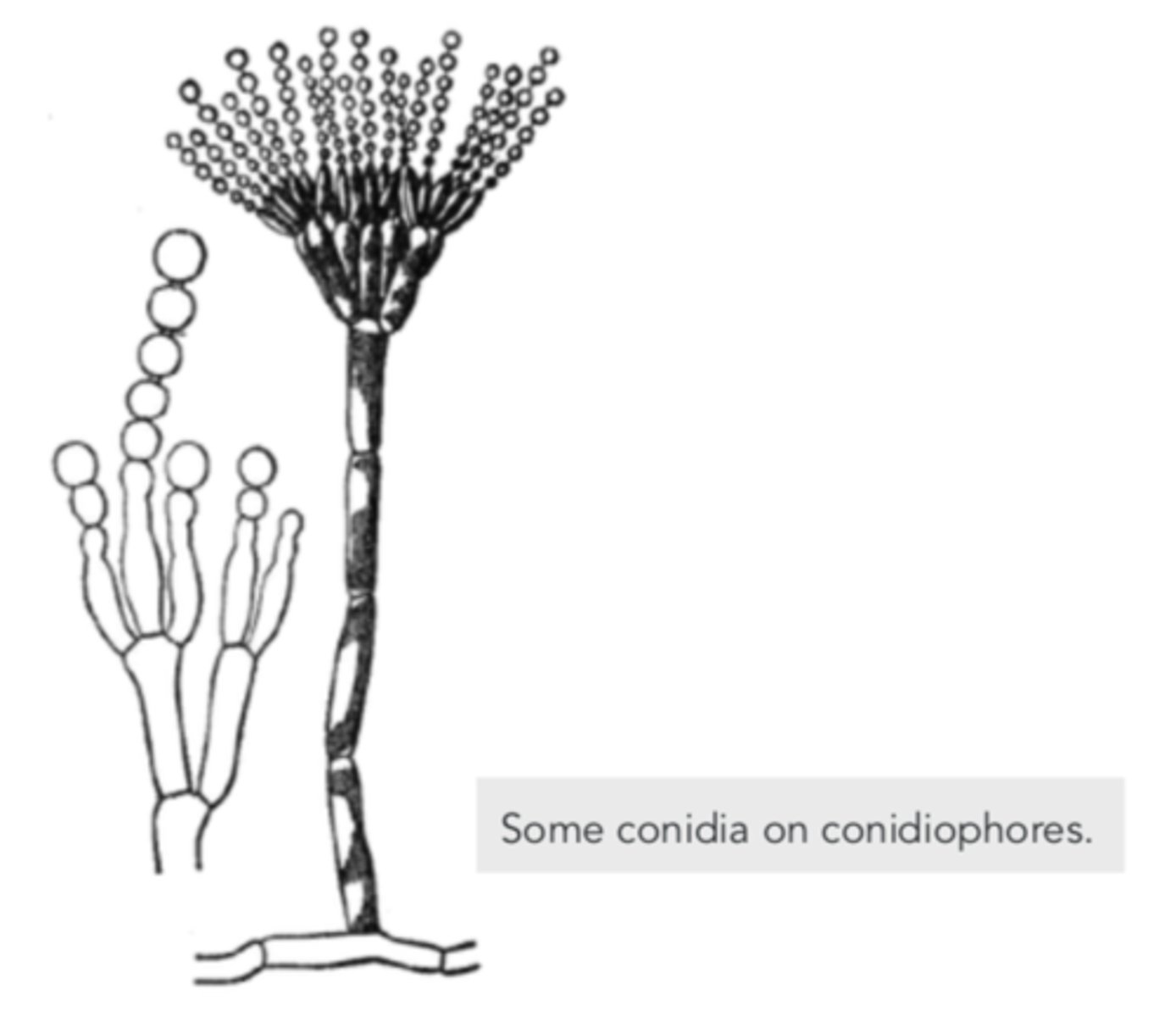
What are asexual spores formed at the tips of specialized hyphae that are not enclosed inside sacs?
conidia
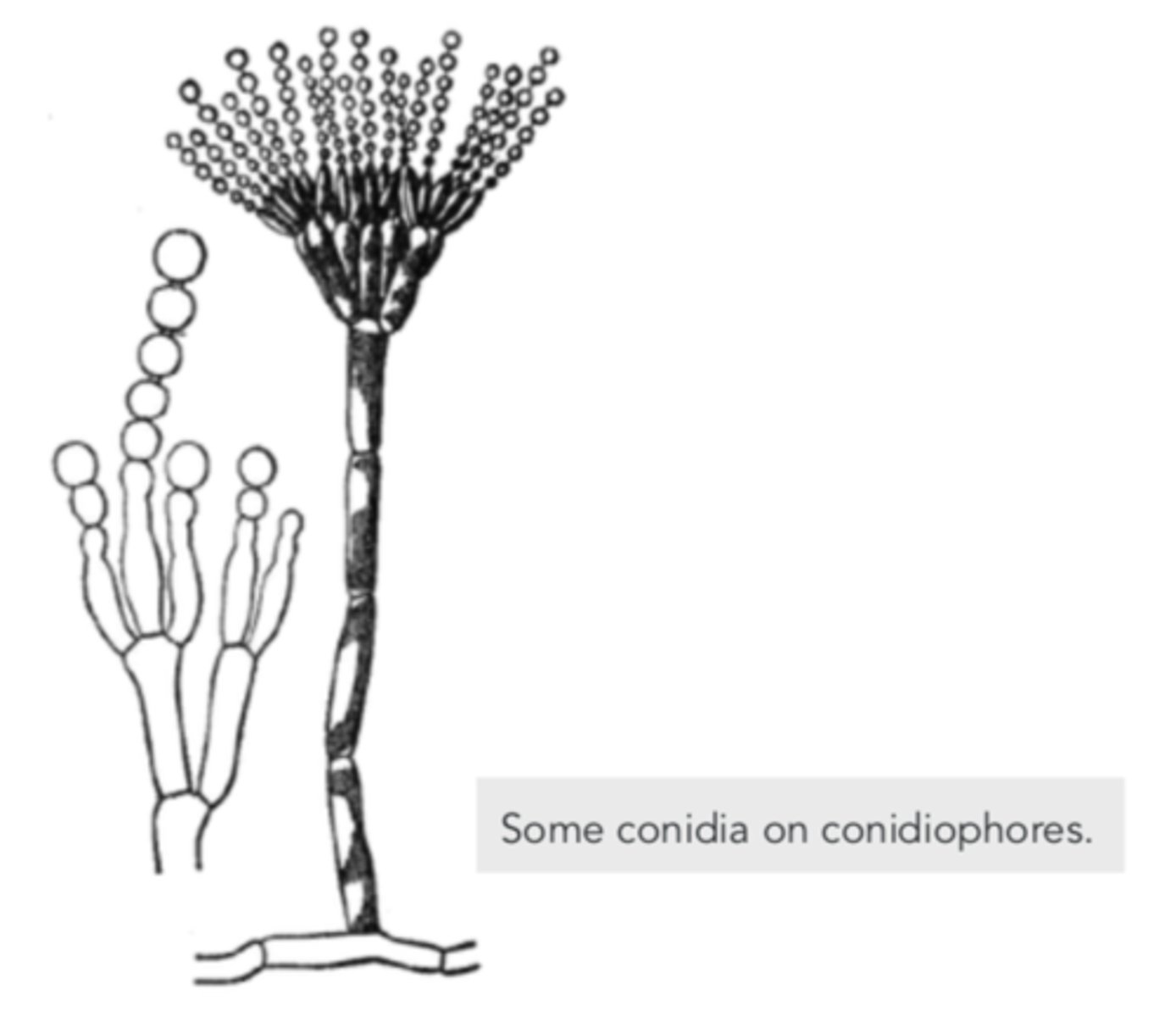
What are hyphae that bear conidia?
conidiophores
What suffixes indicate fungal organisms?
1. -mycota
2. -mycete
Which group of fungi lacks septa except the filaments bordering reproductive filaments?
Zygomycota
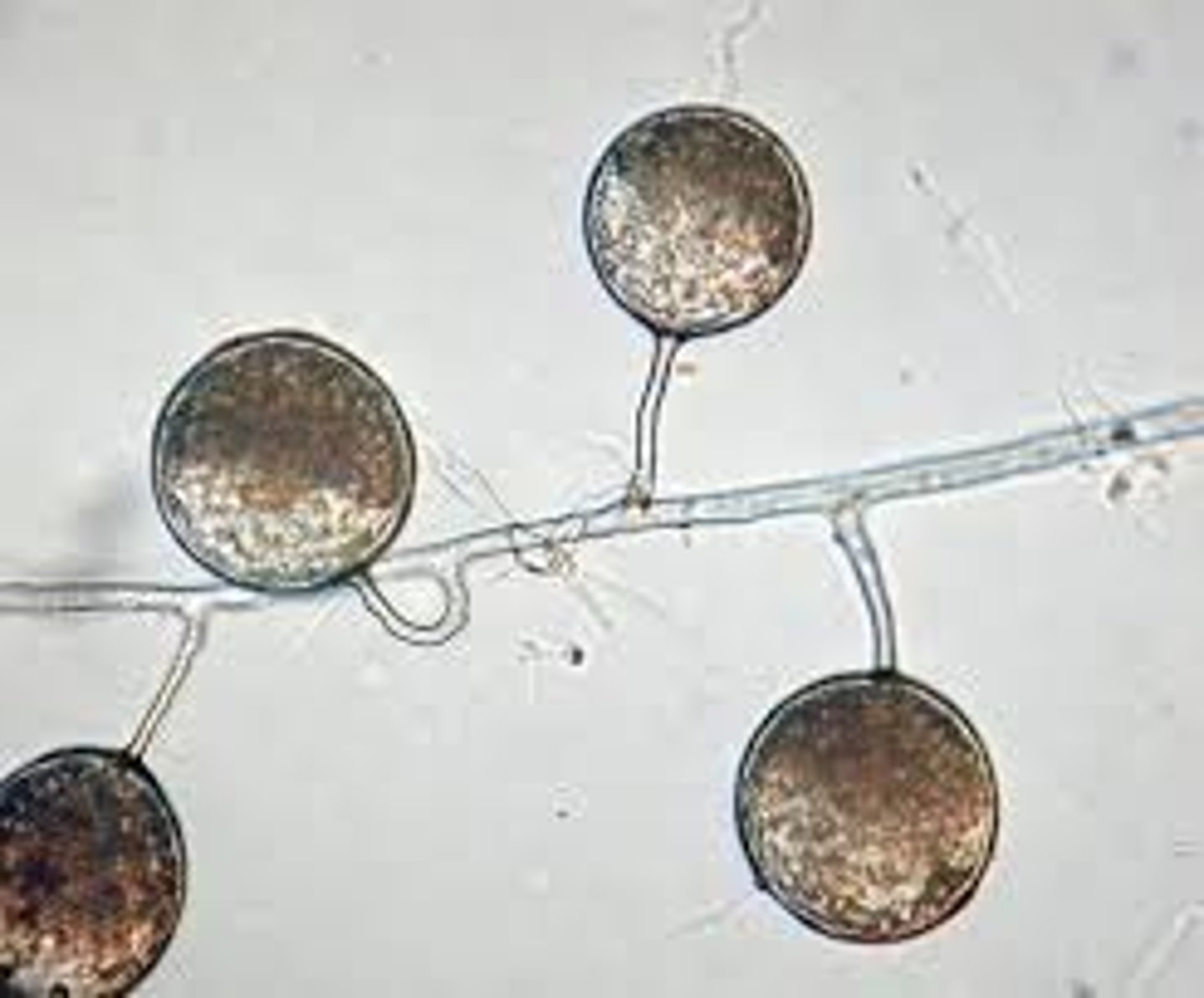
Which group of fungi lacks septa and does not produce zygospores?
Glomeromycota
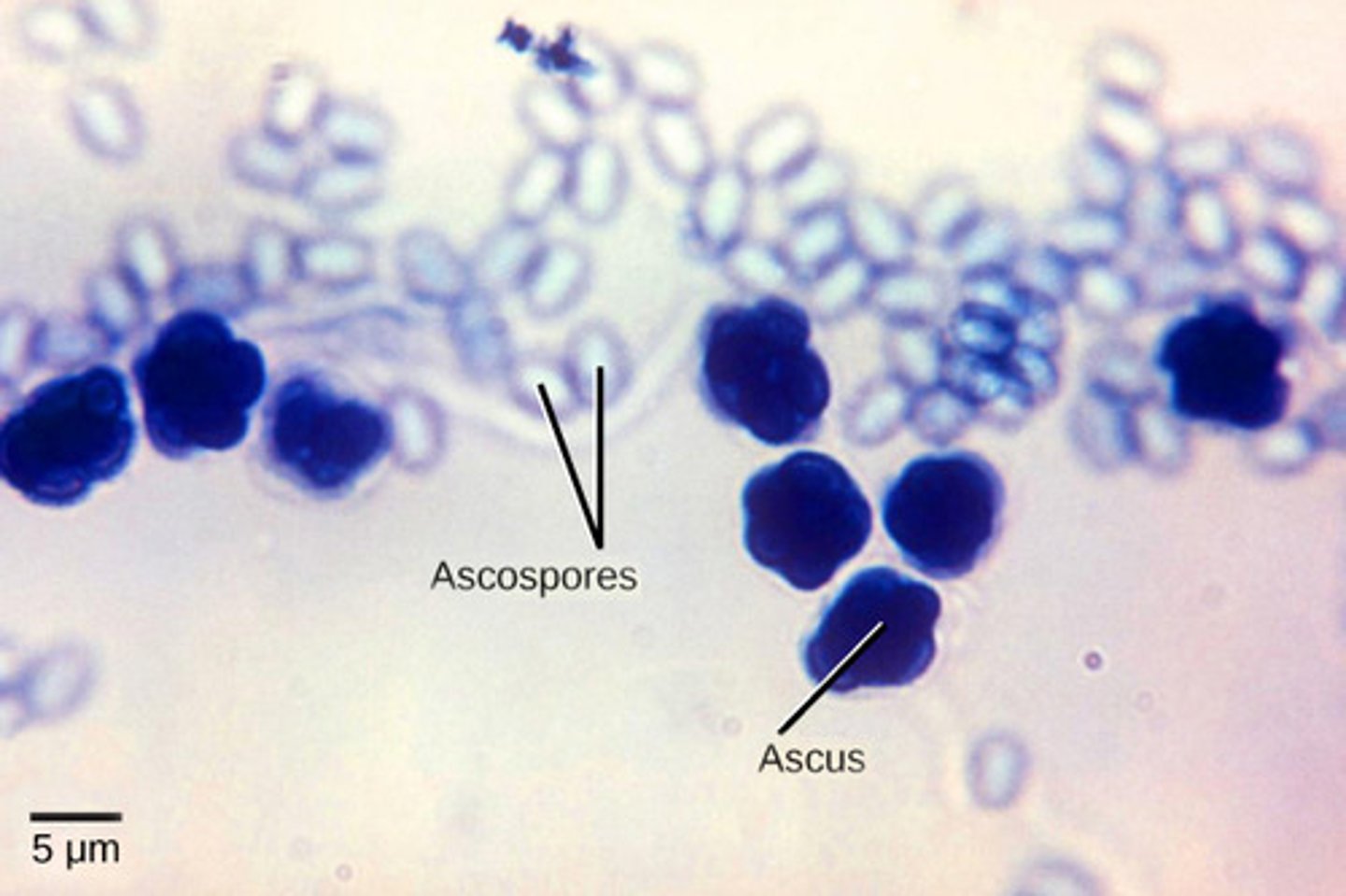
Which group of fungi have septa and reproduce sexually by producing haploid ascospores?
Ascomycota
Which group of fungi has septa and reproduces sexually by producing haploid basidiospores?
Basidiomycota

Which group of fungi contains imperfect fungi and is an artificial group because it has no known sexual reproductive cycle?
Deuteromycota
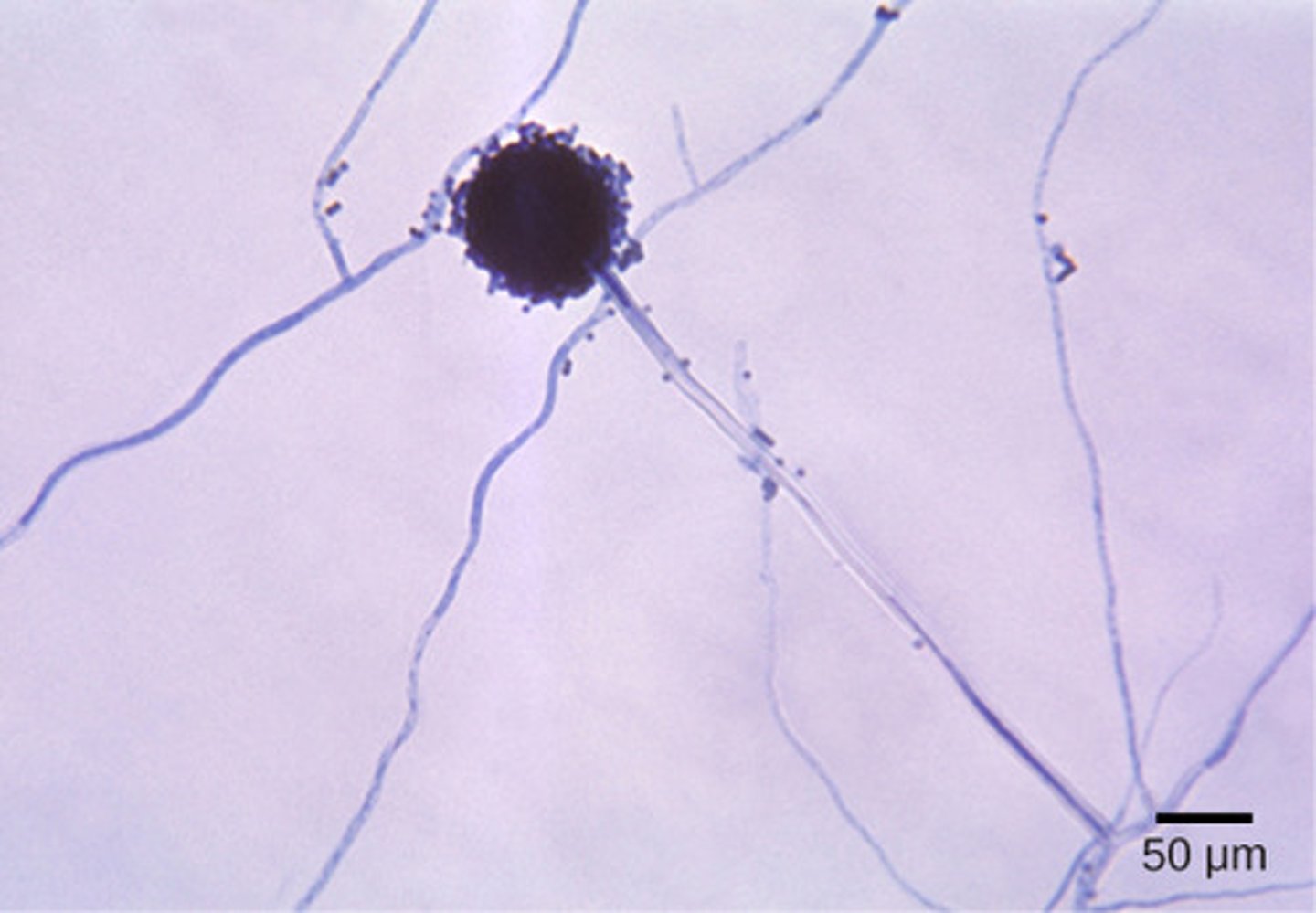
Which group of fungi contains symbiotic associations between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria?
Lichens

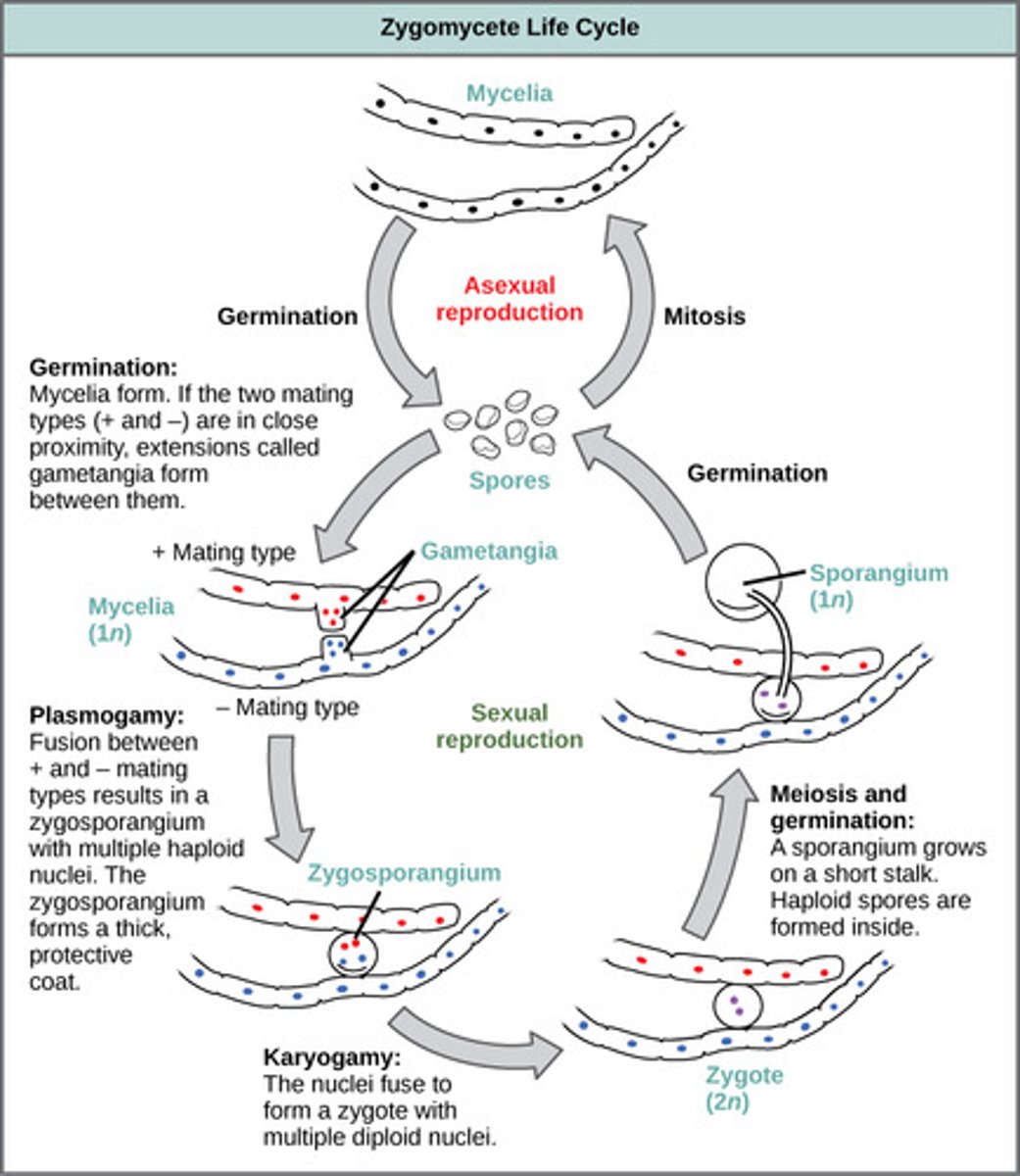
How do fungi in Zygomycota reproduce sexually?
plasmogamy → karyogamy → meiosis
(Note: produce haploid zygospores)
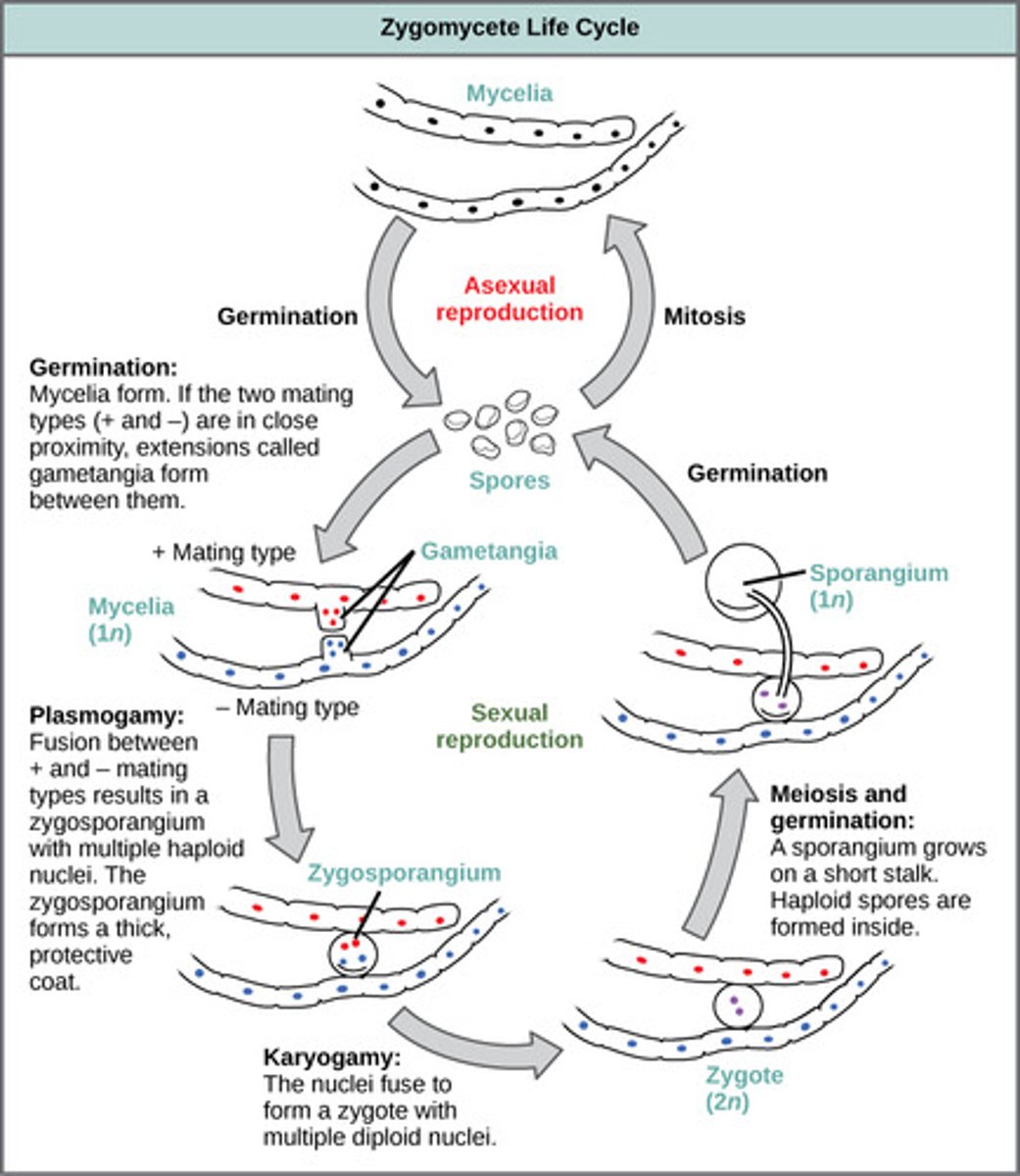
How do fungi in Zygomycota reproduce asexually?
sporangia
Glomeromycota form mutualistic associations with roots of plants called what?
mycorrhiza
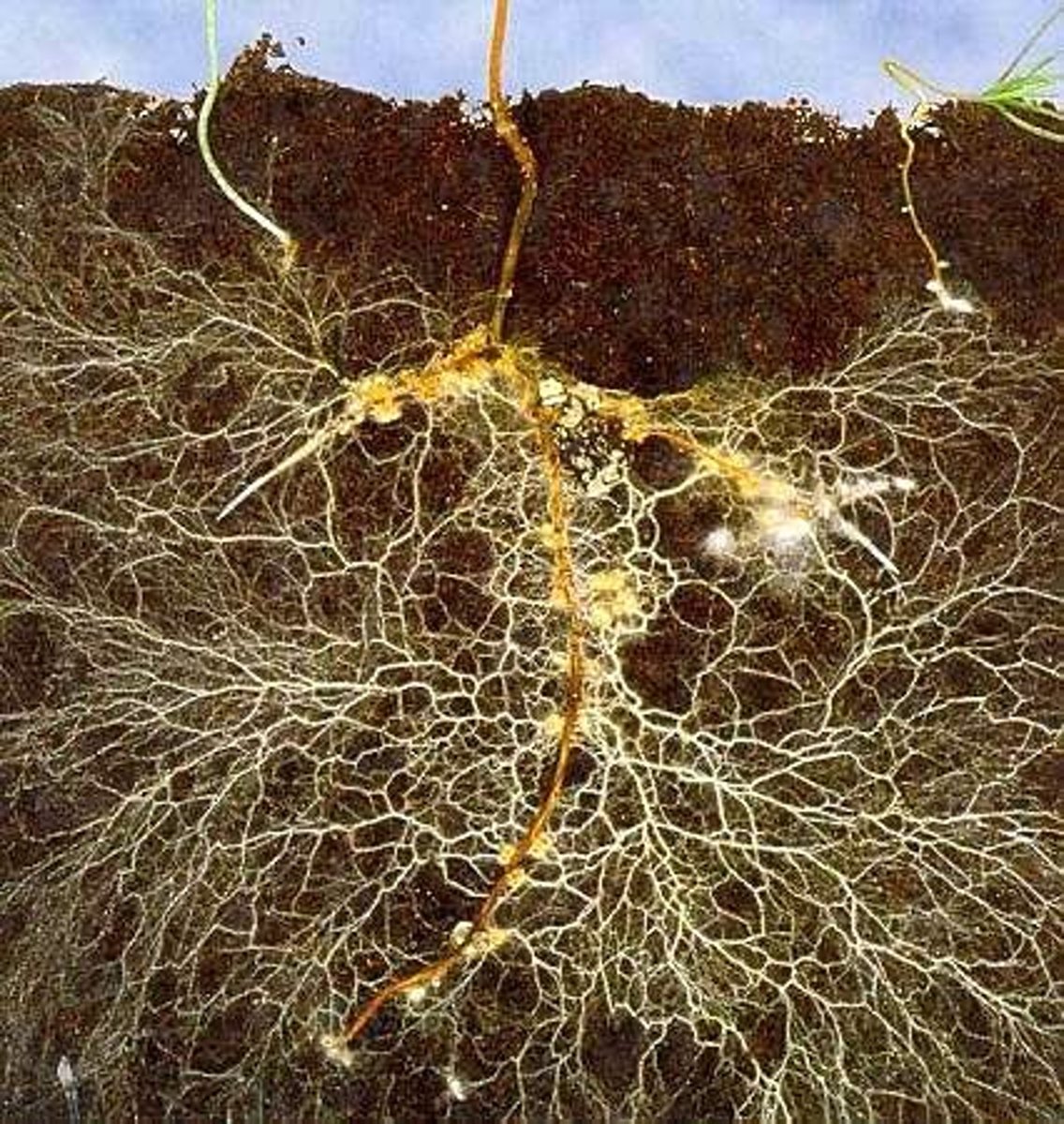

In a mycorrhiza, what do plants provide for the fungi?
carbohydrates
In a mycorrhiza, what do fungi provide for the plants?
ability to absorb nutrients
(Note: especially phosphorus)
After plasmogamy in Ascomycota, dikaryotic hyphae produce what structures?
more filaments by mitosis
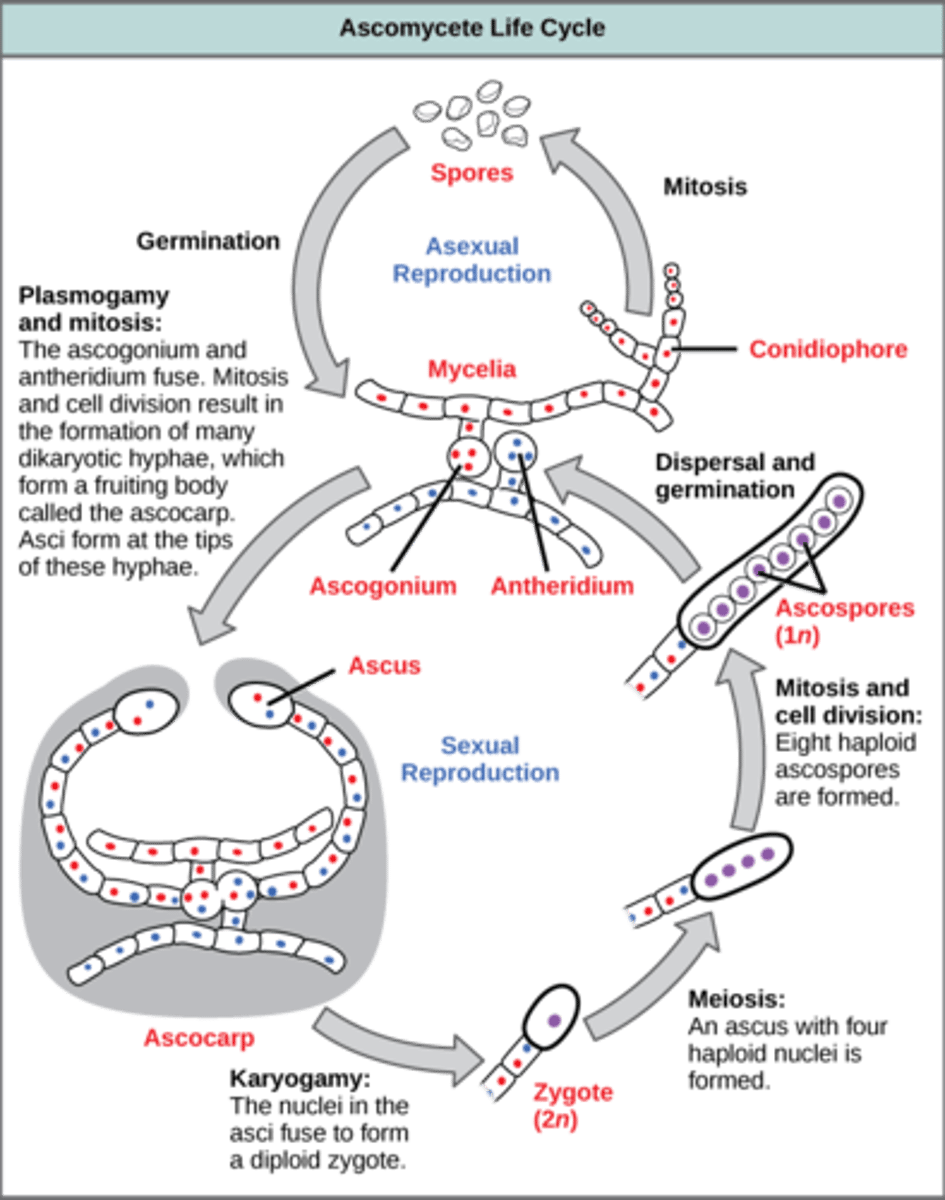
In Ascomycota, karyogamy and meiosis occur where?
terminal hyphae
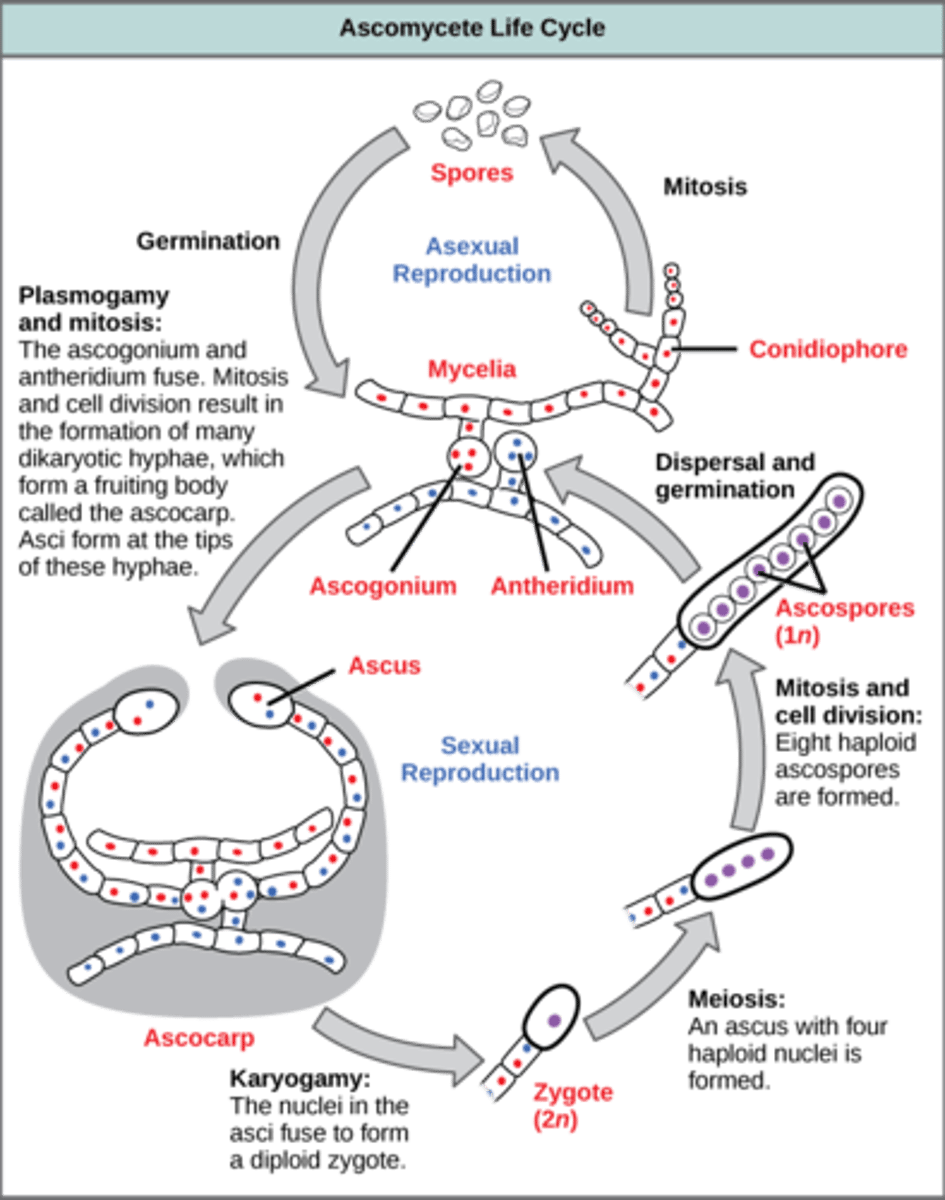
In Ascomycota, karyogamy and meiosis in terminal hyphae produce what cells?
4 haploid cells
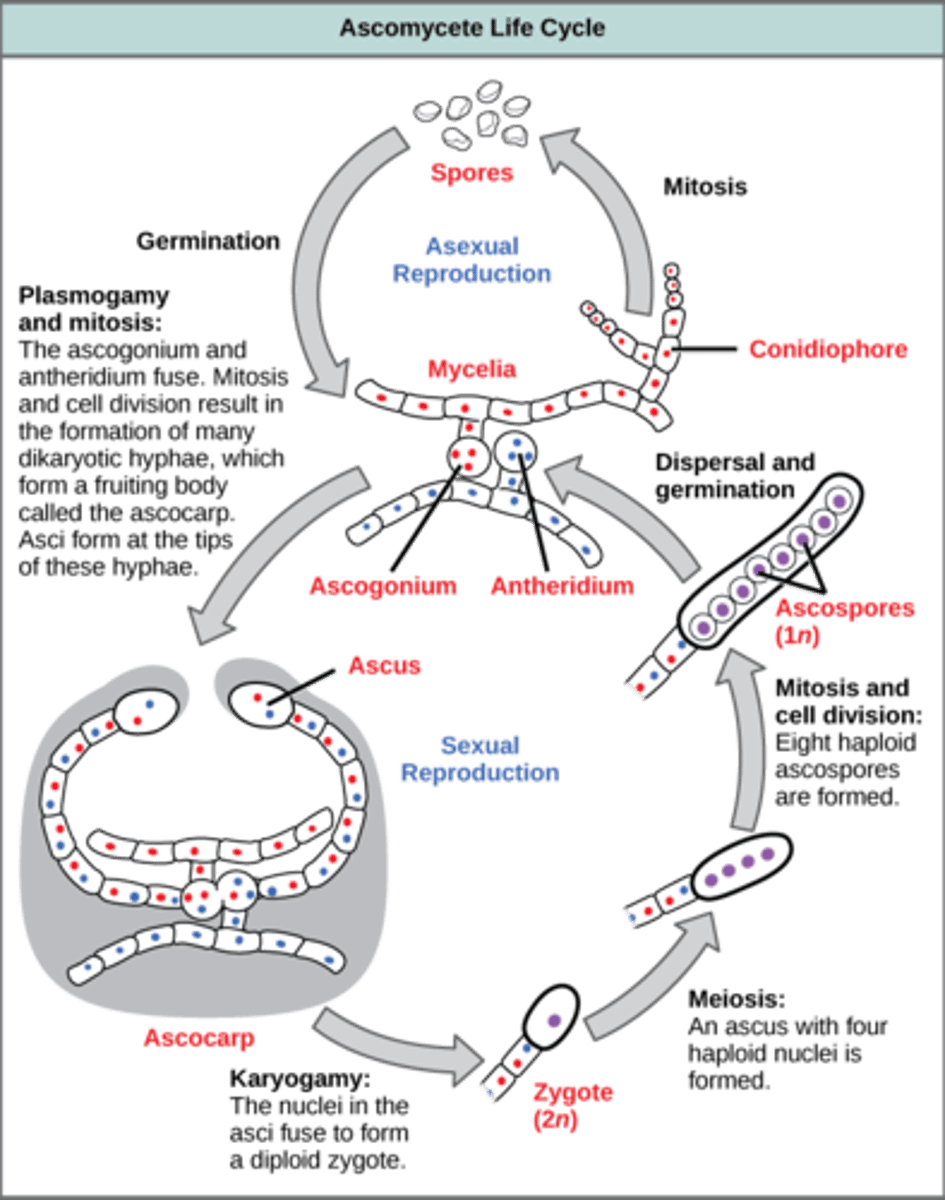
In Ascomycota, mitosis (after karyogamy and meiosis) in terminal hyphae produces what cells?
8 haploid ascospores
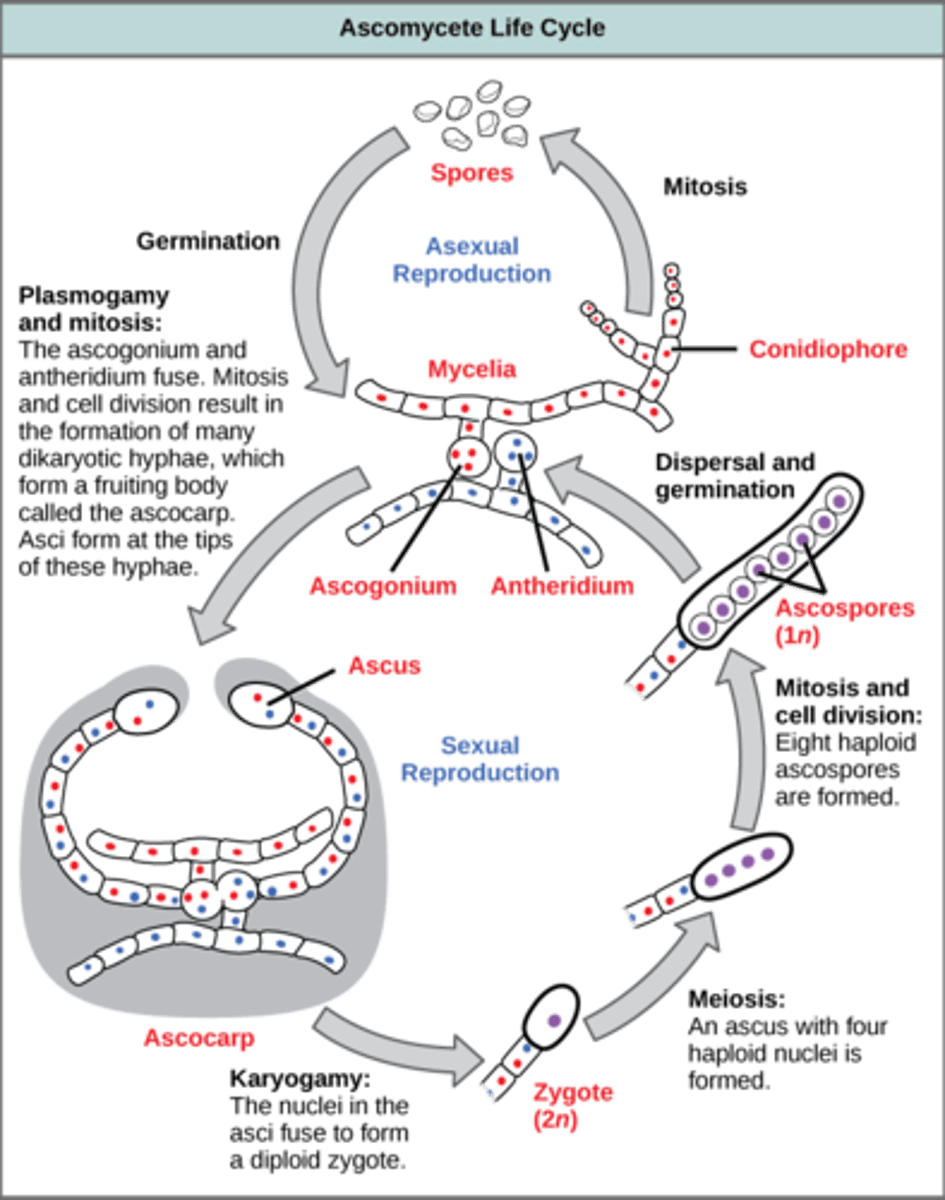
In Ascomycota, what is the sac that holds the 8 haploid ascospores called?
ascus
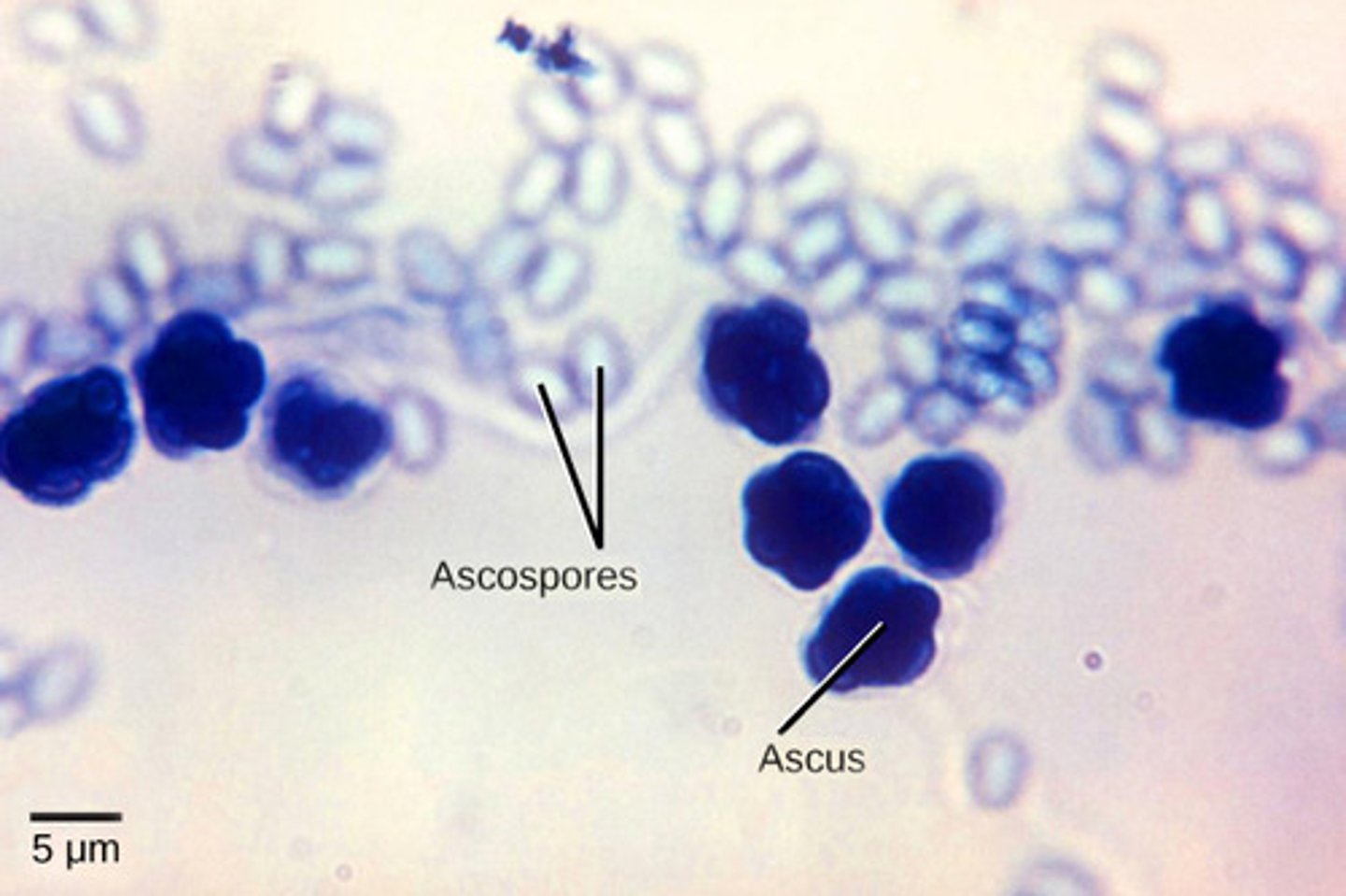
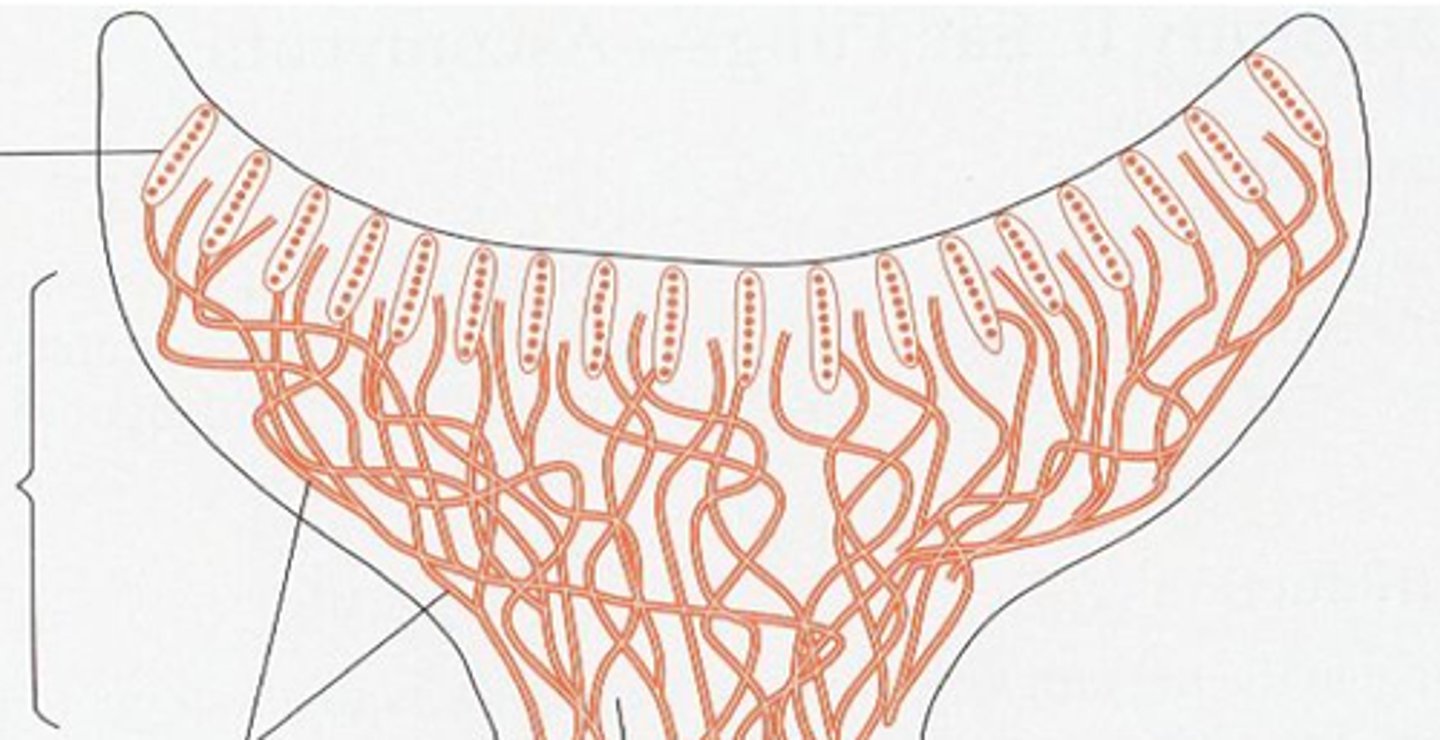
What structure in Ascomycota contain millions of asci?
ascocarp
In Ascomycota, ascospores germinate and develop into what structures?
hyphae
(Note: repeats the life cycle)
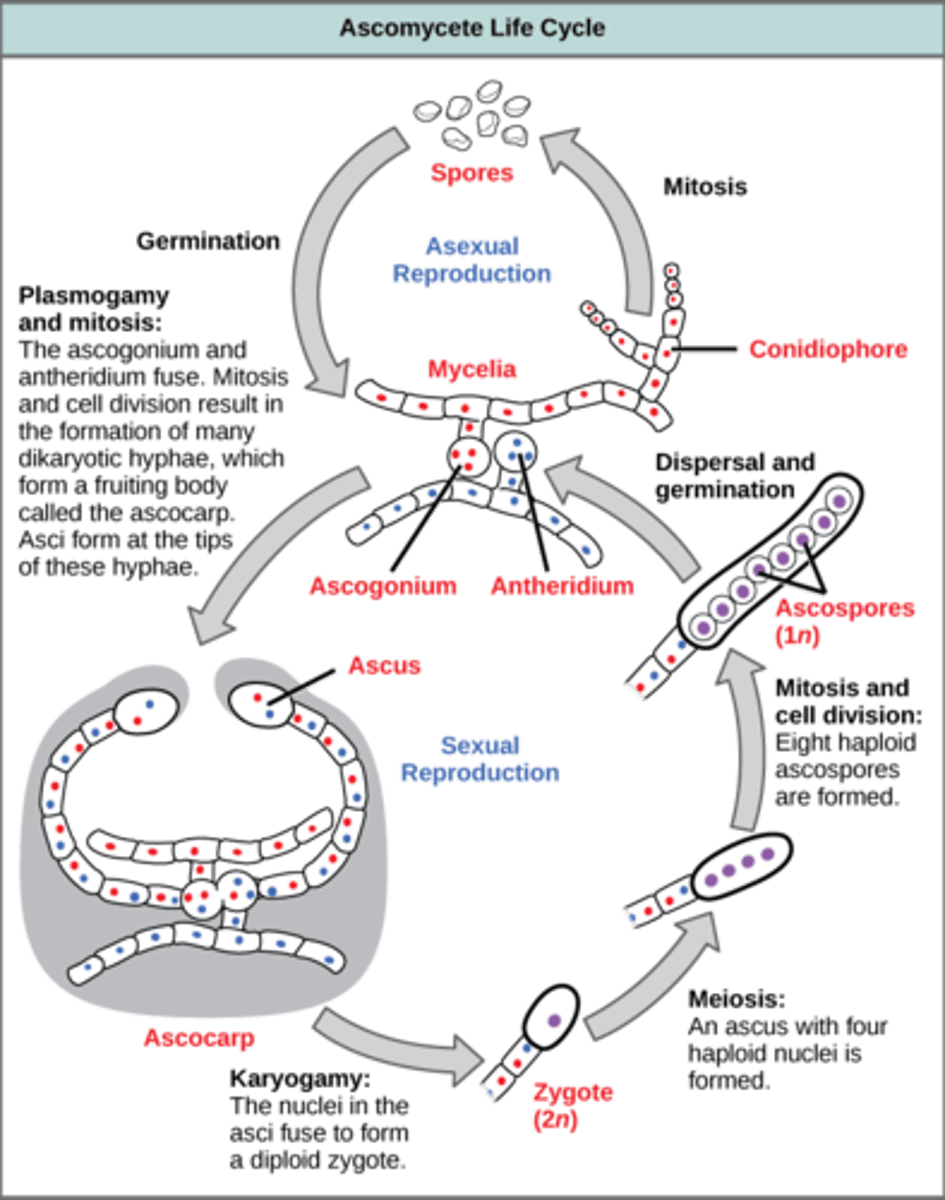
In Basidiomycota, plasmogamy and mitosis leads to the creation of a fruiting body called what?
basidiocarp
(Note: mushrooms)
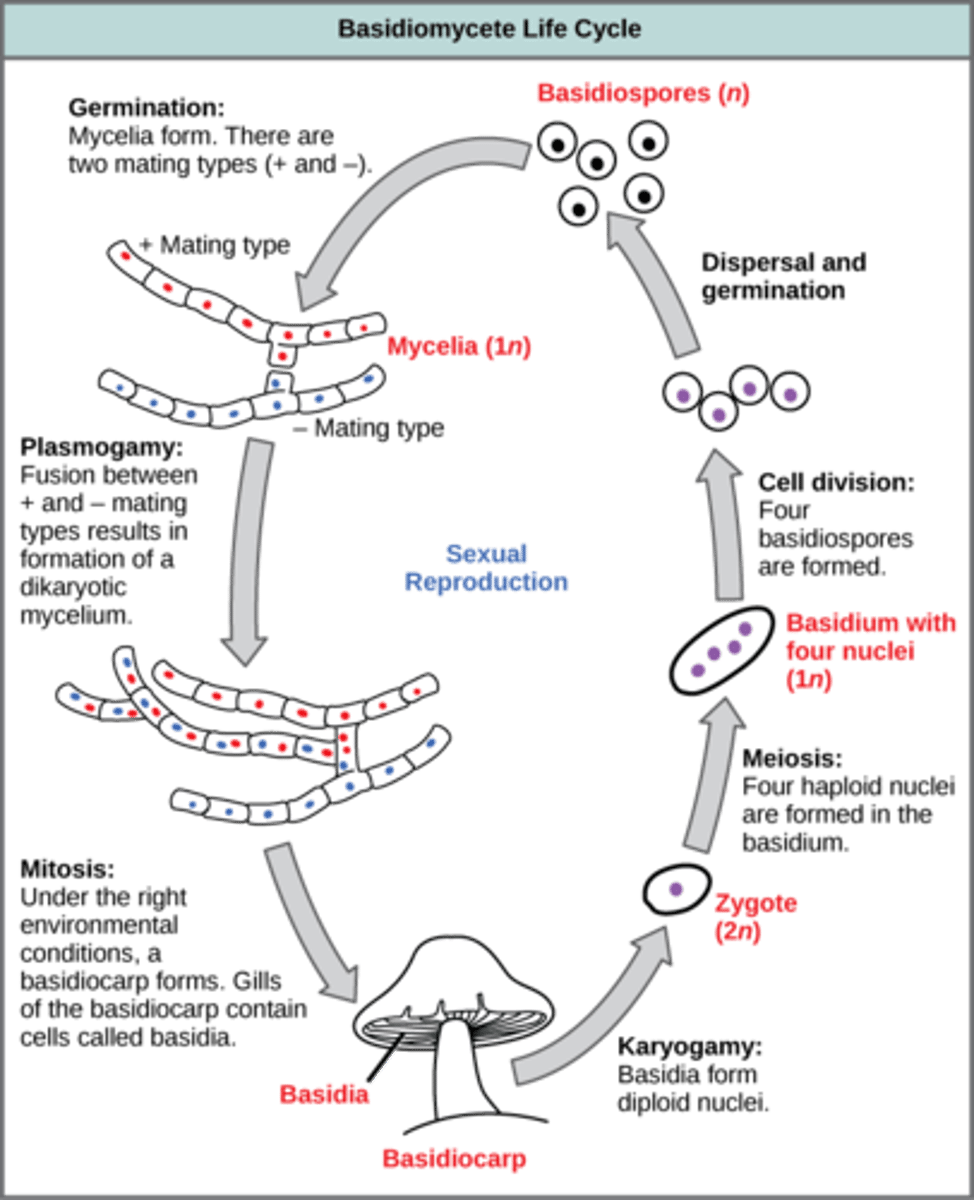
In Basidiomycota, karyogamy and meiosis occur in terminal hyphal cells called basidia to produce what cells?
4 haploid basidiospores
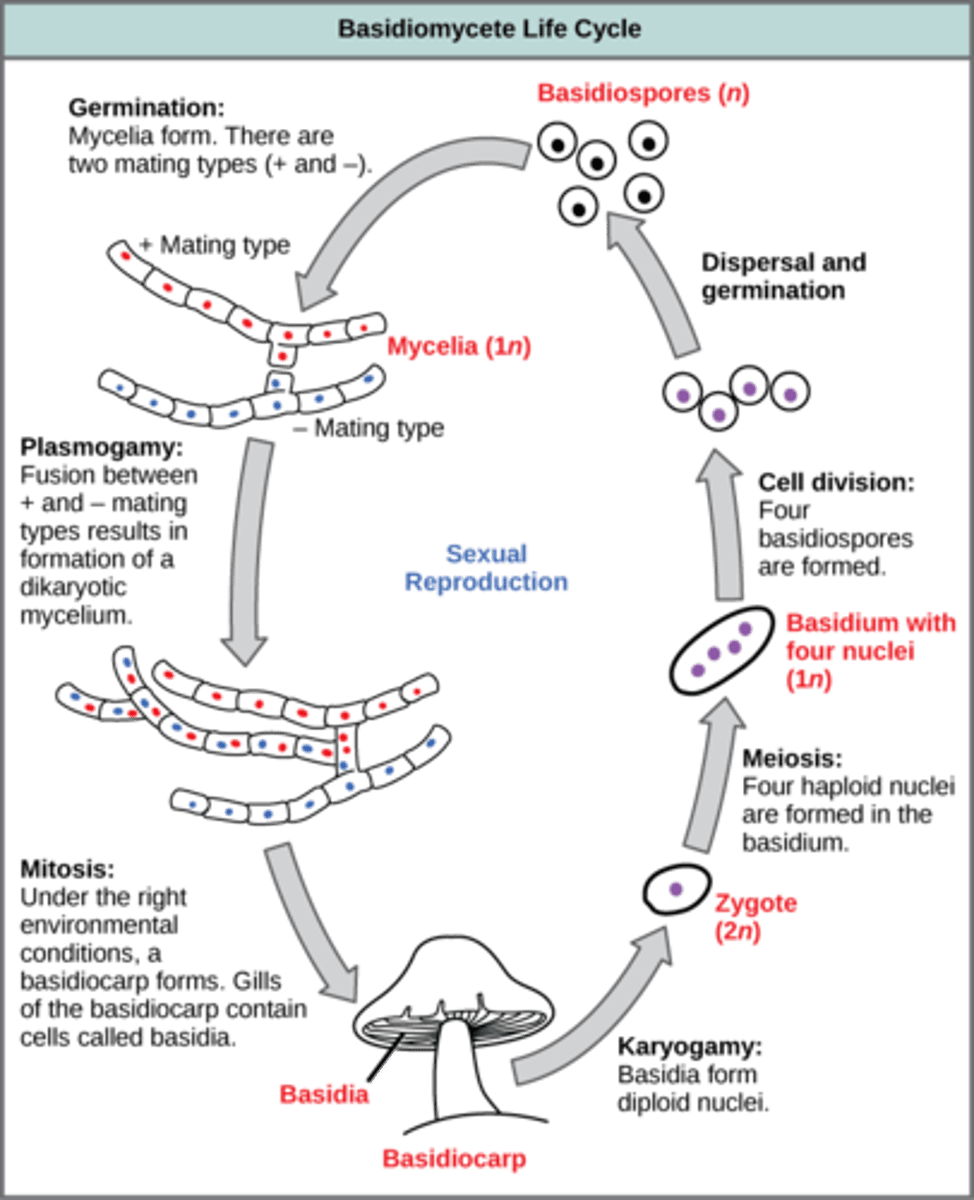
In Basidiomycota, how do basidiospores usually reproduce?
asexually
(Note: less commonly via conidia)
Penicillium is a fungus found within which fungal group?
Deuteromycota
(Note: produces penicillin,
which is an antibiotic that
disrupts bacteria's ability
to synthesize its cell wall)
The fungus in a lichen receive what macromolecule produced by algae or cyanobacteria via photosynthesis?
carbohydrates
if the algae within a lichen is nitrogen-fixing, what substance can the fungi produce?
nitrogen
(Note: demonstrates the mutualism)
What group of fungi usually composes lichens?
Ascomycota

What resources do ascomycetes provide for the algae or cyanobacteria in lichens?
1. water
2. protection
3. UV light (aid in photosynthesis)
In lichens, what substances can a fungus produce to protect against grazers?
toxic chemicals
is a fungal obligate parasite that is involved in food spoilage?
Rhizopus
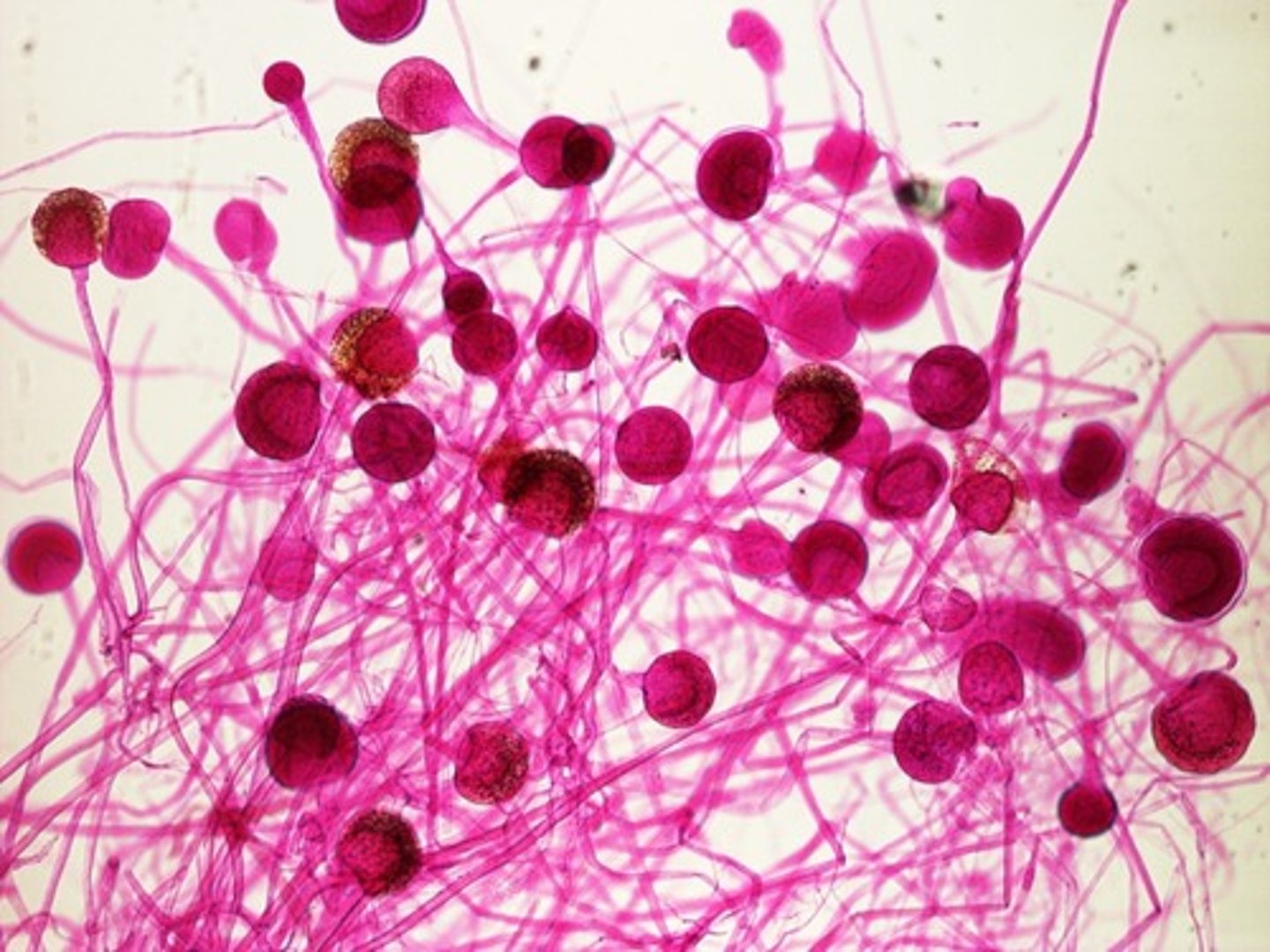
what species is commonly known as the black bread mold?
Rhizopus stolonifer
(Note: type of Zygomycota)
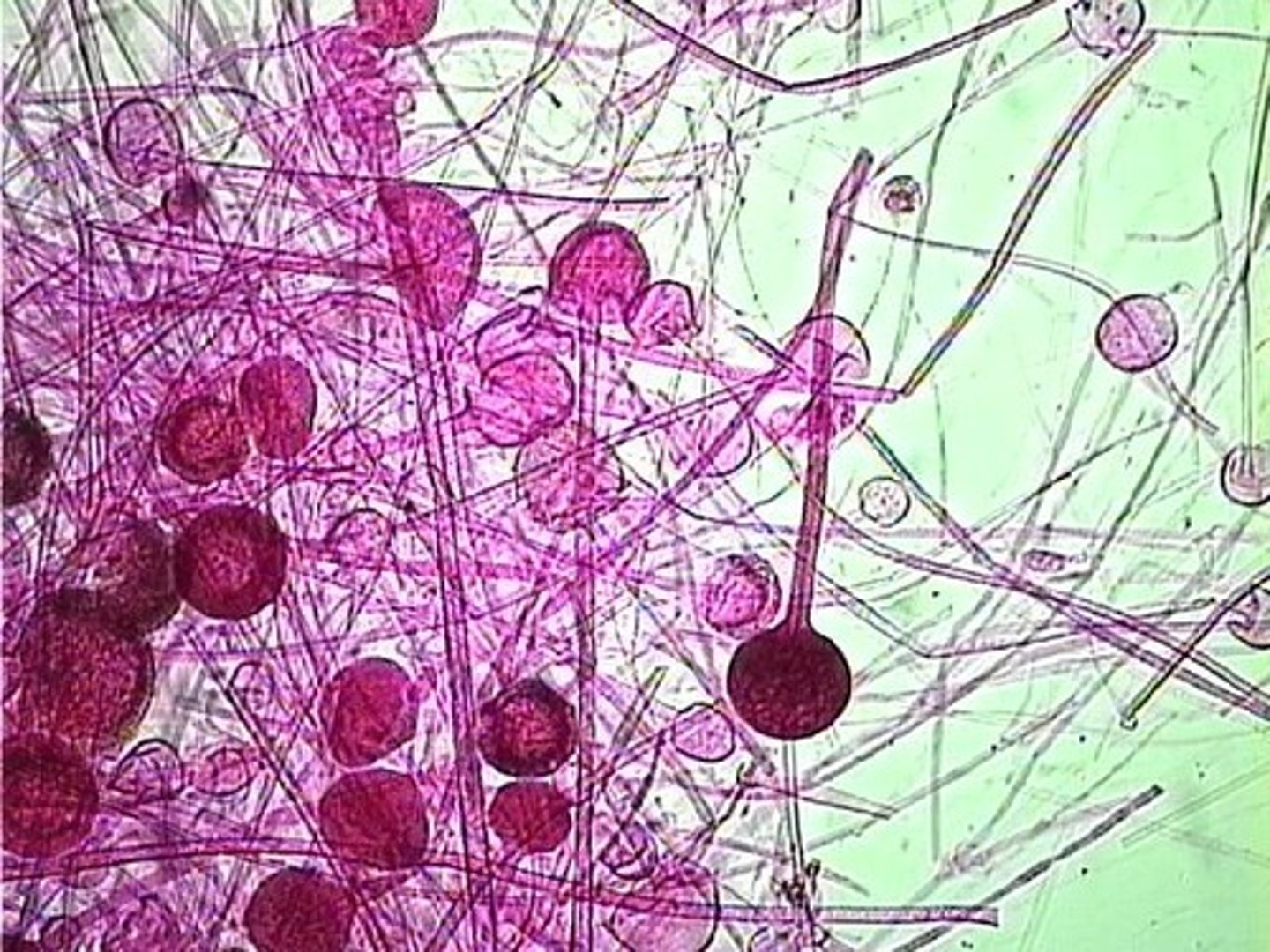
What fungus is involved in infections of mucous membranes?
Candida
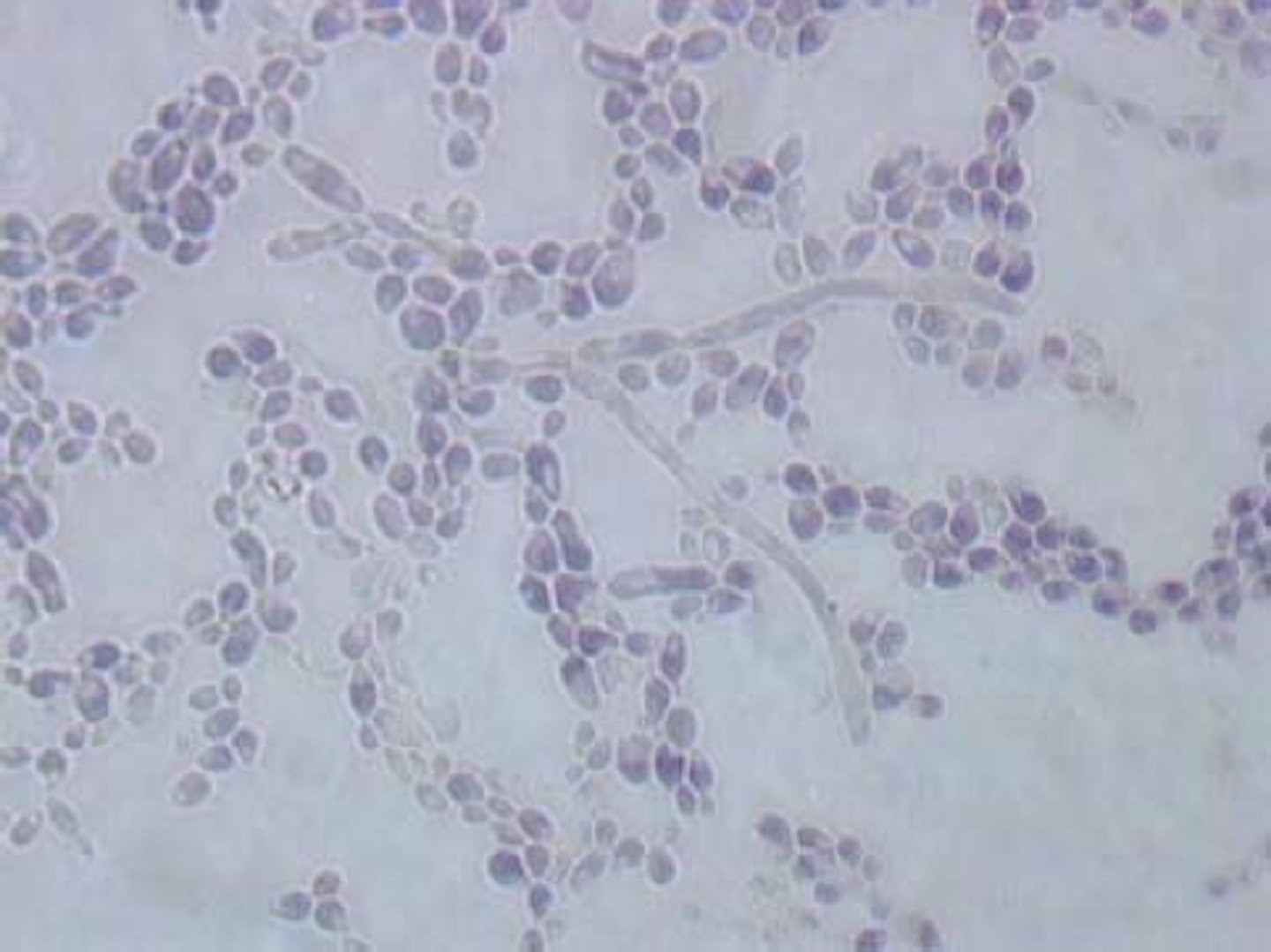
What species is a type of yeast that is involved in fermenting sugars to alcohol?
Saccharomyces cerevisiae