IMSE 311: Antibody & B-Lymphocytes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
B-cell Progenitor (Pro-B Cell)
Earliest development stage
Growth Factor: (secreted by bone marrow stromal cells)
IL-7
Transcription Factors:
E2A
Early B-cell factor (EBF)
Interferon regulatory factor 8 (IFR8)
Paired box protein 5 (PAX5)
Rearrangement of B-cell receptor (BCR) genes: cell surface version of an Ig/Ab molecule that code for heavy and light chains of Ab molecule
Markers:
CD19
CD45R
CD43
TdT
RAG-1
RAG-2 enzyme
B-cell Precursor (Pre-B Cell)
Pro-B cell enters Pre-B cell stage after BCR gene rearrangement
Markers:
Pre-BCR: heavy chains + surrogate light chain
Pre-B Cell Receptor (Pre-BCR)
Formed when a heavy chain combines with a surrogate light chain and signal-transducing subunits (Ig-alpha & Ig-beta) on B-cell surface
Light Chain Gene Rearrangement
Begins when pre-BCRs appear on the B-cell surface
Disulfide bonds
Combines heavy and light chains (immunoglobulins “Ig”)
Immature B-cell
Preparation for antigen-specific response
Marker:
IgM BCR
CD21
CD40
Class II MHC
Central Tolerance
Elimination of B-cells that bear self-reactive receptors
more than 90% of B-cells die in this manner
Mature B-cell / Naive B-cell
In the spleen
Follicular B-cell: recirculate between blood and secondary lymphoid organs in search of specific Ag (Majority of immature B-cells become follicular)
Marginal Zone B-cell: reside mainly in spleen’s marginal zone and respond rapidly to blood-borne pathogens
Markers:
Complete IgM and IgD BCRs
Class II MHC
Plasma Cells
Fully differentiated lymphocyte for antibody production
Minimal surface Ig
Abundant cytoplasmic Ig
Marker:
CD138
Immunoglobulin
Glycoproteins produced by plasma cells found on B-cell surface that serve as receptors that specifically recognize foreign antigens to initiate the immune response
Neutralize toxic substances
Facilitates phagocytosis
Composed of 2 heavy chains and 2 light chains (H2L2) “tetrapeptide”
Valence
Number of antigen-binding sites of an antibody (connected to Fab fragments)
most Ab are bivalent (2 binding sites)
Fab Fragments
Located at at the amino-terminal end and have antigen-binding capability
Consists of
1 light chain
1/2 heavy chain
Fc Fragment
Located at the carboxyl-terminal end and are responsible for important biological activities
Spontaneously crystallized at 4° C
Consists of
2 heavy chains halves
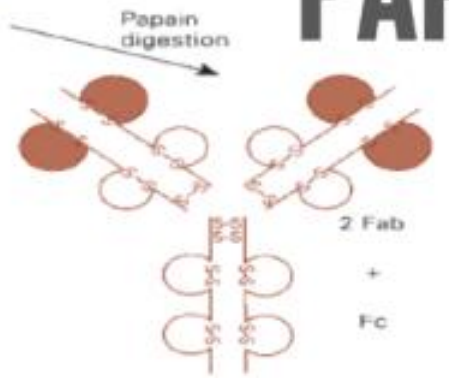
Papain
Proteolytic enzyme that cleaves the Ab molecule above disulfide bond, yielding 3 products
2 Fab
Fc
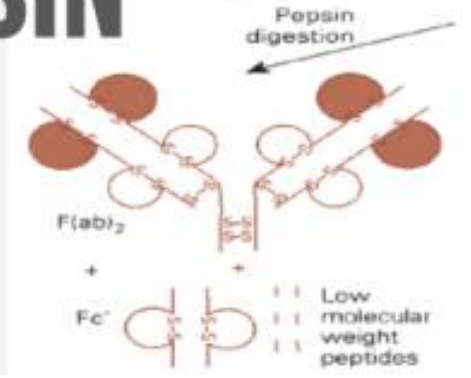
Pepsin
Proteolytic enzyme that cleaves at the carboxyl-terminal side of interchain disulfide bonds, yielding 2 products
F(ab)2
Fc
Antibodies Acc. to Sedimentation + Molecular Weight
S = Svedberg unit (how fast a molecule sediments in a centrifugal field; positive relation to MW)
(high S means faster sedimentation) M E D A G
IgM – 19 S (900 kDa)
IgE – 8 S (190 kDa)
IgG – 7 S (180 kDa)
IgA – 7 S (160 kDa)
IgD – 7 S (150 kDa)
Antibodies Acc. to Abundance
G A M D E
IgG: 70–75%
IgA: 10–15%
IgM: 5–10%
IgD: 0.001%
IgE: 0.0005%
Antibodies Acc. to Formation
M D G A E
IgM
IgD
IgG
IgA
IgE
Hinge Region
Flexible part of the antibody located between CH1 and CH2 region
Determines half-life of antibody
Larger hinge region = more flexibility = shorter half-life
Ig G-A-D: antibodies with a hinge region
Ig M-E: antibodies with no hinge region
Light Chain
Where antigens bind
MW: 25 kDa
Types: (2)
kappa
lambda
Regions: (2)
1 constant: structural integrity (carboxyl-terminal end)
1 variable: forms antigen-binding site, together with variable region of heavy chain (amino-terminal end)
Heavy Chain
Effector functions
MW: 50 kDa
Types: (5)
gamma
mu
alpha
delta
epsilon
Regions (4)
3 constant: determines antibody isotype (carboxyl-terminal end)
1 variable: forms antigen-binding site, together with variable region of light chain (amino-terminal end)
IgG
Monomer
75-80% (most abundant)
23-25 days (longest half-life)
New born immunity (can cross placenta)
Starts complement pathway
IgG1 - large hinge region
IgG2 - short hinge region, least effective in crossing placenta
IgG3 - largest hinge region
IgG4 - short hinge region
IgA
Dimer
10-15%
6 days
Patrol mucosal surfaces
Protection for infant digestive tract
IgA1 - mainly in serum, monomer
IgA2 - mainly in mucus membranes, dimer with J chain
IgM
Pentamer (in body fluids), Monomer (on B-cell surface)
5-10%
6-10 days
First responder
Starts complement pathway (most effective in classical complement pathway)
Agglutination and Opsonization
IgD
Monomer
0.001%
1-3 days
Heat labile
Second to appear
B (memory) cell production
IgE
Monomer
0.0005% (least abundant)
2-3 days (longest half-life)
Most heat labile
Found on BASOs and MASTs
Triggering of acute inflammatory reaction (allergy)
Destruction of large antigen such as helminths