Computers Final quarter one study guide. THE REAL ONE
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Know the 4 basic functions of word processing?
Writing
Editing
Formatting
Printing
What are the shortcut keys for a new document on Mac and Windows?
Windows is Ctrl+N
Mac is Command+N
Name 4 parts of a document that can be formatted?
Characters
Paragraphs
sections
Pages
Name 3 desktop publishing programs
Adobe PageMaker
InDesign
Photoshop
publisher
List six steps to publish a document?
1.Writing
2.Editing
3.Formatting
4.Proofreading
5.Printing
6.Distributing
Let's the hardware devices communicate with one another and run efficiently
Operating system
The Most important piece of hardware in a computer is the ———,which processes data
Central Processing unit(CPU)
A(n) ———— port connects several peripherals to a computer at one time and moves data faster than a serial port.
Universal Serial bus (USB)
A(N) ———— is any hardware device that is seperate from the computer but connected to it
Peripheral
—- is online storage offered on various Web Sites
Cloud/Cloud Storage
Refers to the raw data that is entered into a computer
Input
Refers to the result of the computers processing
Output
—- Refers to the task or tasks carried out by the computer,or what it does with the data
Processing
The last stage of computer processing is ——,the saving of processed information.
Storage
The ——- is the part of the computer where the CPU and memory are located.
Motherboard
Most ——— are about 6’’ wide by 8’’ tall and weigh less than 1 pound.
Tablet/Tablet Computers
The computer to which all computers in a network are connected is the ——-.
Server
Know the difference between hardware and software?
Hardware is for example a keyboard,mouse,monitor,and disk drive. While Software refers to any program that tells a computer what to do and how to do it.
A group of 8 or more bits is a byte. True or False
True
Data is coded in 0’s and 1’s true or false
True
Know the difference between digital and analog computers?
Digital computers work with data that have a fixed value, used for playing games or searching internet. While an Analog computer measures data on a scale with many values, used heavily in 1970’s.
What are the two types of software?
Utility and Application Software
Know the Difference between Serial ports and Parallel ports?
Serial ports move data one bit at a time; meanwhile, Parallel ports move data in groups of 8 bits (1 Byte) at a time.
— are programs designed to help you with specific tasks
Application Software
Are Programs that perform maintenance and repair jobs.
utility Software
—- is a type od software that allows a computers hardware devices to communicate and run efficiently.
Operating system (OS)
Know the Difference between ROM and RAM?
ROM-is Read Only Memory
RAM- is Random Access Memory
The area where data and instructions are stored while the computer working is called——. It is considered Volatile.
RAM- Random Access Memory
Instructions that start the computer when turned on. Instructions dont change. PERMANENT
ROM-Read Only Memory
What types of businesses use mainframes?
Finance
A —— is a computer that allows people to access the same dat at the same time.
Mainframe
Partial window seen in split screen
Panes
Some programs also split the screen by showing text in one pane and a list of the document's headings in the other. This list is called a
Document map
From the row of keys at the top of the keyboard that are labeled F1, F2, and so on.
Function key
a collection of predefined styles that go together.
Style sheet
shows everything in a document-margins, graphics, headers, page numbers, and text.
Print preview
Place where you insert text
Insertion Point
The program automatically starts a new line, or "wraps" the text, when the current line is full.
Word Wrap
Know the difference between basic view,print layout view, web layout, and outline view?
The most basic view, called Normal view or Draft view, shows text in the correct font and has character format- ting like bold and italic. vThe Print Layout view shows how a docu- ment will look when it is printed. Web Layout view, which shows how a document will appear when published on the World Wide Web. An Outline view reveals the structure of a doc- ument. It breaks down the document into its major headings, subheadings, and text.
Know the basic Mac command shortcuts? p.155
Command +
Know what an extension is?
In Windows, file names have extensions, such as .txt, .rtf, .docx, or .wpd, although these extensions may be hidden from view.
What is formatting?
Controllling how text appears in your document, etc.)
What are margins?
This is the space between the four paper edges and the text.
Know difference between source file and destination file?
The file that contains the original data is called the source File, and the file where you place the shared data is called the destination file.
Be able to label the parts of a worksheet on excel!!! p.173
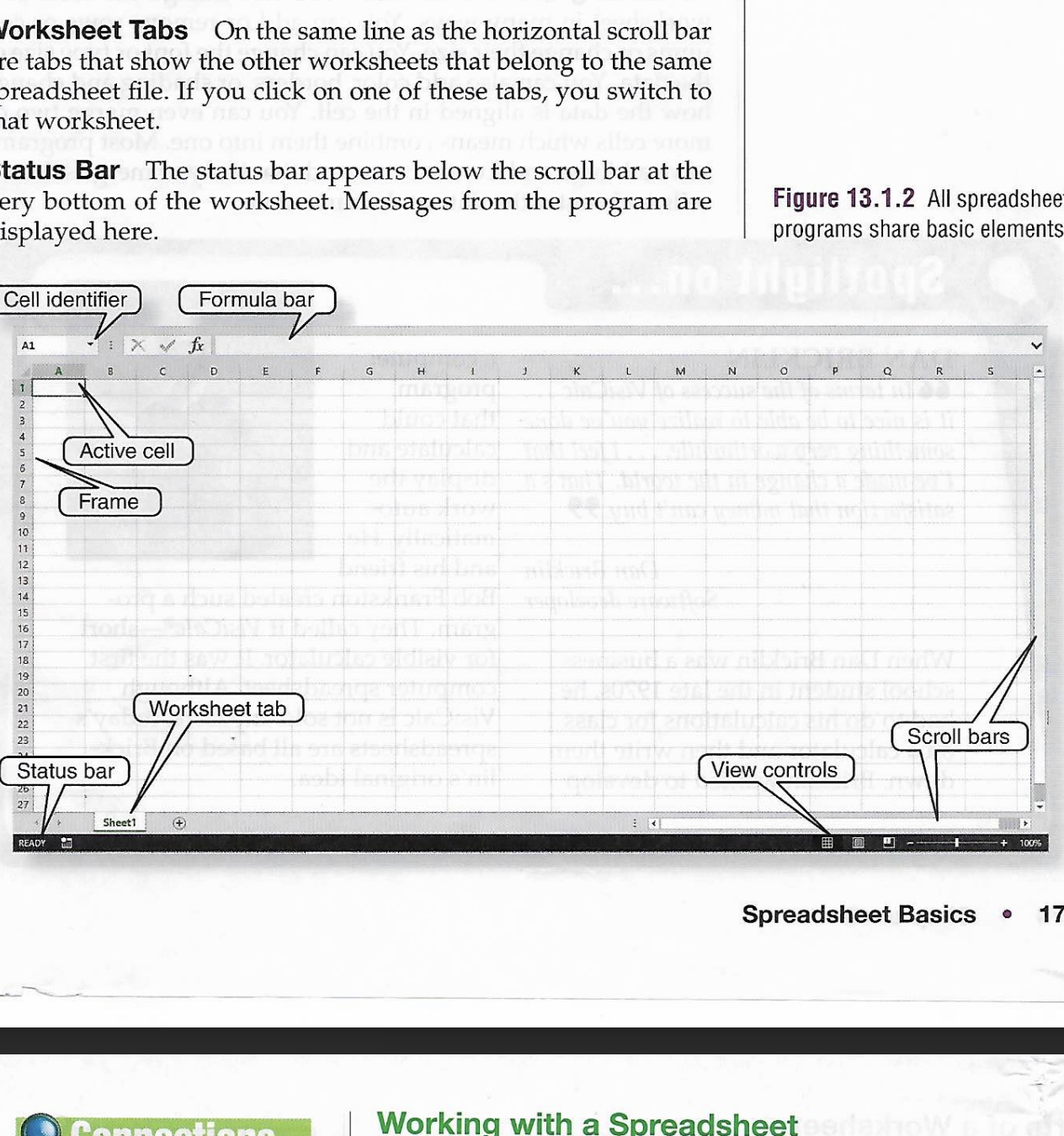
Know how to write an excel formula!
Ex- =SUM(E3:E4)
Know the difference between embedding and linking?
The simplest way is to copy the data in the source file and paste it into the destination file. This process is called Embedding. There is a way to export data that keeps objects up-to- date. This is called linking. To link data, you begin in the same way-by copying the data from the source. However, instead of using the Paste command in the destination, you use Paste Special.
Know data and number formats?
Data Formats You can change the look of either labels (text and numbers) or values (numbers used in calculations) in the selected cells.Number Formats Number formats, such as percent, cur- rency, decimal, or fraction, affect the way numbers display.
Know types of charts?
Pie, line etc.
Know difference between relative and absolute reference?
A relative reference automatically changes when it is copied or moved so that it uses cell addresses that are specific to its new location.An absolute reference does not change if you copy or move it to a different cell. You should use this type of reference when your formula or function must refer to a specific cell or range
a group of cells next to each other.
Range
A ——— is a set of data that changes by a constant value
Data Series
When data increases
Increment
When data decreases
Decrement
Each function has its own ——-, or rules of wording, that specifies how it must be entered.
syntax
A ——— is a set of mouse actions, keystrokes, or commands that you can record and put into action again and again.
Macros
When you nest a function, you include it within another function.
Nesting
An ———, which is data the function must use. This is often a reference to a cell or a range of cells but may be a number, date, or other data. A function's ——— are usually enclosed in parentheses.
Arguement, argument’s
a ——— is a commonly used formula built into a program.
Function
A ——— is a number, such as a whole number, a frac- tion, or a decimal.
Value
A ——- is text or a combination of numbers and text. —— are typically used for headings or explanations.
Label, Labels
The —— forms the top and left borders of the work- sheet. It includes the column and row headings.
Frame
The formulas discussed so far have used values. But formulas can also use cell references, or cell addresses. Example——- A1
cell reference
To use ——, you only need to enter the first one or two values in the series. Then, move the mouse to the lower-right corner of the first cell until a small plus sign or arrow appears. Drag across a row or down a column until you reach the last cell in the series. The data in the series appears in the cells.
autofill
Know different views? p.271-272
Normal View- Text and graphics can be added, removed, or edited in Normal view. Normal view splits the screen to show a Slide view and a Navigation pane.
Slide Sorter View- displays thumbnails of all of the slides in a presentation. This view allows you to change the order of the slides by dragging them to different locations.
Notes Page View- part of the screen dis- plays the slide and the rest of the screen shows a text box.
Slide Show View- The primary on-screen method of preview- ing and displaying slides during a presentation is called Slide Show view. Slides are displayed full-screen, one after another, in order.
Reading View- is similar to Slide Show view, except the slides are not displayed full-screen.
Master Views- Many programs let you use Master views to make universal style changes to every slide, notes page, and/or handout pages.
Know 7 tips to make an effective presentation? p.276-277
One Idea Per Slide
Keep It simple
Display Key Facts
Mix it up
Use color cautiously
Watch the fonts
Make it readible
Know ways to enhance your presentation? p.287
Insert images
Add animation,video, or sound
Adding transitional Effects
Adjusting timing- A slide can stay on the screen for a certain amount of time
Know presentation delivery methods? p.290
On-Screen presentation mode
interactive presentations
Internet delivery
Audience handouts
Pow- erPoint drawing tools also include ready-to-use shapes, called—-
Autoshapes
Moving pictures, etc.)
Animation
A series of dialog boxes that guides you through a step- by-step procedure.
wizard
A preformatted version of a certain type of docu- ment.
template
An area within a slide layout designed to hold data such as text or pictures.
placeholder
Miniature version of each slide
thumbnail
a default template that is applied to all slides of a certain type.
master slide
—- project an image directly from the computer through a lens and onto the screen.
digital projectors
What do some companies do with your personal information?
Gather information from public records kept by the government.They may also access information that people volenteer about themselves.
What is cybercrime?
The term ——— often refers specifically to crimes carried out by means of the Internet.
What are cookies?
A small file that is saved to your hard drive when you visit some Web sites.
What is a superuser?
Person who administers a system. (Might Be Wrong.)
A program called a superzapper allows au- thorized users to access a network in an emergency situation by skipping security measures. In the hands of an intruder, a super- zapper opens the possibility of damage to the system.
Superzapping
They may create a virus, worm, or ——— program to infiltrate computers and damage or delete data. Or, they may use a variety of other criminal tech- niques.
Trojan horse
The illegal copying of computer pro- grams.
Software piracy
Action that highlights a block of text before you change it
Select Text
Part of a document that contains specific format settings
section
Saves a document automatically as often as you want
Autosave
Used to insert an item copied or cut to the clipboard
Paste
Software that allows you to write, edit,format, and print a document
Word Processing unit
How and where the text is positioned on the page
Page formatting
Preset format in program
Default
Places a duplicate of the selected text on the clipboard
Copy
Automatically moves text as you type a new line
Word wrap
Corrects common spelling mistakes as you type them
AutoCorrect
A type of program used to create high quality publications
Desktop Publishing
Place in a document where text you type will appear
Insertion point
Area where cut or copied text is temporarily stored
Clipboard
Automatically starts an new page when one is full
Pagination
Puts an accidentally deleted word back
Undo
Removes selected text from a document and places it on the clipboard
Cut
Puts a change back in effect after canceling it with undo
Redo