Unit 7: Quantum, Atomic, and Nuclear Physics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It deals with the concepts from quantum, atomic, and nuclear part of physics.
Physics
Quantum Physics
AP Physics 2: Algebra-Based
Unit 7: Quantum, Atomic, and Nuclear Physics
atomic physics
nuclear physics
quanta
photon
photo-electric effect
wave theory of light
bohr model of atom
wave-particle duality
wave function
realtivity
isotopes
nuclear force
binding energy
nuclear reactions
decays
disintegration energy
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Quanta
Light being emitted as individual packets of constant energy called quanta.
2
New cards
Photon
A quantum of electromagnetic energy is known as a photon.
3
New cards
Photoelectric effect
Light behaves like a stream of photons, and this is illustrated by the photoelectric effect.
4
New cards
Photoelectrons
The released electrons are known as photoelectrons.
5
New cards
Wave theory of light predictions:
* The significant time delay between the moment of illumination and the ejection of photoelectrons.
* Increasing the intensity of the light could cause the electrons to leave the metal surface with greater kinetic energy.
* Photoelectrons would be emitted regardless of the frequency of the incident energy, as long as the intensity was high enough.
* Increasing the intensity of the light could cause the electrons to leave the metal surface with greater kinetic energy.
* Photoelectrons would be emitted regardless of the frequency of the incident energy, as long as the intensity was high enough.
6
New cards
Atomic Spectra
The light from a glowing gas, passed through a prism to disperse the beam into its component wavelengths, produces patterns of sharp lines called atomic spectra.
7
New cards
The wavelength of photon
Photon’s wavelength:
* λ = wavelength
* c = speed of light
* f = frequency
* h = Planck’s constant (6.626 × 10 -34 joule·s)
* λ = wavelength
* c = speed of light
* f = frequency
* h = Planck’s constant (6.626 × 10 -34 joule·s)
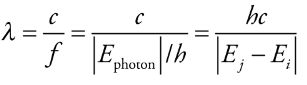
8
New cards
De-Broglie Wavelength
De-Broglie wavelength explains matter's wave-like behavior in quantum mechanics.
The equation is
***λ = h/p***, where
* λ is De-Broglie wavelength, h is Planck's constant, and p is particle momentum.
* As momentum increases, the wavelength decreases. This is important for understanding particle behavior at the quantum level.
The equation is
***λ = h/p***, where
* λ is De-Broglie wavelength, h is Planck's constant, and p is particle momentum.
* As momentum increases, the wavelength decreases. This is important for understanding particle behavior at the quantum level.
9
New cards
Wave-Particle Duality
Electromagnetic radiation propagates like a wave but exchanges energy like a particle. This is known as wave-particle duality.
10
New cards
The wave function
The probability that a particle will be measured to be at a particular position when the position is measured. That probability is related to a new physical parameter called the wave function.
11
New cards
Theory of relativity
The results of physical experiments will be the same in any-nonaccelerating reference frames.The speed of light is constant.
12
New cards
Time dilation
Demonstrated by synchronized atomic clocks.
13
New cards
Length Contraction
To be consistent with time dilation, there must also be disagreement about distances. This is known as length contraction.
14
New cards
Isotopes
The nuclei that contain the same number of neutrons are called isotopes.
15
New cards
Mass number
The total number of nucleons (Z+N), is called the mass number, and is denoted by A
16
New cards
Atomic number
The number of protons in a given nucleus is called the atom’s atomic number denoted by Z.
17
New cards
Nuclear force
The strong nuclear force is a fundamental force which binds neutrons and protons together to form nuclei.
18
New cards
Binding energy
It tells us how strongly the nucleus is bound.
19
New cards
Nuclear fusion
It is of small nuclei at extremely high temperatures.
20
New cards
Nuclear fission
The emission of a particle or splitting of the nucleus.
21
New cards
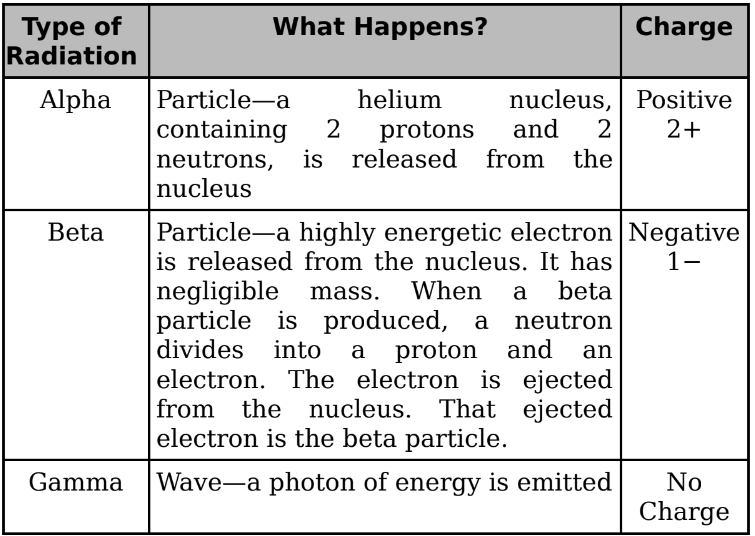
Decays
Alpha, Beta, and Gamma decay:
22
New cards
Disintegration energy
It involves emission or absorption of energy.