Psychobiology Final Exam (MASTER)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Where does the Dorsal Stream Project?
parietal lobe
Where does the Ventral Stream Project?
temporal lobe
Cause of Prospopagnosia, Visual Form Agnosia, Achromatopsia, Apraxia
injury to the "what pathway" aka ventral stream which identifies what an object is
Parvoceullar Input
derive from different population of cells in visual axis
recieve input from cones
sensitive to color
Magnoceullar Input
derive from different populations of cells in visual axis
recieve input from rods
sensive to light
Classification of Somatosensory Receptors
- Nocioception
- Hapsis
- Proprioception
Nocioception
perception of pain and temperature (free nerve endings for pain; sharp and dull
Hapsis
perception of objects we grasp and manipulate or that contact the body, perception of fine touch and pressure
Types of Hapsis
- Meissner's corpuscle (touch)
- Pacinian corpuscle (flutter)
- Ruffini corpuscle (vibration)
- Merkel's receptor (steady skin indentation)
- Hair receptors (flutter or steady skin identation)
Proprioception
perception of location and movement of the body
Location of human A1 Auditory
w/in herschl's gyrus
Location of Broca's Area
left frontal lobe
region just in front of the central fissure
Broca's Aphasia
unable to speak despite normal language comprehension and intact vocal apparatus
Location of Speech
left frontal lobe
Location of Music Interpretation
cortex of the right Heschl's gyrus
Prefrontal Cortex
functions to plan complex behaviors
does not specify precise movements that should be made but specifies the goal toward which movements should be directed
Premotor Cortex
produces complex sequences of movement appropriate to the task
organized movements, but does not specify the detail of how each movement is to be carried out
Primary Motor Cortex
specifies details of motor movements
primary motor cortex is responsible for executing skilled movements
Amygdala
responsible for fear and anxiety, located anterior to the temporal pole of the hippocampus
Thalamic Projection
modulates the size or force of a movement that the cortex produces, influenced by internal globus pallidus, part of basal ganglia circuits
Where does the superior colliculus send its most direct connections?
pulvinar
What part of each retina receives input from the right visual field?
left hemisphere
What part of each retina receives input from the left visual field?
right hemisphere
Inner Hair Cells
auditory receptors
movement of basilar and tectorial membrane cause cochlear fluid to flow past cilia of inner hair cells, bending them back and forth
movement of cilia in direction of tallest cilia result in depolarization which opens calcium channels and leads to the release of the transmitter onto the dendrites of the cells that form the auditory nerve
movement in direction of shortest cilia result in hyperpolarization and corresponding decrease in transmitter release
Outer Hair Cells
sharpen resolving power of the cochlea
cilia of the outer hair cells are embedded in an overlying membrane called the tectorial membrane
by contracting or relaxing these cilia, the outer hairs cells change the stiffness of the tectorial membrane and thereby influence its effect on the inner hair cells
Globus Pallidus
-influence the thalamic projection (which modulates the size or force of a movement that the cortex produces)
thought of as a volume dial on a radio because its output determines whether a movement will be weak or strong
Role of Cerebellum in Movement
acquiring and maintaining motor skills
timing of movement and maintenance of movement accuracy
o acts like clock/pacemaker to ensure both movement and perceptions are timed appropriately
o acts like an error detection device making moment-to-moment adjustment on movements
divided into right and left hemispheres
contains about ½ of all neurons in the nervous system
o lateral parts of cerebellar hemispheres (movement of body appendages)
o medial part of cerebellar hemispheres (movement of body midline)
o floccular lobe (eye movements and balance)
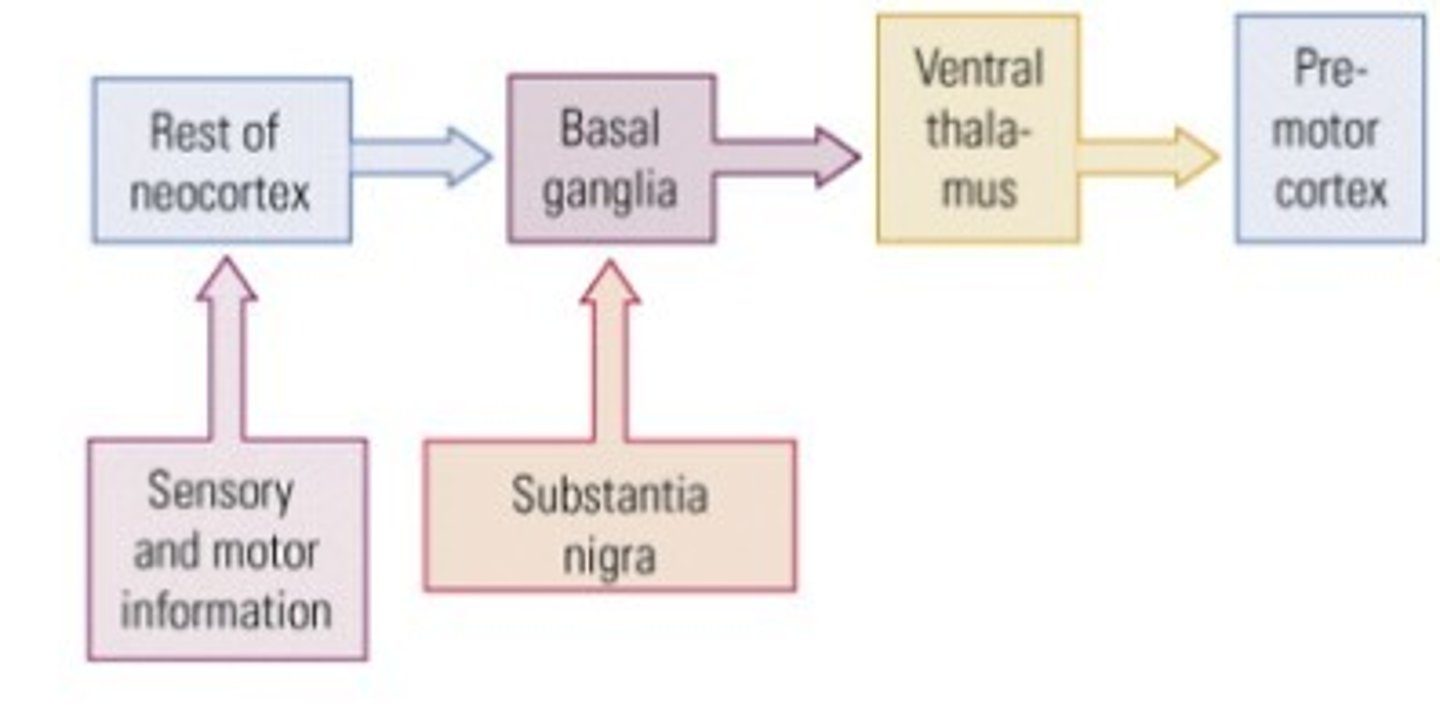
Role of Basal Ganglia and Movement
- The basal ganglia are a collection of nuclei in the forebrain that make connections with the motor cortex and with the midbrain
- The basal ganglia are involved in modulating movements
- The basal ganglia receive inputs from two main sources:
1. All areas of the neocortex and limbic cortex, including the motor cortex
2. The substantia nigra, a cluster of darkly pigmented cells of the midbrain, makes a dopaminergic projection to the basal ganglia
- The basal ganglia project back to both the motor cortex and the substantia nigra
- If cells of the caudate and putamen are damaged, unwanted choreiform (writhing and twitching) movements occur
o EX: Huntington's chorea and Tourette's syndrome
- Loss of the dopaminergic input from the substantia nigra results in an inability to produce normal movements, such as in Parkinson's disease
Types of Neurons in the Retina
- Ganglion cell
o Form pathway called geniculostriate system
§ Bridge between thalamus and striate cortex
- Amacrine cell
- Bipolar cell
- Horizonal cell
Frequency
rate at which waves vibrate measured as cycles per second, hertz, corresponds to our perception of pitch
Pitch
characteristic of perceived sound, corresponds to frequency
Timbre
characteristic of sound, corresponds to complexity
Amplitude
corresponds to loudness, intensity of sound, measured in decibels
Loudness
corresponds to amplitude
Complex Tones
corresponds to timbre, most sounds are a mixture of frequencies, particular mixture determine the sound's timbre or perceived uniqueness, timbre provides information about the nature of the sound
Dorsal Spinothalamic Tract
- Formed by the axons of somatosensory neurons dividing when they enter the spinal cord
- Made up of haptic proprioceptive axons that ascend the spinal cord on the same side of the body where they entered
- Synapse on neurons in the dorsal column nuclei at the base of the brain which then cross over midline and synapse onto neurons in the ventrolateral thalamus
- The neurons of the ventrolateral thalamus send most of their axons to the somatosensory cortex, but some axons go to the motor cortex
Ventral Spinothalamic Tract
- Formed by the axons of somatosensory neurons dividing when they enter the spinal cord
- The nocioceptive axons synapse onto neurons in the dorsal part of the spinal cord’s gray matter whose axons cross to the other side of the spinal cord and ascend to the ventrolateral thalamus as the ventral spinothalamic tract
- This tract joins the medial lemniscus in the brainstem to continue on to the ventrolateral thalamus and eventually to somatosensory cortex
Cause of depolarization of inner hair cells
- Movement of the basilar and tectorial membranes cause cochlear fluid to move past cilia
- Movement of the cilia in the direction of the tallest cilia
What is the fovea?
- region at the center of the retina specialized in high acuity.
- It's receptive fields are at the center of the eye's visual field
- Compose of cones
What is included in the ossicle?
Hammer, anvil, stirrup
What are the differences between outer and inner hair cells?
- There are 3,500 inner hair cells vs. 12,000 outer hair cells
- Inner hair cells are the auditory receptors vs. outer hair cells sharpen resolving power of cochlea
- Inner hair cells are most responsive to louder sounds vs. outer hair cells are responsive to softer sounds
- Bipolar cell only receives info from one inner hair cell
What is a pain gate?
- activity in the haptic-proprioceptive pathway inhibits the pain pathway in the spinal cord through axon collaterals and interneurons
Where is the "danger detector" in the brain?
Amygdala
What are the parts of the limbic system? (MACHAP)
- Mamillary nucleus of the hypothalamus --> Anterior thalamus --> Cingulate vortex --> Hippocampal formation --> Amygdala --> Prefrontal cortex
What neurotransmitter is associated with reward?
Dopamine
Why is Implicit Memory Unconscious?
Because the basal ganglia (place where implicit memories are formed) receive input from the entire cortex. BUT this connection is unidirectional (it does not procide information back to the neocortex)
What parts of the brain are involved in explicit memory?
- Hippocampus --> <-- entorhinal --> <--perirhinal, parahippocampal cortex --> <--frontal, paritetal, temportal occipital and cingulate cortex
Where is Object recognition memory?
- Perirhinal region
Visuospatial memory?
Parrahippocampal region receives input from parietal cortex
Most likely cause to amnesia
Damage to the medial temporal lobe = explicit memory was completely gone
First to Show Cell Death in Alzheimer's
entorihinal
What parts of the brain are involved in implicit memory?
Relationship between hippocampus and memory
Entrorhinal cortex projects to hippocampus --> Hippocampus believed to be primarily involved in forming spatial memories
What did we learn from the cases of H.M. and J.K?
H.M.: bilateral medial temporal lobe resection performed on H.M. to control epilepsy -->H.H. became amnesic after surgery --> unable to recall anything since his surgery in 1953 --> explicit memory gone, implicit memory remained intact
J.K.: had Parkinsons and was Unable to recall how to perform simple tasks, but was Aware of daily events and could recall explicit memories
Homunculus and Parts Represented
Within the motor cortex: cortical area
Electrical stimulation elicits movements of body parts corresponding to the map of the body
What disease is associated with the loss of neurons in the substantia nigra?
Parkinson's Disease
What type of cells are found in the olfactory bulb?
Olfactory cells, in the olfactory bulbs, synapses are formed with mitral cells
What is light?
Light is electromagnetic energy
- Light travels from outside world --> through the pupil into the eye --> strikes a light sensitive surface on the back of the eye called the retina
- Light represented as a continuously moving wave
o Vary in length fom 400 nm to 700 nm
- Range of visual light constrained by our visual receptors
What are rods?
Rods are a photoreceptor specialized for functioning at low light levels
What is a blind spot?
point of entry of the optic nerve on the retina: NO RODS OR CONES insensitive to light
Trace the auditory pathway (e.g., from vibrating waves of air molecules to the temporal cortex
· Pinna catches sound waves and deflects them into the external ear canal 🡪 waves amplified and sent to ear drum causing ear drum to vibrate 🡪 ossicles vibrate 🡪 ossicles amplify and send vibrations to oval window 🡪 oval window vibrations send waves through cochlear fluid 🡪basilar and tectorial membranes bend 🡪 cilia of outer hair cells embedded in tectorial membrane bend & generate neural activity
Role of the "how" Pathway
Dorsal stream = how pathway = enable action to be visually guided toward objects
Role of the "what" Pathway
Ventral stream = what pathway = identifies what an object is
Structure in the Limbic System
mamillay nucelus of the hypothalamus, anterior thalamus, cingulate cortex, hippocampal formation, amygdala, prefrontal cortex,
Who discovered the limbic circuit
·James Papez: found that the limbic lobe and the associated subcortical structures provide the neural basis of emotion
Papez circuit: circuit by which emotion could reach consciousness in the cerebral cortex
What is the Amygdala involved with?
Limbic system: receives inputs from all of the sensory systems (limbic neurons are multimodal)
Amygdala sends connection to the hypothalamus and brainstem and influences neural activity associated with emotions and species typical behavior
Sends connections to the prefrontal cortex (process which regulates emotions)
Where does Dopamine originate?
· Ventral tegmental area
Relationship Between Arousal and Memory
Low arousing words were remembered immediately but were forgotten over time. High arousal words were not remembered immediately (well) but were remembered over time (@ 24 hour mark)
Transmitter Involved in LTP and LTP Occurence
· NMDA
Environmental event triggers glutamate-releasing activity into the synapse 🡪postsynaptic membrane is depolarized at the same time 🡪 then results in the induction of LTP