Biology Vocabulary Review (Summer Work)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Cell
The Cell is the smallest unit of life, which is composed of organelles. The two types of cells are prokaryotic and eukaryotic.

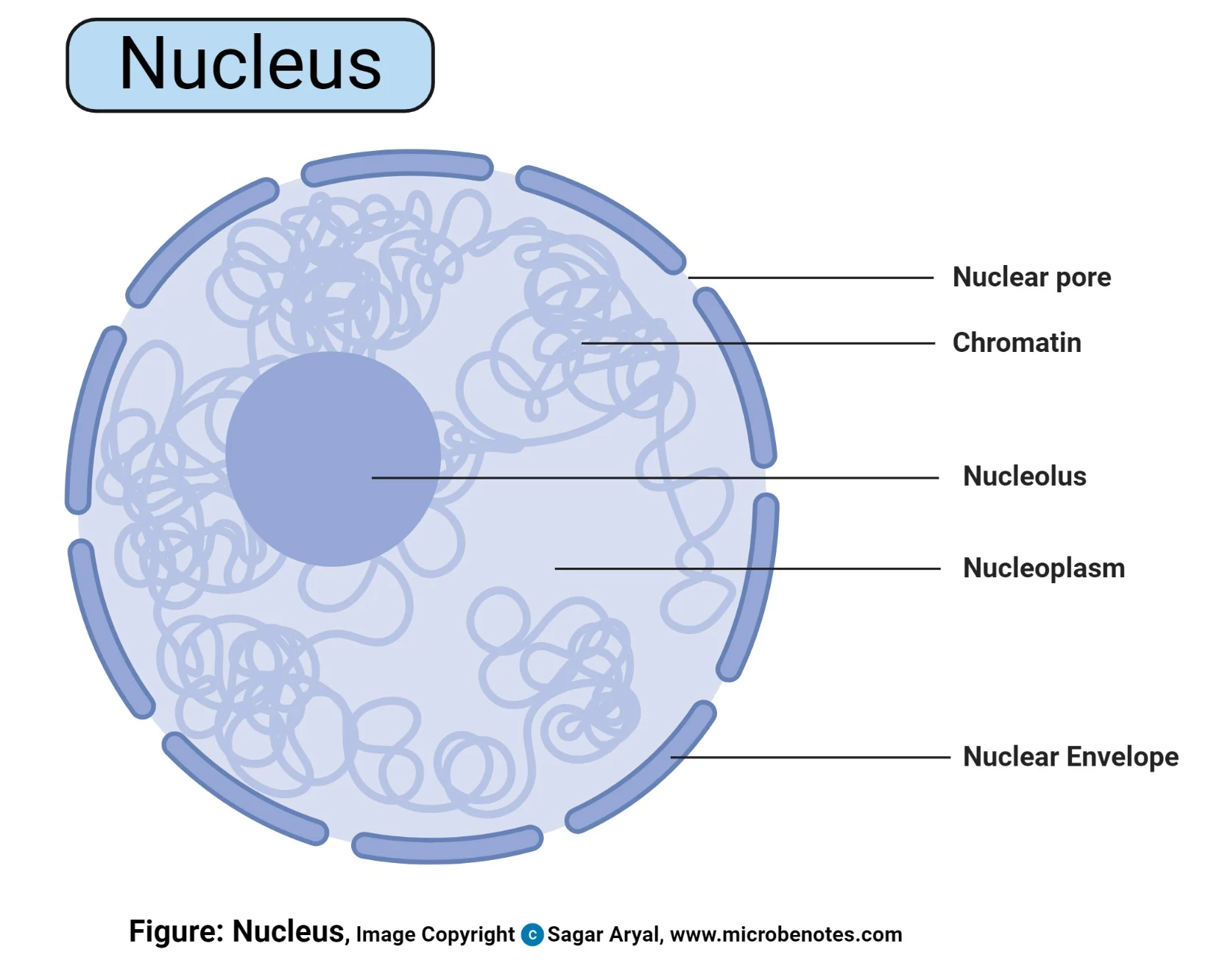
Nucleus
An organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains a cell’s genetic information, with a membrane to separate it from the cytoplasm, and contains the nucleoplasm. Prokaryotic cells do not have a Nucleus
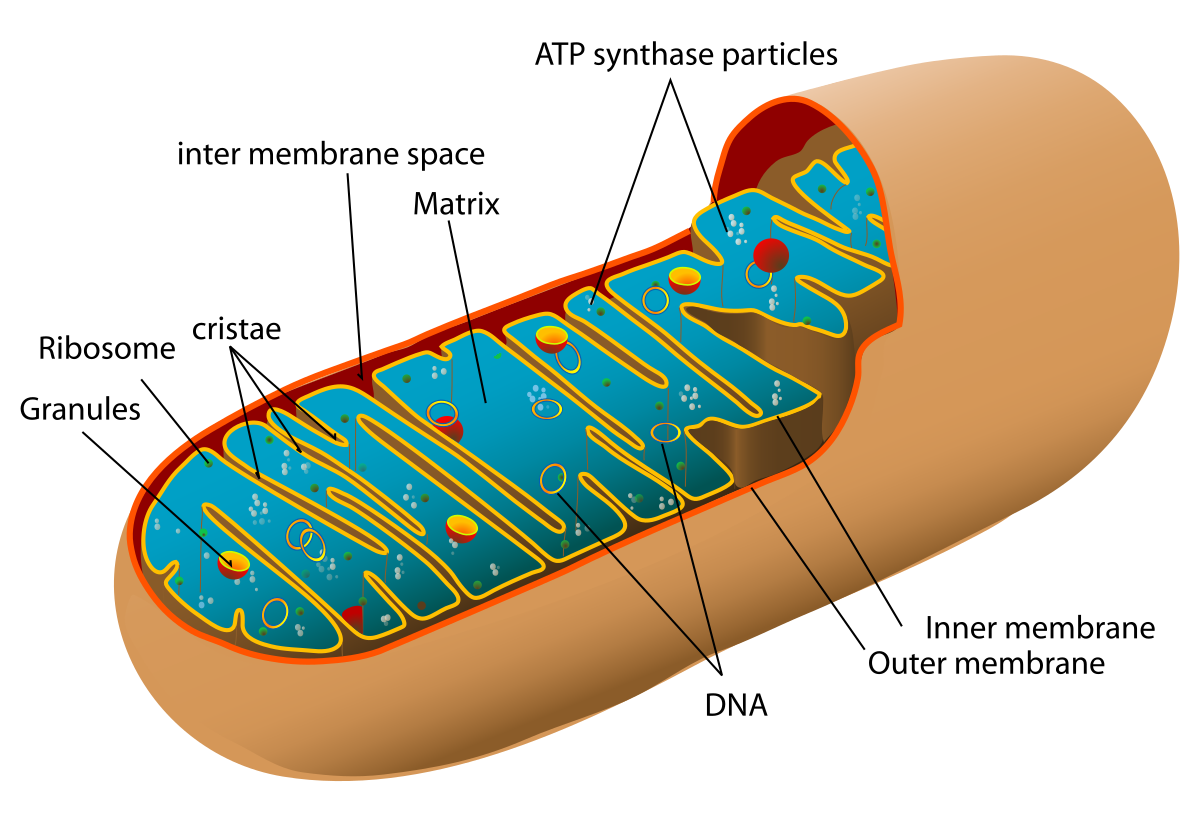
Mitochondria
An organelle found in most eukaryotic cells that performs cellular respiration to make ATP/energy for the cell. It is not found in prokaryotic cells. An analogy often used is that it’s like the power plant of the cell.
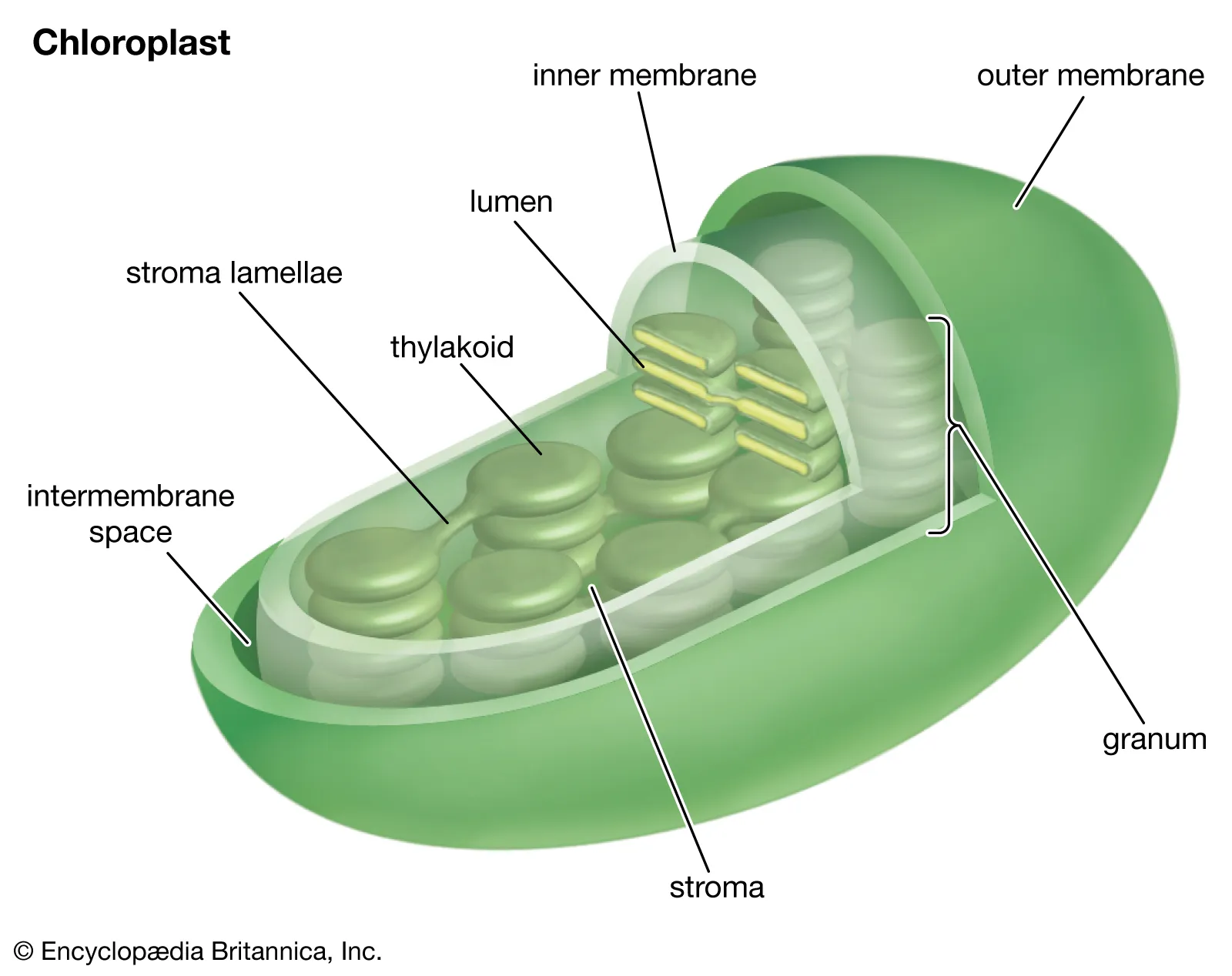
Chloroplast
An organelle that specializes in photosynthesis to create ATP and/or NADPH. It's like the mitochondria for plants.
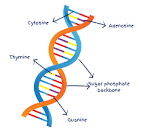
DNA
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is genetic information. A common analogy is that it's essentially the instruction or blueprint for how to build you if the DNA were from you. DNA is what codes for you. DNA is in a beautiful double helix shape for us, but it can be in different shapes.
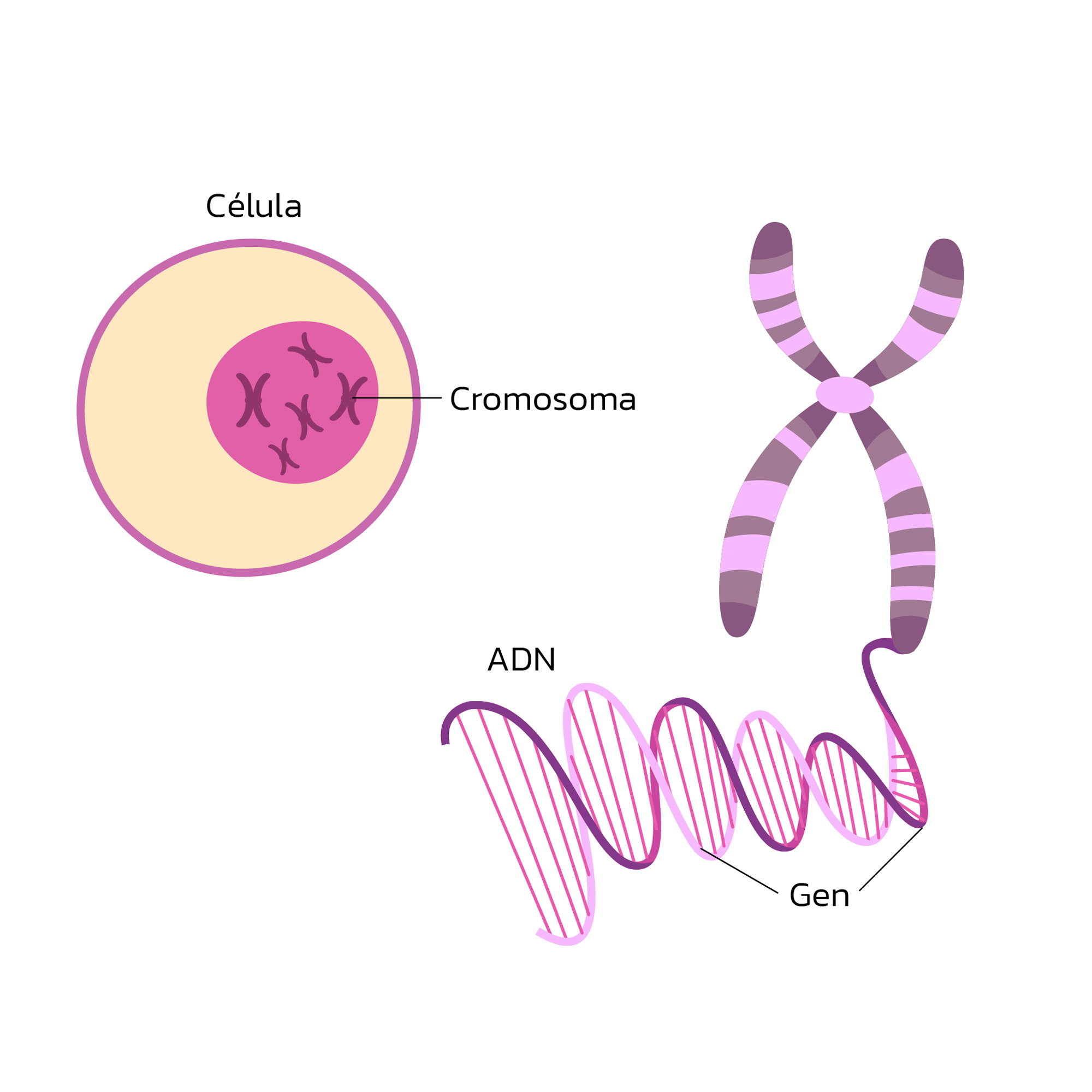
Gene
A gene is a portion of DNA specifically located on a chromosome in the nucleus of the cell. This is essentially just a smaller unit of DNA. Just like DNA, a gene codes for a portion of you. 1% codes for proteins, the rest regulates them.
Organism
An organism is any living thing that can maintain homeostasis, has different levels of organization, reproduces, grows, uses energy, responds to stimuli, and adapts to its environment.

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants to create ATP and/or NADPH (energy). To do this, they use a combination of chlorophyll, water, and CO2. Oxygen is also created as a byproduct of photosynthesis.

Respiration
When referring to respiration, there are two main types you could be referring to. The first is just normal breathing, where you inhale oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. The second is cellular respiration, which is a process that occurs in cells to create ATP.
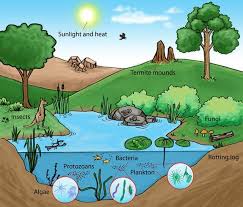
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a group of organisms that interact, and together they keep the balance. Ecosystems vary in size, so something as small as or smaller than a rock can be an entire ecosystem, like the little bugs under a rock. And technically, the entire world is an ecosystem.
Producer
A producer is a plant (in most cases) that makes its food, so it is the foundation of every organism. For example, say all the producers did. If this happens, the primary consumers will die quickly, then the secondary consumers, and so on.

Consumer
There are many types of consumers, including primary, secondary, etc, and then tertiary. The primary are the ones who eat the produce, then the secondary eat them, and so on, the tertiary eat all consumers, and the others eat everything below them.

Decomposer
Decomposers are organisms that decompose waste. They may not seem important, but they are vital to sustaining a healthy ecosystem. For example, say in a jungle ecosystem where decomposers thrive and are especially important. In an ecosystem, there are so many plants dying and growing and dying again that without decomposers, the new plants would not be able to grow due to the thick pile of waste they could not sprout from under that, and without plant producers, everything would die.

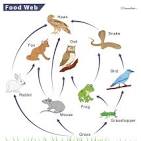
Food web
A food web is basically just a network of food chains, or another way to say it is a bunch of food chains jumbled then strung again. So, a food web is often is done correctly a great representation of an ecosystem, excluding the decomposers in most cases. So it includes producers, secondary consumers, etc, until tertiary consumers. Also, they kinda look like a web.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is critical to a healthy ecosystem and even a healthy Earth. Biodiversity is how diverse and how much variety a place or ecosystem has.

Adaptation
An adaptation is a process that is critical to survival for organizations. Adaptation is caused by a process called natural selection. It is where an organism adapts to its environment by evolving.
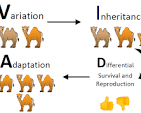
Evolution
It is a more influential form of adaptation. So it still happens through natural selection, except in most cases it changes the organism even more, nd they are often renamed, nd it often takes generations for this to happen.

Natural selection
Natural selection is where the organisms that have evolved and/or adapted to their environment are more likely to survive, and in turn, more of their offspring survive until the unevolvedunadapted organisms either die or evolve also.

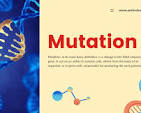
Mutation
A mutation is an unexpected change in an organism’s DNA sequence. This is very often referred to when fighting viruses or bacteria with medicine because these creatures reproduce and die and live so fast that mutations such as antibiotic resistance are a lot more likely. But in most cases, mutations are bad; they can cause disabilities and many other bad things.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is an organism's ability to maintain a stable internal environment. This is critical for survival because diabetes is due to a mutation that causes people to not be able to maintain stable blood sugar levels, and they sometimes die because of this. Also, in many cases when scientists are trying to classify something as dead or alive, they ask a question about homeostasis itand can’t maintain a stable ininternal environmenthisplays a big role in determining if it’s alive or not.

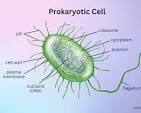
Prokaryote
A Prokaryote is a type of organism that is single-celled and does not contain a nucleus. Prokaryotes are also often smaller. The other organisim type is ukarotes, by the way. One example of prokaryotes is bacteria.
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is the other type of organism. These organisms do have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and as prokaryotes are often smaller, these are often bigger. An example of a ukariote is you, a human.
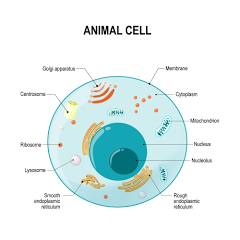
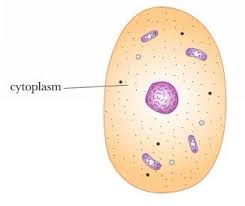
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance very similar to the nucleoplasm of the nucleus. This substance is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In the cytoplasm are the organelles are found. And it is contained in and/held in by the cell membrane.
Ribosome
This cell structure uses protein sythesis to convert MRNA into proteins for the cell.
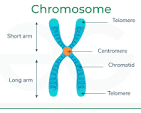
Cromosome
This is also a structure of DNA that is one size up from a gene. And is also found in the nucleus of your DNA. This is essentially just a medium unit of DNA. Just like DNA, a chromosome codes for a portion of you.
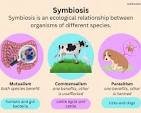
Symbiosis
It is a close, long-term relationship between two different organizations/species. There are three main types of mutualism where both species benefit, commensalism species the other is unaffected, and parasitism, one species is harmed, other benefits.
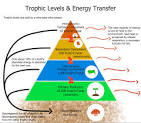
Trophic Level
The levels in an ecosystem of a food web or food chain. These include producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, etc, until tertiary consumers.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum quantity of organisms an environment or ecosystem can support. For example, a desert has a much lower carrying capacity than a jungle due to sources unless all the desert organisms have evolved and adapted, which could increase the carrying capacity.
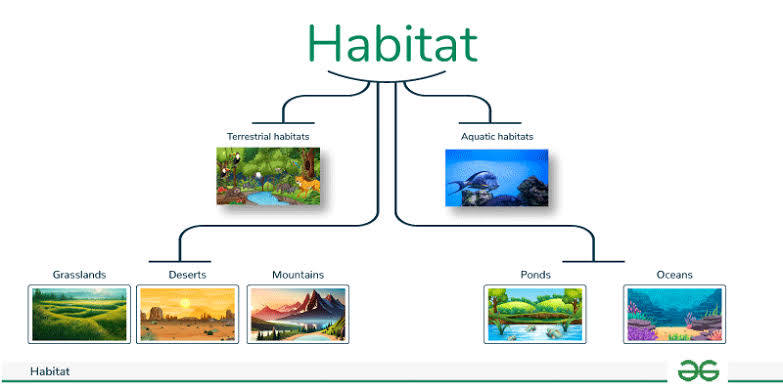
Habitat
The natural place/environment an organism lives/survives. A habitat can be an ecosystem housing many organisms.
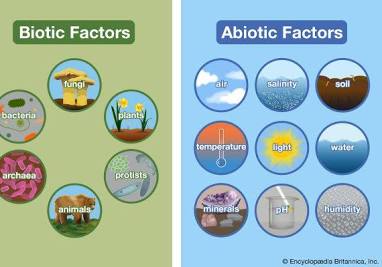
Biotic vs. antibiotic factors
The living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. These can influence carrying capacity and many other things.