Types of Epithelial Cells (location and function)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How is epithelial cells classified?
Shape and layers
What are the classifications of the cell layer? (just names)
Simple: One Layer
Stratified: 2 or more
Pseudostratified: Appears stratified (lies) due to differing height of cells (only happens to columnar)
Transitional: Stratified, multiple layers
What are the classifications of the cell shape? (just names)
Squamous: flat thing scale-like cells
Cuboidal: cube shaped
Columnar: tall rectangular cells
Where is the Simple Squamous found?
The alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs, for gas exchange.
The lining of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels (called endothelium).
The lining of serous membranes in body cavities (such as the pleura in the lungs, pericardium around the heart, and peritoneum in the abdomen), which is known as mesothelium.
The glomeruli of the kidneys, where it participates in filtration.
What is the function of the Simple Squamous?
Allows passage of Materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; produces lubricating fluid in serosae
What is the location of simple cuboidal epithelial cells?
Kidney tubules (tiny tubes in the kidneys that returns nutrients, fluids, and others in to the blood)
Ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surfaces.
What is the function of Psuedostratified columnar epithelium.
Secretion, particularly mucus, propulsion of mucus by ciliary action (respiratory system, like the hairs in your nose catching dust particles, basically snot.)
Notice the fuzzy hair on the image, literally the hair that would be in your nose. hair=cillia
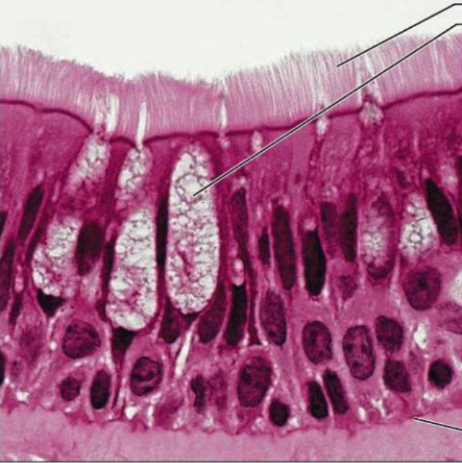
Location of Psuedostratified columnar epithelium.
Nonciliated version (non hair) in male’s sperm carrying duct (dih)
And ducts of large glands
Ciliated variety lines of trachea (windpipe), most upper respiratory tract
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Absorption (for nutrients);
secretion of mucus, (goblet cells used to protect stomach inside from the digestive acids)
enzymes (in stomach), and other substances
ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells dih) by ciliary action
Location of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum)
Gallbladder
Excretory ducts of some glands
;cillated variety lines
small bronchi (lung airway)
uterine tubes, and some other uterus regions
Function of transitional epithelium
Stretching & recoiling: Surface cells change shape (dome-shaped → flat) when the organ fills.
Barrier: Prevents urine (which is chemically harsh) from leaking into underlying tissues.
Protection: Multiple layers of cells protect against mechanical stress from expansion.
The skin can stretch, but thats because of elastic fibers.
Things that are made to stretch alot, like an erection are made of transitional epithelium
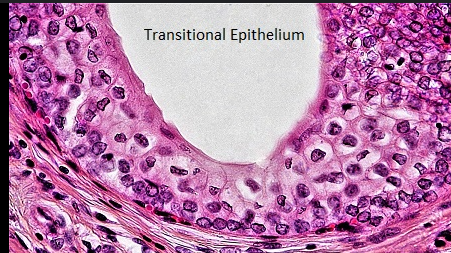
Location of transitional epithelium
Urinary bladder ✅ main site
Ureters
Proximal part of the urethra
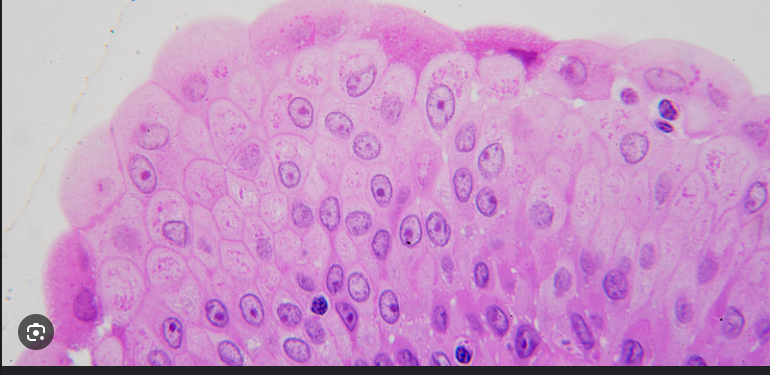
What does stratified mean?
Multiple layers of cells (heavy armor piercing)
Function of stratified squamous epithelium is to…
Protection against:
Mechanical abrasion (friction, scraping)
Chemical damage
Pathogens (microbes)
Location of stratified squamous epithelium cells
Everywhere on the surface of your skin.
Skin, oral cavity (lining of the mouth, tongue, and everything exposed)
Esophagus (lining of digestive tract) (connects throat to stomach)
Vagina
Cornea eye to keep moist
What happens when squamous epithelium cells keratinize?
Adds water proofing and extra toughness
(It’s the white part that comes when you scratch your skin)
(keratinized cells are dead cells filled with keratin)
Difference between Stratified and transitional
Stratified is made for strength (durability)
Transitional is made for mobility (stretch)
Both are layered
Stratified WILL have keratinization at the top, looks like uneven waves… if its keratinized
Stratified squamous = stack of pancakes → always flat on top
Transitional = balloons → dome-shaped at rest, can stretch and flatten
Function of Stratified cuboidal epithelium (rare)
protection:many layers of girth
secretion: in glands, mostly for sweat or other secretions
Location of Function of Stratified cuboidal epithelium (rare)
sweat glands (sweat)
mammary glands (breasts, used for milk)
salivary glands (produces saliva, oral)
Function of stratified columnar (rare)
Protection (anti tank)
secretion: in glands or ducts
Its main function is to protect and potentially secrete or absorb substances.
Location of stratified columnar (rare)
primarily found lining the larger excretory ducts of certain glands like the salivary glands and pancreas, as well as in the conjunctiva of the eye, parts of the pharynx, anus, male urethra, and vas deferens. Large ducts of some glands
Male urethra
Conjunctiva of the eye (partially)