entomology species quiz 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
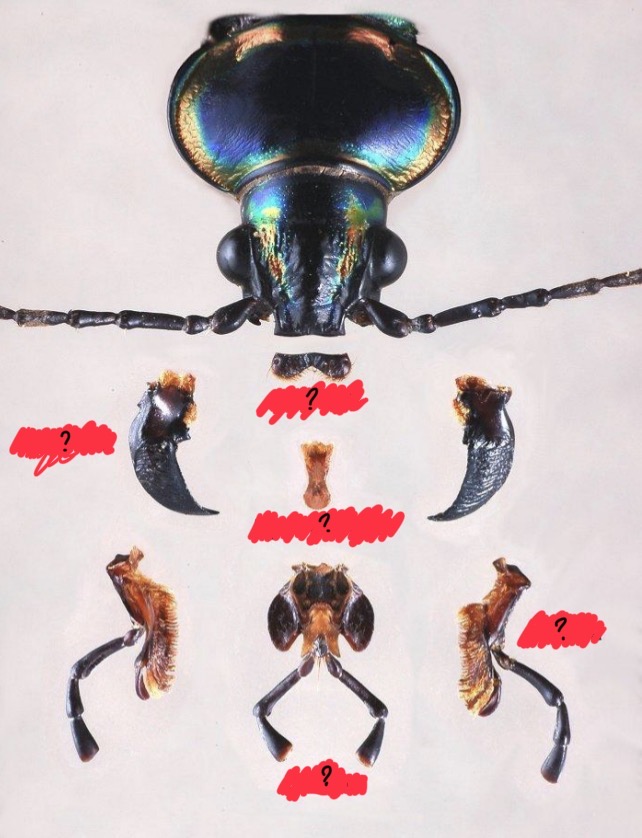
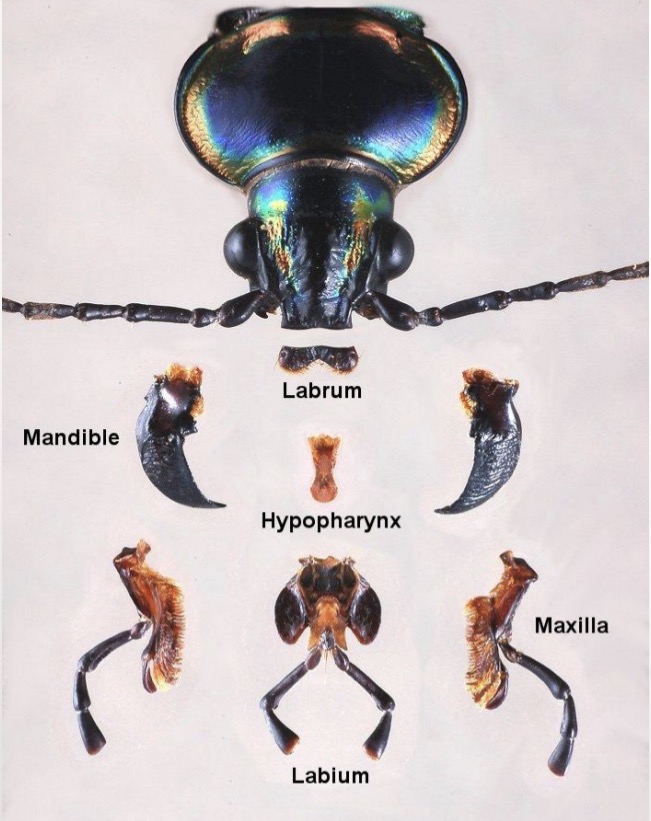
Labrum
Forms pre oral cavity
Covers base of mandibles
hypotharynx
Tongue-like structure
Objects forward from back of preoral cavity
Mandibles
Jaws
Apical portion→ cutting
Base→ grinding
Maxillae
Helps mandibles process food
Inner most portion→ lacina (helps macerate food)
Galea and maxillary palps
Sensory covered in setea w/ mechnoreceptors and chemoreceptors
Labium
Bottom of preoral cavity
2 regions:
proximal prementum (floor)
Labial palps (sensory)
What are the potential functions of the cuticle?
Protection
Mate attraction
Muscular attachment
Protection against foreign molecules
Act as metabolic reserve
Repository for hormones/pheromones
Cuticle
=exoskeleton
Secreted by epidermis
Made up of epicuticle and procuticle
(Lining trachial tubes, fore & hind guts, coat gland ducts)
Epicuticle
Secretes cuticle
Made up of cement layer, wax layer,
Outer epicuticle, inner epicuticle
Cement layer
Outer hardened protective layer
Wax layer
Lipid layer
Hydrophobic, made of hydrocarbons/fatty acid chains
Outer epicuticle & inner epicuticle
Produce some waxy layers
Procuticle
Made up of exocuticle, endocuticle, and mesocuticle
Exocuticle
Strong, more inflexible region, made up of many layer of chitin, scleritized region, makes proteins water insoluble
Endocuticle
Hundreds of layer of chitin, strength from H bonds
Mesocuticle
When there isn’t a clear indistinction between end/exocuticle

Should the cuticular structure and composition be the same in all insects?
No
Should the cuticle structure and composition be the same in all regions of an insects body?
No
What regions of an insects body may need increased flexibility
Joints
Between segments
Wings and bases
Neck
Sensory regions
Abdomen (respiration, feeding, reproduction)
Cuticular outgrowths
Spines, horns, spurs, setae
Spines/horns
Immovable
Spurs
Moveable
Setea
Hairs, microtrchia, trichoid sensilla sensory and glandular
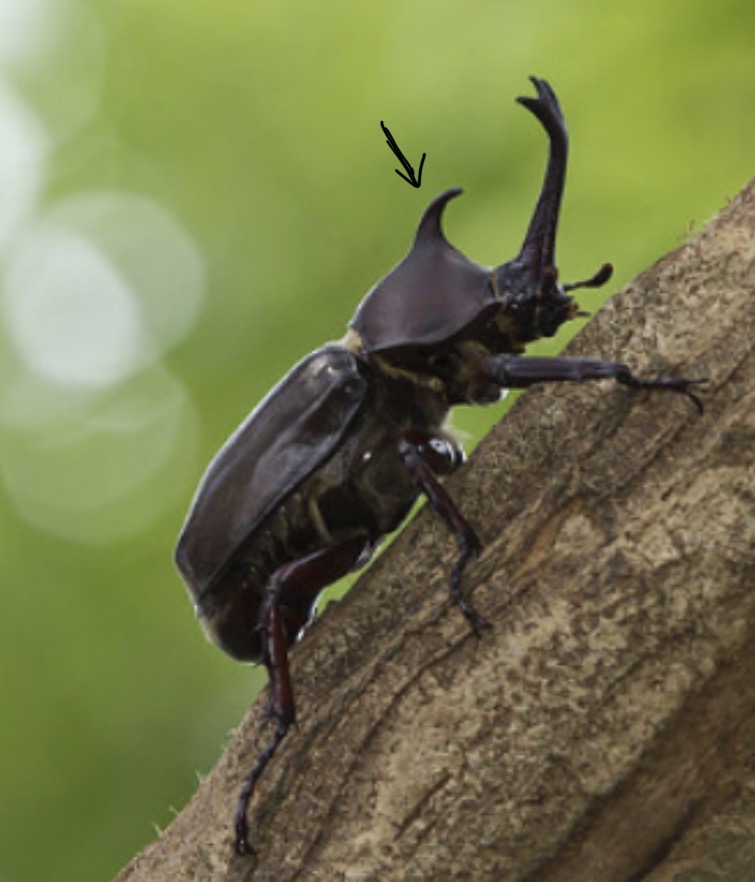

What structure is this?
Horn, immovable cuticular outgrowth
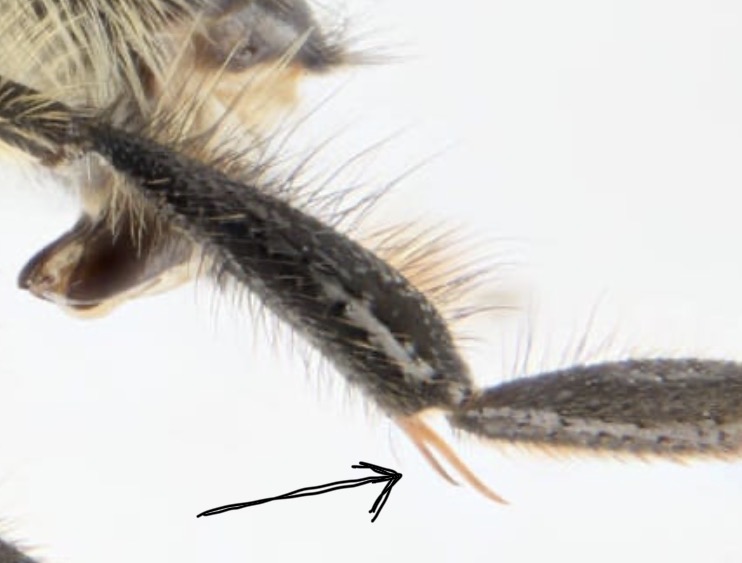

What structure is this?
Spurs, moveable cuticular outgrowth

What structure is covering this insect?
Setae, sensory/glandular cuticular outgrowth
Cuticular ingrowth
serve as points for muscle attachments
Serve as structural support
Physical coloration
Reflect/diffract whole wavelength of visible light
Result of light scattering,interference, and diffraction
Pigmentary colors
Absorption of visible light by a range of chemicals
In what ways can pigment form?
Insect metabolism
From food source
Microbial symbiotes
Why is coloration important?
Camouflage
Aposematism (warning/mimicry)
Thermoregulation and/or UV protection
Startle/distract
What are the 2 openings in head structure?
Occipital foramen (allows for connection to thorax)
Oral opening
What are the fused segments in a head structure? Which ones are preoral or post oral?
Preoral
preantenal-protocerebral
Labral
Mandibular
Antennal
Post oral
maxillary
Labial
Hypognathus
Ventral mouth orientation
Prognathus
Anterior mouth orientation
Opisthognathus
Posterior mouth orientation
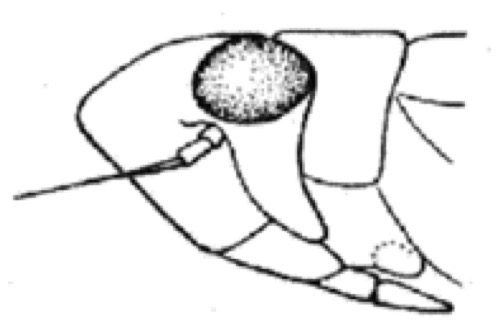
Which mouth orientation is this?
Opisthognathus
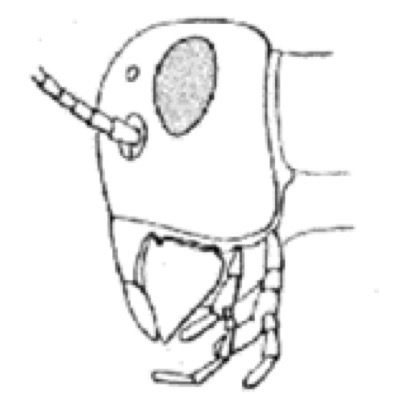
Which mouth orientation is this?
Hyponathus
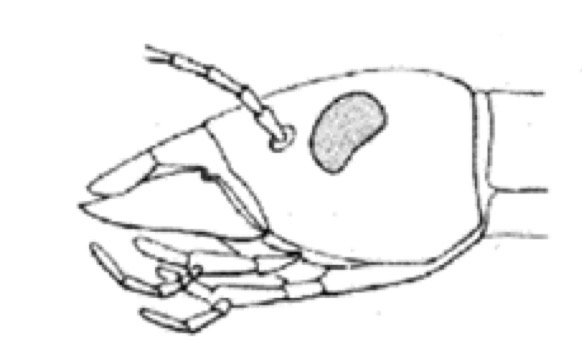
Which mouth orientation is this?
Prognathus
Sutures
Show remnants of segmentation
Ecdysal lines
Grooves that reflect internal structures

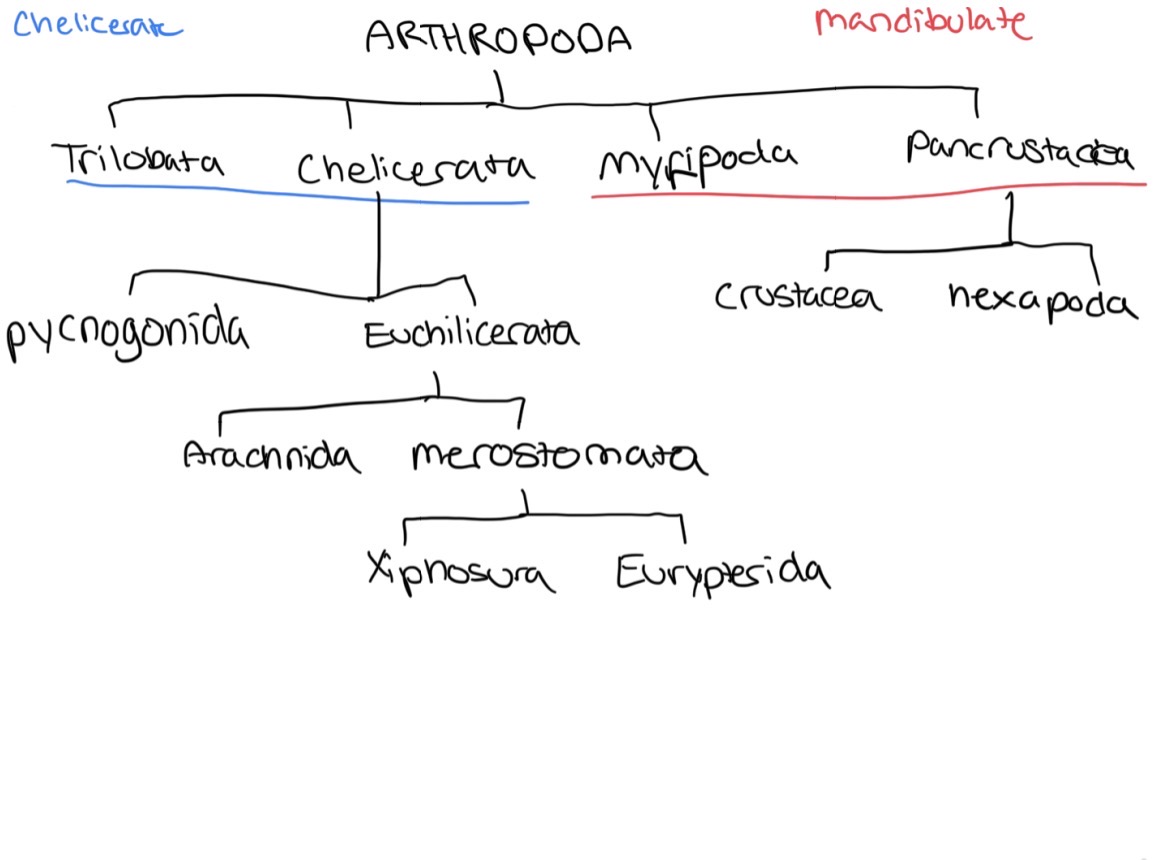

Tentorium
Ingrowths of cuticle
2 major sets of arms
Help race cranium and provide muscular attachment
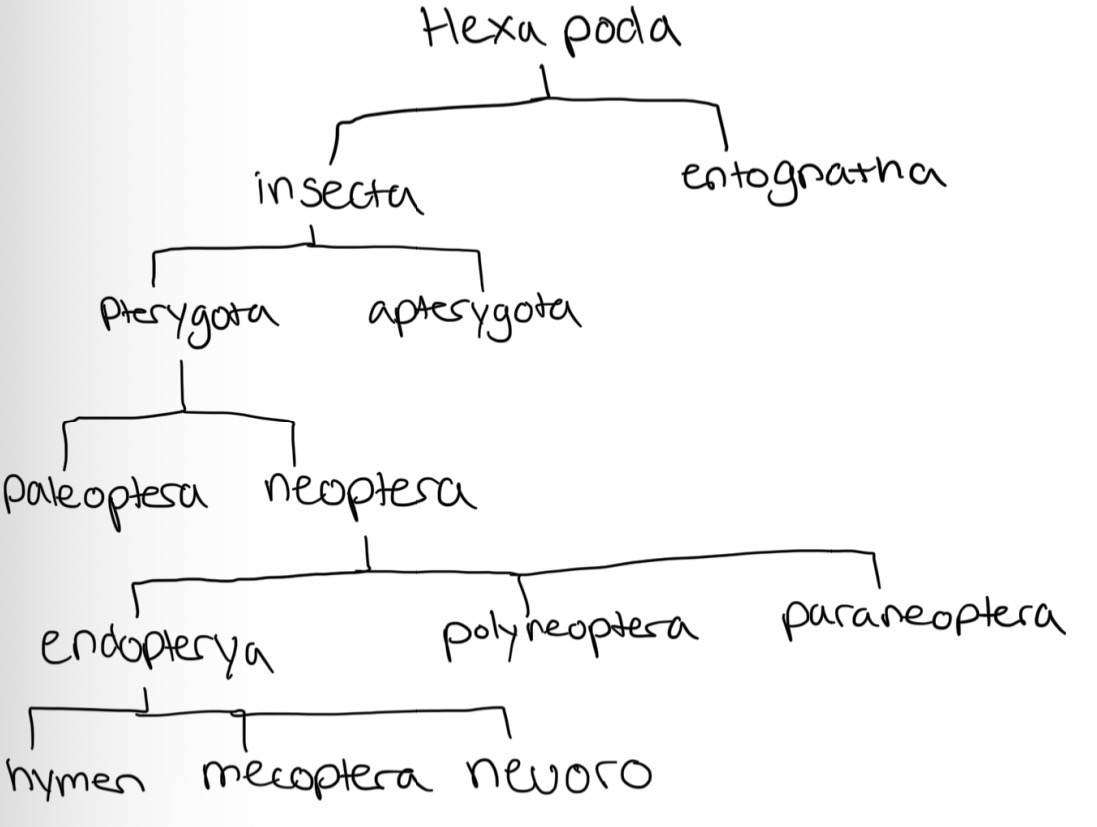
Key features of hexapoda
6 legs
3 tagma
head/cephalon
Thorax
Abdomen
5 wingless classes/orders
Protura
Collembola
Diplura
Archaeognatha
Zygentoma
Why would the evolution of wings be advantageous?
Escape prey
Better dispersal
Access to different populations
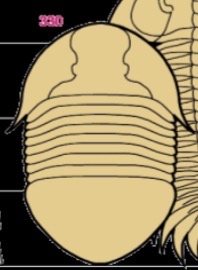
Label the 3 tagma
Head- cephalon
Middle- thorax
Bottom- pygidium (anus)
Chelate
Pincher like morphology
Subchelate
Spider fangs