DDS Lecture 6 Content
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Liquid dosage form categories
non-sterile (aqueous or non-aqueous)
sterile (free from microbes, aseptic, can be injected)
Non-Sterile Aqueous Liquid dosage forms
suspensions
emulsions
solutions
syrups
elixirs
tinctures
topical sprays and solutions
aromatic waters
douches
enemas
gargles
mouthwash
Non-sterile, non-aqueous liquid dosage forms
liniments
colloidions
extracts
Syrup
concentrated aqueous preparations of sugar or sugar substitute with or without flavoring agents and medicinal substances
syrups containing flavoring agents but not medicinal substances = non-medicated or flavored vehicles/syrups
most contain:
purified water
medicinal agents (if applicable)
sugar (usually sucrose): provide sweetness/viscosity
antimicrobial preservatives
flavorants
colorants
Meperidine HCl
syrup
Demerol Syrup (Sanofi-Synthelabo)
50 mg/5mL
opioid analgesic for the relief of moderate to severe pain, adjunct to general anesthesia
Antihistimine Syrup formula
chorpheniramine maleate = active ingredient (antihistimine)
glycerin = thickening agent, sweetening agent, levigating/wetting agent
syrup = sweeting agent, solvent
Sorbitol solution = sweetening agent
Sodium benzoate = preservative
Alcohol = solvent, preservative
Color and flavor = coloring, flavoring agent
purified water = solvent
Elixirs
clear, sweetened hydroalcoholic solutions intended for oral use and are usually flavored to enhance their palatability
non-medicated elixirs = vehicles
Medicated elixirs = therapeutic effect of the medicinal substances they contain
less sweet, less viscous than syrups
lower proportion of sugar
less effective than syrups in masking taste
hydroalcoholic character makes them better able than aqueous syrups to maintain both water-soluble and alcohol soluble components in solution
preferred over syrups because of stable characteristics and easy of solution
Phenobarbital Elixir
phenobarbital
orange oil
propylene glycol
alcohol
sorbitol solution
color
purified water
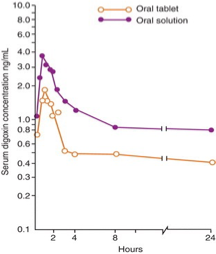
Absorption in solutions vs tablet
drug absorption from solution dosage form is higher than in tablet form
must use lower concentrations of solution to achieve same serum concentration in body
solutions have higher bioavailability compared to tablets
Cmax= maximum concentration
Tmax= time required for maximum concentration (~2 hours on graph)
Tinctures
alcoholic or hydroalcoholic solutions prepared from vegetable materials or from chemical substances
vary in preparation, strength, alcoholic content, intended use
when prepared from chemical substances (iodine, thimerosal), prepared by simple solution of chemical agent in solvent
Examples of tinctures applies to skin
Green soap tincture
65% API
alcoholic
detergent
iodine tinctures
2% API
hydroalcoholic
topical anti-infective
compound benzoin tincture
alcoholic
topical protectant
podophyllin
benzoin tincture
removal of genital warts
Vaginal Douches
irrigation cleansing of vagina
com
solutions may be prepared from powders or from liquid solutions/concentrates
in using liquid concentrates, patient is instructed to add the prescribed amount of concentrate (usually teaspoonful or capful) to certain amont of warm water (qt)
Components of Douche powders
Boric acid
Astringents
Antimicrobials
Quaternary ammonium compounds
Detergents
Salts
Aromatics
Retension Enemas
administered rectally for local effects or systemic adsorption
minimizes undesirable gastrointestinal reaction
clinically effective blood levels of agents usually obtained within 30 minutes following rectal instillation
Evacuation Enemas
cleanse the bowel
commercially available in disposable plastic squeeze bottles containing pre-measured amount of enema solution
instruction from pharmacist is advantageous to ensure patient correctly uses products
patient should be advised to gently insert the tip of the product with steady pressure and be told that it is not necessary to squeeze all of the contents out of the disposable plastic bottle
patient should be told that product will probably work within 5-10 min
Hydrocortisone
corticosteroids administered as retention enemas or continuous drip as adjunctive treatment of ulcerative colitis
administered rectally for local effects
Aminophylline
administered rectally for systemic absorption
minimizes undesirable GI reactions associated with oral therapy
Enema solution agents
sodium phosphate and sodium biphosphate
glycerin and docusate potassium
light mineral oil
Liniments
alcoholic or oleaginous solutions or emulsions of various medicinal substances intended to be rubbed on the skin
liniments with alcoholic or hydroalcoholic vehicle are useful when rubefacient (produces redness of skin, used to treat pain), counterirritant, or penetrating action is desired
Oleaginous liniments employed when massage is required
Collodoins
liquid preparations composed of pyroxylin dissolved in a solvent mixture usually composed of alcohol and ether with or without added medicinal substances
Pyroxylin
nitrocellulose, soluble gun cotton, collodion cotton
obtained by mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acids on cotton
consists chiefly of cellulose tetranitrate
appearance of raw cotton when dry but harsh to touch
available commercially moistened with ~30% alcohol
Solvents for liquid preparations
alcohol, ethyl alcohol, ethanol
diluted alcohol (50% alcohol, 50% water)
alcohol, rubbing (only topical use)
glycerin
isopropyl rubbing alcohol (only topical)
propylene glycol
purified water
Alcohol
most useful solvent in pharmacy other than water
used as primary solvent for many organic compounds
forms hydroalcoholic mixture with water that dissolves both alcohol-soluble and water-soluble substances
useful in extraction of active constituents from crude drugs
by varying proportion of two agents, active constituents may be selectively dissolved and extracted or allowed to remain behind according to solubility
Alcohol, USP: 94.9-96% C2H5OH by volume when determined at 15.56 degrees C
Dehydrated Alcohol, USP
absolute alcohol
not less than 99.5% C2H5OH by volume
used when essentially water-free alcohol desired
Diluted Alcohol, NF
prepared by mixing equal volumes of alcohol, USP and purified water (USP)
final volume is generally about 3% less than expected because liquids contract upon mixing
50ml alcohol + 50 ml water ~97ml diluted alcohol
concentration of diluted alcohol is slightly greater than half of concentrate
useful hydroalcoholic solvent in various pharmaceutical processes and preparations
Rubbing alcohol
70% ethyl alcohol by volume
30%: water, denaturants, color, additives, perfume oils, stabilizers
Glycerin, USP
aka Glycerol
clear, syrupy liquid
sweet taste
miscible with water and alcohol
comparable solvent with alcohol, but solutes are slowly soluble because of viscosity (rendered less viscous by heating)
preservative qualities
often used as stabilizer and auxiliary solvent in conjunction with water or alcohol
used in many internal preparations
Isopropyl Rubbing Alcohol
70% isopropyl alcohol by volume
30% water, color additives, stabilizers, perfume oils
used externally as rubefacient and soothing rub
vehicle for topical products
Propylene Glycol, USP
viscous
miscible with water and alcohol
useful solvent
substitution for glycerin
Purified Water, USP
prepared by distillation, ion exchange, or reverse osmosis
Naturally occurring water
exerts solvent effect on most substances it contacts
impure
contains dissolved inorganic salts (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Cl, sulfates, bicarbonates), dissolved and undissolved organic matter, microbes
Oral solutions and preparations for oral solution
dry mixtures for solution
oral solutions
oral rehydration solutions
oral colonic lavage solution
magnesium citrate oral solution
sodium citrate and citric acid oral solution
Very Soluble
less than 1 part solvent required for 1 part solute
Freely soluble
1-10 parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Soluble
10-30 parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Sparingly Soluble
30-100 parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Slightly Soluble
100-1000 parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Very slightly soluble
1000-10,000 parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Practially insoluble or insoluble
10,000+ parts solvent required for 1 part solute
Order of solubility descriptions
very soluble
freely soluble
soluble
sparingly soluble
slightly soluble
very slightly soluble
practically insoluble/insoluble
Order of solubility parts of solvent required for 1 part solute
<1
1-10
10-30
30-100
100-1000
1000-10,000
10,000+
If given that water solubility of atropine is 455, it means that
455 mL of water required to dissolve 1 g of atropine
Considerations for making solutions
do not quantity sufficient with stirring rod in graduate
dissolve salts in a minimum amount of water before adding to viscous vehicle
constant mixing when adding two liquids together
minimum measurable quantity in graduate cylinder
insoluble materials: levigate (grind to fine smooth powder while in moist condition)
Percent weight in volume
%w/v
grams of constituent in 100 ml preparation
Percent volume in volume
%v/v
mL constituent in 100 mL of preparation
Percent weight in weight
% w/w
grams constituent in 100g preparation
Ratio strength: weight in volume
a:b w/v
grams of constituent in stated ml’s of preparation
Ratio strength: volume in volume
a:b v/v
mls of constituent in stated mls of preparation
Ratio strength: weight in weight
a:b w/w
grams of constituent in stated number of grams
Liquid dosage forms can be sterile of non-sterile (T/F)
True
Stability considerations in the preparations of oral liquid dosage forms
stability unfavorable for only 6/83 dosage forms (small %)
small % have stability issues
minimum risk associated with dosage forms and pharmacists taking cognizance of various factors:
drug stability (less than 10% drug loss)
mechanisms
routes of degradation
hydrolysis
oxidation
microbial
potential interactions with excipients in the tablets and/or capsules utilized in the formulation
Major issue with liquid dosage forms
stability
stability changes with temperature, container choice, light exposure
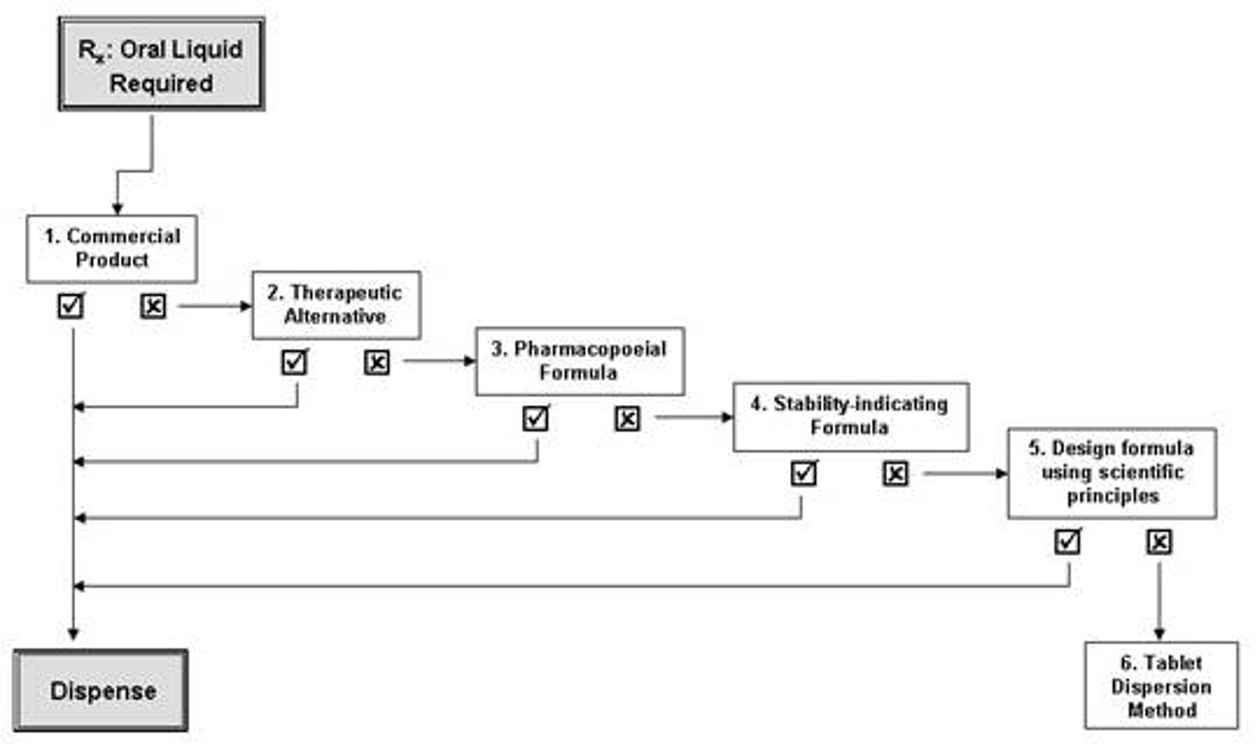
Management of oral liquid preparations in practice
Commercial product
If no suitable commercial product, consider therapeutic alternative that is available in suitable dosage form (other commercially available drug in same class)
Pharmacopoeial formula
consult USP
must be used if formulary requires API in powder form (as opposed to crushing tablet)
if API not available in pure form, literature search for a suitable stability-indicating formula using tablets or capsules for API must be sought
Stability-indicating formula
literature
get from other vendors (Allen’s Compounded Formulations, Nahata and Hipple’s Pediatric Drug Formulations, Trissel’s stability of compounded formulations)
Design formula using scientific principles
if not in literature, must use science principles
consider potential degradation of API, storage /packaging considerations, assigning suitable shelf-life, interactions between excipients and API (esp if tablets or capsules used as API)
Tablet dispersion method
crush tablet, dissolve in water
Preservative selection
must not adversely affect container, closure
must be soluble in water
must be non-irritating, non-toxic
concentration of preservative must not be too high (harmful to patients)
concentration of preservative must not be too low (ineffective)
must consider pH of solution (proportion of preservative remaining undissociated at pH of preparation makes it capable of penetrating microorganisms)
ex. 15% v/v alcohol will prevent microbial growth in acidic medium (18% v/v in alkaline)
Benzoic acid, boric acid, p-hydroxy benzoates
preservative
mode of action: denatures proteins
widely used
Phenols, chlorinated phenolic compounds
preservative
mode of action: lytic and denaturation action on cytoplasmic membranes, oxidation of enzymes
Alcohols
preservative
mode of action: lytic denaturation action on membranes
Quaternary compounds
preservative
lytic action on membranes
Mercurials
preservative
mode of action: denaturation of enzymes by combining with thiol
Common Preservatives
Benzalkonium chloride
Glycerin
Methyl Paraben
Benzoic acid
sodium benzoate
Pharmaceutical preservatives have different modes of action such as denaturation of proteins or membrane, combine with -SH groups and protect from light (T/F)
T
Major criterion in drug design and evaluation
stability
Rates and orders of reactions
velocity with which reaction occurs
depend on reactant concentration, temp, pH
Drugs most frequently undergo degradation by either oxidation or hydrolysis (T/F)
T
Degradation by Hydrolysis
molecules interact with water to yield breakdown products
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid) + water → salicylic acid + acetic acid
causes drug decomposition for drugs containing: amides, lactones, lactams
Degradation by Oxidation
loss of electrons for a molecule
each electron lost is accepted by some other molecule, reducing recipient
many pharmaceutical have tendency to undergo auto oxidation: atmospheric oxidation proceeds slowly at first, then rapidly
destroys aldehydes, alcohols, phenols, sugars, alkaloids, unsaturated fatty acids, oils
for inorganix compounds: ferrous (Fe2+) to ferric (Fe3+)
Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients
Food and Chemical Codex
2 books
monographs of excipients
each monograph includes:
non-proprietary
chemical
commercial names
empirical and chemical formula
physical properties
incompatibilities and interactions with other drugs and excipients
regulatory status
applications in pharmaceutical formulation or technology
Buffering Agent
used to resist change in pH on dilution or addition of acid or alkali
ex. potassium monophosphate, potassium phosphate monobasic, sodium acetate
Chelating agent
substances that form stable water-soluble complexes (chelates) with metals
aka sequestering agents
ex. Na2-EDTA, eidetic acid
Humenctant
used to prevent drying of preparations, particularly ointments and creams
ex. glycerin, propylene glycol, sorbitol
Litigating agent
liquid used as intervening agent to reduce particle size of powder by grinding, usually in mortar
ex. mineral oil, glycerin propylene glycol
Ointment base
semisolid vehicle for medicated ointments
ex. lanolin, petrolatum
Stiffening agent
used to increase thickness or hardness of a preparation, usually ointment
ex. cetyl alcohol, paraffin, stearyl alcohol
Suspending agent
viscosity increasing agent used to reduce sedimentation rate of particles in a vehicle in which they are not soluble
ex. agar, bentonite, carbomer,tragacanth veegum
Vehicle
carrying agent used in formulating a variety of liquids for oral and parenteral administration
Degradation tests/inspections for topical creams, ointments, lotions, solutions, gels
appearance
color
homogeneity
odor
pH
resuspendability
consistency
particle size distribution
strength
weight loss
Degradation tests or inspection for emulsions
appearance (phase separation)
color
odor
pH
viscosity
Pharmaceutical ingredients have a specific role in the preparation, however, some ingredients have multiple uses in the preparation (Glycerin, propylene glycol) T/F
T
Gargles
aqueous solutions containing antiseptics, antibiotics, anesthetics
local effect for pharynx, nasopharynx, by forcing air from lungs through the gargle held in throat
gargle is expectorated
sometimes diluted before use
Mouthwash
aqueous solutions often in concentrated form
therapeutic and non-therapeutic
recent uses in stomatitis (painful side effect of chemotherapy)
combination with antihistimines, hydrocortisone, nystatin, tetracyline
suspension, powder, syrup, solutions
Mouthwash composition
Alcohol: flavor, sharpness, mask unpleasant taste, solubilizer for flavoring agents
Glycerin, sorbitol: humectant
surfactant: aid solubilization
flavor
color
Oleo vitamins
fish liver oils diluted with edible oils (vegetable oils)
vitamin A and D
Vitamin D = ergocalciferol
synthetic vitamin A
unstable preparations = use tight container
protect from light and air
Categories of medicated syrups
analgesics
bronchodilator
cholinergic
Special Solutions and Suspensions
applied topically to eye, nose, ear
suspensions, solutions, gels, ointments, drug containing inserts
Ophthalmic drug delivery
treat surface or intraocular infections/conditions
volume of tear film in eye varies between 7-8 mcL
limited capacity to retain fluid
single drop of ophthalmic solution contains 50 mcL (most fluid is lost)
Pharmacological categories of topical Ophthammic drugs
anesthetics
provide temporary relief for ophthalmic trauma
antibiotic and antimicrobial agents
combat ophthalmic infections
antifungal agents
fungal keratitis
antiinflammatory
allergic cognitivists
antiviral
herpes
Pharmaceutical Requirements for opthalmic drugs
sterility and preservation
isotonicity
osmotic pressure similar to surrounding fluid
tears, blood have osmotic pressure of 0.9% solution of sodium chloride
buffering
viscosity and thickening agents
Opthalmic sterility
must be sterile
benzalkonium chloride or chlorobutanol used as antimicrobial agent
Nasal Preparations
most preparations intended for intranasal use contain adrenergic agents
decongestant
nasal drops/sprays
Inhalation Solutions
drugs or solutions of drugs administered by nasal or respiratory route
local action on bronchial tree or systemic effects through absorption from lungs
ex. isoproterenol inhalation solution
Nasal route for systemic effect
when you ned route that is neither oral or parenteral
ex. synthetic, biologically active peptides/polypeptides (insulin)
Inhalants
designed for drug to be carried into the bronchial/respiratory tree of patient
mist reaches the affected area and provides relief
used for bronchial, nasal congestion
Nebulization
gives sufficient fine particles, droplets, uniform in size
attached to face mask
intermittent positive pressure breathing machine
metered dose inhalers
The otic, nasal, and ophthalmic drug delivery products consisting of solutions and suspensions are considered as special drug delivery systems (T/F)
T
Otic preparations
ear or aural preparations
solutions, suspensions, ointments
curumen removing
removes ear wax
anti-infective
fungal/other infections
anti-inflammatory
swelling and inflammation
analgesic
relieves symptoms of acute otitis media
Quality control of liquids
final volume
appearance
odor
clarity
specific gravity
pH
active drug assay
determines concentration is correct
rheological properties/pourability
Quality assessment
weight/volume
pH
specific gravity
active drug assay
clarity
globule size range
rheological properties/pourability
physical observation