AP Psychology Module 9-15, Research Methods, and Neurotransmitters
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Modules 9-15 + Research Methods + Neurotransmitters AP Psychology
Last updated 4:13 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
1
New cards
biological psychologist
Psychologists who analyze the biological factors influencing behavior and mental processes.
2
New cards
neurons
Cells that are highly specialized to receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another.
3
New cards
dendrite
A neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body.
4
New cards
axon
A long, thin fiber that transmits signals away from the neuron cell body to other neurons, or to muscles or glands.
5
New cards
myelin sheath
Allows message to go quickly and accurately down the axon.
6
New cards
action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
7
New cards
refractory period
The "recharging phase" when a neuron, after firing, cannot generate another action potential.
8
New cards
threshold
Level of stimulation needed to trigger a neural impulse
9
New cards
all-or-none response
a nerve or muscle fibre responds completely or not at all to a stimulus
10
New cards
synapse
A physical gap between two neurons that functions as the site of information transfer from one neuron to another.
11
New cards
neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers manufactured by a neuron.
12
New cards
reuptake
A neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
13
New cards
endorphins
"morphine within"--natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
14
New cards
agonist
A chemical that mimics the action of a neurotransmitter.
15
New cards
antagonist
A chemical that opposes the action of a neurotransmitter
16
New cards
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the PNS and CNS
17
New cards
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
18
New cards
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
19
New cards
Nerves
bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting theCNS with muscles, glands, and sense organs
20
New cards
sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
21
New cards
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
22
New cards
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
23
New cards
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
part of PNS- controls the skeletal muscles and transmits sensory information. (you do the moving)
24
New cards
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
part of PNS that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms. (like the knee tapping at the doctor)
25
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
26
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
27
New cards
reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
28
New cards
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
29
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
30
New cards
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
31
New cards
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
32
New cards
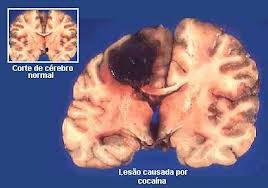
Lesion
Tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of the brain tissue.
33
New cards
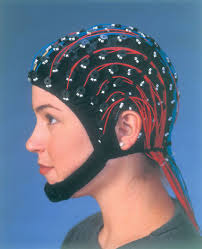
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brains surface. These waves are measures by the electrodes placed on the scalp.
34
New cards
CT scan (computed tomography)
A series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by a computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain's structure. Also called a CAT scan.
35
New cards
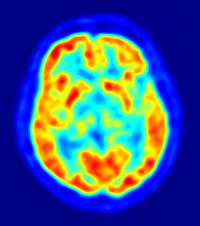
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
A visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task.
36
New cards
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. These scans show brain anatomy.
37
New cards
fMRI (functional MRI)
A technique for revealing blood flow, and therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. These scans show brain function as well as its structure.
38
New cards
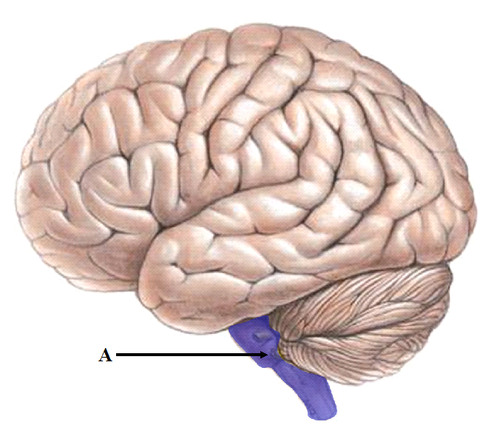
brainstem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions.
39
New cards
medulla
The base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing.
40
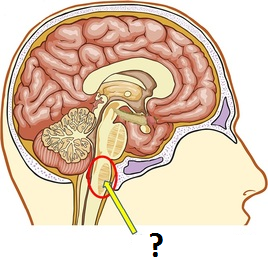
New cards
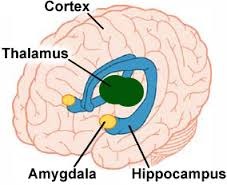
thalamus
The brains sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
41
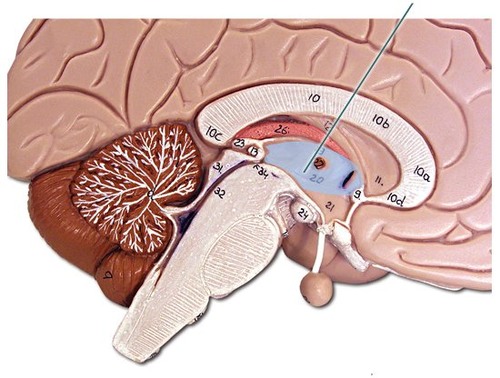
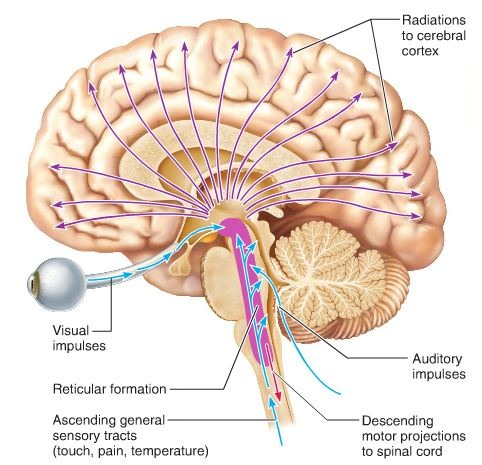
New cards
reticular formation
A nerve network that travels through the brain system and thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal.
42
New cards
cerebellum
The "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory.
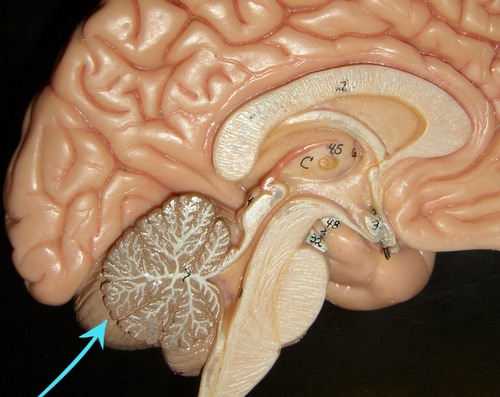
43
New cards
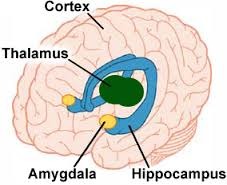
limbic system
Neural system( including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus) located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives.
44
New cards
amygdala
Two lima bean sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.

45
New cards
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities( eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland and is linked to emotion and reward.
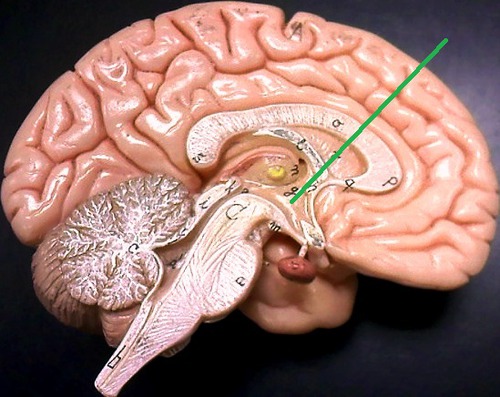
46
New cards
hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
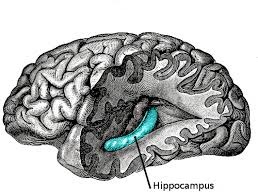
47
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
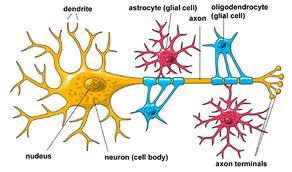
48
New cards
Glial Cells
Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons.
"Glue cells"'
Worker bees
provide nutrients and insulating myelin
guide neural connections
mop up ions and neurotransmitters
"Glue cells"'
Worker bees
provide nutrients and insulating myelin
guide neural connections
mop up ions and neurotransmitters
49
New cards
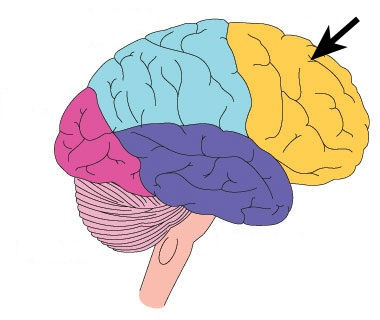
Frontal Lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgements.
50
New cards
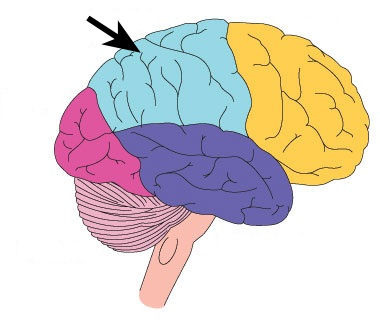
Parietal Lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position.
51
New cards
Occipital Lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
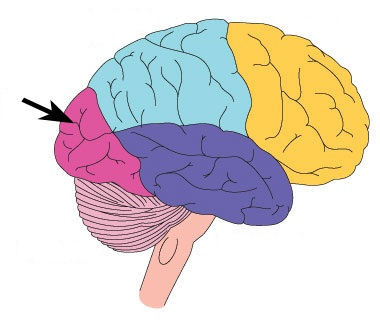
52
New cards
Temporal Lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear.
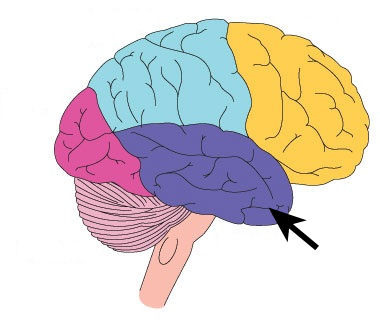
53
New cards
Motor Cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
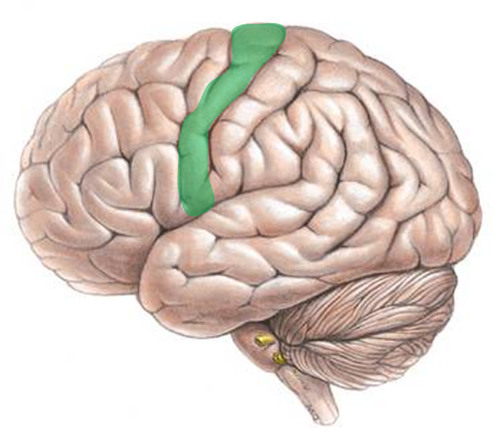
54
New cards
Plasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience.
55
New cards
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
56
New cards
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
57
New cards
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them.
58
New cards
consciousness
our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment; it helps us cope with novel situation, act in our long-term interests rather than short-term interests/pleasures, and promotes our survival by anticipating how we seem to others, and helping us read their minds.
59
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language).
60
New cards
dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks.
61
New cards
Blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it
62
New cards
visual perception track
enables us "to think about the world", to recognize things, and to plan future actions
63
New cards
visual action track
guides our moment-to-moment movements.
64
New cards
parallel processing
processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously; generally used to process well-learned information or to solve easy problems.
65
New cards
sequential processing
processing one aspect of a problem at a time; generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems.
66
New cards
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior.
67
New cards
Heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
68
New cards
Enviornment
every nongenetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us.
69
New cards
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes.
70
New cards
DNA
a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
71
New cards
Genes
the biochemical units of heredity that makes up the chromosomes; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins.
72
New cards
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes.
73
New cards
identical twins
develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms.
74
New cards
fraternal (dizygotic) twins
develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than ordinary brothers and sisters, but they share a prenatal environment.
75
New cards
Heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes. It may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied.
76
New cards
interaction
the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as environment) depends on another factor (such as heredity).
77
New cards
molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes.
78
New cards
molecular behavior genetics
the study of how the structure and function of genes interact with our environment to influence behavior.
79
New cards
Epigenetics
"above" or "in addition to" genetics; the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change.
80
New cards
Evolutionary Psychology(ists)
study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
81
New cards
Critics argue that evolutionary psychologists:
- start with an effect and work backwards to an explanation - do not recognize social and cultural influences - absolve people form taking responsibility for their sexual behavior
82
New cards
Behavior Genetics
focus on genetic and environmental roots of human diffferences
83
New cards
Charles Darwin
- principle of natural selection in behavior and mental processes - organisms' varied offspring compete for survival - certain biological and behavioral variations increase organisms' reproductive and survival chances in their particular environment - offspring that survive are more like to pass their genes - population characteristics change
84
New cards
Natural Selection and Adaptation
- genes and experience together wire the brain - adaptive flexibility in response to differing environments contributes to our fitness--ability to survive and reproduce
85
New cards
Mutations
random error in gene replication that leads to a change
86
New cards
Genetic Legacy
- genes of individuals not so disposed tended to be lost from the human gene pool - as enhancing genes continued to be selected, behavioral tendencies and thinking and learning capacities emerged that prepared out Stone Age ancestor to survive and reproduce
87
New cards
Genetic Differences in Sexuality
- men have stronger sex drives - men have lower threshold for perceiving a warm response as a sexual come-on
88
New cards
Natural Selection and Mating Preferences-
women approach sex more relational- - women usually nurses one infant at a time- - attracted to men who re mature, dominant, bold, long-term mating- men more recreational- - men can spread genes through other females- - look for healthy, fertile-appearing partners
89
New cards
Reflections on Nature and Nurture
- genes form us, as well as experiences forms us- gender roles shape us- biopsychosocial
90
New cards
Roger Sperry
- believed complex human brain give rise to something different: consciousness
91
New cards
Biopsychosocial
- individual development results form interaction of biological, psychological, and social-cultural influences - Bio: human genome; individual variation, prenatal environment, sex related genes... - Psychological: gene-environment interactions, effect of experience on neural networks, responses evoked by characteristics: gender and personality, beliefs, feelings... - Soc-Cul: parental, peer, cultural traditions
92
New cards
acetylcholine (ACh)
Released by motor neurons controlling skeletal muscles. Contributes to the regulation of attention, arousal, and memory.
Agonist for nicotine and caffeine.
Deficiency associated with Alzheimers Disease.
Agonist for nicotine and caffeine.
Deficiency associated with Alzheimers Disease.

93
New cards
dopamine (DA)
Associated with voluntary movement, emotion, attention, and a key component in the reward pathway.
Excess - Schizophrenia / Hallucinations
Deficiency - Parkinson's Disease / tremors
Cocaine, meth, opiates all involve excess dopamine.
Excess - Schizophrenia / Hallucinations
Deficiency - Parkinson's Disease / tremors
Cocaine, meth, opiates all involve excess dopamine.
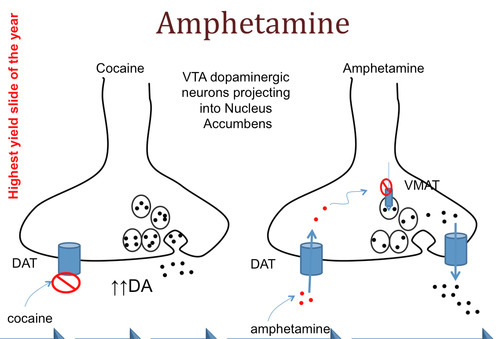
94
New cards
norepinephrine (NE)
Alertness, arousal, flight or fight response
Deficiency - Depression (can be treated with SNRIs, which block reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin)
Excess - Anxiety
Deficiency - Depression (can be treated with SNRIs, which block reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin)
Excess - Anxiety

95
New cards
serotonin
Involved in mood regulation, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Deficiency - Depression (Treated with SSRI's - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; prevent serotonin from being reabsorbed in uptake, leaving more in synapses), eating disorders, OCD
Excess - Mania
LSD and ecstasy act on serotonin.
Deficiency - Depression (Treated with SSRI's - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; prevent serotonin from being reabsorbed in uptake, leaving more in synapses), eating disorders, OCD
Excess - Mania
LSD and ecstasy act on serotonin.

96
New cards
GABA
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter
Deficiency - Seizures, insomnia, tremors, anxiety
Alcohol is an agonist.
Deficiency - Seizures, insomnia, tremors, anxiety
Alcohol is an agonist.
97
New cards
glutamate
Main excitatory neurotransmitter that creates links between neurons that form basis of learning and long-term memory.
Excess - Seizures & Migraines (Avoid foods with MSG - monosodium glutamate; overstimulate brain)
Alcohol is antagonist.
Excess - Seizures & Migraines (Avoid foods with MSG - monosodium glutamate; overstimulate brain)
Alcohol is antagonist.

98
New cards
Endorphins
-Pain control & relief - Stress reduction
-Feelings of pleasure
-Natural opiates
With opiate addiction, body decreases natural supply of endorphins
Opioids are agonists for endorphins
-Feelings of pleasure
-Natural opiates
With opiate addiction, body decreases natural supply of endorphins
Opioids are agonists for endorphins
99
New cards
theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations
100
New cards
hypothesis
a proposal intended to explain certain facts or observations