1. Fermentation
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Definition of food fermentation
A bioprocess driven by microorganisms and their enzymes. Yielding a food pr
Fermentation vs spoilage
In a well conducted fermentation process, desirable microorganisms (“the good”) are abundant/dominant
A spoiled/rotten food product is dominated by undesirable microorganisms (“the bad” and “the ugly”)
Why fermenting?
prevents spoilage
Increases the microbial safety
Improves digestibility
Adds taste and aroma
Improves textural properties
& adds nutritional value
&
Fermented foods are abundant in human diet
It is a sustainable and natural processing technology
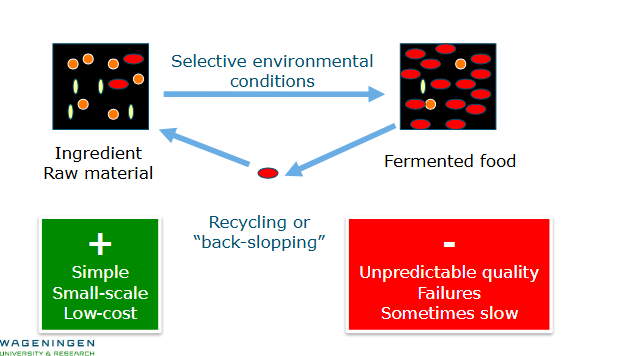
How to start a fermentation process?
Spontaneous fermentation;
Raw material not sterile
Depends on “contaminating” resident microbiota
Back-slopping procedure
Addition of sample previous batch
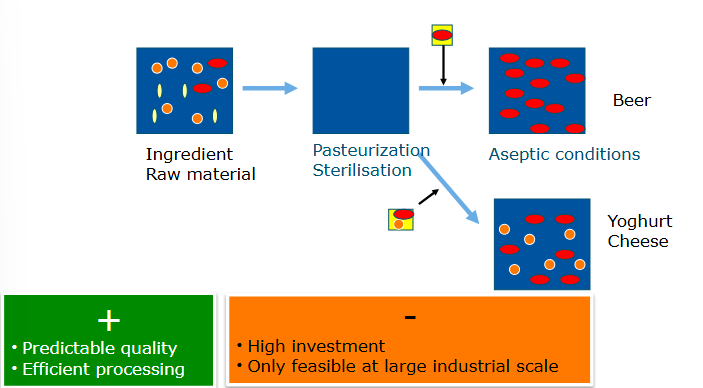
Starter cultures:
Undefined mixed culture
Defined mixed culture
Defined single strain starter
Natural fermentation
Might contain pathogenic microbes
Or spoilage causing microbes
Makes fermentation rate unpredictable and conditions not constant
Fermentation with defined starters
Different bacteria used for fermentation
LAB
Yeast
Moulds