1.6 Anti Gout agents med chem
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
su
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
example of anti-inflammatory anti-gout agent
colchicine
colchicine class
anti-inflammatory agent for gout
Probenecid class
URAT1 inhibitor
lesinurad class
URAT1 inhibitor
allopurinol class
xanthine oxidase inhibitor
febuxostat class
xanthine oxidase inhibitor
pegloticase class
recombinant uricase
what is gout
painful form of inflammatory arthritis caused by excess uric acid in the blood and urine
gout is assoc with elevated levels of ____ in the serum and urine
uric acid
uric acid is an excretory product of ___ metabolism
purine
uric acid is hydrolyzed to _____ by uricase
allantoin
uric acid is hydrolyzed to allantoin by …
uricase
allantoin is hydrolyzed by allantoinase to ____ and then ____
urea; glyoxylic acid
acute gouty arthritis results from the accumulation of needle shaped crystals of ____ in joints, synovial fluid, and periarticular tissue
urate monohydrate (MSU)
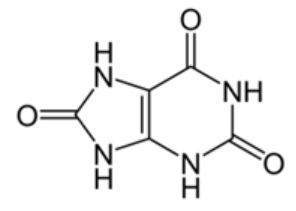
what dis
uric acid
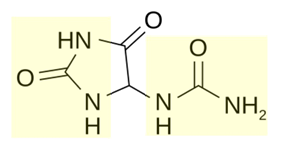
what dis
allantoin
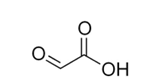
what dis
glyoxylic acid
uric acid is weak and with very ____ water solubility
low
at body pH, uric acid exists as a ____ which is more water soluble
monosodium salt (MSU)
monosodium urate water solubility
300 mg/100 mL
uric acid solubility
6 mg / 100 mL
which organ has the dominant role in urate elimination
kidney
excretion of urate requires _____ which is located in renal proximal tubule cells
urate anion transporter (URAT1)
where is URAT1 found
renal proximal tubule cells
what is URAT1
urate anion transporter that is required for excretion of urate, its targeted by anti-gout agents
acute gout attacks can be controlled by drugs that reduce inflammation caused by…
deposited urate crystals
acute gout attacks can be controlled by drugs that inhibit uric acid biosynthesis by inhibiting which enzyme?
xanthine oxidase
acute gout attacks can be controlled by drugs that increase the excretion rate of ____
urate
anti gout therapy aims to…
reduce inflammation
lower urate
is allopurinol competitive or nah?
competitive
is febuxostat competitive or nah?
nah!
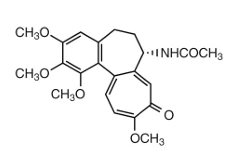
colchicine:
stops inflammation initiated by uric acid deposition but does not…
alter serum acid level
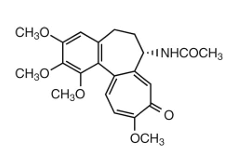
which of the following statements about colchicine is true?
a. its light sensitive
b. it decreases serum uric acid levels
c. increases release of lysosomal enzymes
d. all of the above
a
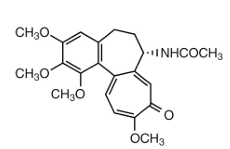
colchicine:
is ____ sensitive
light
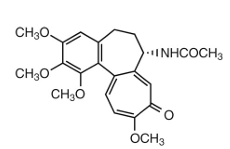
colchicine:
why is it light sensitive?
extended conjugation
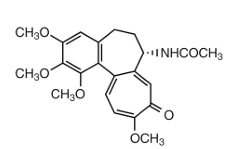
colchicine MOA:
diminishes phagocytosis by ________ to decrease inflammation
polymorphonuclear leukocytes
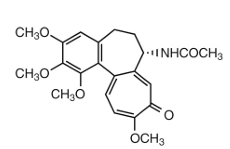
colchicine MOA:
diminishes phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes to _____
decrease inflammation
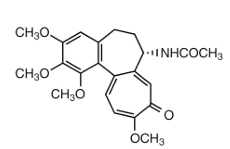
colchicine MOA:
increases pH of synovial fluid due to _____ which leads to decreased uric acid deposition
decreased lactic acid production
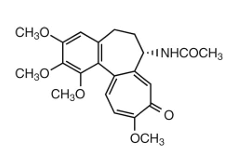
colchicine MOA:
increases pH of synovial fluid due to decreased lactic acid production which leads to…
decreased uric acid deposition
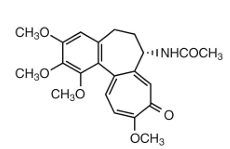
colchicine MOA:
increases pH of _____ due to decreased lactic acid production which leads to decrease uric acid deposition
synovial fluid
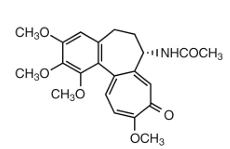
colchicine MOA:
inhibits release of ____ during phagocytosis to decrease inflammatoin
lysosomal enzymes
colchicine:
typically combo with which gout agent?
probenecid
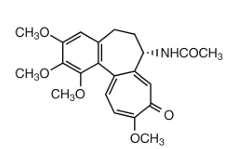
colchicine metabolism:
metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4 via ______ to make a primary amine metabolite
CYP3A4 N-deacetylation
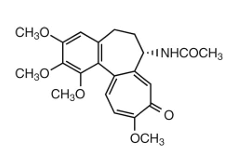
colchicine Metabolism:
metabolized in the liver by CYP3A4 N-deacetylation to make…
primary amine
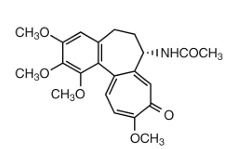
colchicine:
toxicity can be increased by…
urine alkalinization
colchicine inhibits: (select all that apply)
a. CYP3A4
b. URAT1
c. OAT4
d. P-gp
a and d
colchicine toxicity can be decreased by urine ____
acidification
probenecid is _____in water and acidic solutions
insoluble
probenecid is ____ in alkaline solutions
soluble
probenecid promotes ____ in the renal tubules and reduces it deposition in the joint
uric acid excretion
probenecid promotes excretion of uric acid by…
inhibiting URAT1
probenecid inhibits URAT1 which leads to reabsorption of ____ into the plasma instead of uric acid
probenecid
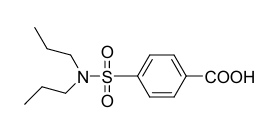
probenecid is a ____ benzoate
N-dialkylsulfamyl
probenecid:
increased uric acid excretion occurs with ____ substituents
smaller N alkyl
probenecid:
competitively inhibits the reabsorption of uric acid through ____ at the proximal tubules
OAT (organic anion transporter)
probenecid inhibits OAT which leads to…
increased urate excretion
what is an OAT and what it do
transports drugs and metabolites from blood into proximal tubules as the first step of tubular secretion
overall effect of probenecid
increased urate excretion
probenecid inhibits ____which plays a role in intercellular communication of inflammation
pannexin 1
probenecid inhibits pannexin 1 which leads to…
reduced inflammation
T or F:
probenecid lowers urate levels and reduces inflammation
T
probenecid metabolism:
almost completely absorbed and is hella plasma protein _____
bound
probenecid metabolites include…
w-1 OH
N-dealkylation products
glycine conjugate
acyl glucuronide conjugation (major)
what is probenecid’s major metabolite
acyl glucuronide conjugation
probenecid metabolites:
if the metabolite contains ___ then it is an active URAT1 inhibitor
COOH (CO2H)
probenecid metabolite:
if the metabolite contains COOH then it is an active _____ inhibitor
URAT1
probenecid metabolites:
the ____ metabolite is an active OAT inhibitor
glycine conjugate
the glycine metabolite of probenecid is an active ____ inhibitor
OAT
Lesinurad inhibits both ___ and ___
URAT1 and OAT4
Lesinurad inhibits URAT1 and OAT4 which are both sodium independent transporters that are involved in…
excretion of organic acid
Lesinurad is associated with ____ caused by diuretics
hyperuricemia
Lesinurad is a _____ steroisomer
atropisomer
what the f word is an atropisomer???
stereoisomers made from hindered rotation about a single bond or axial chirality where the energy differences are due to steric strain or other contributors that create a barrier to rotation leading to the isolation of individual rotamers
Lesinurad is metabolized by which enyzme?
CYP2C9
Lesinurad is metabolized by CYP2C9 to make ___ metabolites
inactive
lesinurad is ____ by CYP2C9 to M3 and M4
oxidized
lesinurad interacts with drugs that inhibit ____
CYP2C9
Allopurinol is an isomer of _____
hypoxanthine
Allopurinol acts as a ______ of xanthine oxidase
substrate/ reversible inhibitor
Allopurinol leads to uric acid synthesis ____
inhibition
Allopurinol leads to serum levels of xanthine and hypoxanthine _____
elevations
T or F
Xanthine and hypoxanthine are substantially less H2O soluble than urate
F
xanthine and hypoxanthine are both ____ H2O soluble than urate
much more
Allopurinol major metabolite
oxypurinol (alloxanthine)
what is alloxanthine (oxypurinol)
active metabolite of allopurinol that is also an xanthine oxidase inhibitor
chronic allopurinol admin leads to accumulation of ___ which leads to increased uricosuric activity
alloxanthine
chronic allopurinol admin leads to accumulation of alloxanthine which leads to…
increased uricosuric activity
early treatment with allopurinol must be combo with which drug
colchicine
Febuxostat was the first ____ XO selective inhibitor
nonpurine
Febuxostat is a noncompetitive inhibitor of both___ and ___ forms of xanthine oxidase
oxidized and reduced
what drug is a non competitive inhibitor of both oxidized and reduced forms of xanthine oxidase?
Febuxostat
Febuxostat MOA
Noncompetitive xanthine oxidase inhibitor blocks the entry of xanthine or hypoxanthine, or any other substrate, into the catalytic cleft
Febuxostat does not inhibit enzymes involved in _____ so it has less ADE than allopurinol
purine or pyrimidine metabolism
Febuxostat does not inhibit enzymes involved in purine or pyrimidine metabolism so it has…
less ADE than allopurinol
Febuxostat has a ___ step metabolism
2
febuxostat is metabolized by which enzymes in the first step?
CYP1A2
CYP1A1
CYP2C9
febuxostat is metabolized by which enzyme in the second step?
xanthine oxidase
Pegloticase indicated for tx of chronic gout in pts who failed…
traditional small molecule therapy
Pegloticase is a _____ uricase
recombinant porcine like
Pegloticase MOA
enhances elimination of uric acid by converting it to allantoin