Water and Aqueous Solutions, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to the structure of water, amino acids, peptides, proteins, and related biochemical principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Water Structure
Water has 4 electron pairs in sp3 orbitals, leading to a net dipole moment and hydrogen bonding.
Hydrogen Bonding
The ability of water to form hydrogen bonds allows substances that can form H-bonds to be more soluble in water.
Rank the imfs
Ionic > hbond > dipole dipole > van Der waals
What substances or molecules are soluble in water?
Polar, OH group
Hydrophobic Effect
Lowers system entropy and favors ligand binding, as binding sites are often hydrophobic.
pH and Buffers
pH is defined as -log[H+], and buffers consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
Strong acid, small or large pka?
Small pka, large Ka
Buffer capacity
Midpoint ± 1 pH unit
Isoelectric Point
The pH at which the net charge of a molecule is zero.
Chirality
Chiral molecules cannot be superimposed on their mirror images; achiral molecules can.
Peptides
Small condensation products of amino acids, usually under 10 kDa.
Chromatography
A technique to separate compounds; larger molecules elute first in size-based chromatography.
Peptide Hormones
Biologically active molecules like insulin and oxytocin that play crucial roles in physiology.
Cofactors
Non-amino acid components that assist enzyme functions, including coenzymes and prosthetic groups.
Affinity chromatography
Protein of interest elute last
examples of hormones
Insulin, oxytocin, sex-peptides
Net charge chromatography
Negative beads = negative particles elute last
Example Neuropeptides
Substance P
Antibiotics example (peptides)
Polymyxin B (gram -), Bacitracin (gram +)
Toxin peptides
Amanitin (mushrooms), conotoxin (cone snails), chlorotoxin (scorpion)
Electrophoresis, who stays at the top of the field?
Negative and más pesadas
What’s is Sanger protein sequencing for?
determine amino acid terminus ( gly at amino side)
Determine amino acid content by hydrolysis
Cleavage into smaller polypeptide
Cleveage points of trypsin
Lysin and arginine
What does sequence define?
Structure
What does structure define?
Function
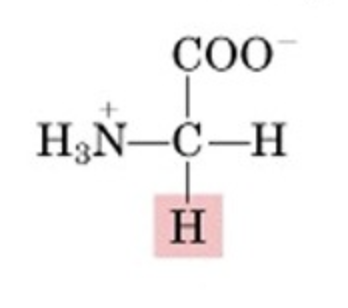
What’s this aminoacid?
glycine
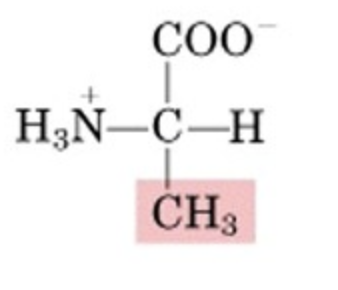
What’s this aminoacid?
alanine
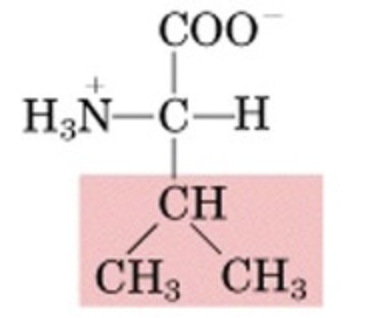
What’s this aminoacid?
valine
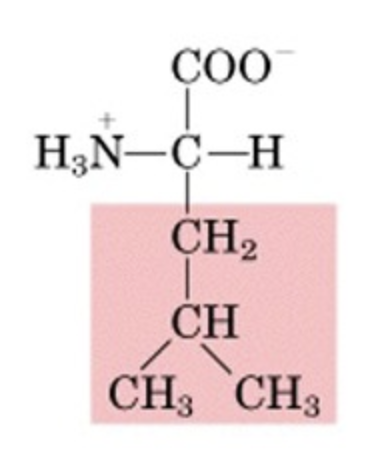
What’s this aminoacid?
leucine
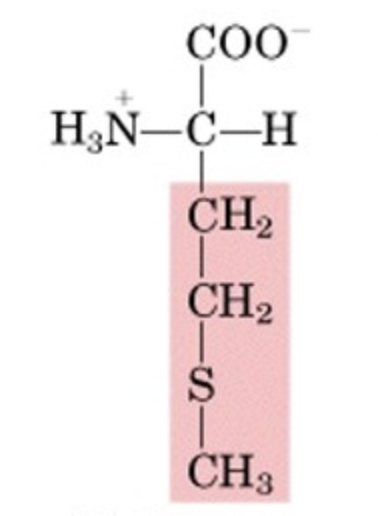
What’s this aminoacid?
Methionine
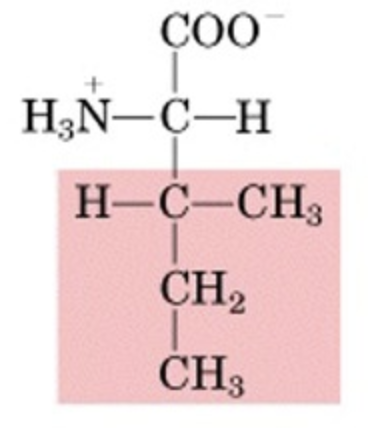
What’s this aminoacid?
Isoleucine
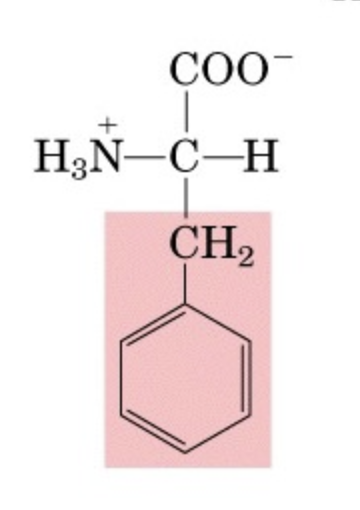
What’s this aminoacid?
phenylalanine
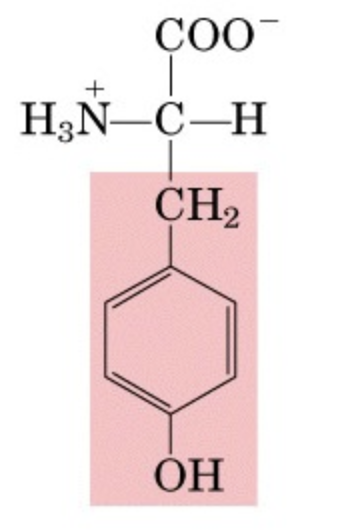
What’s this aminoacid?
Ty
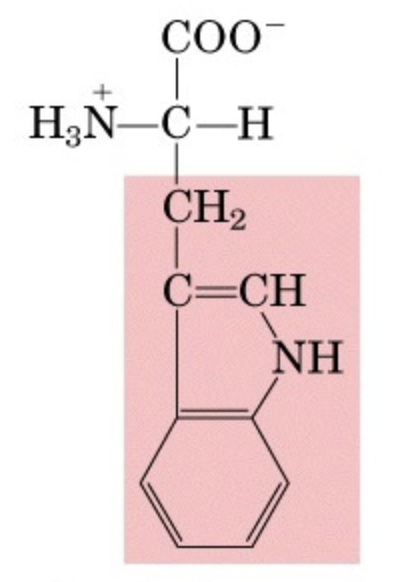
What’s this aminoacid?
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid used in protein synthesis and a precursor for serotonin.
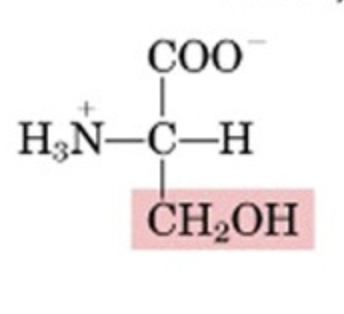
What’s this aminoacid?
serine
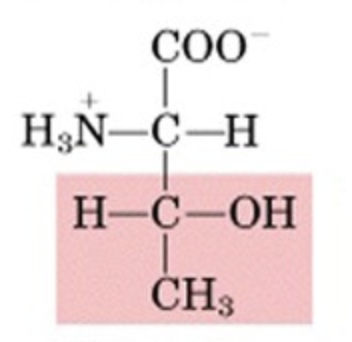
What’s this aminoacid?
threonine
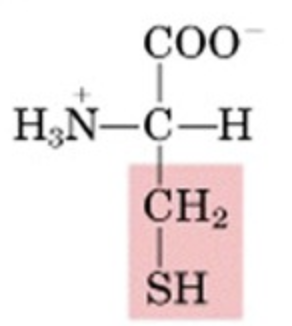
What’s this aminoacid?
cysteine
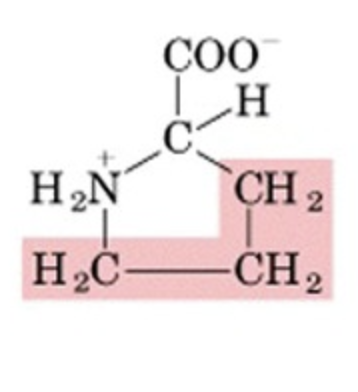
What’s this aminoacid?
proline
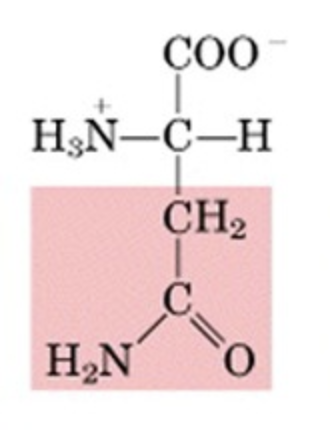
What’s this aminoacid?
asparagine
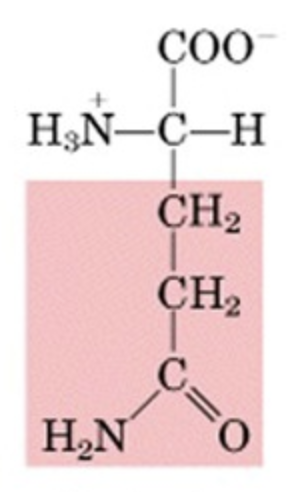
What’s this aminoacid?
glutamine
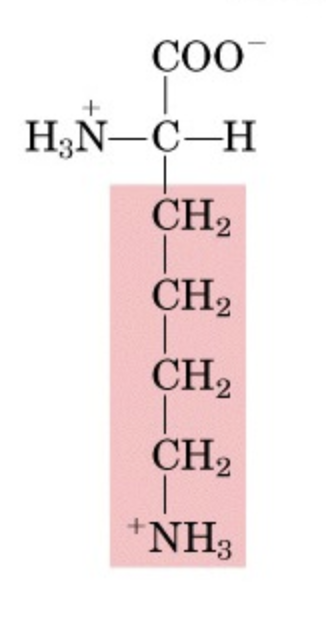
What’s this aminoacid?
lysine
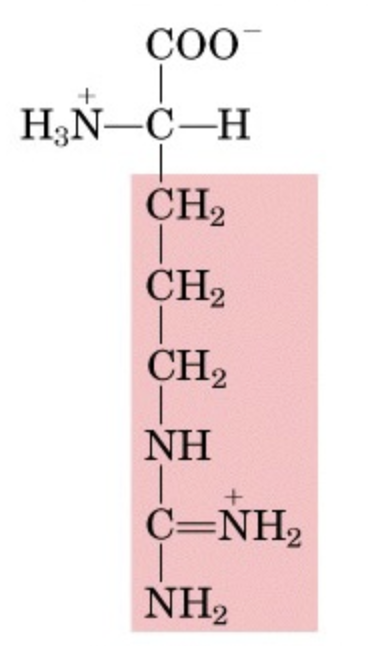
What’s this aminoacid?
arginine
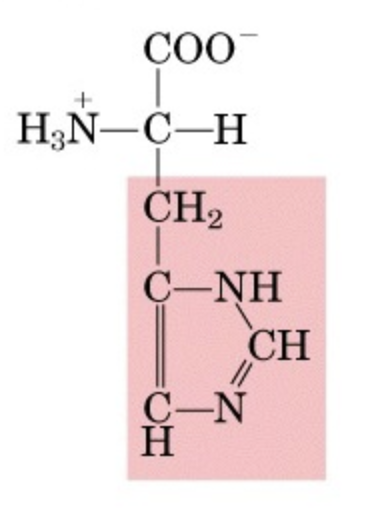
What’s this aminoacid?
histidine
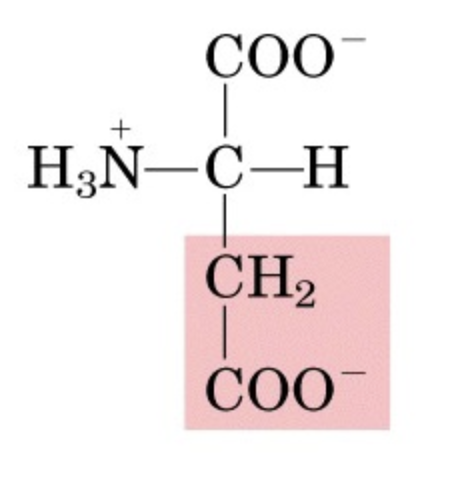
What’s this aminoacid?
aspartate
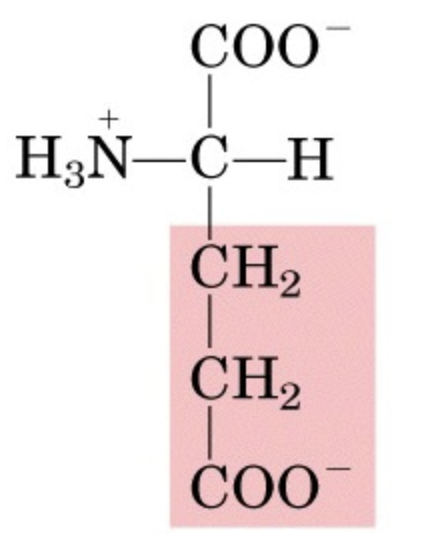
What’s this aminoacid?
glutamate
which one is the smallest aminoacid?
glycine
Only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds?
cysteine
CO is toxic to humans because
It binds to the Fe atom in hemoglobin and prevents the binding of O2
what is post-translational modiication?
The chemical alteration of a protein after its translation, adding functional groups like phosphates or sugars, or undergoing cleavage, changes its activity and structure.
example of post-translational modification
phosporylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination and acetylation.
Model of ligand binding to proteins, conformational may occur upon ligand binding
Induced fit
Model of ligand binding to proteins, it is assumed that complementary surfaces are preformed
lock and key
condition to unfold a protein
high temperature
loss of 3D structure and loss of activity
denaturation
method to determine the 3D structure of a protein
x-ray crystallography
experiment that demonstrated the sequence alone determines the native fold of a protein
ribonuclease refolding
The interaction of N-H and C=O of the peptide bond leads to local regular structures such as alpha helixes
h-bond
In a globular protein, the amino acids Asparate, Lysine, Glutamate, and Histidine would be found more often in where?
external surface of the protein
Rate at which proteins fold into their native structures.
Leevinthal’s paradox