CM3 (C5)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Fracture complications
Pseudarthrosis
Infection
Arthrosis
Perifocl ossification
Callus
Delayed
Abnormal
Hypertrophic
Fracture Healing
CALLUS GENESIS
Fibrino-proteic (1st 7 days)
Provisional fibrous (7-16 days)
Raw bone ( from day 16)
Definitive (6-12 maths)
Rx
Definitive: normal bone structure
Raw: NO structure
visible after 20-60 days
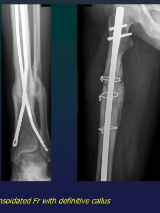
Rx assessment of Fr (peculiar types)
According to AGE
Children
greenstick
buckled (impacted)
epiphyseal loosening
Elderly: OP
Skin status: closed / open
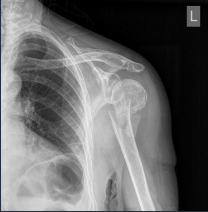
Rx assessment of Fr alignment (dislocation)
Lateral
Angulation
Rotation
Longitudinal (along the bone axis)
Distancing
Intermission
AScent (straddling)
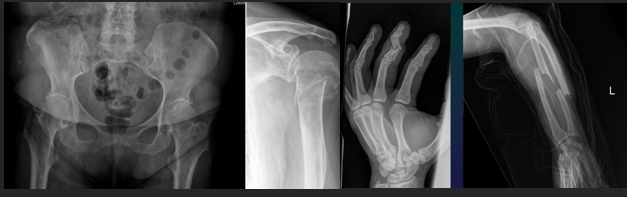
Rx assessment Fr appearance and course
APPEARANCE
Fissure (subtle)
Complete (total disruption)
Incomplete (ONLY one cortical disrupted)
COURSE (single or multiple)
Transverse (diaphysis)
Oblique (bending)
Helical (torsion)
Cominuted
Layered
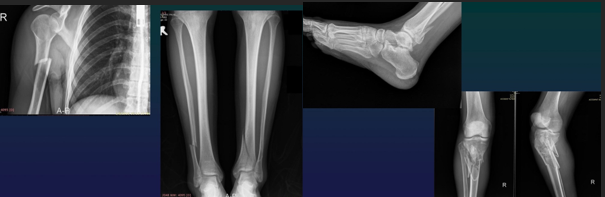
Rx assessment of Fr location
Short
Flat
Long
Metaphysis
Diaphysis
Epiphysis (intra / extra articular)
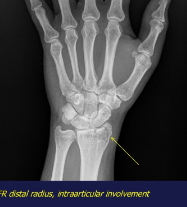
Rx assessment of Fractures
Loc (anatomic)
Extent
Type (complete / incomplete)
Course (carry): fr line VS bone long axis
Aligment bone fragments (annulation, rotation, ascent, spacing)
Special types
Skin
Assoc lesions (Fr + luxation / spacing)
Fractures Classif
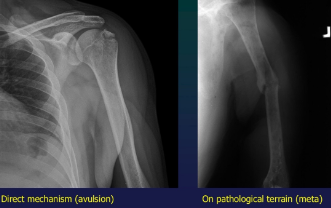
Mechanism
direct (direct blow or bone allusion due to ligamental traction)
indirect (bending, torsion, traction, suqatting-crush)
Terrain
commo,, trivial
stress (fatigue)- long term microtrauma
PATHO- on preexisting bone lesion
Diastasis def
Luxation of synarthroses
Luxation def
Complete loss of contact between joints surfaces
+ subluxation
Fracture def
Disruption of bone continuity, installed abruptly, as a csq of trauma
+ incomplete fracture
MSK Trauma Rof of Imaging
Positive Dg + lesion type
Monitoring + Dg complications
METHODS
CT (complex fractures)
Conventional Xray
Nuclear Medecine (sometimes)
Arthrography
Angiography (concomitant vascular involvement)
MRI (soft tissue, bone concussion)
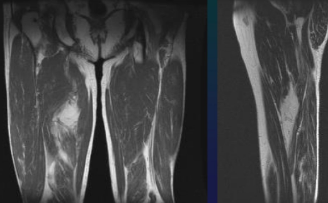
Thigh Rhabdmiosarcoma
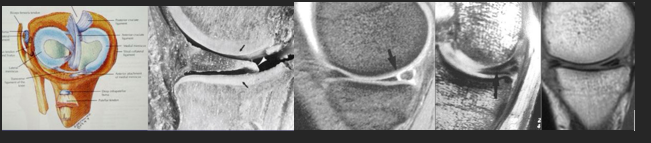
Meniscal tear
Achille's tendon rupture
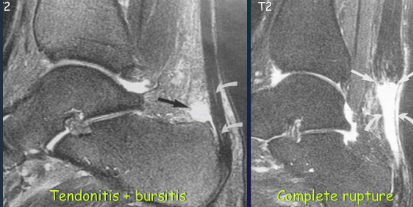
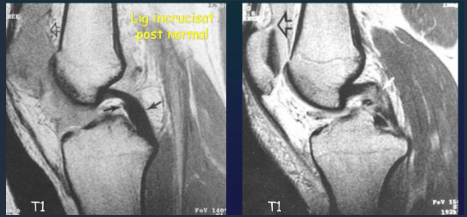
Rupture of cruciate ligaments
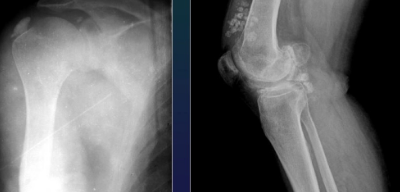
Periarthrisits, intraarticlar chondromatosis
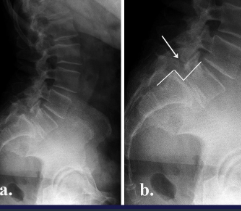
Spondylolisthesis + Spondylolysis
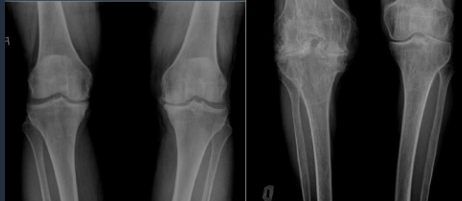
Knee
Gonarthrosis
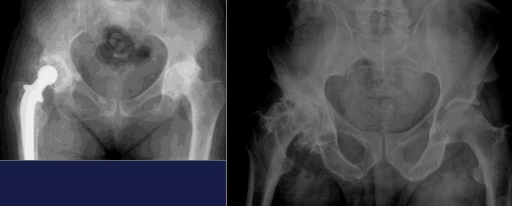
Hip
Coxarthrosis
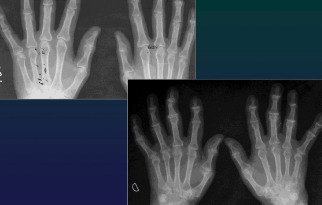
Hand
Polyarthrosis (DIPh, Trapezo MC1)
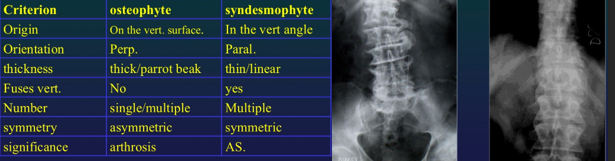
Difference Osteophyte Syndesmophyte
Spondylosis
Osteophytosis
any segment, at 1st horizontal, then vertical
McNab Osteophyte
Discarthosis
narrowing, bulging, vacuum phenomen
OS
Intraspongious hernias (schoolroom nodules)
Disk calcification
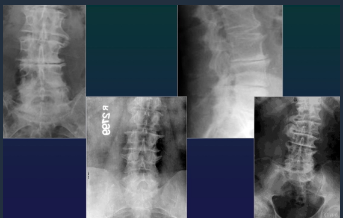
Spine
Spondylotis
Arthrosis of small posterior joints
Spondylarthrosis
Uncarthrosis
Arthrosis Rx
GENERAL Rx signs
Joint space narrowing (even or uneven)
Subchondral OS
Subchondral cysts
Osteophytes
Technique: 2 views AP + prophyle
CHANGES
Joint space narrowing : slow, expressed in %
Osteophytes: marginal, subcartilaginous
Subchondral OS & subuxation
Synovitis: joint effusion (US, MRI)
Pathology of Arthrosis
Cartilage changes (thinning)
Sbchondral bone sclerosis
OP
Osteophytes (chondro-synovial junction)
Subchondral cyts
Narrowing of joint space but NEVER disappearance
Arthrosis NEVER produces bone ankylosis
There is NO relation between Rx changes and clinical symptoms
Degenerative Articular Changes (ARTHROSIS)
Heterogenous group of disease, joint changes due to a joint cartilage degeneration (aging) & consecutive subchondral bone changes (affecting the whole joint)
Other names: osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, deforming arthrosis
Based on:
Joint cartilage thinning
Consecutive change of bone surface
OSteophytes
Joint deformity
The most fq arthropathy (primary and secondary)
Etio: multifactorial
Genetic / Habitus
Endocrine
Nutritional / Metabolic
Mechanic
Age
GOUT Imaging recommendations
Rx
Soft tissue masss, NO tophi => MRI
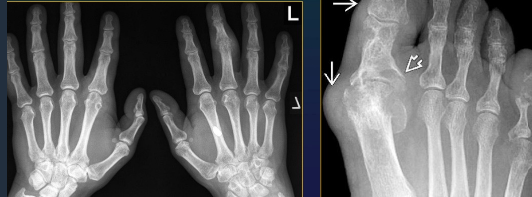
GOUT Imagistics
Rx (N in first year)
Cartilage destruction (advanced stage)
Tophi
Density, sometimes calcified, eccentric, NOT necessary with neighboring joint changes
RARELY intraosseous calcification
Circumscribed erosions + sclerotic margins
Juxtaarticular, often intraarticular
MR
Effusion: hypoT1, hyperT2
Edema: soft tissue / bone
Tophi: intermediate homogenous T1
Synovial panus: hypoT1, hypoT2, peripheral enhancement
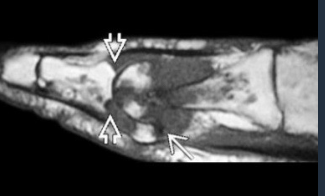
Gout Dg Clues
Dense tophi, erosiosn
LOC
MTPh 1
Lower extremities > up
Small joints > large
Any loc
Oligo, BUT may be polyarticular, asymmetric
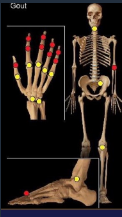
Gout CharaK
Synovial
Idiopthic, familial
Hyperuricemia => uric acid deposits on soft tissues => cartilage, bone => inflammation, destruction
Primary: acute attack
Chronic: gouty tophi
GOUT
Epidemio: <5% of hyperuricemia pts, 5% of arthritis pts
Age: 30-60 yrs
M:F = 20:1
Predispo F: metabolic syndrome => obesity, HBP, diabetes, endstage renal D+, alcohol, diuretics
AS Dg recommendations
Early: MRI (detect early infection)
Late / advanced: Rx
Sacroilic Rx= business card of AS patient
Complication or trauma: CT, MRI
Enthesopathy AS = spicules, brush
Tendon insetion
Iliac crest
Grater trochanter
Ischiatic tubeerosity
Calcanean enthesitis
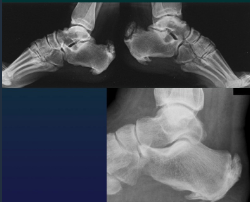
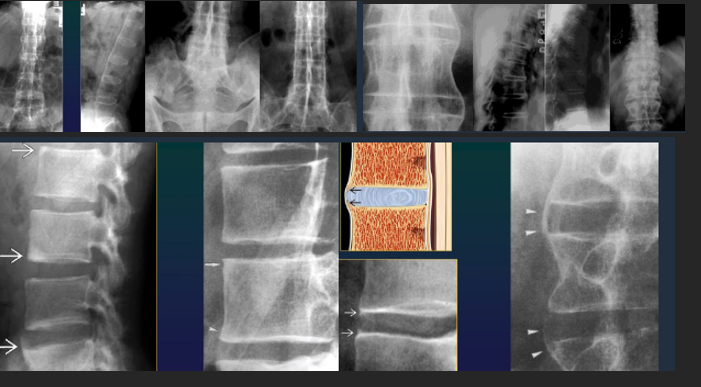
Spine AS
Shiny corners
Square vertebrae
Syndesmophites
Bamboo stick
Calcifications
Interspinate
Yellow lig (tram line)
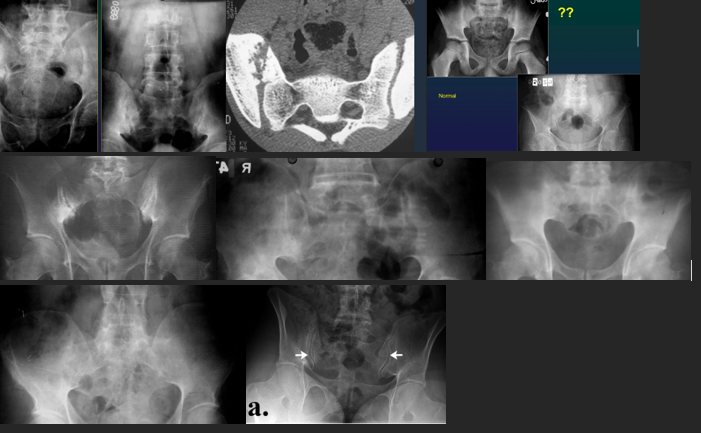
Sacroiliitis AS
Bilat, symmetrical
Subchondral OS
Erosions + false widening
Bone bridges, narrowing
Fusion : ankylosis
ARA Dg criteria AS
Lumbar pain > 3 maths, NOT eased by resting
Pain + stiffness in chest
Limmited breathing movements
Limited spinal mobility
Iritis
Sacroileitis Rx
Syndesmophytes Rx
AS Dg
Dg: syndesmophyes + bilat sacroilitis
LOC
SI joints (synovial part inf 1/2-1/3)
Large proximal joints : hips, shoulder
Spine (DL)
Anterior margins
Anterior fibers of fibrous ring
AS
Inflammatory arthropathy & enthesopathy located mainly in the axial skeleton
HLA-B27
Incidence: 0,1 % pop (15-30 y) - B:F = 2,5-5 : 1
CLINIC
Persistent, progressive
Nocturnal
Bilat
Sensitivity on local pressure
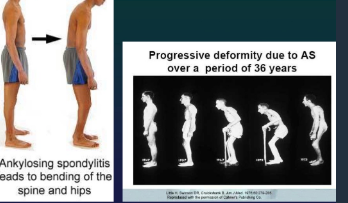
LATE: wolf neck, skier position and stepping
OBJECTIVE SIGNS
Occipital : wall dist
Finger : ground dist
Schober Test
Ches expansion
Rheumatoid Arthritis Dg
Rx = business card of RA patients
RM (early US)
Follow up
US + Doppler, contrast (synovitis, effusion)
RX (MR) = erosions
EXTRA articular changes
rheumatoid lung
rheumatoid lung nodules
pleuraal effusion
pericarditis
RA MRI
Panusul
Effusion
Bone edema
Erosions
Cysts
Tendons + contrast
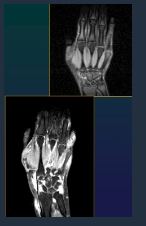
RA US
Small fluid effusion of joints
Panus
Erosions
Rheumatoid nodules
RA
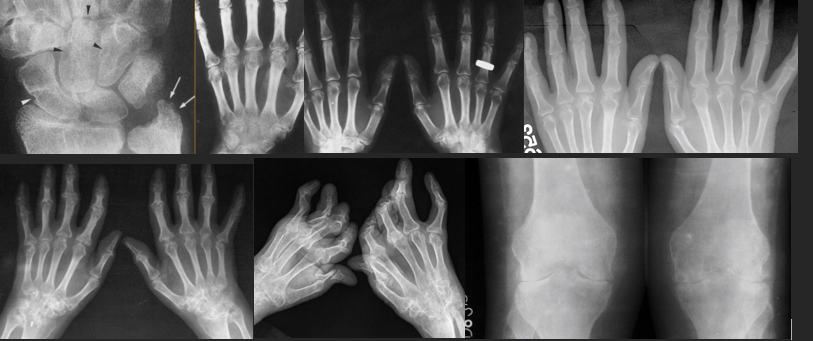
CharaK RA hands
Focal soft tissue swelling
early=> MCPh, PIPh, ulnar styloid
OP
early=> juxtaarticular, band
late=> diffuse
Erosions
early=> decreased cortical differentiation (dot dash pattern)
marginal = moue ears at basis of the phalanges
subchondral=> pen in cup, destruction of ulna, carpal bones
Cartilage destruction
early false increased of joint space (effusion)
destruction & narrowing of joint space
Subchondral cysts
Malalignement
carpal: ulnar deviation and scaphoid luxation
fingers: MCPh, ulnar deviation, subluxation
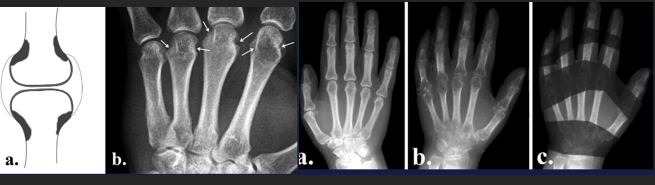
RA Patholoy
Papilomatous synovial hypertrophy
Panus
Cartilagee destruction
Bone destruction
Luxation / subluxation
Ankylosis
Inner organ disease
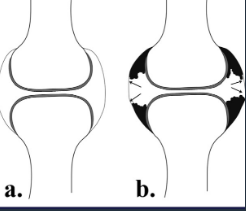
RA hand joints
Dg CLUES
Purely erosive
OP
Joint alignement changes
LOC
Classic: symétrie (+ unilateral in early stages)
Early: MCPh, distal RU, RC
Late: PIPh, IC
Almost NEVER involved DIPh
ARA positive Dg criteria RA
Morning stiffness
Pain upon movement or pressure (at least 1 joint)
Joint swelling > 6 wks
Swelling of another joint < 3 mths
Bilateral swelling MCPh, PIPh, MTF, NOT DIPh
Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules
typical RX changes
Positive rheumatoid factor
Pathology= rheumatoid nodules
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Chronic inflammation disease primary involving the small joints of extremities
1% of the population (F:M= 3:1)
Joints involved: MCF 85%, carpal 80% and PIPh 75%
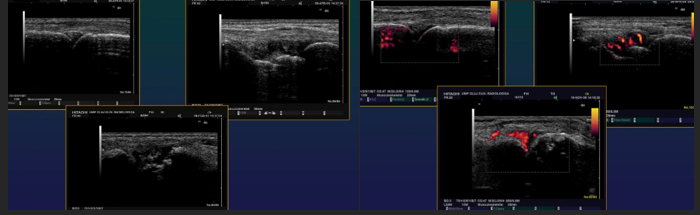
Septic Arthritis US
Small fluid effusions
Thickened synovial membrane + Doppler signal in acute phase
US guided joint punctures (Dg, therapeutic)
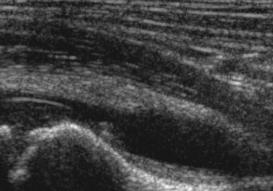
Septic Arthritis (Pseudomonas)
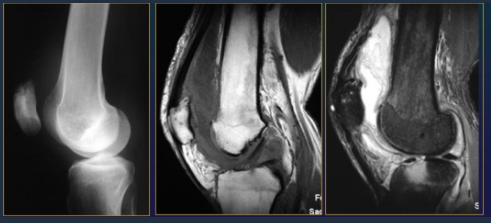
Septic Arthritis MRI
Within 24 hrs from onset
T1: subchondral hyposignal on both bones
Fluid sensitive sequences: hypersignal fluid in joint, surrounding edema
Post contrast:
Synovial enhancement
Subchondral enhancement
Soft tissue abscess
Septic Arthritis CT
Rarely used / same as Xray
Guided puncture
Septic Arthritis Rx
Normal Rx
Intraarticular effusion
Periarticular OP
Joint space narrowing
Blurred cortical bone
Subcondral bone destruction
Erosion + osteomyelitis
Ankylosis (rare)
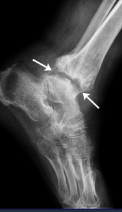
Septic Arthritis
Agent: Staph
Seeding: hematoG, direct and contiguity
Predispo F:
local: RA, arthrosis, trauma, microcristal arthritis, neurotropathy
general: hémopathies, DM, cancer, chronic renal failure, immune deficit, drug abuse
Loc: any joints
more fq= hip (kids), knee (adults) and SI or sternoclavicular in DM, HIV and drug abuse
Ankylosis
Disappearance of joint space => bone fusion across a joint
ONLY produced by arthritis
NEVER produced by arthrosis
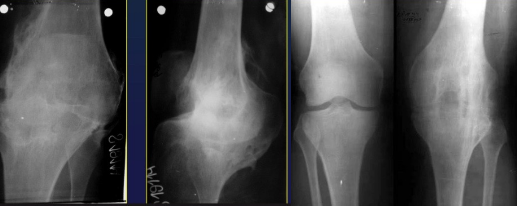
Osteomyelitis Complication
Septic Arthritis
PATHO fractures with PATHO healing
Limb deformity (shortening / lengthening)
Osteomyelitis (peculiar- bone whitlow= infection of the soft tissue of the fingers)
Soft tissue swelling
Surface osteolysis
NO periostosis
EVO (complication)
Septic arthritis
PATHO fracture with PATHO healing
Limb deformity (shortening / lengthening)
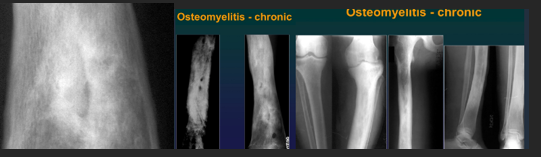
Chronic Osteomyelitis MRI
Active foci
Abscess
Fibrosis
Sequestration
Soft tissue abscess
CharaK Osteomyelitis
Chronic, evolution in bursts
Single bone, single place
Involves etaphyses an diaphyssis NOT epiphysis NOR joints
Xray CharaK
Bone sequestration
Osteosclerosis
Periostosis
Hyperostosis
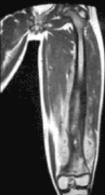
MRI Osteomyelitis
Paraosseous hyperT2 (soft tissue edema)
In bone marrow : hypoT1 and hyperT2
Increased Ga Uptake
Osteomyelitis (nelaton in 1844)
Agent: Staph Aureus (75%) or streptococci & other germs
Contamination
Hematogenous
Contiguity
Direct seeding: accidental & iatrogenous
Affecting: any age, more fq in children M/F=3/1
Slow emergence
at 24-48h: increased soft tissue opacity and thinning if adipose tisse
at 7-10 d: OP, foci of Osteolysis and thinning blade shaped periostosis (3-6 wks)
Chronic Osteomyelitis CT
Sequestration
Cortcal thinnign
Fistulae (fistulography)
Soft tissue absecess (+ contrast)
US Osteoyelitis (7,5-10 MHz)
Edema
Periosseous abscess (transonic)
Periostosis (irregular bone surface)