BIS 2C Lab Practical
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
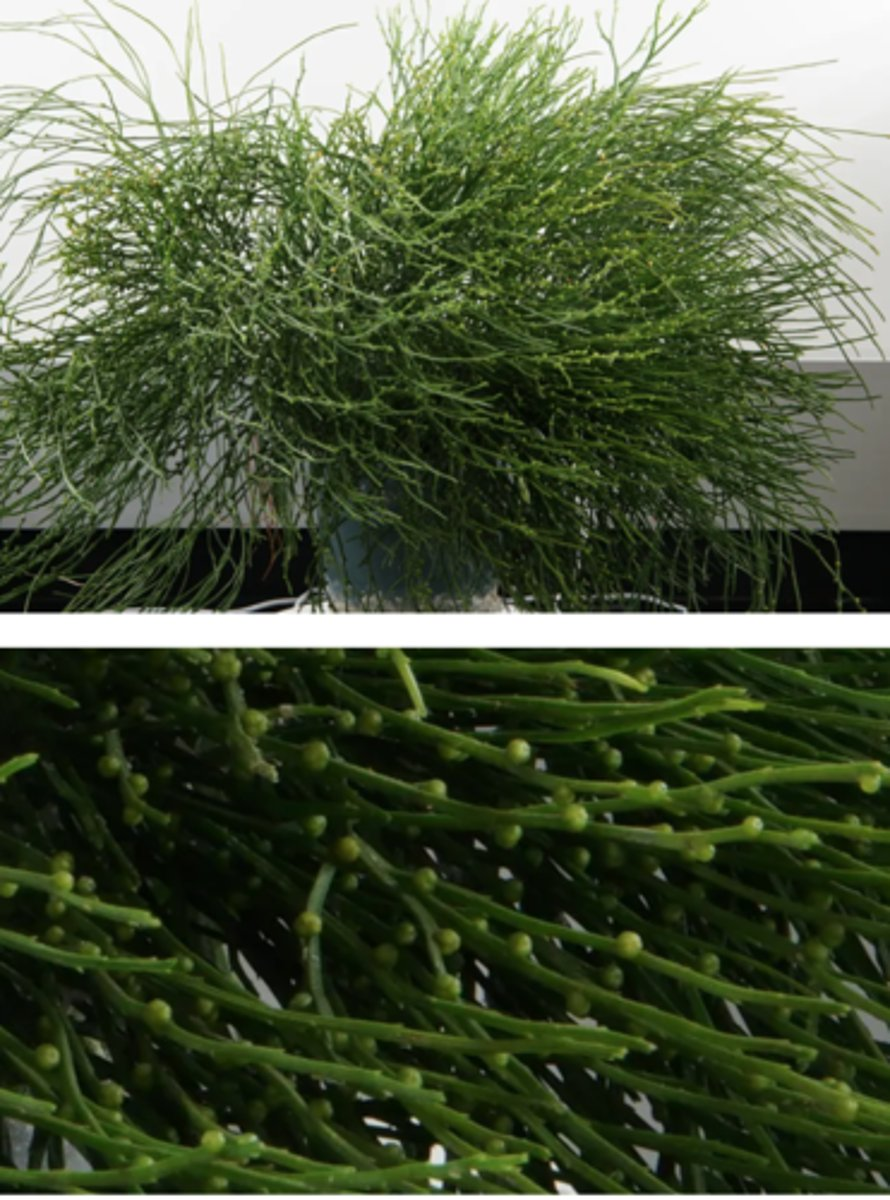

Which of the following characteristics are associated with the plant depicted above?
-Vascular tissue
-Sporophyte not dependent on gametophyte
-Homospory
-Spores are dispersal stage
-Chloroplast DNA inversion

Which of the following characteristics are associated with the plant depicted above?
-Xylem
-Sporophyte not dependent on gametophyte
-Production of spores by meiosis
-Homospory
-Swimming sperm

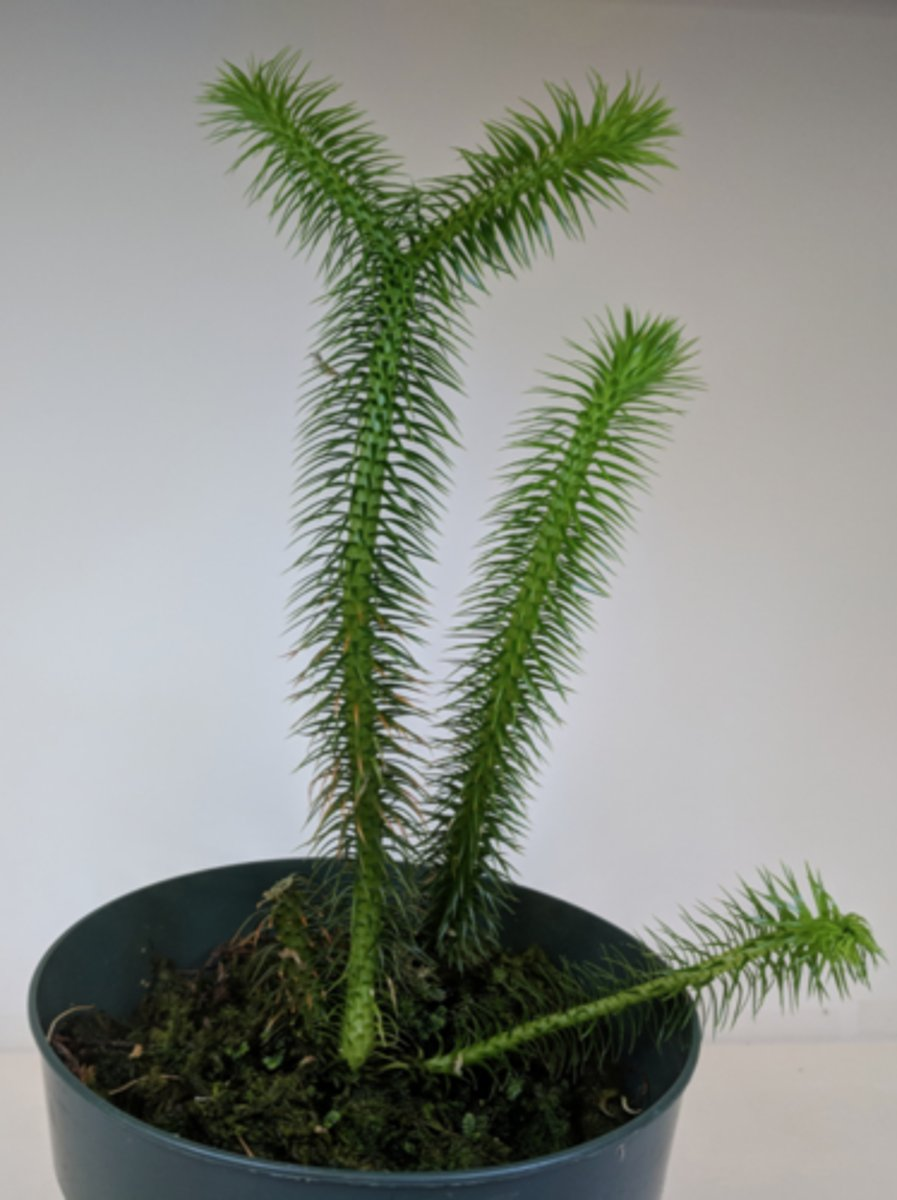
Which of the following characteristics are associated with the plant depicted above?
-Phloem
-Dominant sporophyte
-Production of gametes by mitosis
-Seeds
-Fruit
-Secondary growth
-Heterospory
-Chloroplast DNA inversion

Consider the monophyletic group defined by the MRCA of the two plants shown above. Which of the following are synapomorphies of this group?
-Seeds
-Pollen
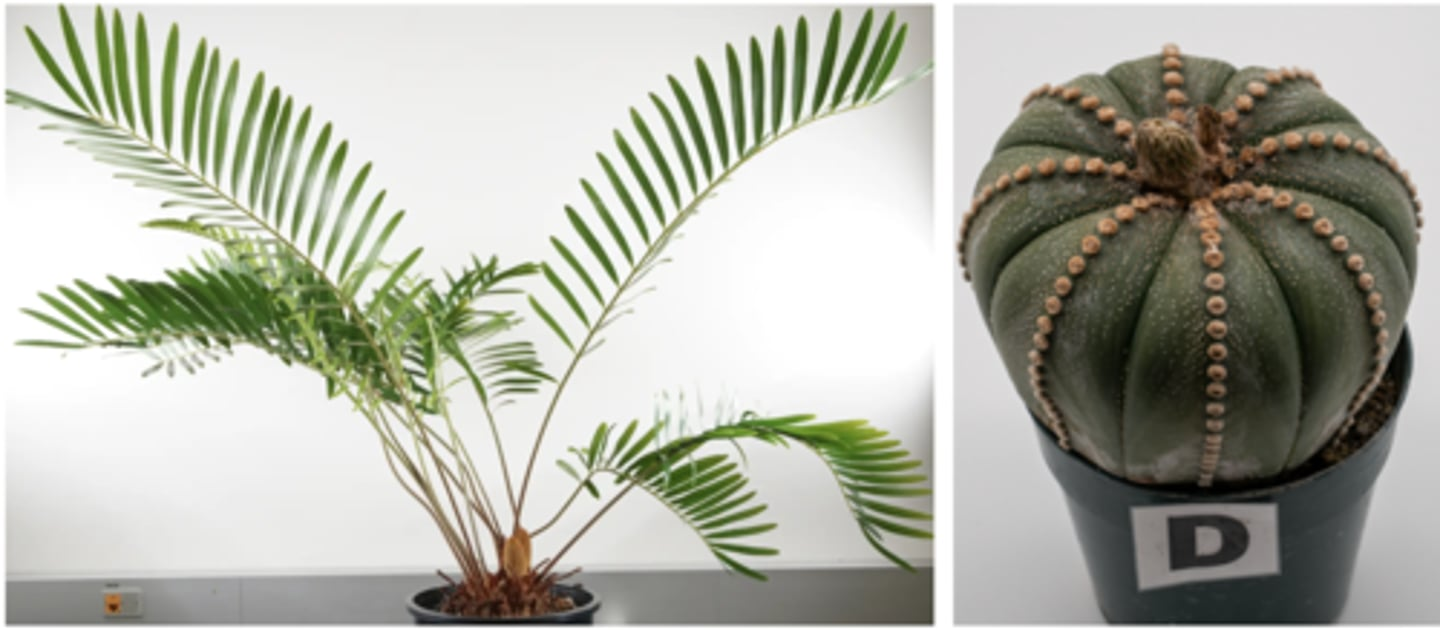

Consider the monophyletic group defined by the MRCA of the two plants shown above. Which of the following are found in all members of this group, but are NOT synapomorphies of that group? (see image above)
-Vascular tissue
-Stomata
-Waxy cuticle
-Multicellular sporophyte
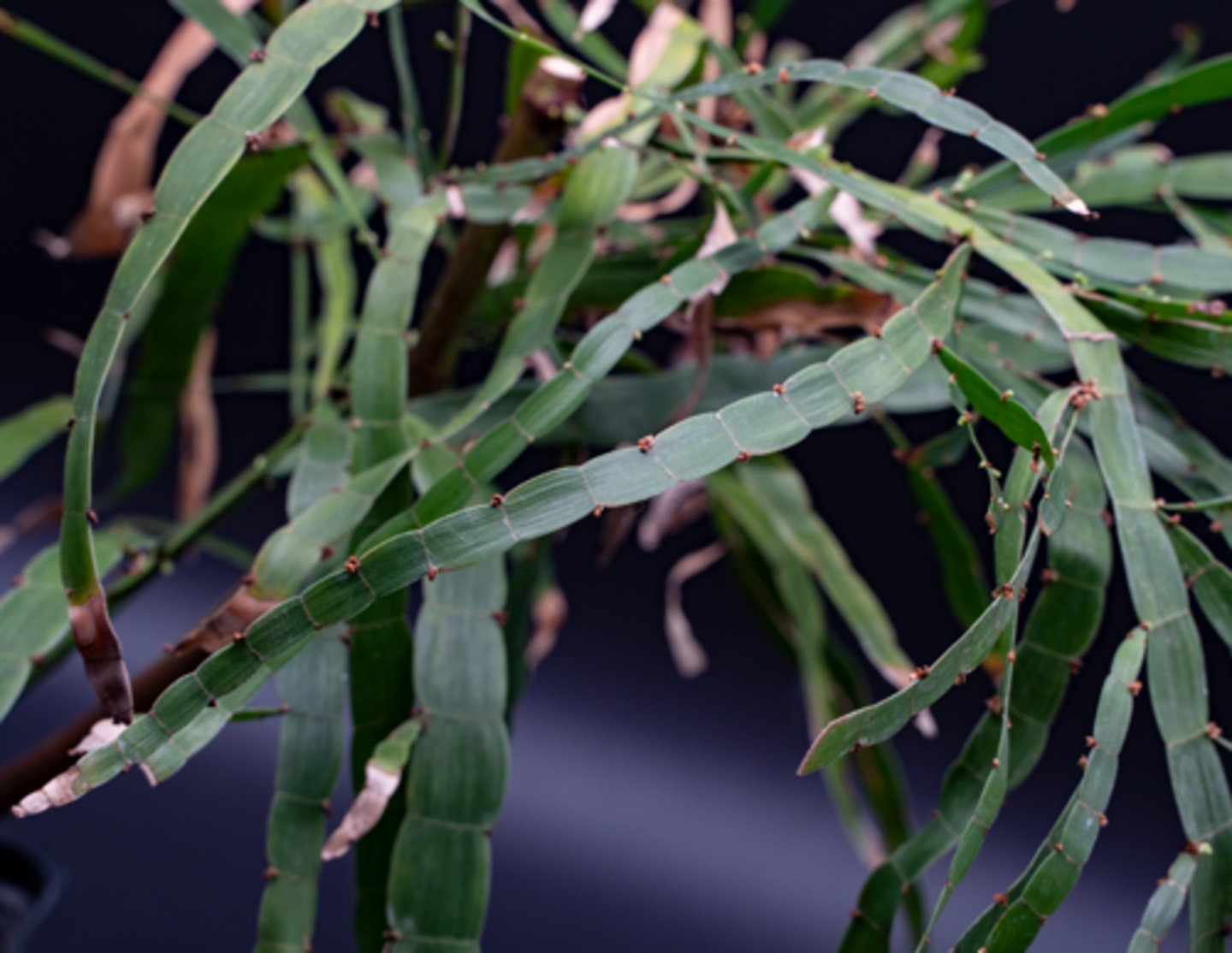

Which of the following apply to the modifications that have evolved in this plant?
-The stem has been modified to perform photosynthesis
-The leaves have been lost to reduce water loss
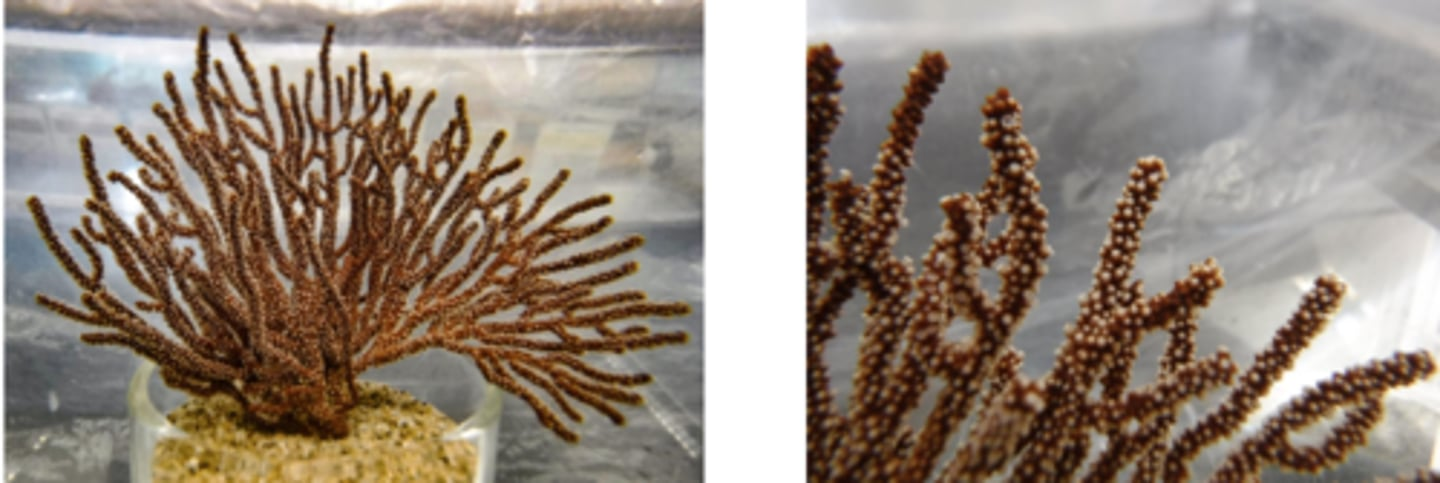

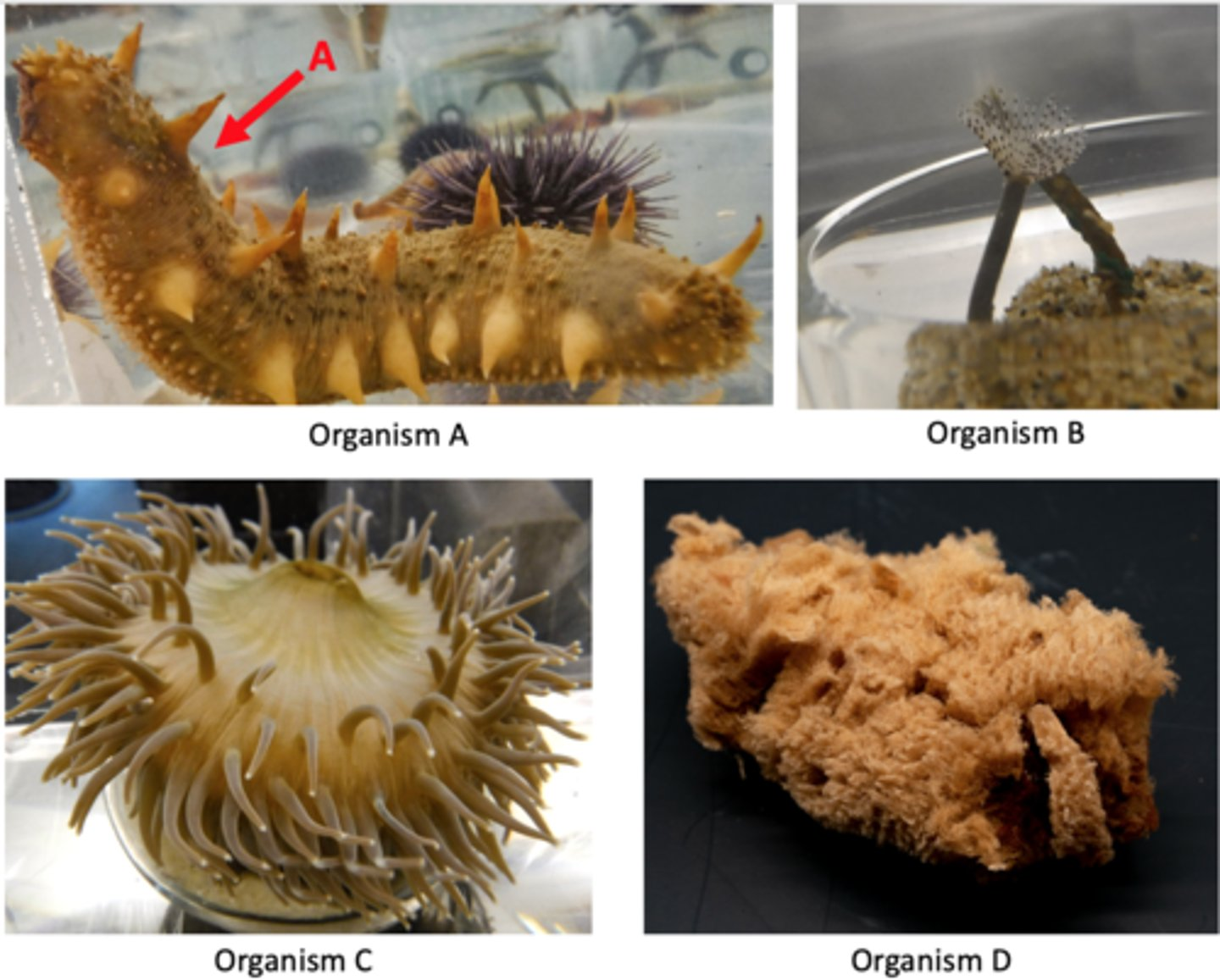
Which of the following characters are associated with the animal shown above?
-Cnidocytes
-Two-way gut

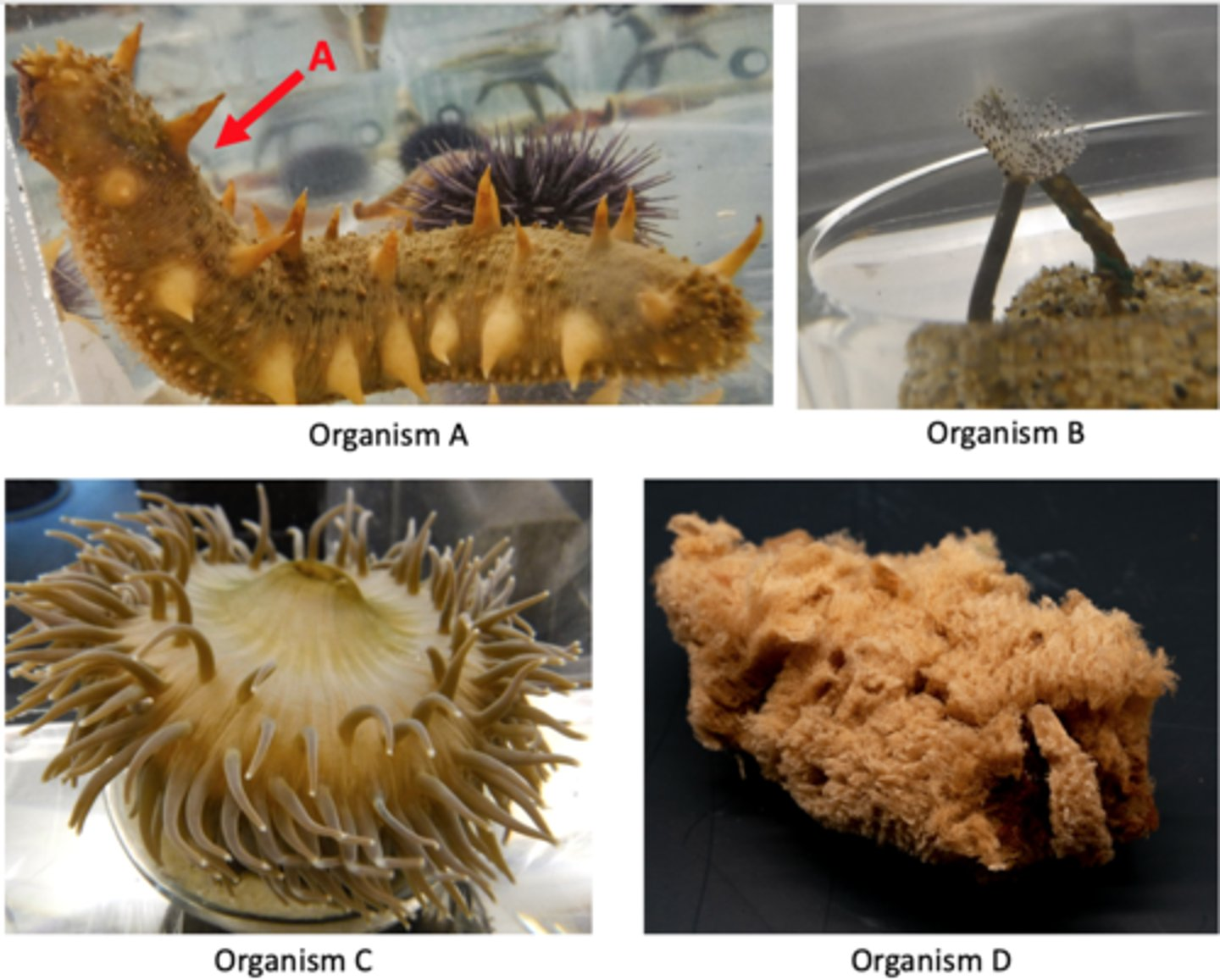
Which of the following characters are associated with the animal shown above?
-Triploblastic
-1-way gut
-Ecdysis
-Bilateral symmetry

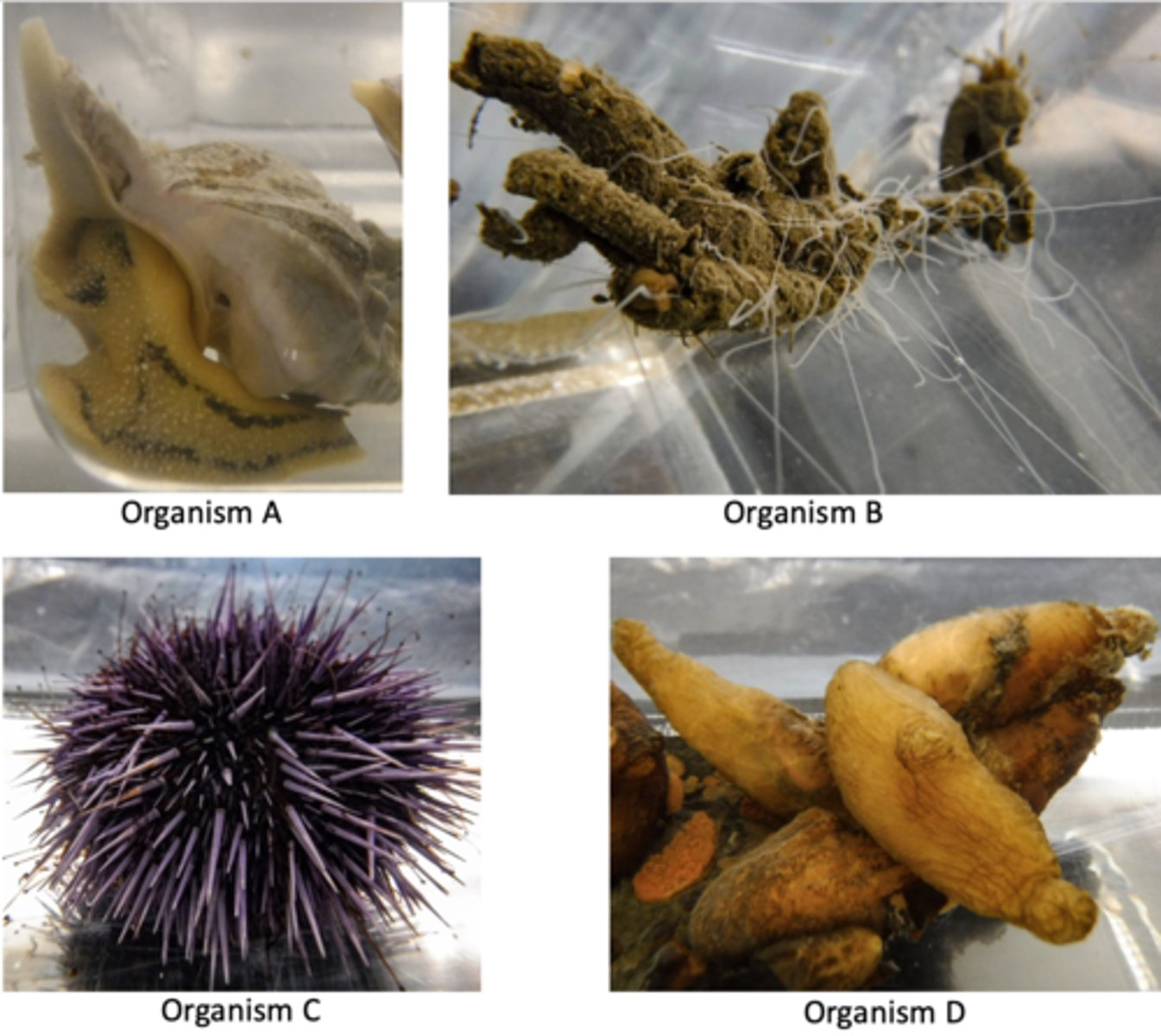
Which of the above animals is most closely related to animal A?
B

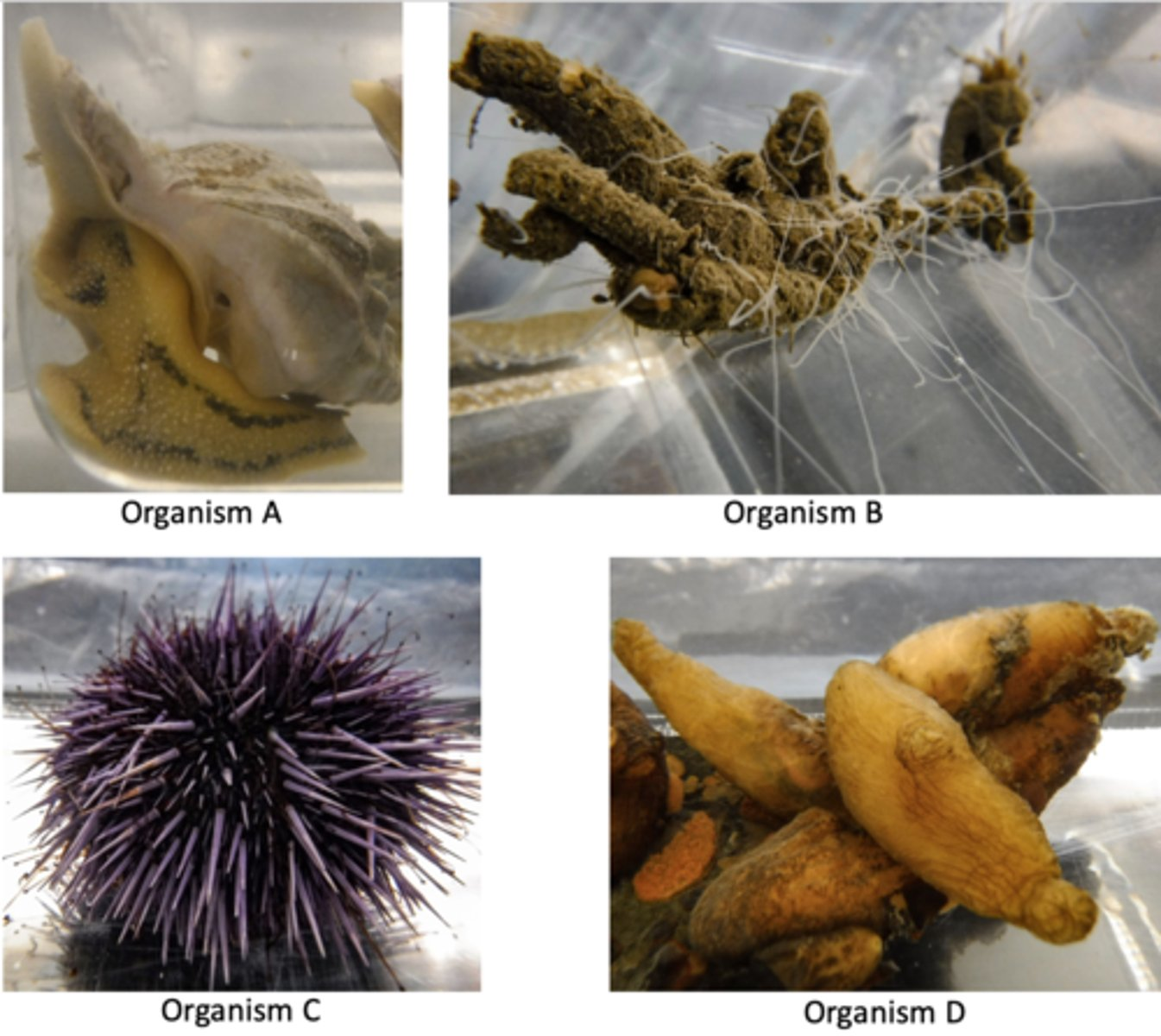
In which of the animals shown above does the blastopore develop in the anus?
A

Which of the organisms shown above is most closely related to humans?
D

Match the organisms shown above to the correct character from the provided list.
A- radula
B- paired setae
C- water vascular system
D- Notochord
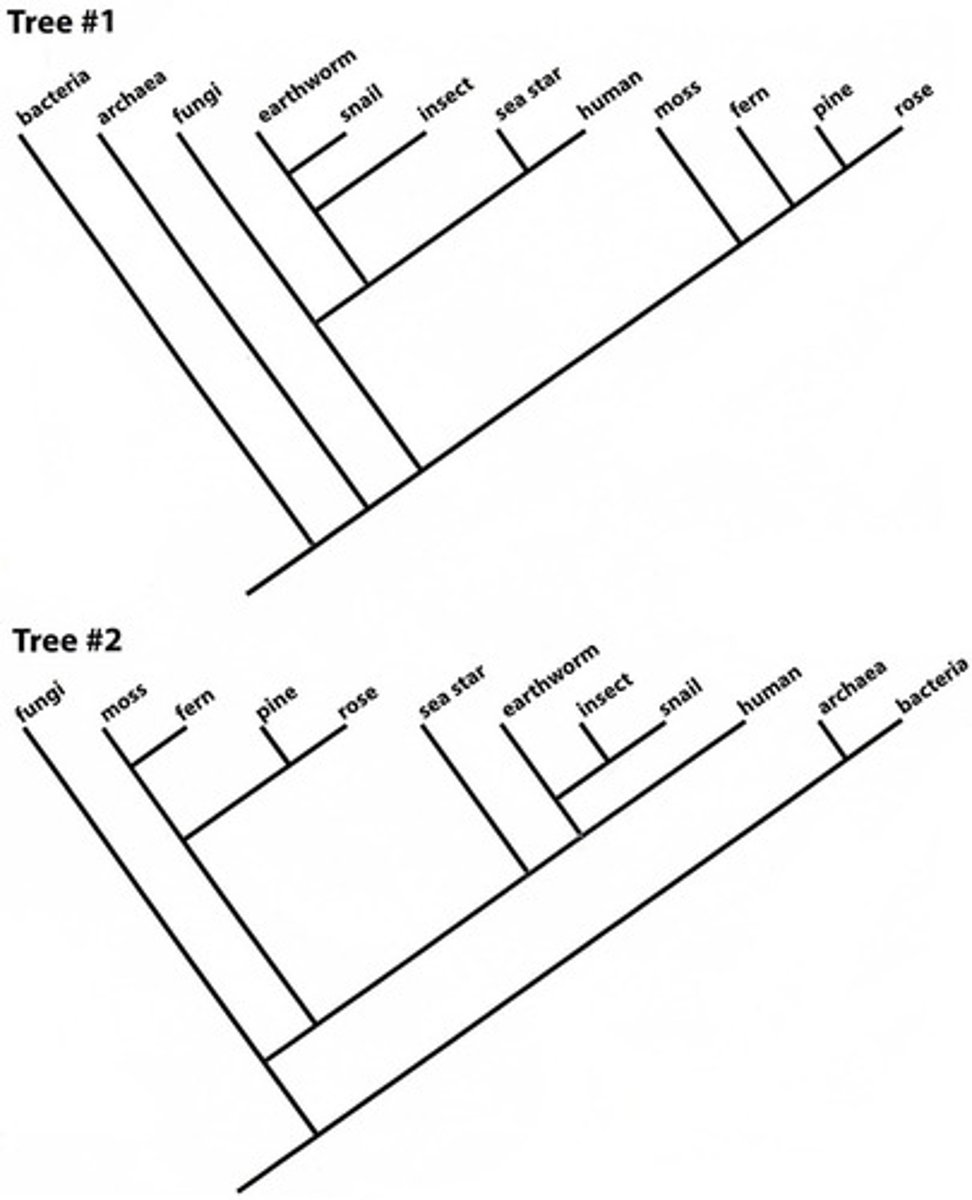
On which of the phylogenies above do Fungi and Metazoa form a clade?
Tree 1
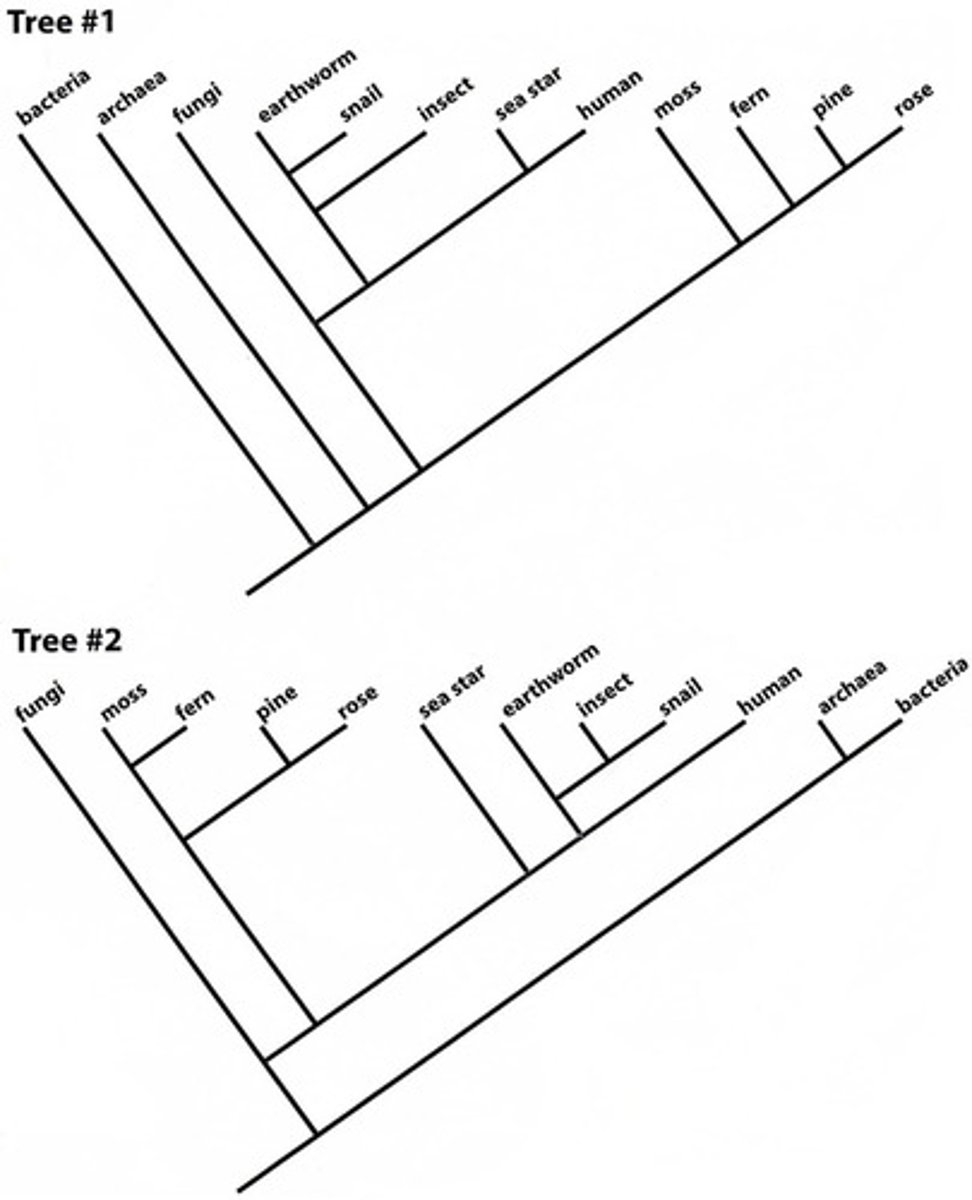
The phylogenetic trees presented above are best described as:
Cladograms
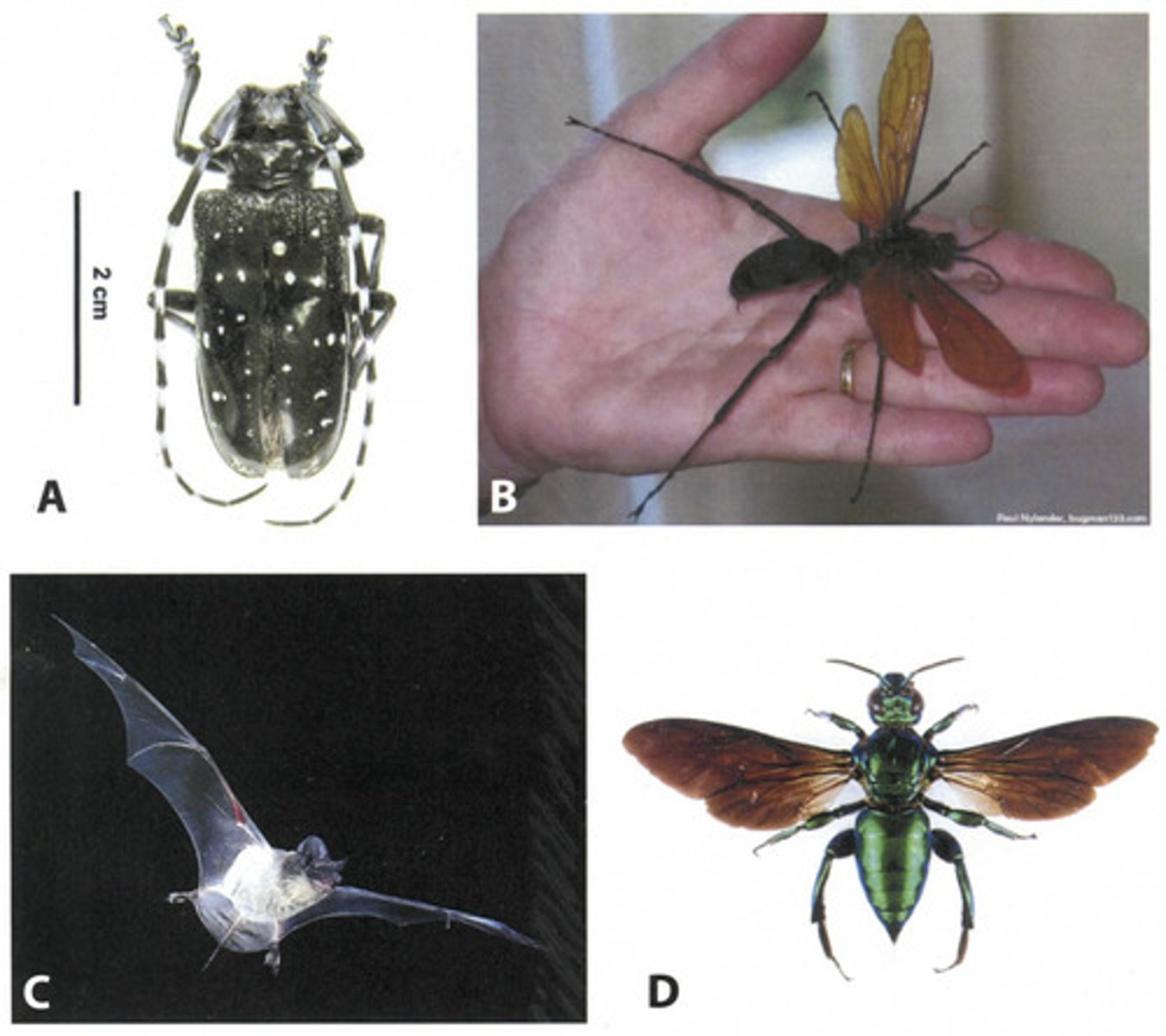
Which of the following characters would be parsimony informative for building a phylogeny of the four organisms depicted above?
None of the above
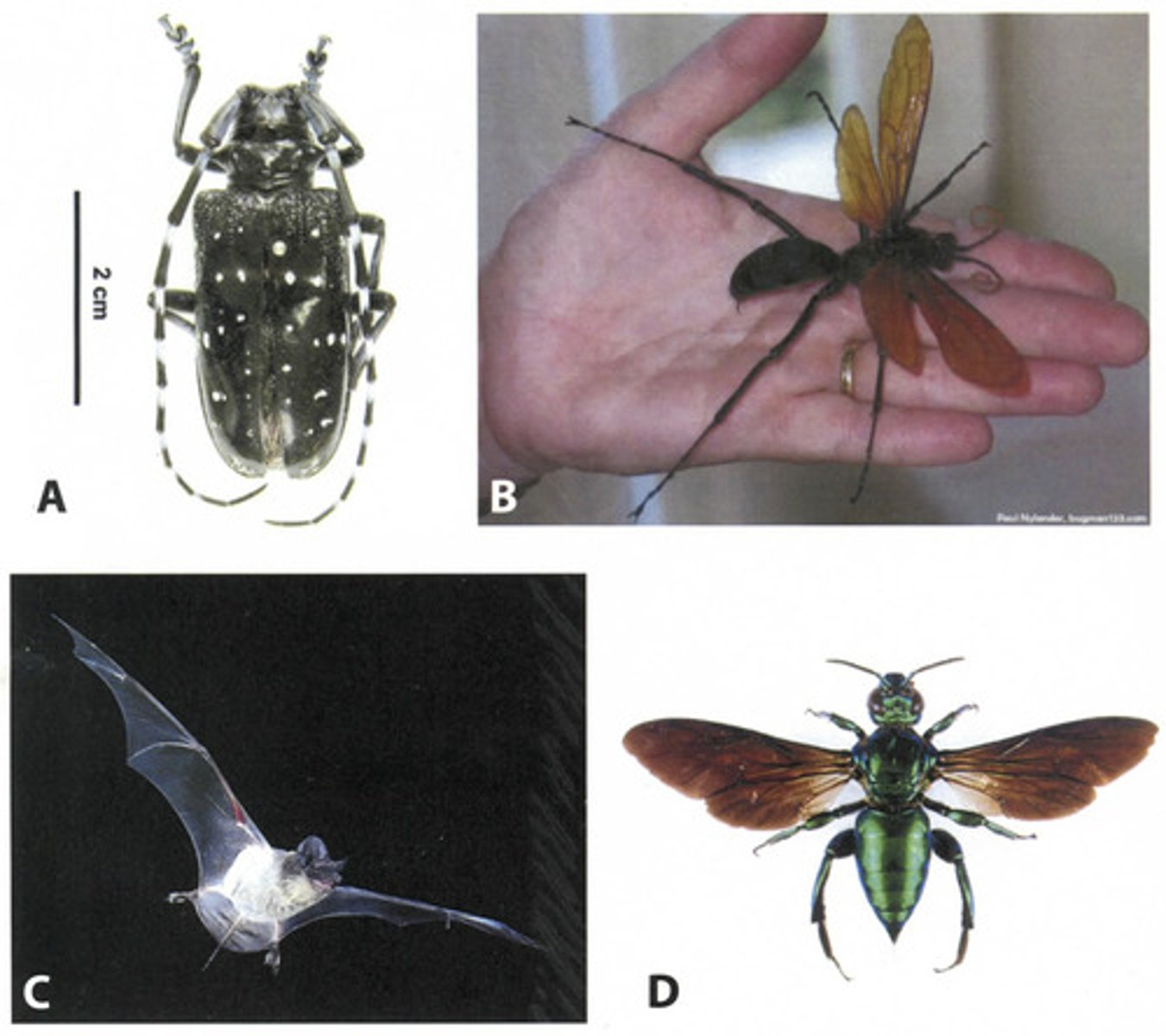
Among organisms A- D above, the presence of wings would be considered a:
Homoplasy
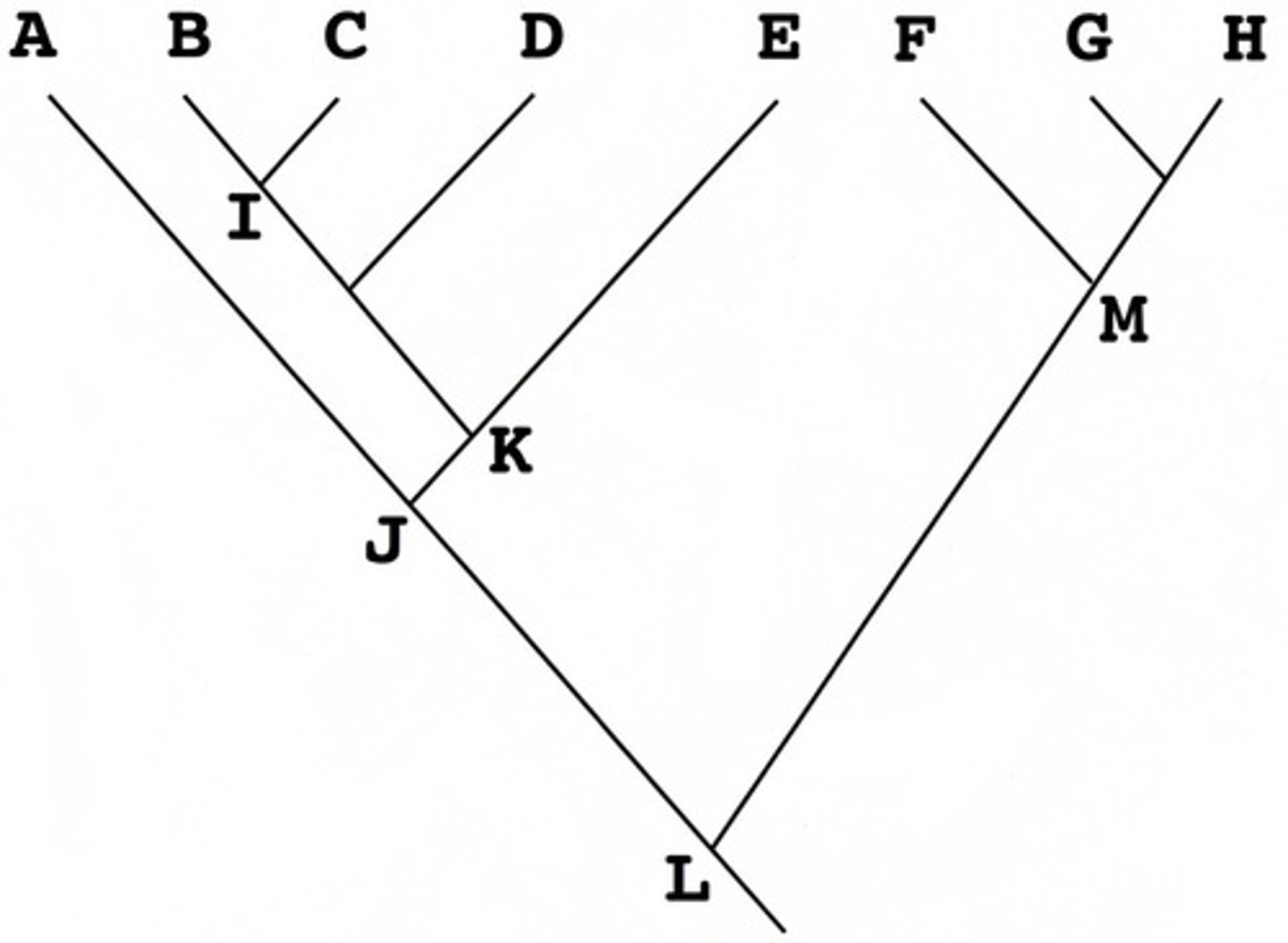
On the phylogenetic tree above, which taxon is sister to taxon A?
B+C+D+E
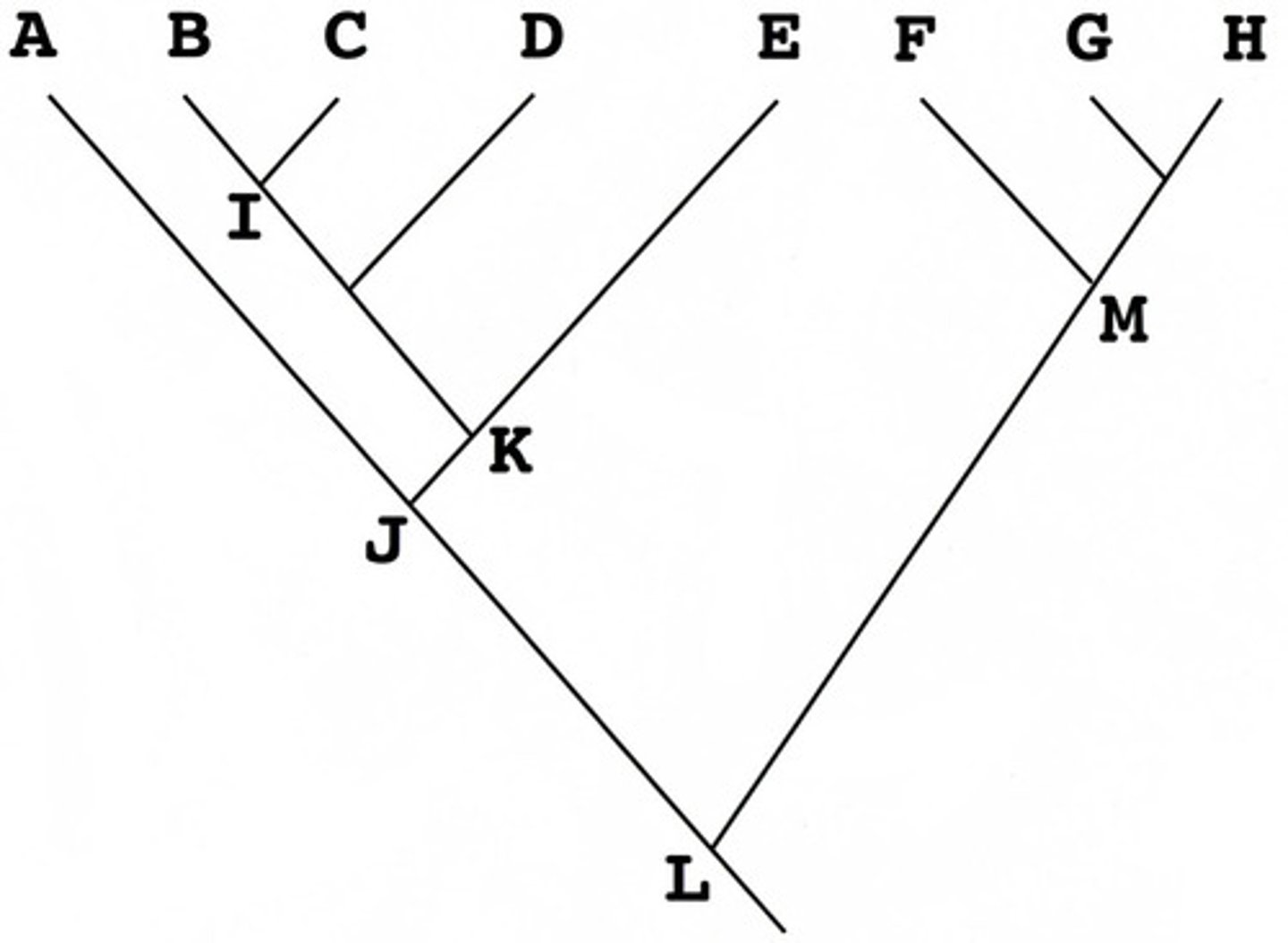
Based on the phylogenetic tree above, which of the following groups is paraphyletic
A+B+C+D
Which of the following is NOT a feature you would expect to find in the above organism?
Ether-linked membrane lipids
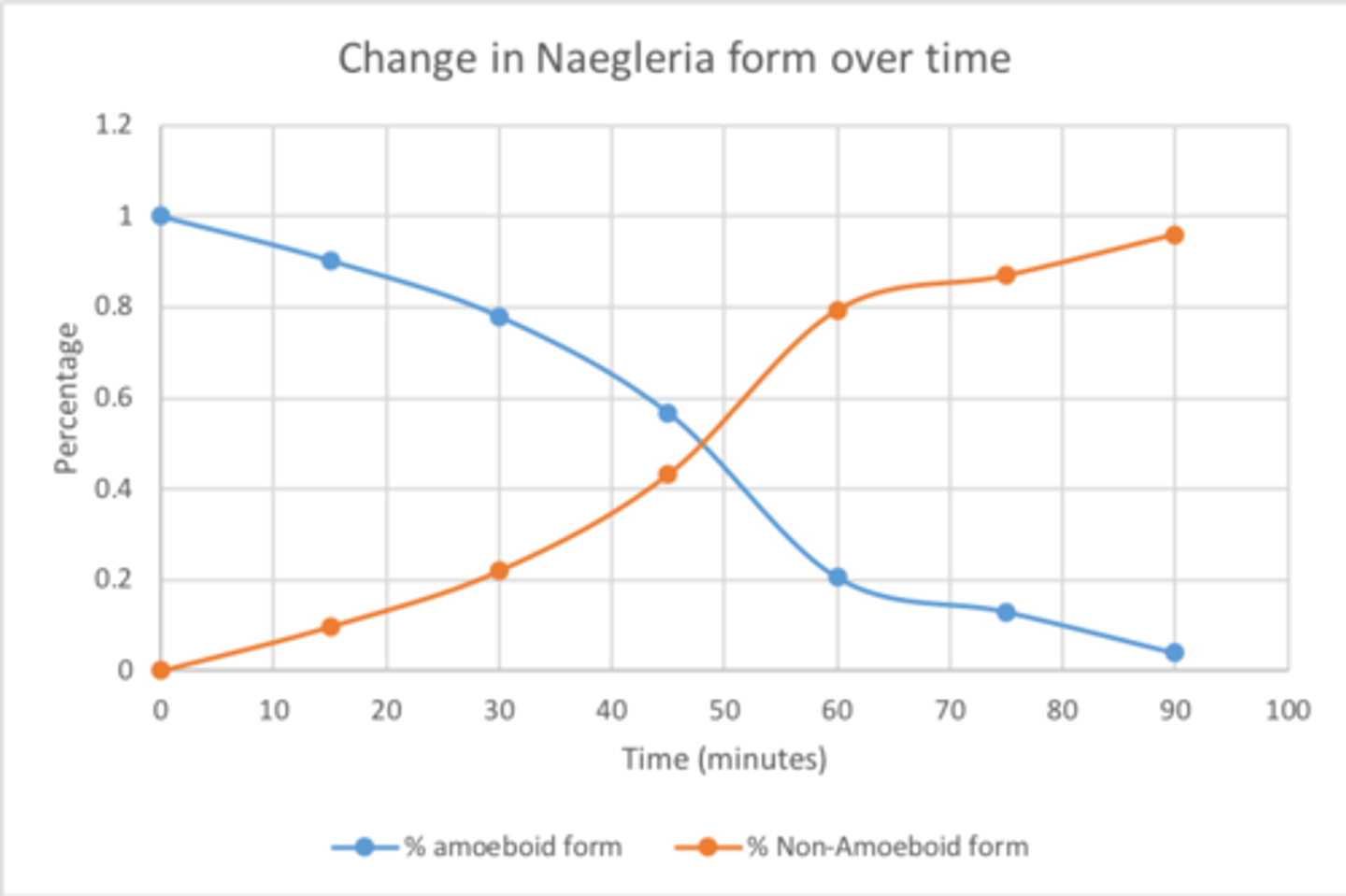
The graph above shows data from the Lab 3 Naegleria experiment. What is the best explanation for what the graph shows?
The removal of food from the culture led to a shift from the amoeboid to the flagellate form over time.
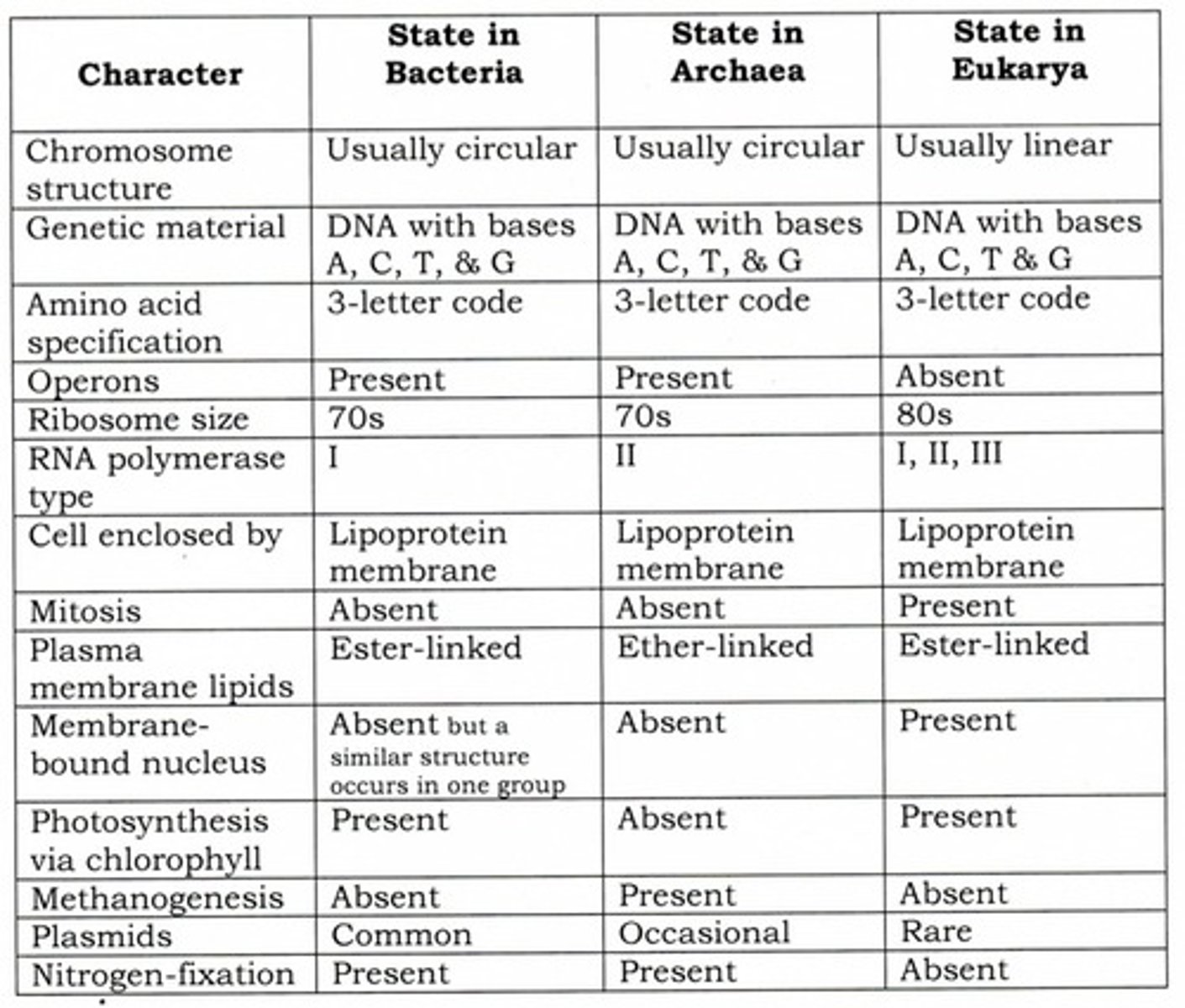
Based on the data matrix above, which of the following characters was most likely present in LUCA?
Lipoprotein membrane
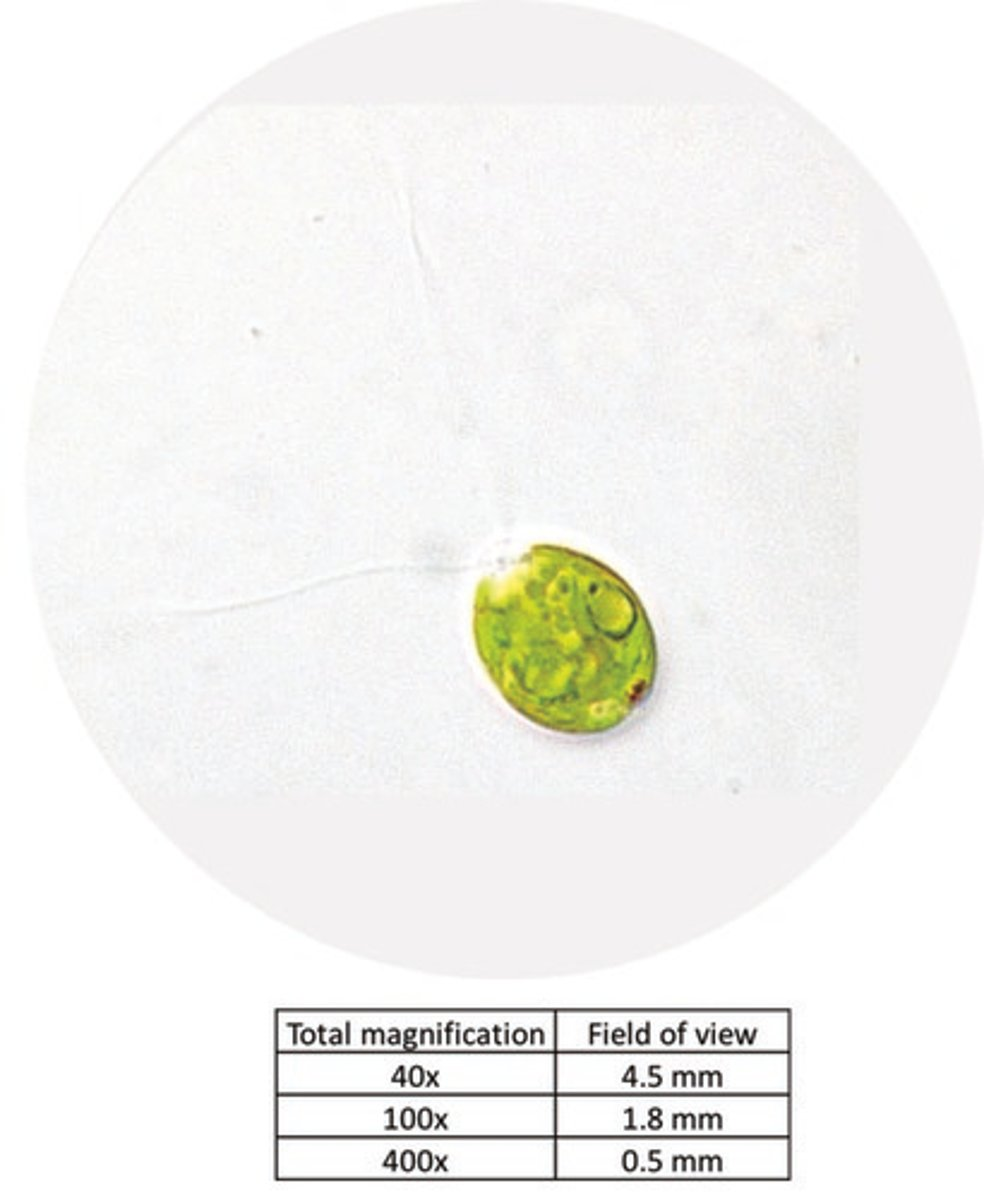
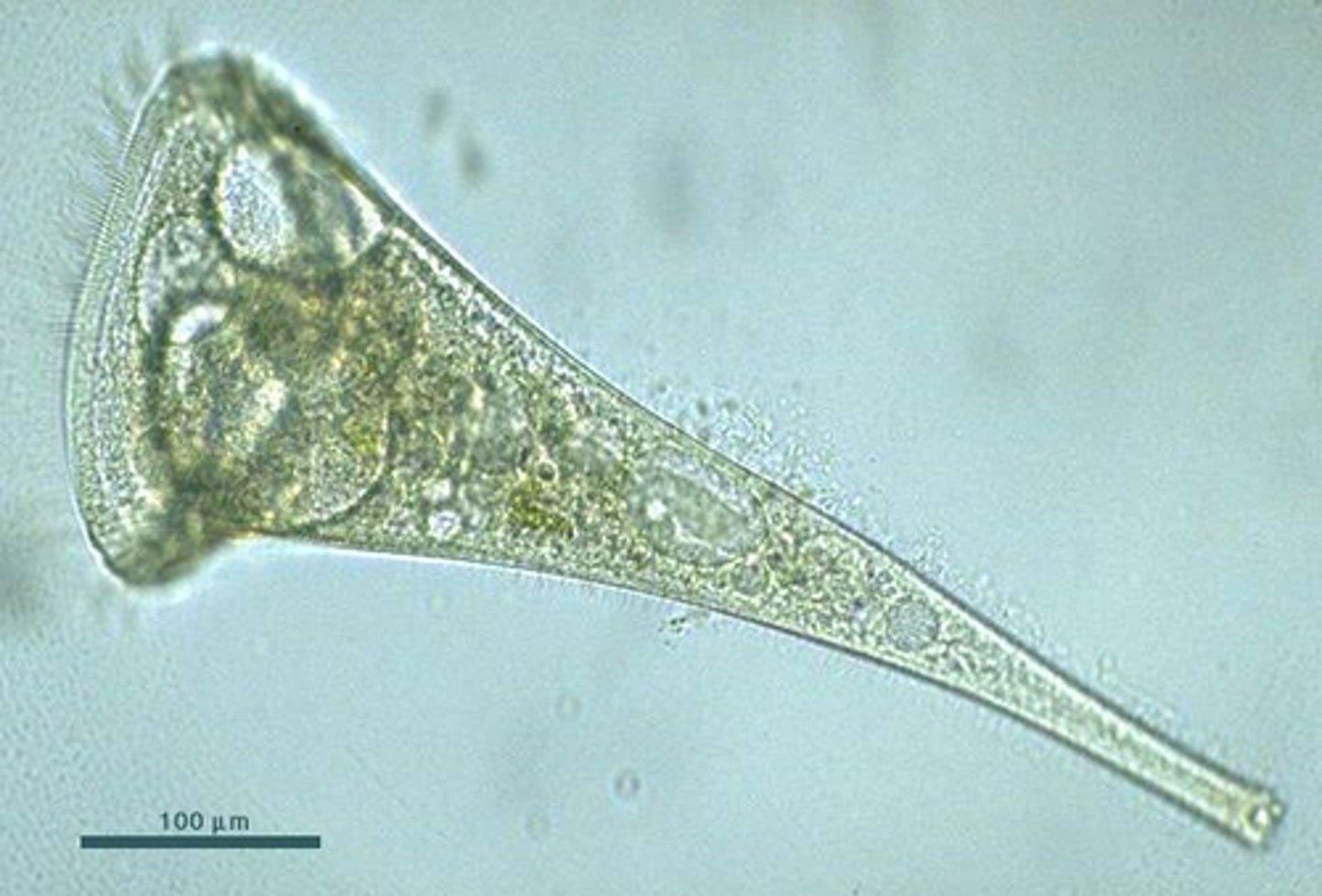
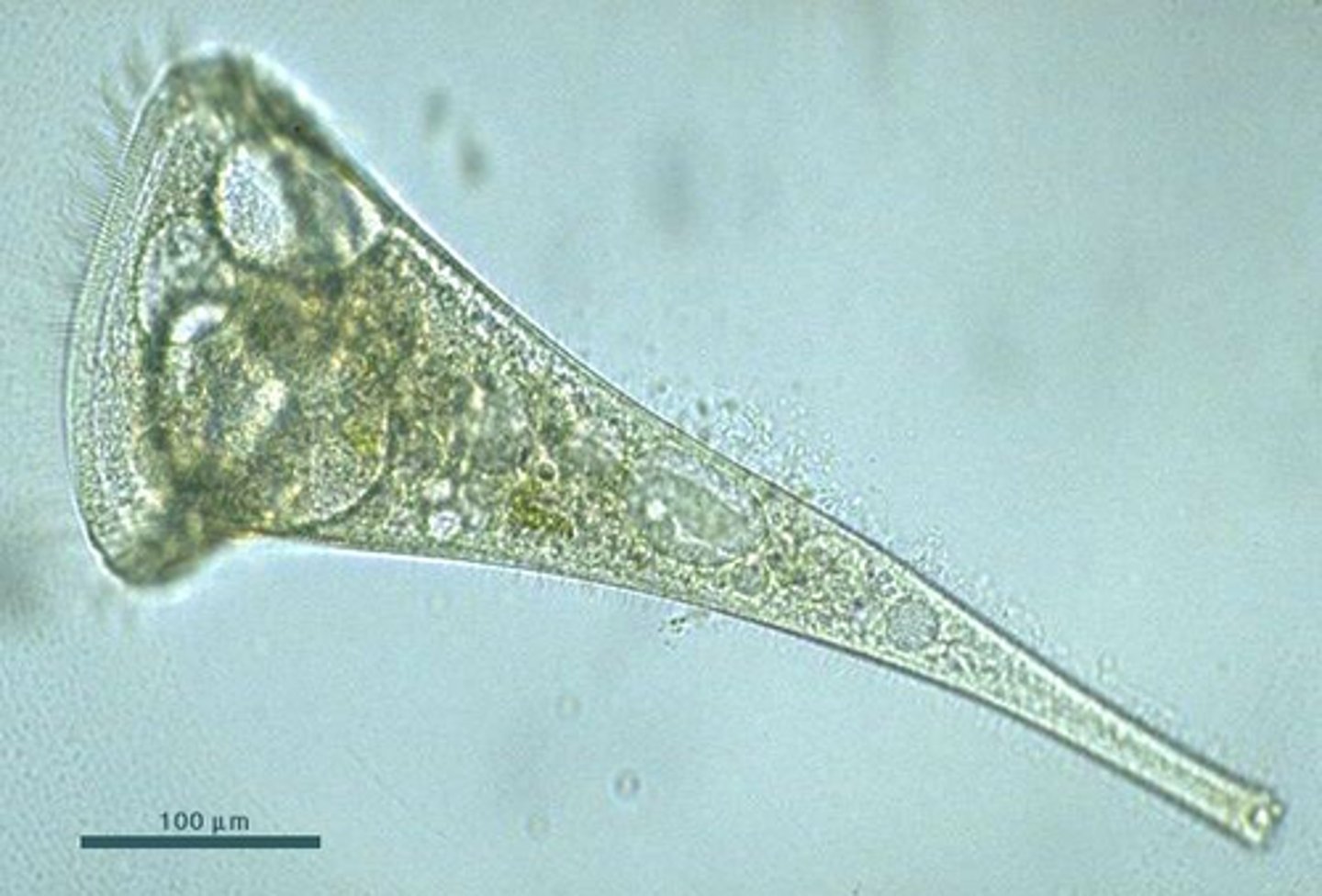
You observe the above organism through a microscope with the 40x objective. Based on the image and the provided table, which of the following is the best estimate of this organisms size?
.125 mm
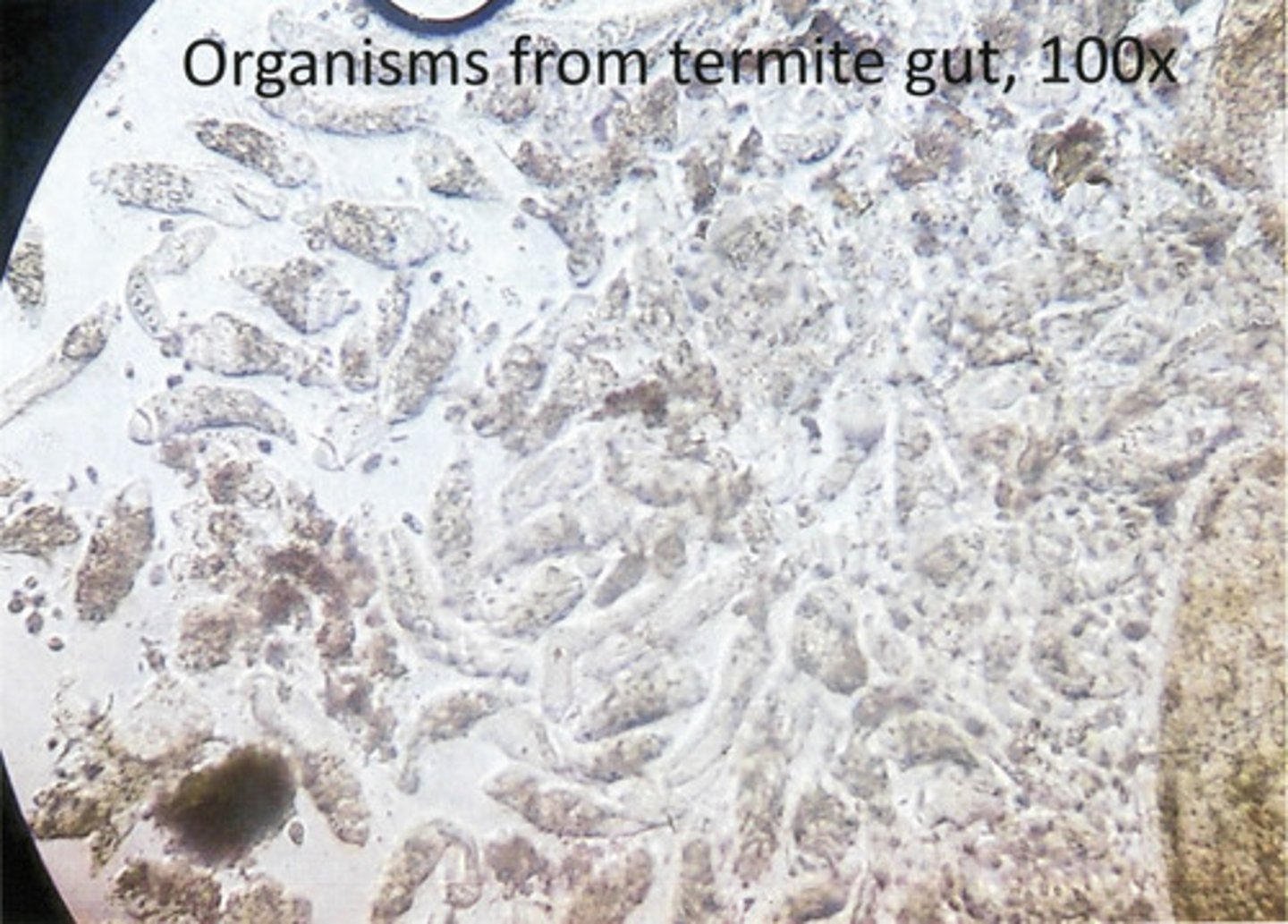
You are examining the hindgut of a termite using 100x magnification and no UV light and observe the relatively large organisms shown in the image above. What are they?
Microbial Eukaryotes
If we examined the sample above under UV light (and with buffer solution), which other group of organisms would we observe?
Archaea
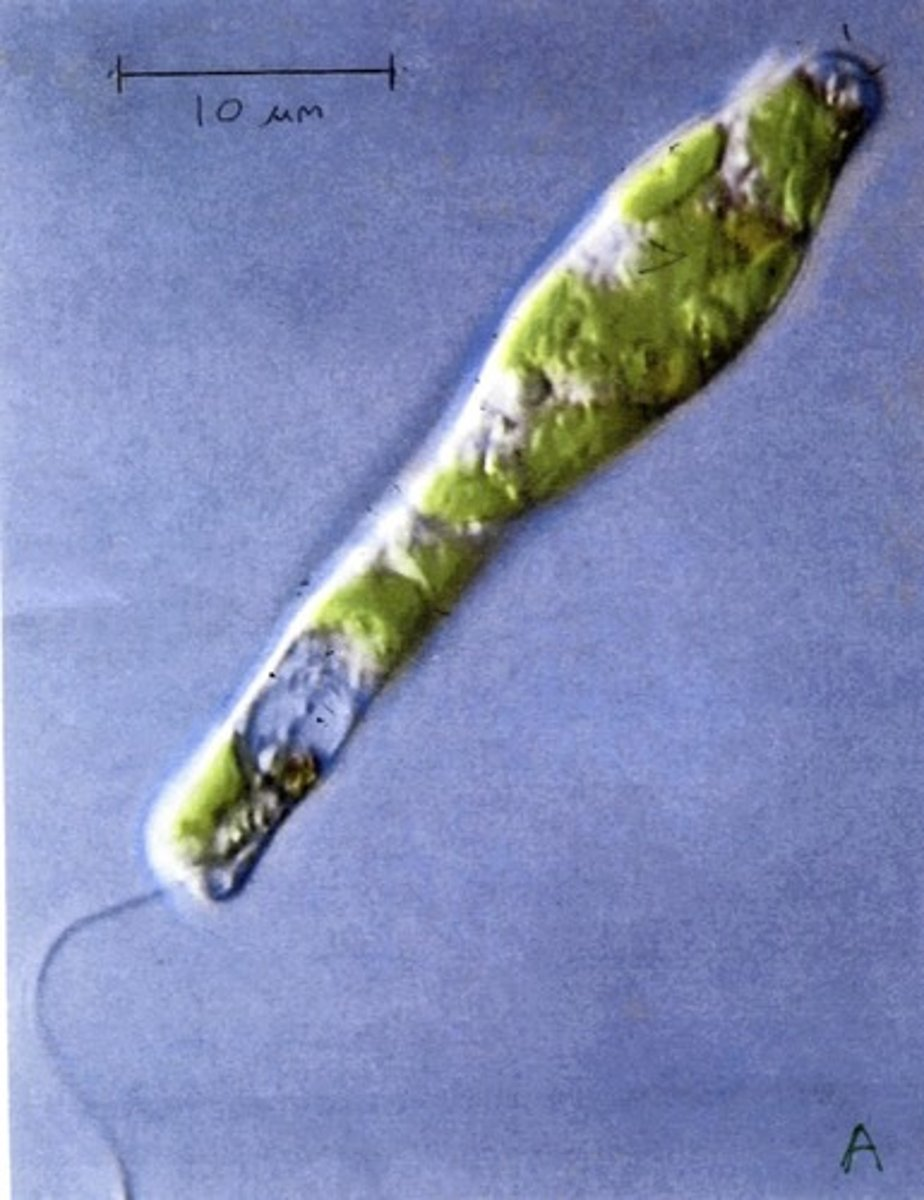
The thin wire-like structure that extends from organism A is a(n):
Flagella
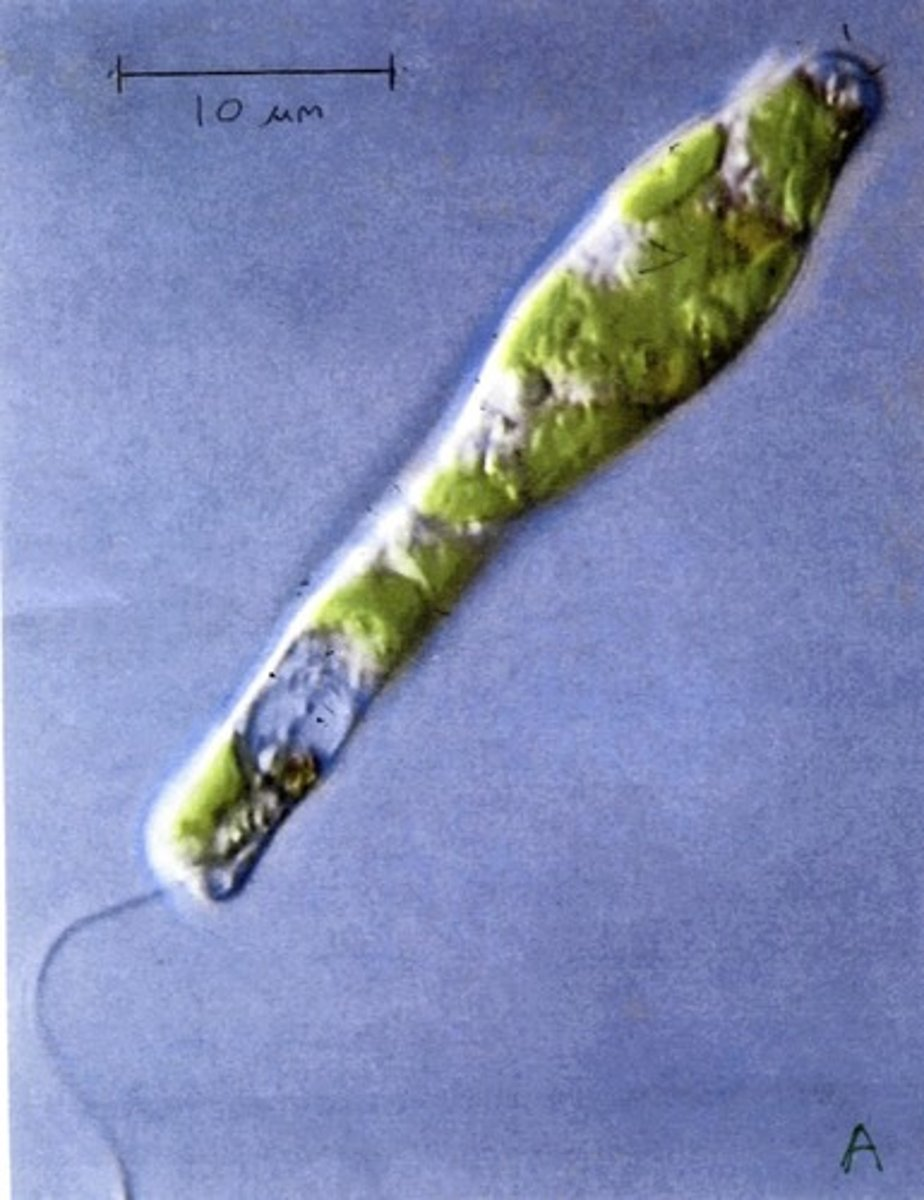
Organism A gets it's energy via
Phototrophy
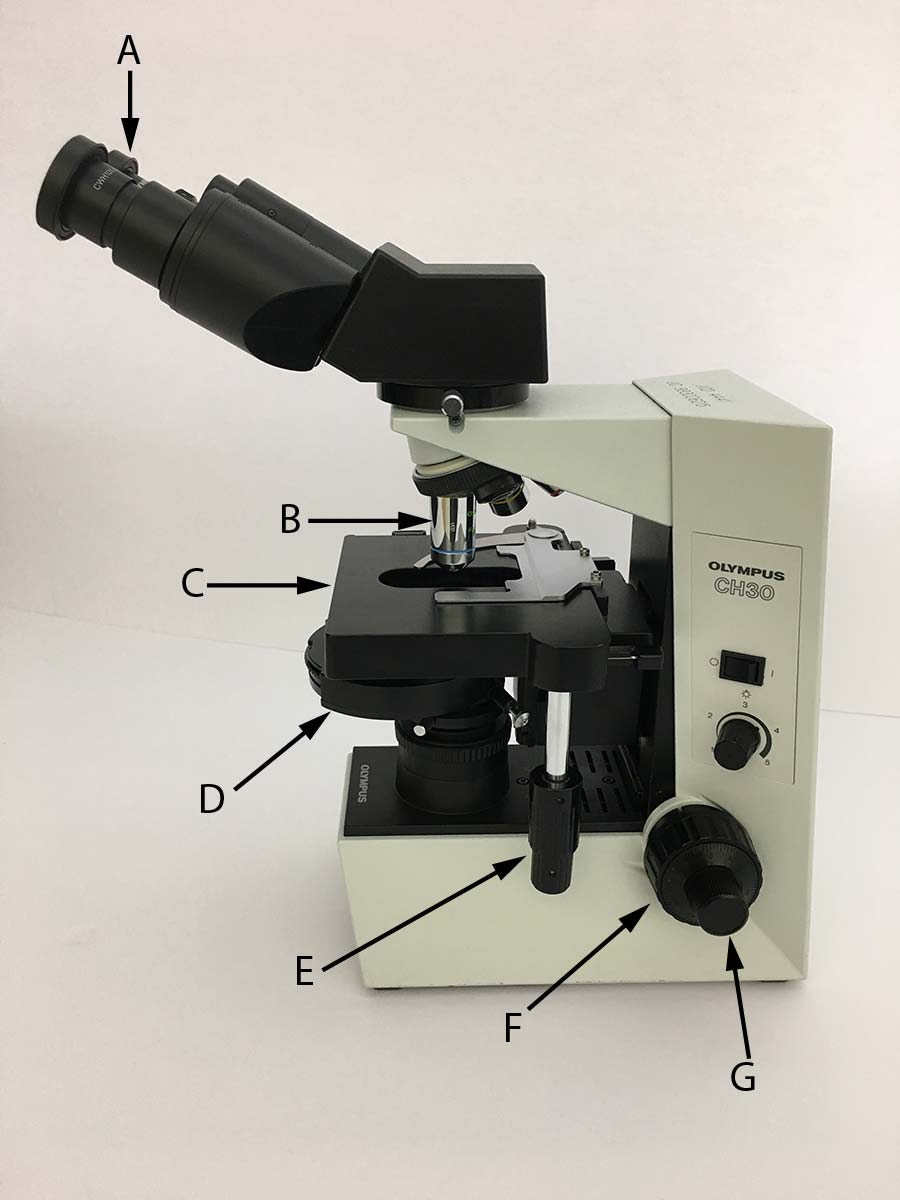

Which of the following microscope controls would you use to move the slide from left to right?
E
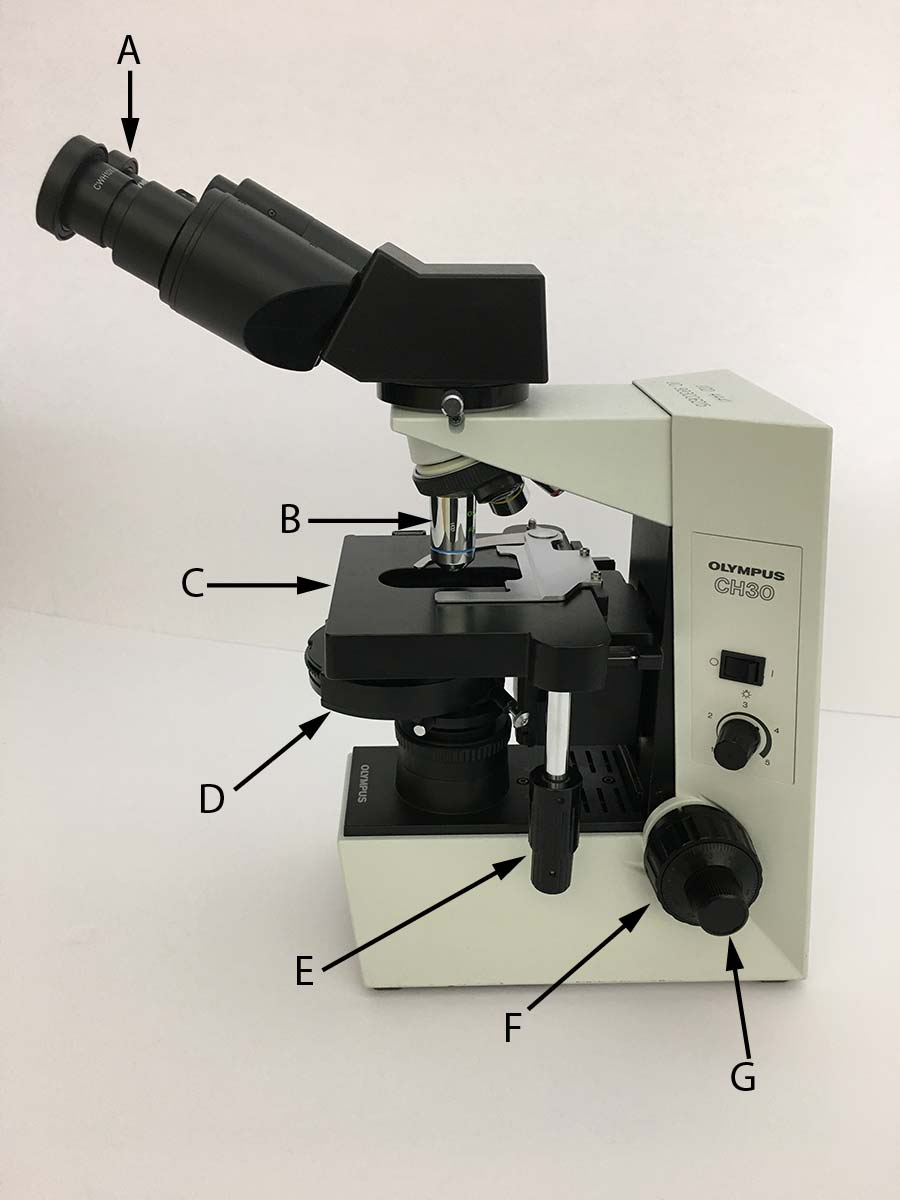

Which of the following microscope controls would you use to adjust the focus if the total magnification was 40x?
F
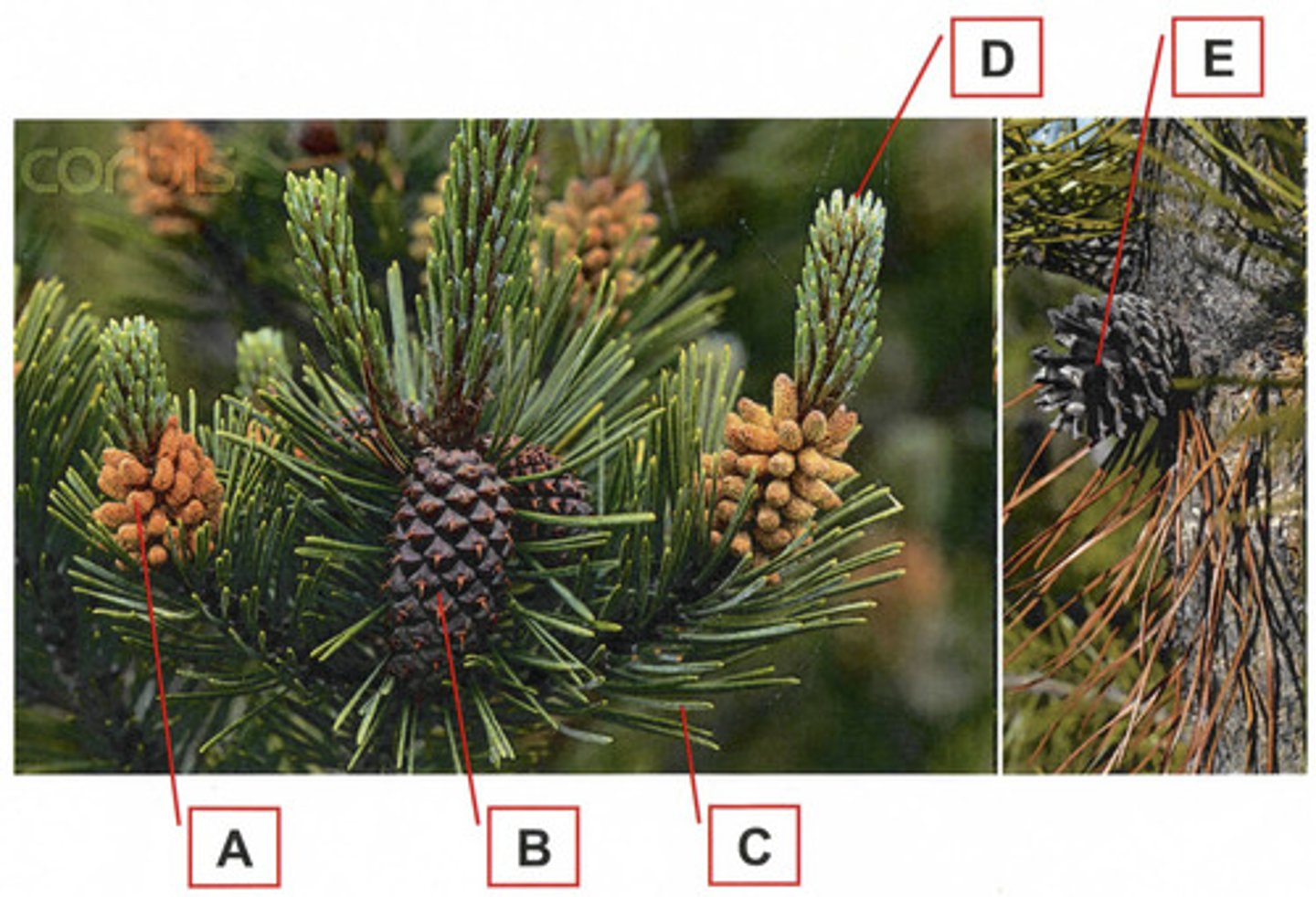
Structure A is a:
Male strobilus that produces microspores
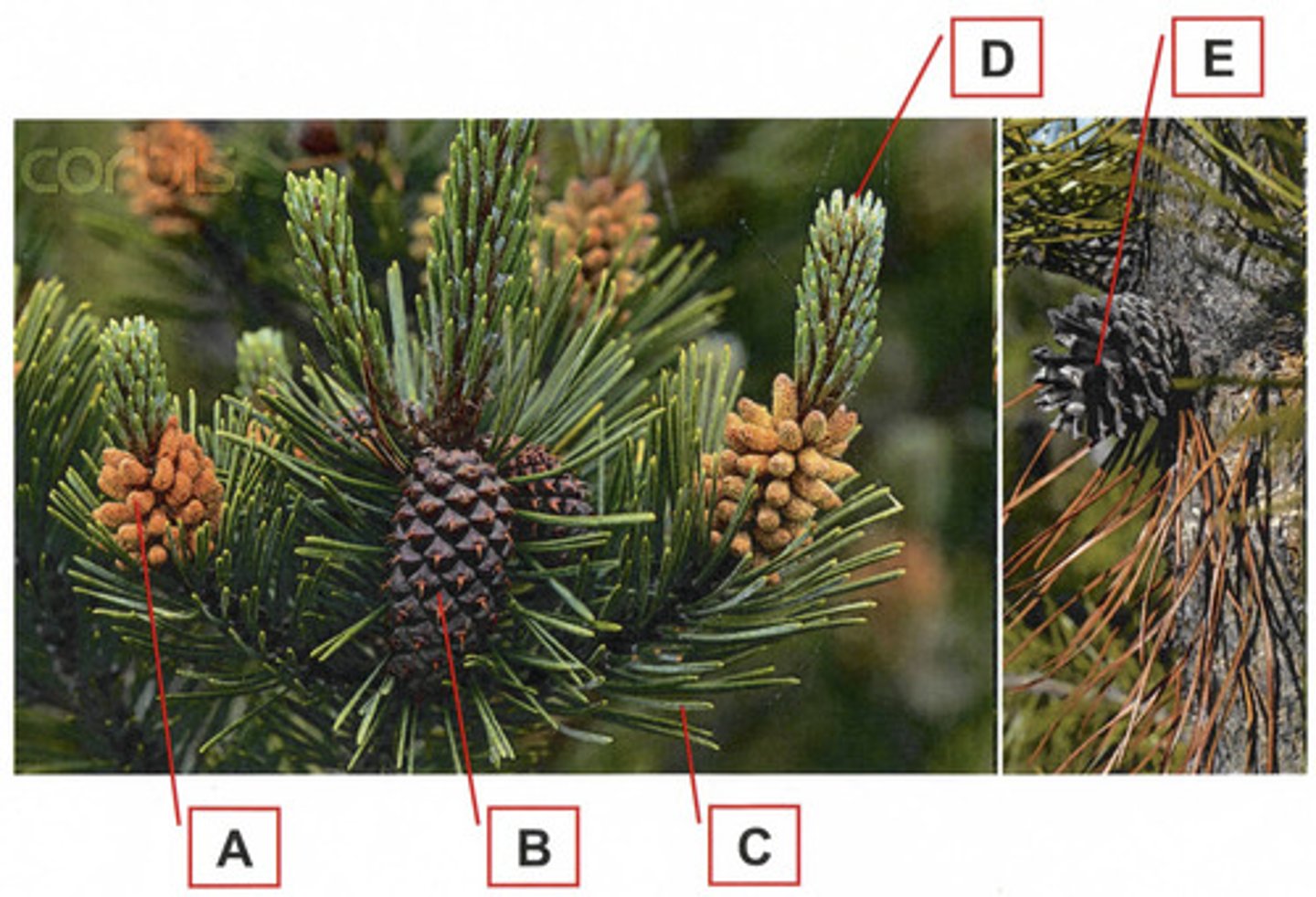
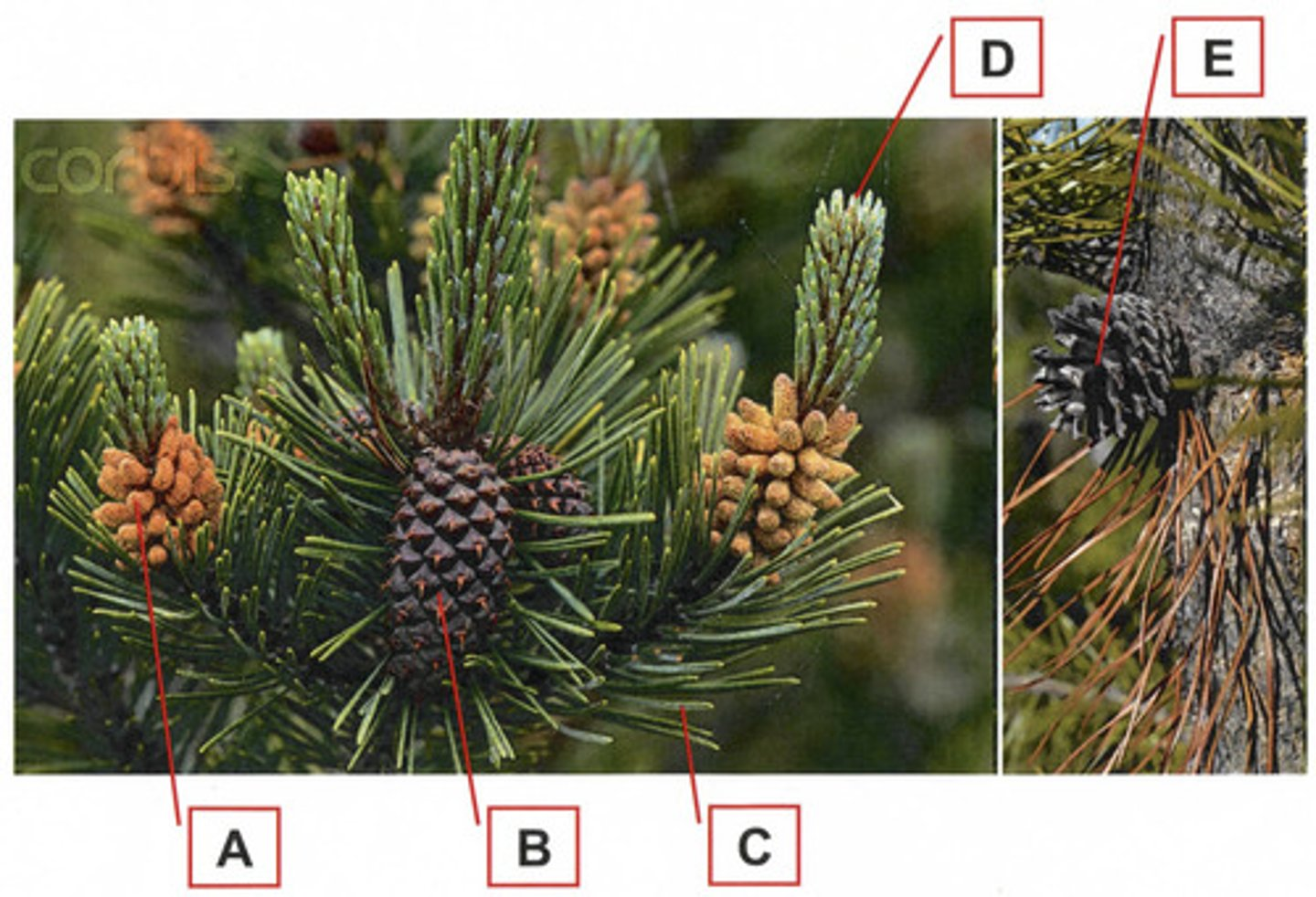
In the above diagram, which structure is most likely to contain a megagametophyte?
B
On which structure does a pollen grain land to effect pollination?
B
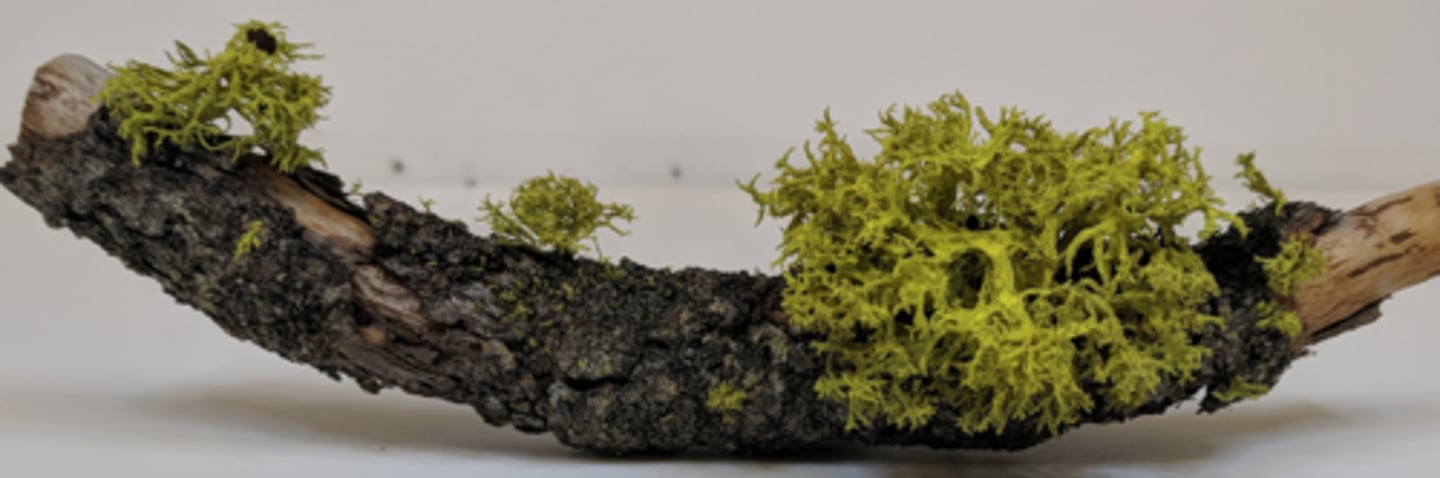

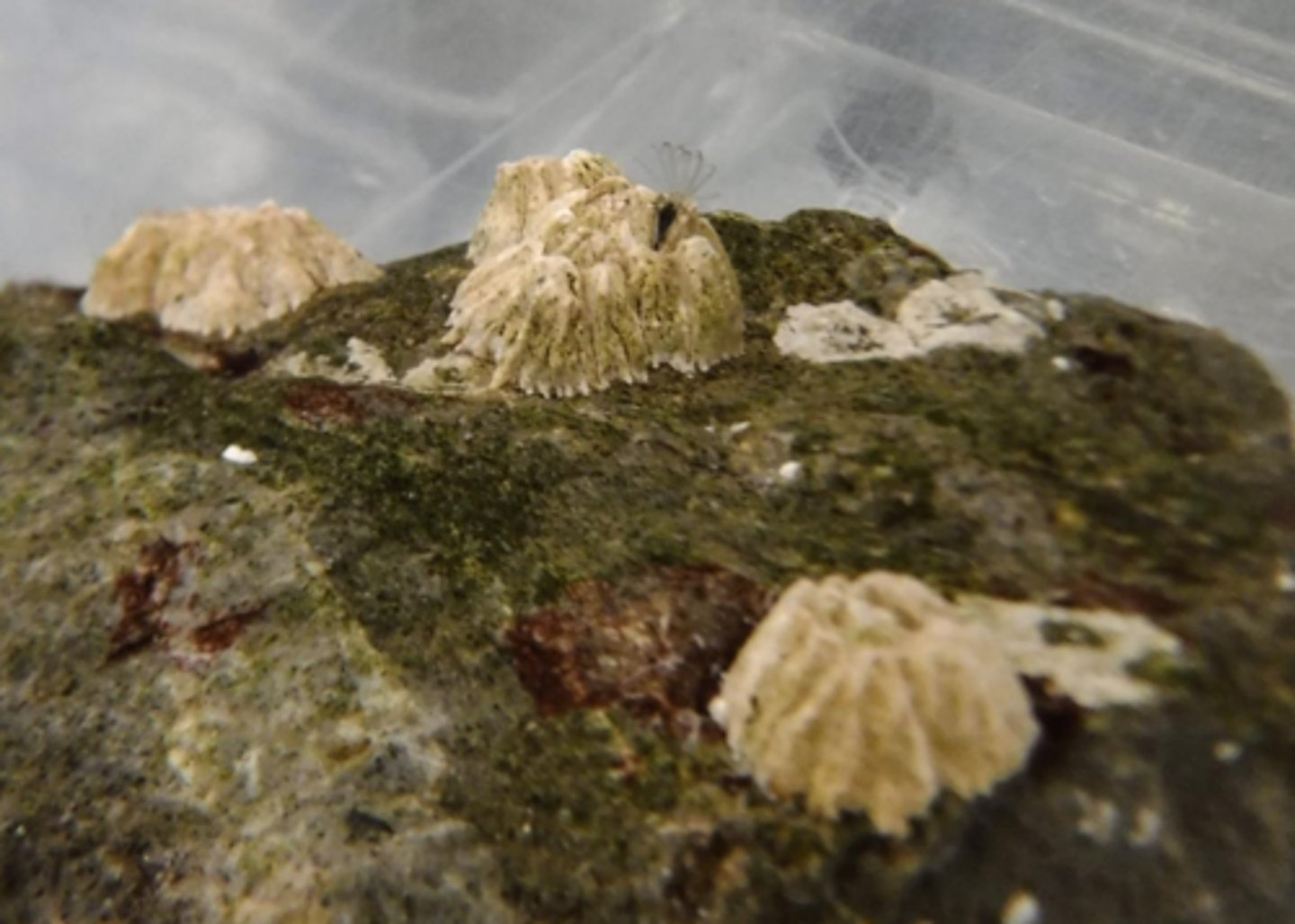
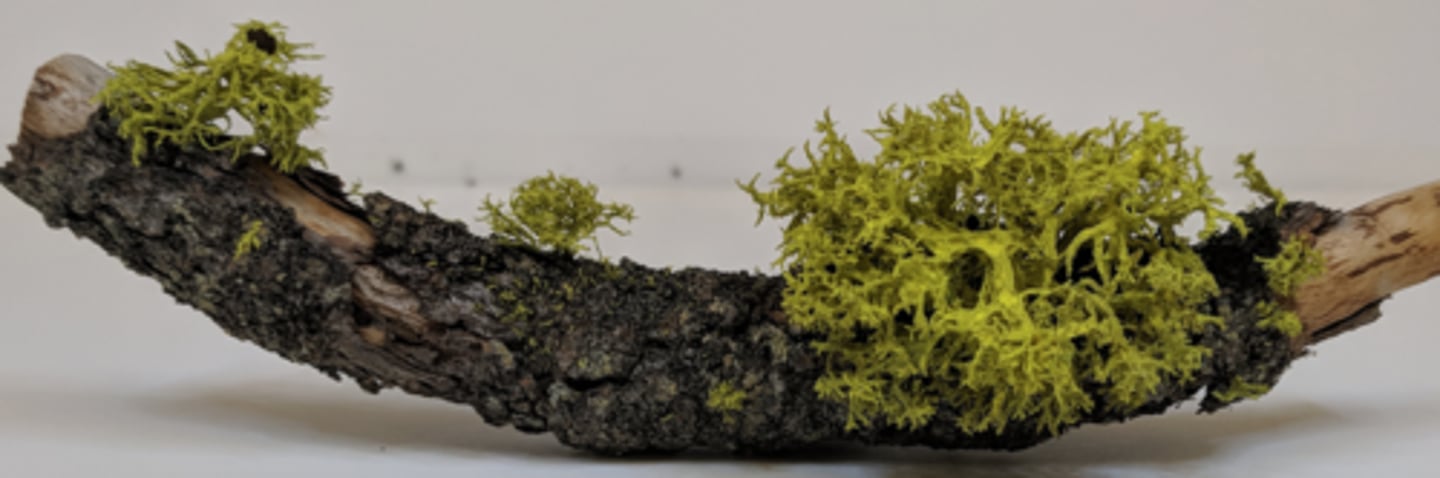
The green organism growing on the stick is a:
Lichen
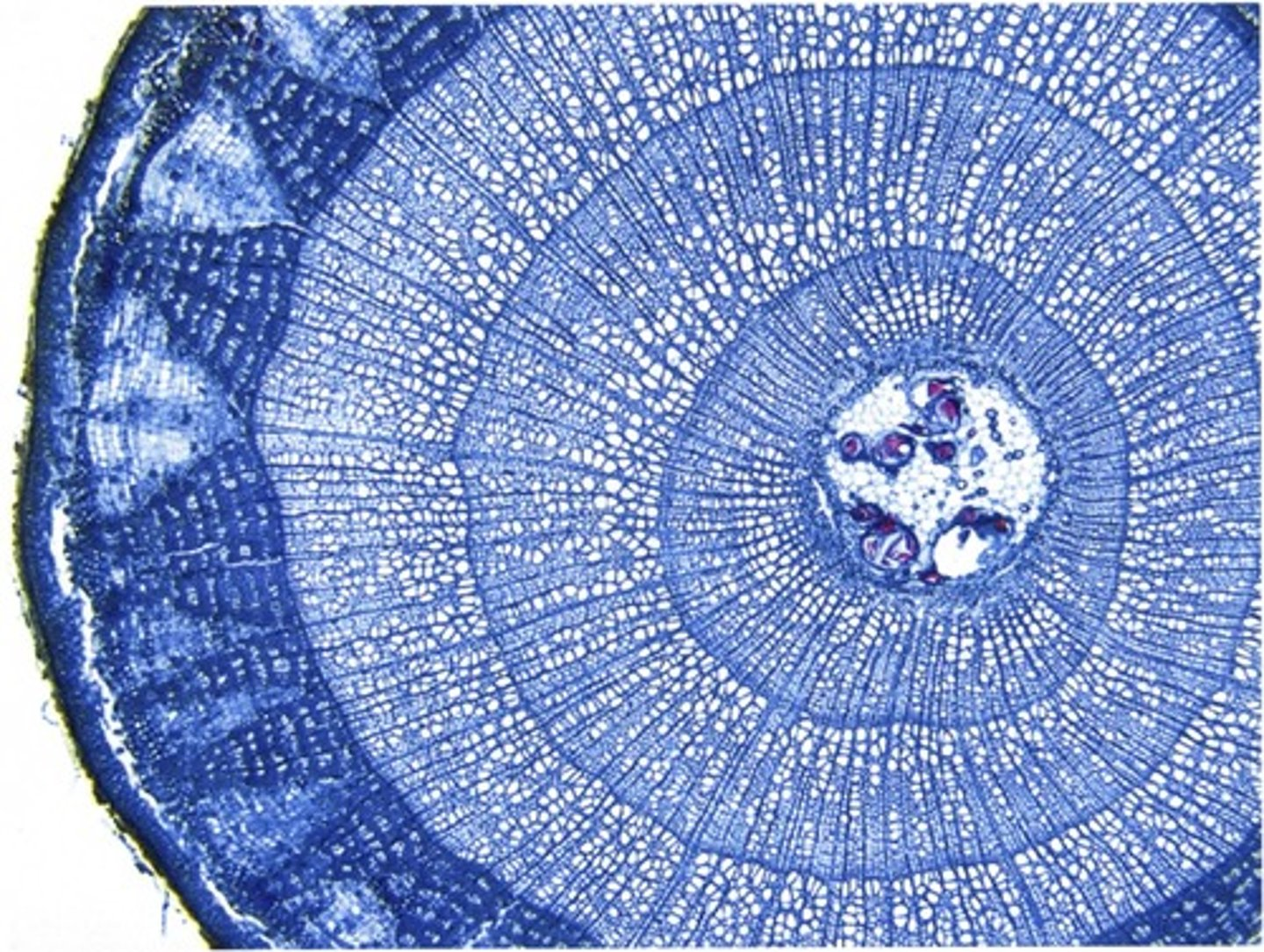


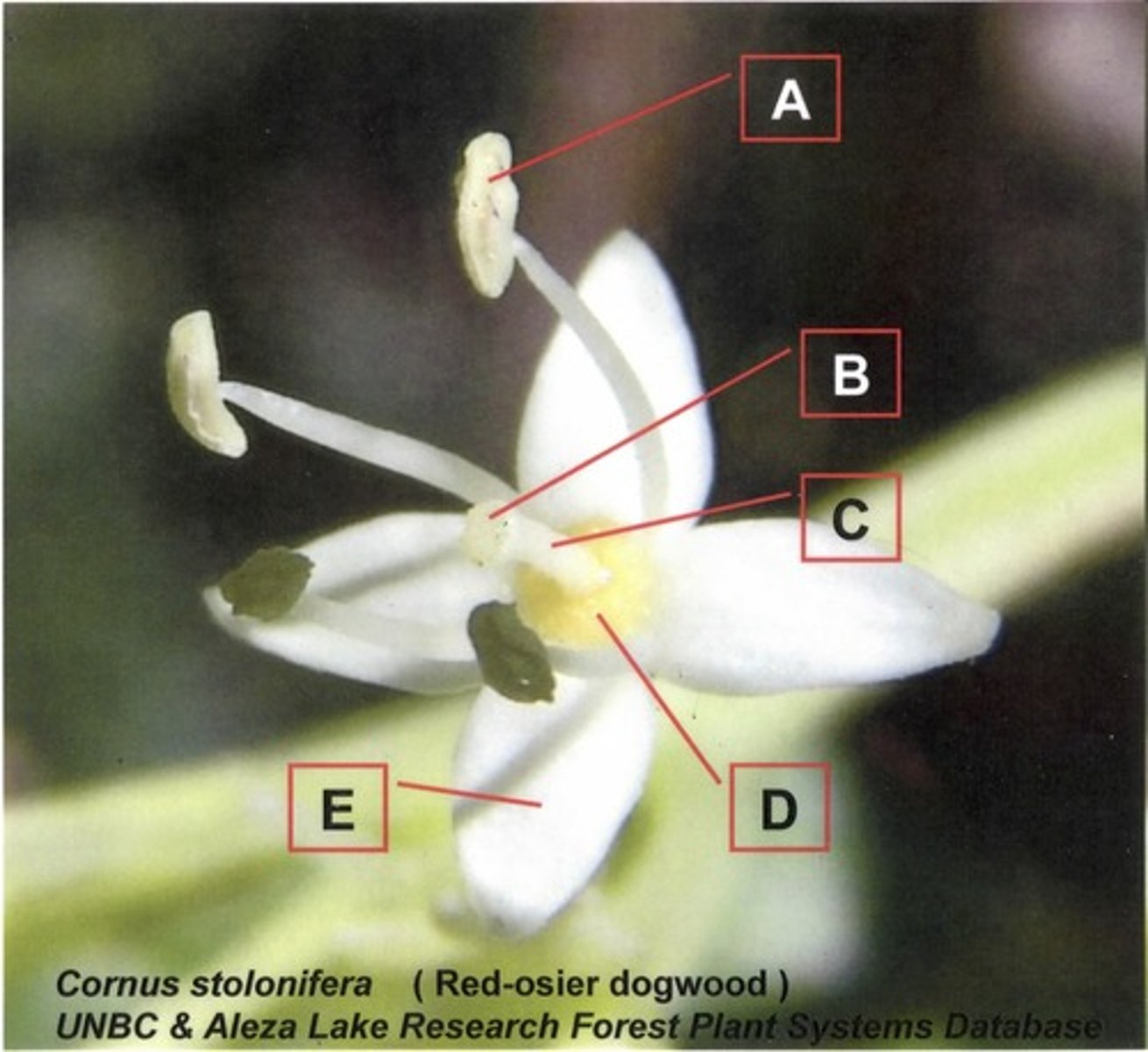
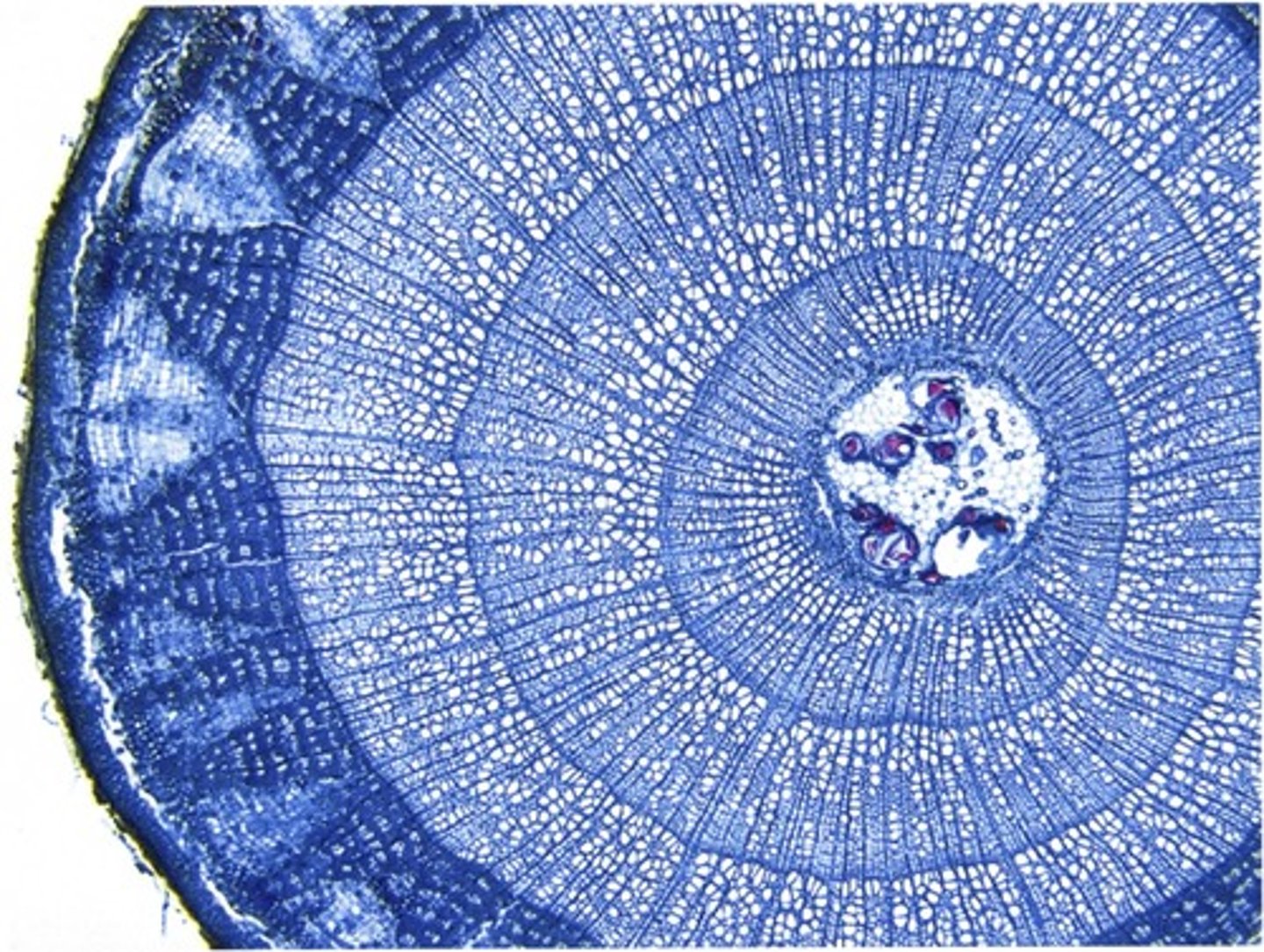
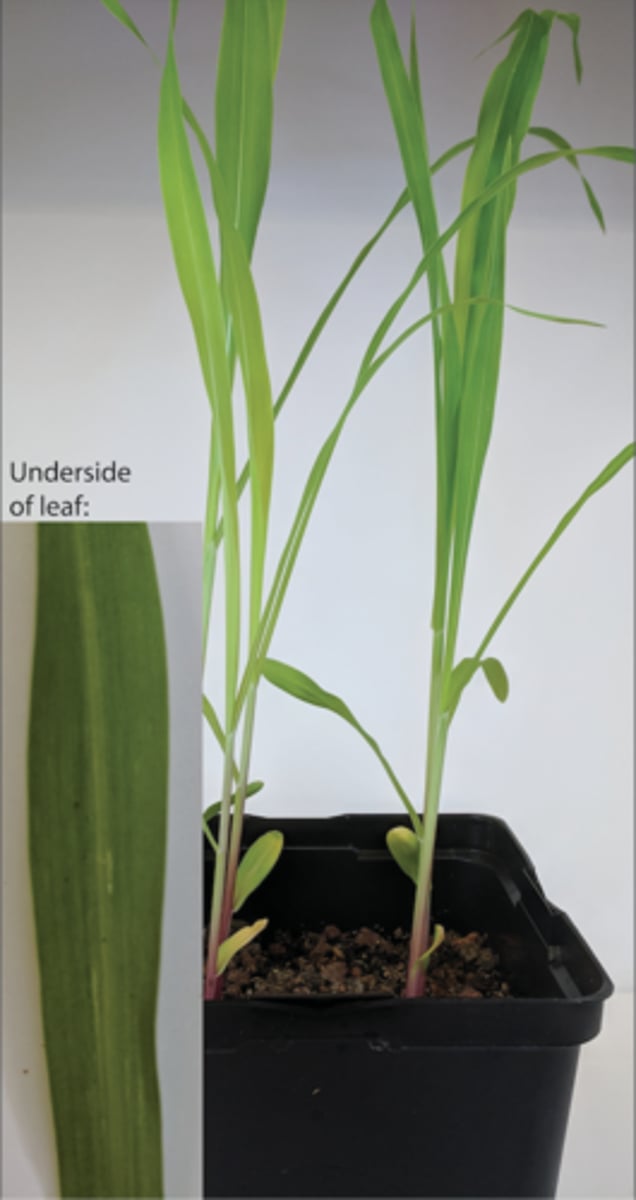
Based on the stem cross-section in the image above, what can you say about the plant it came from?
It has a bifacial vascular cambium
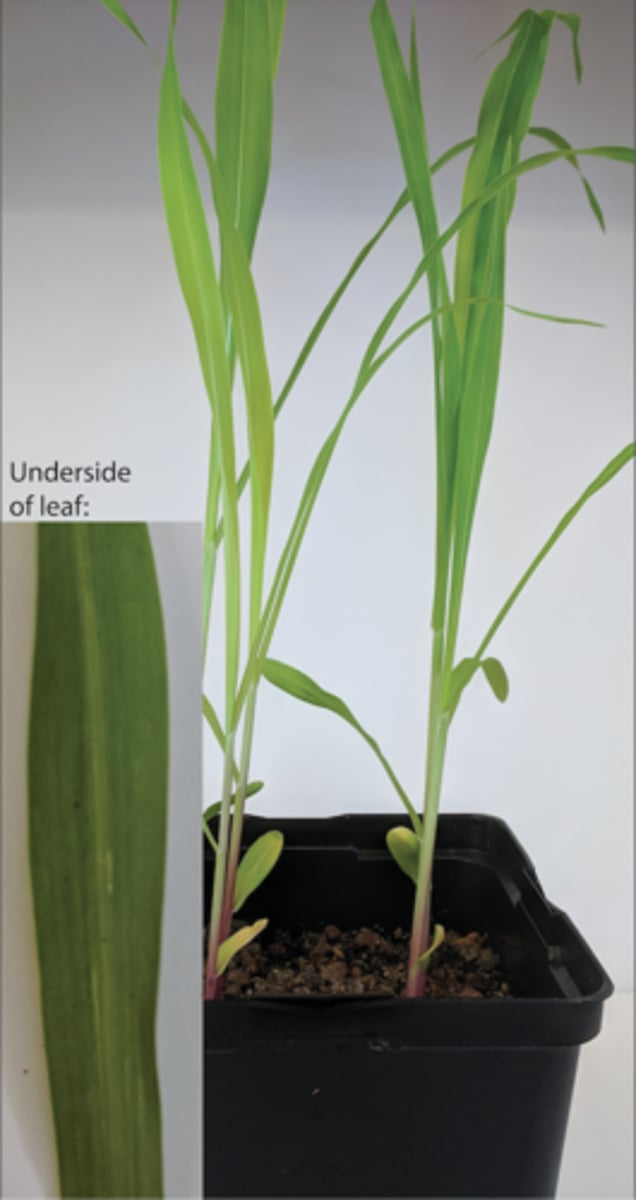


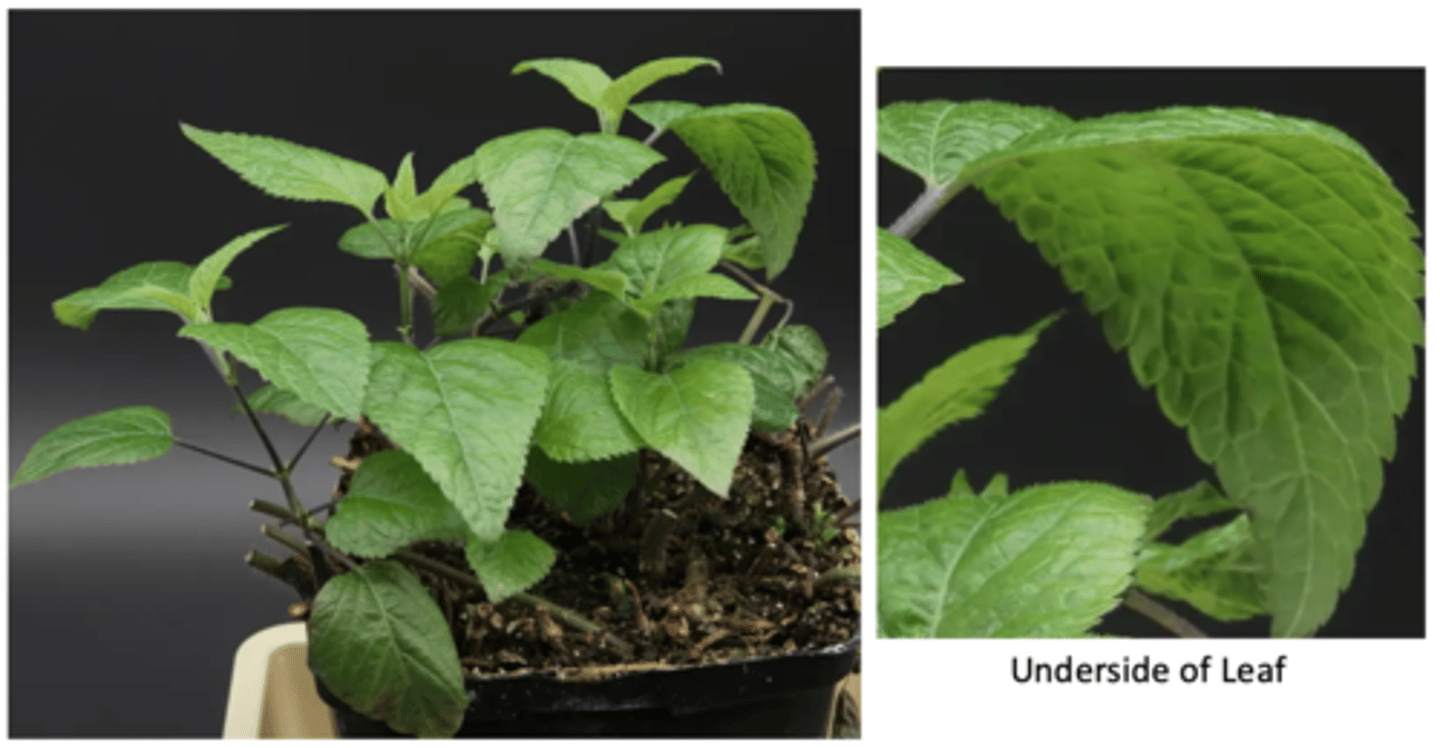
Which of the following features are not associated with the plant pictured above?
A seed with two cotyledons

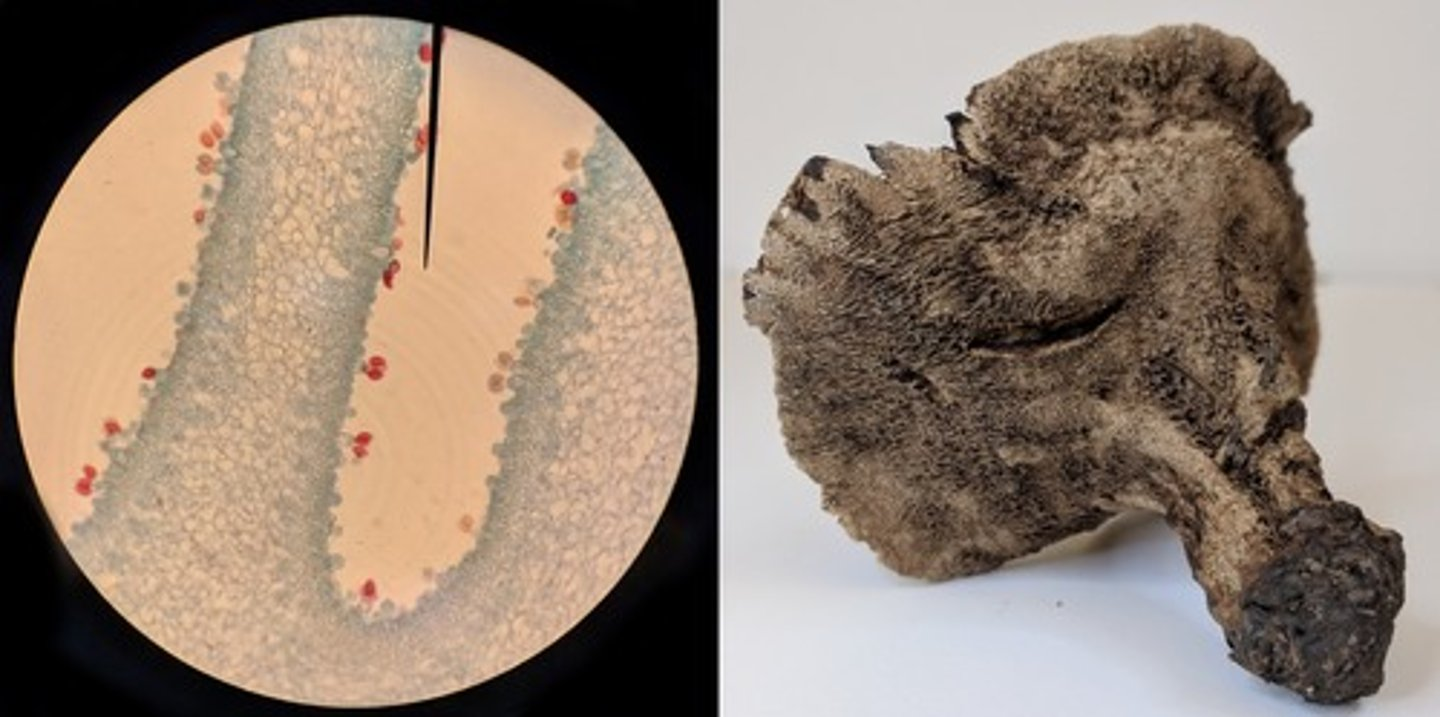
Based on the images above and the provided dichotomous key, what is the identity of this fungus?
Hydnellum
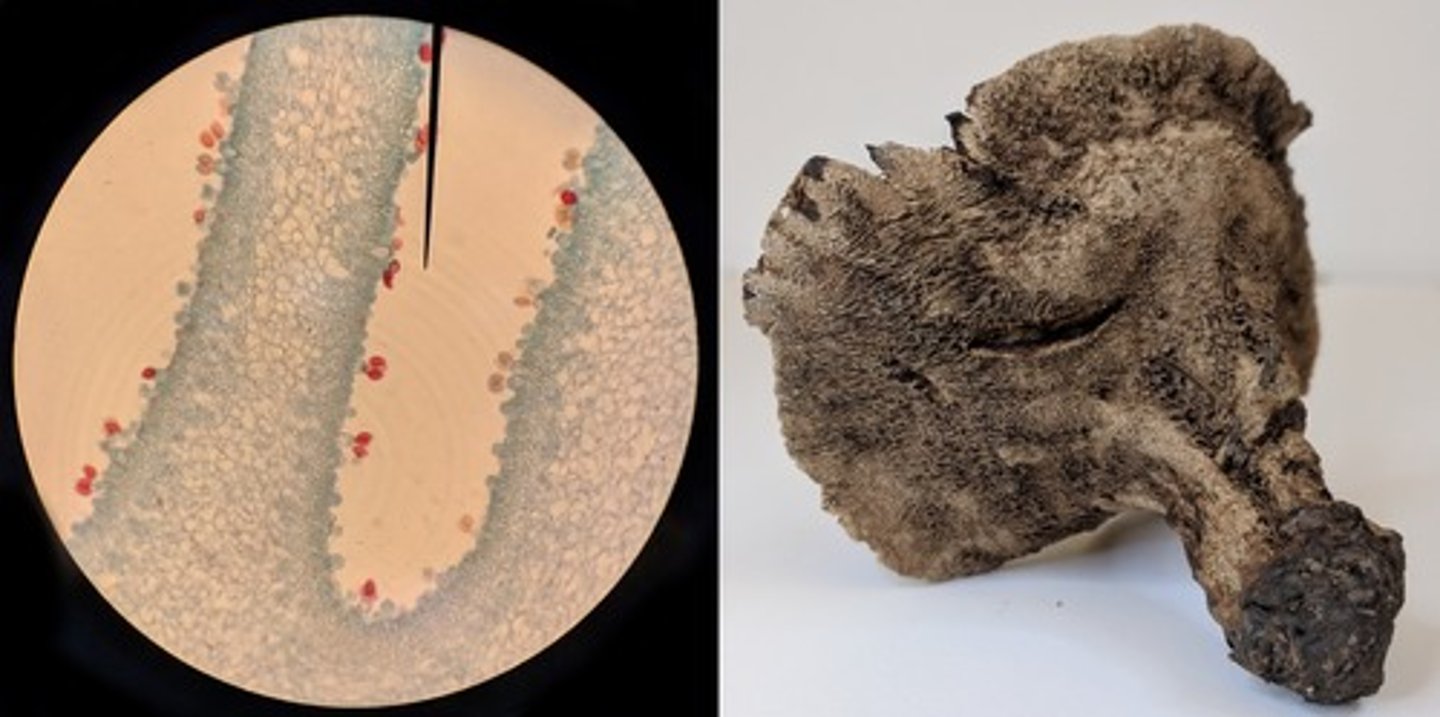
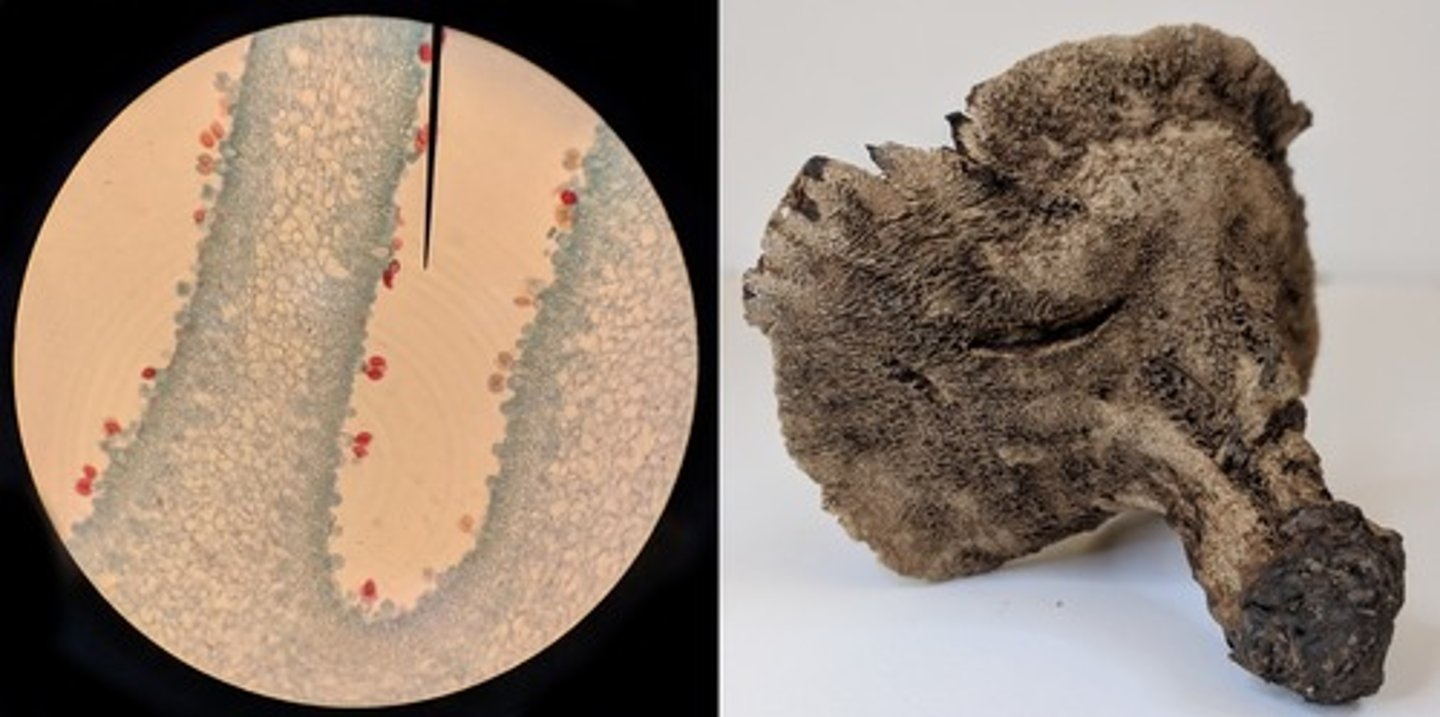
Which of the following structures would not be found in the life cycle of the fungus shown above?
Multicellular diploid tissue

Which of the above animals are you most closely related to?
A
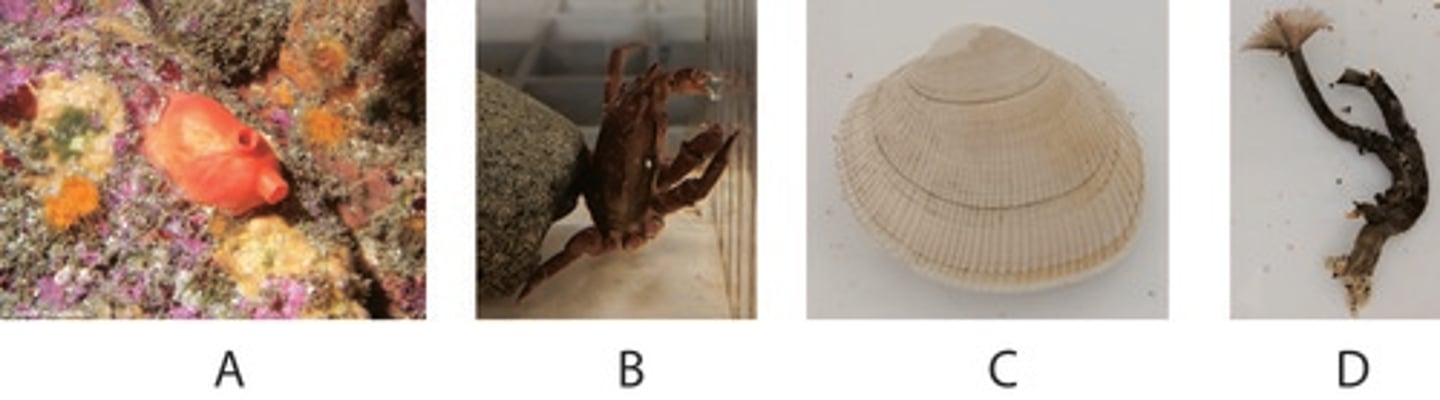
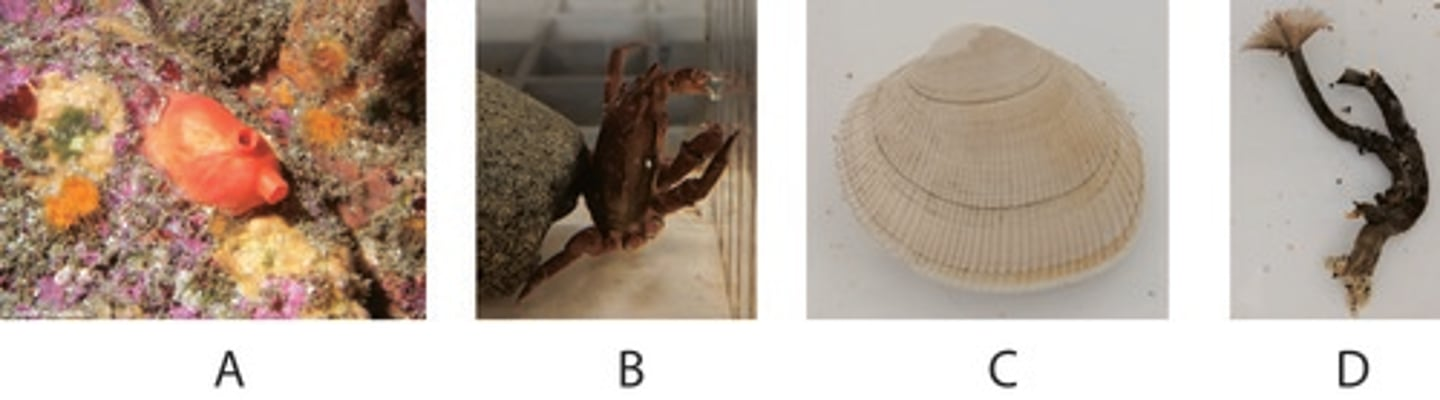


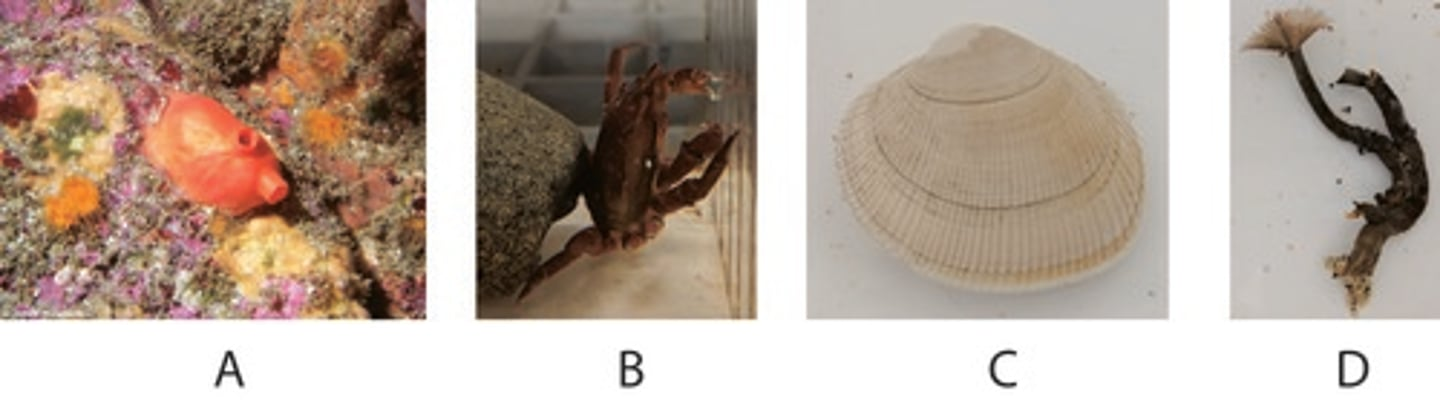
Which of the above animals have trocophore larva?
C,D
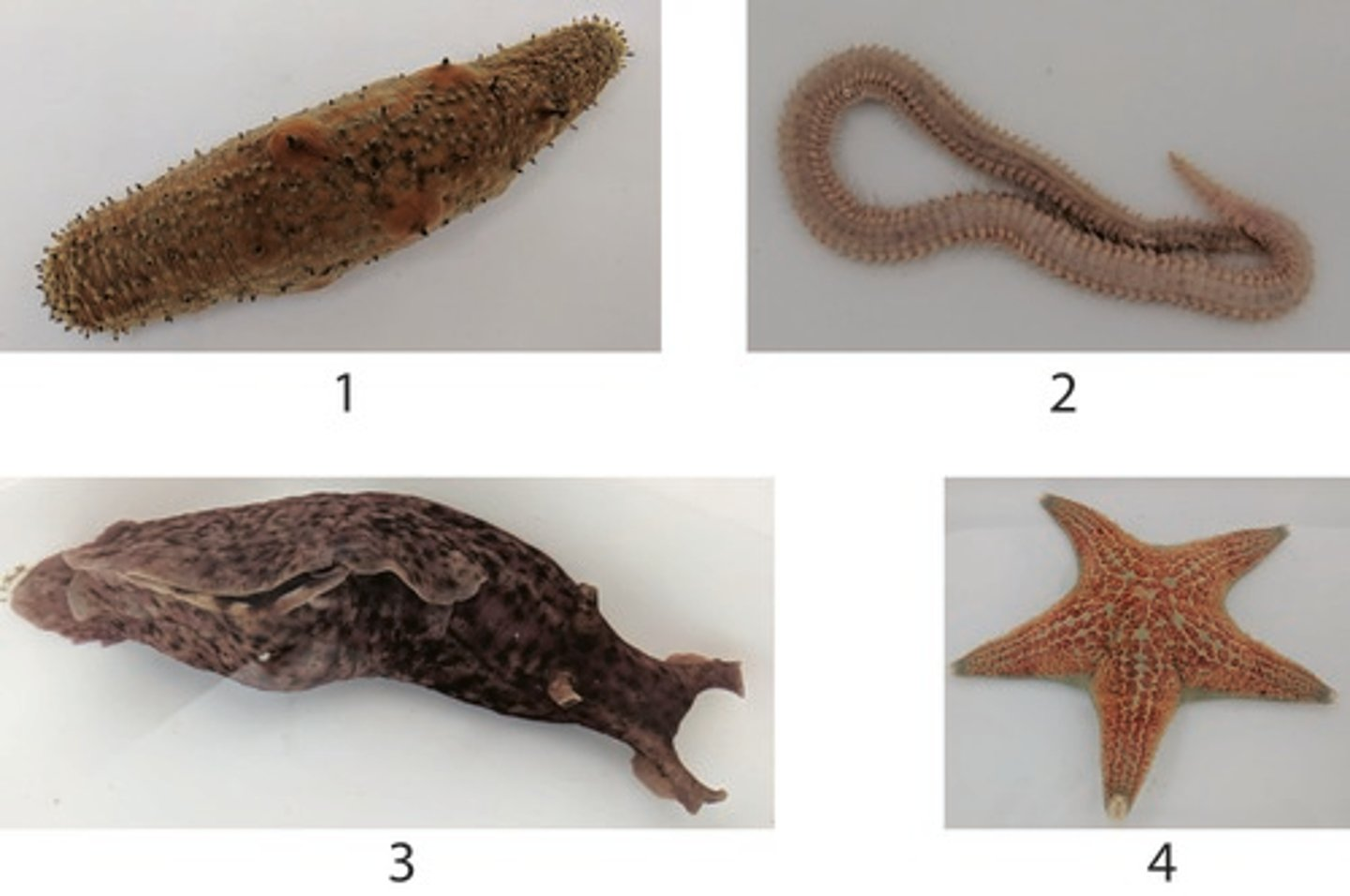

Which of the above animals has a mantle?
3
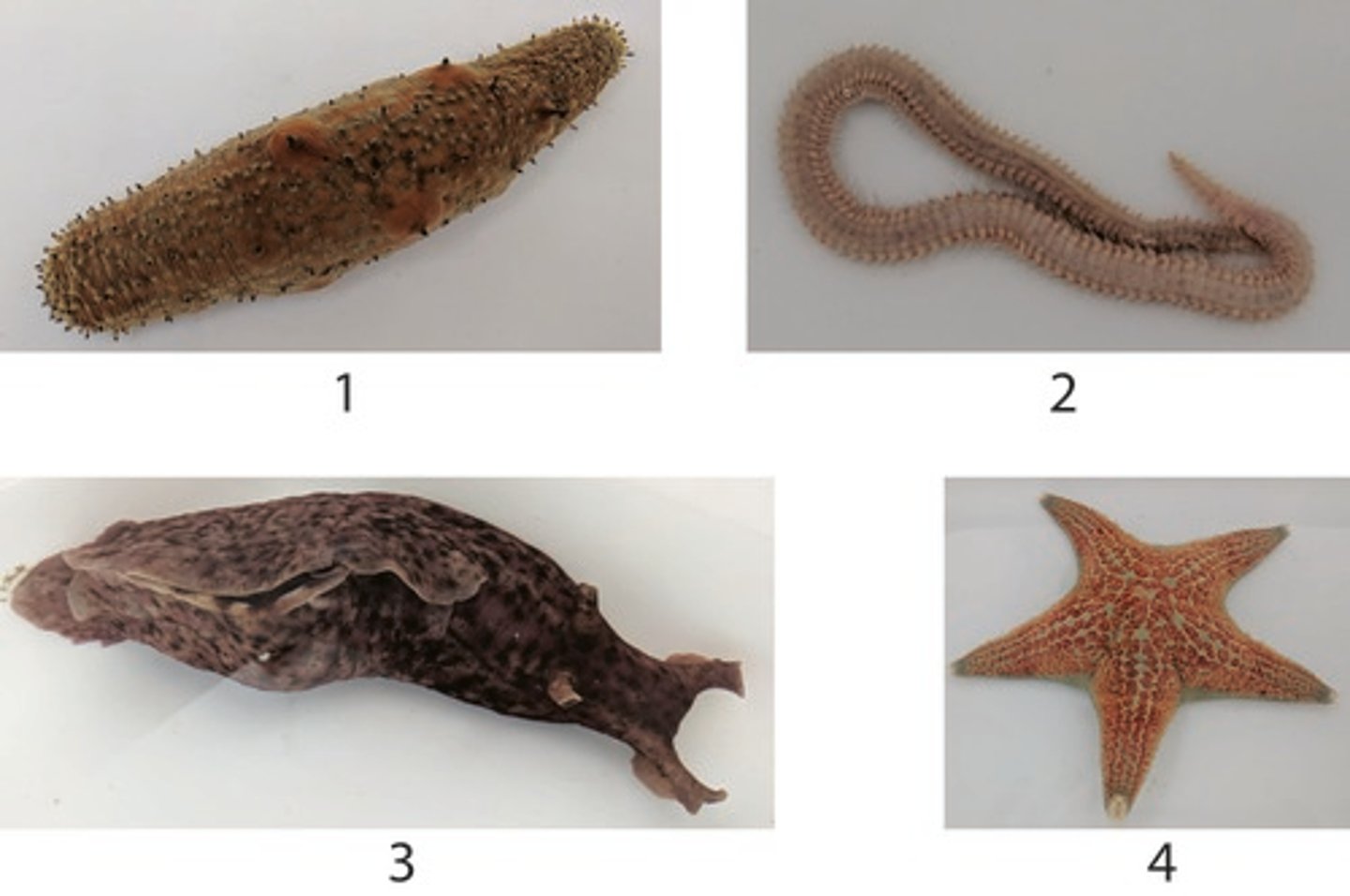
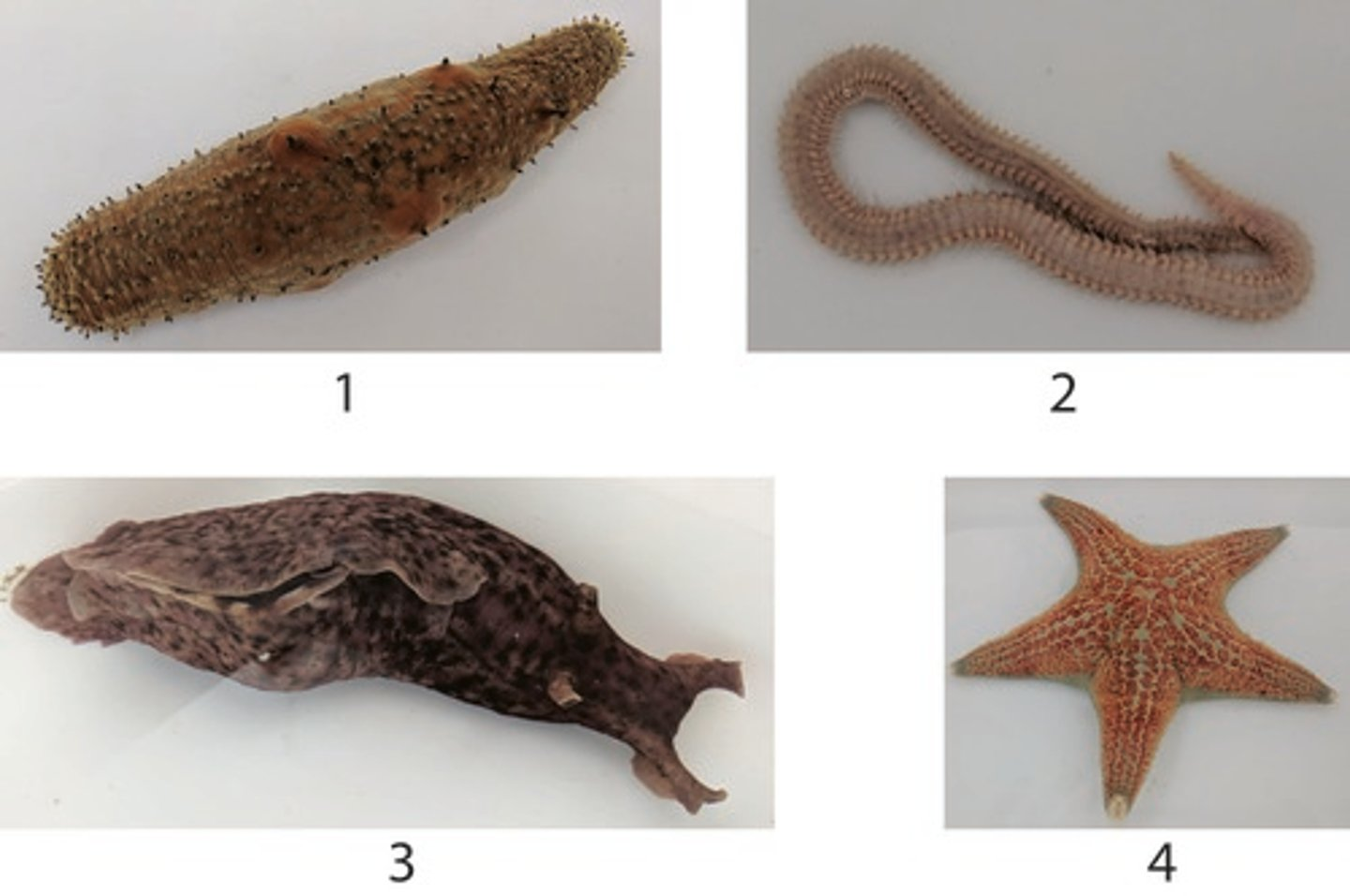


Which of the following features is NOT found in ALL of the above organisms (1-4)?
Cephalization
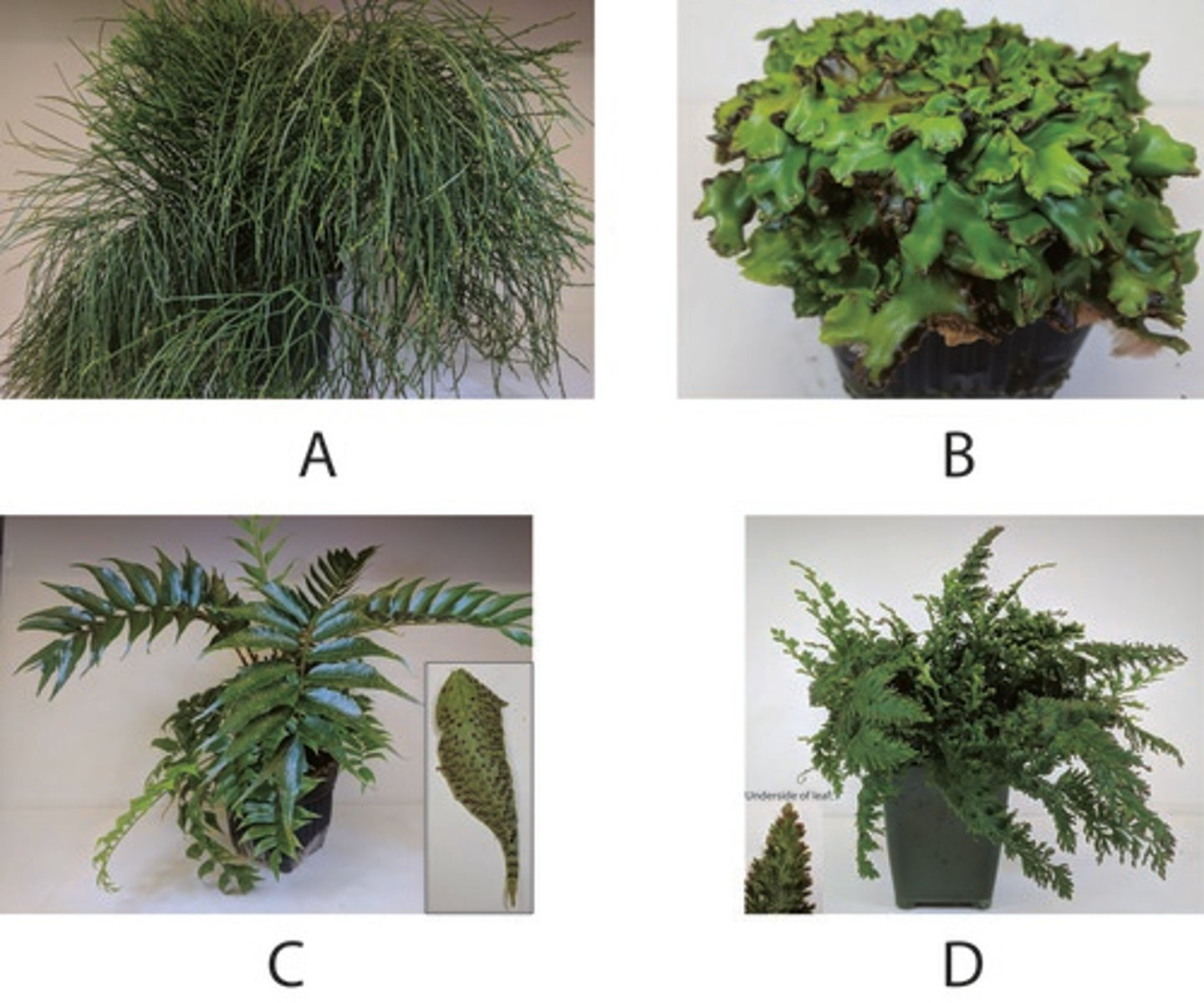
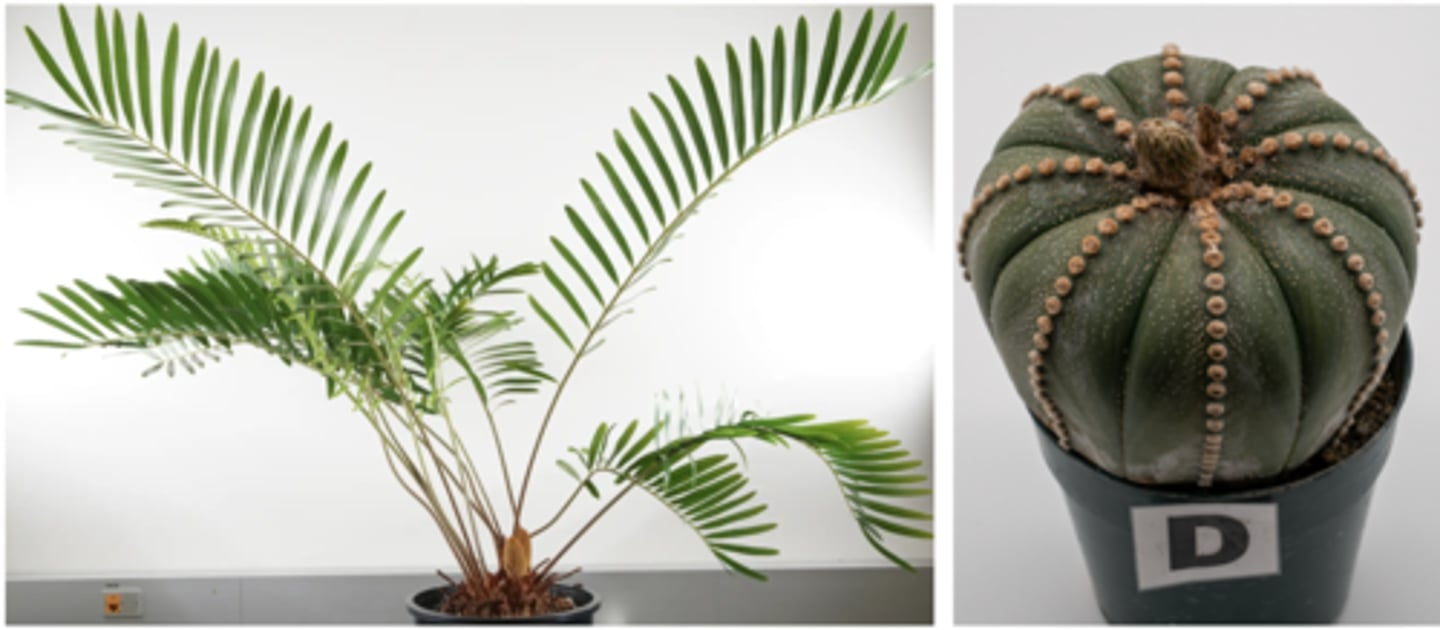
How many of the above plants have a homosporous life cycle?
3
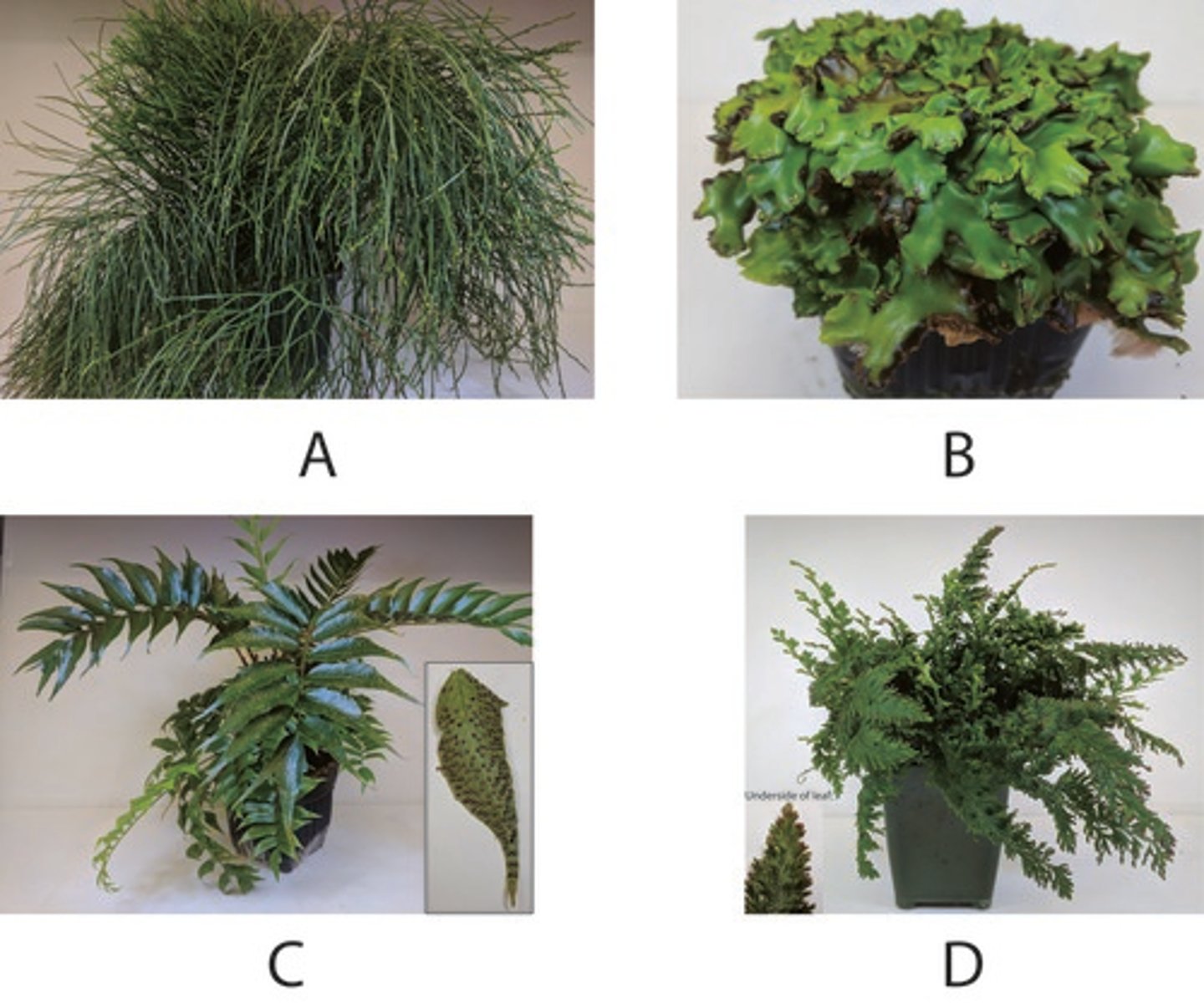
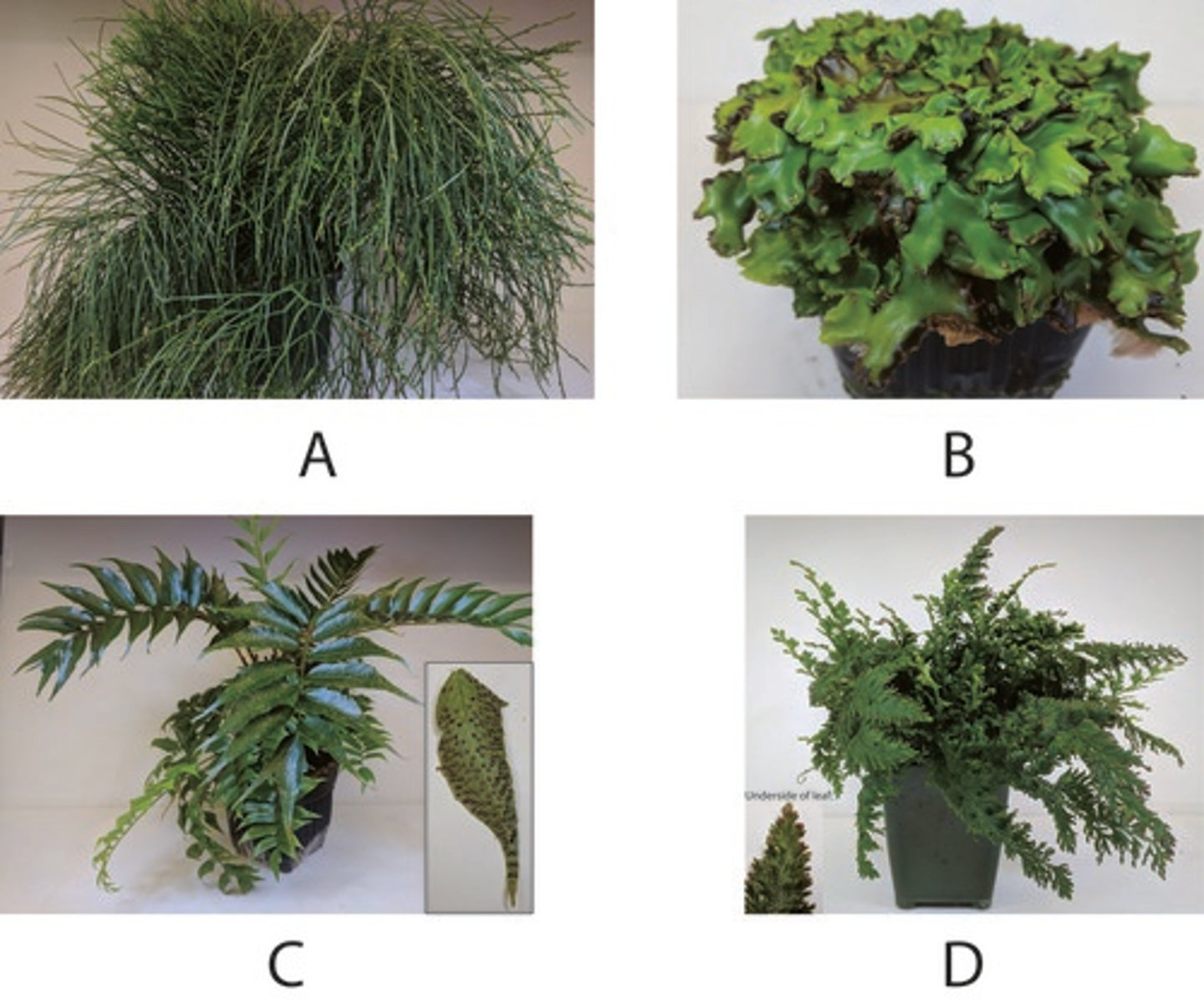
Which of the above plants does NOT have tracheids?
B
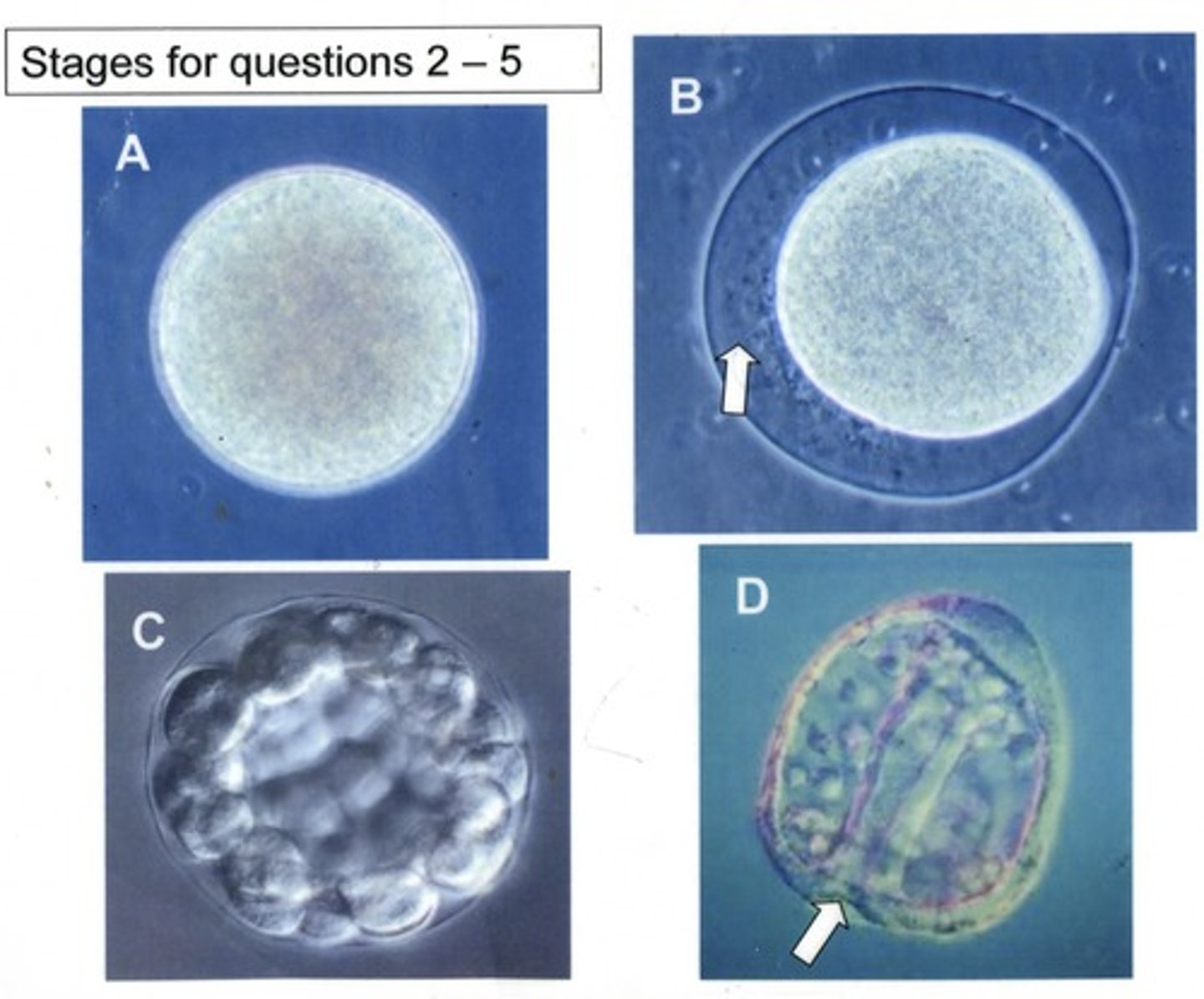
These four images show different stages in sea urchin development. What structure in the adult stage will be formed from the arrow shown in figure D?
Anus
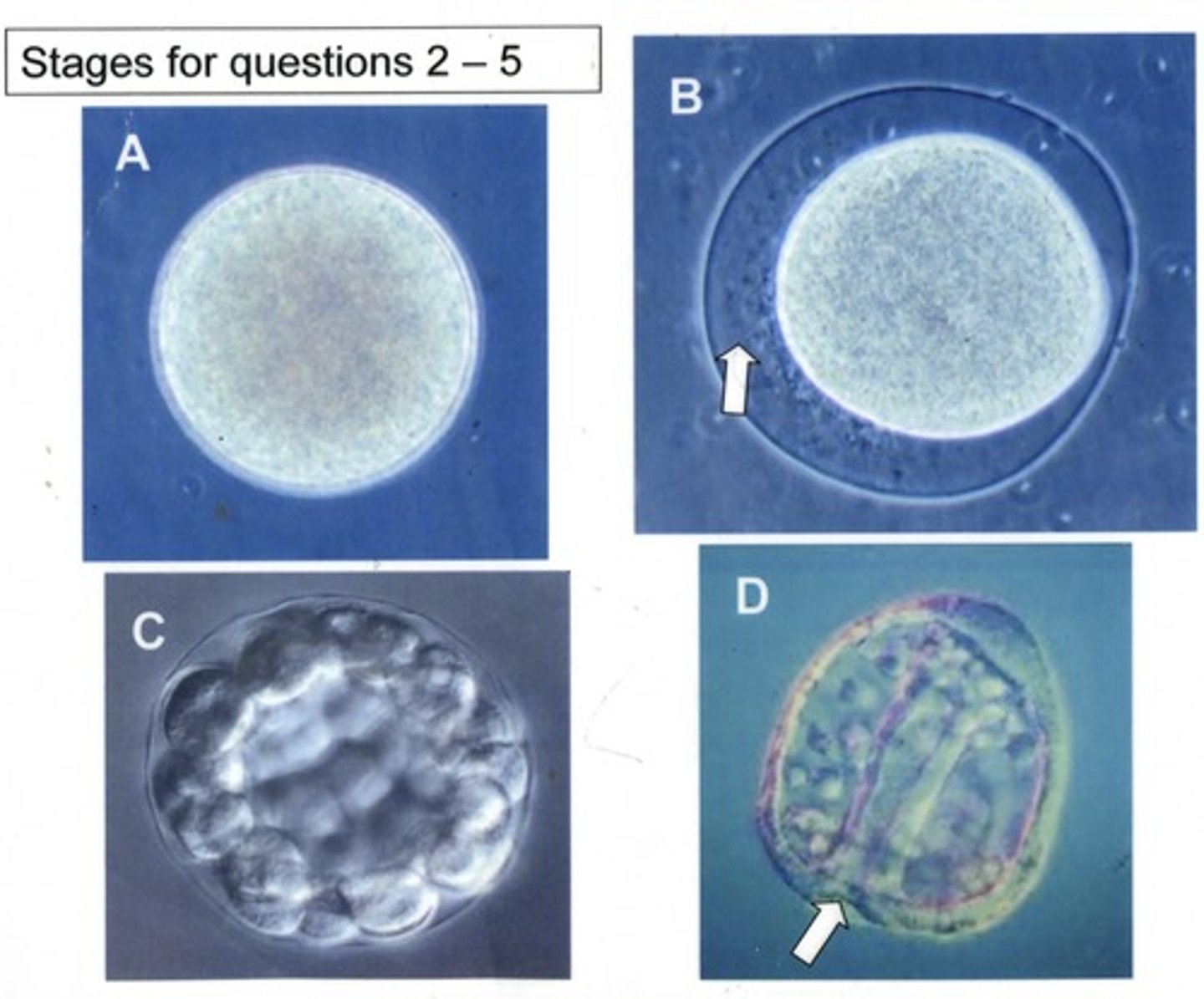
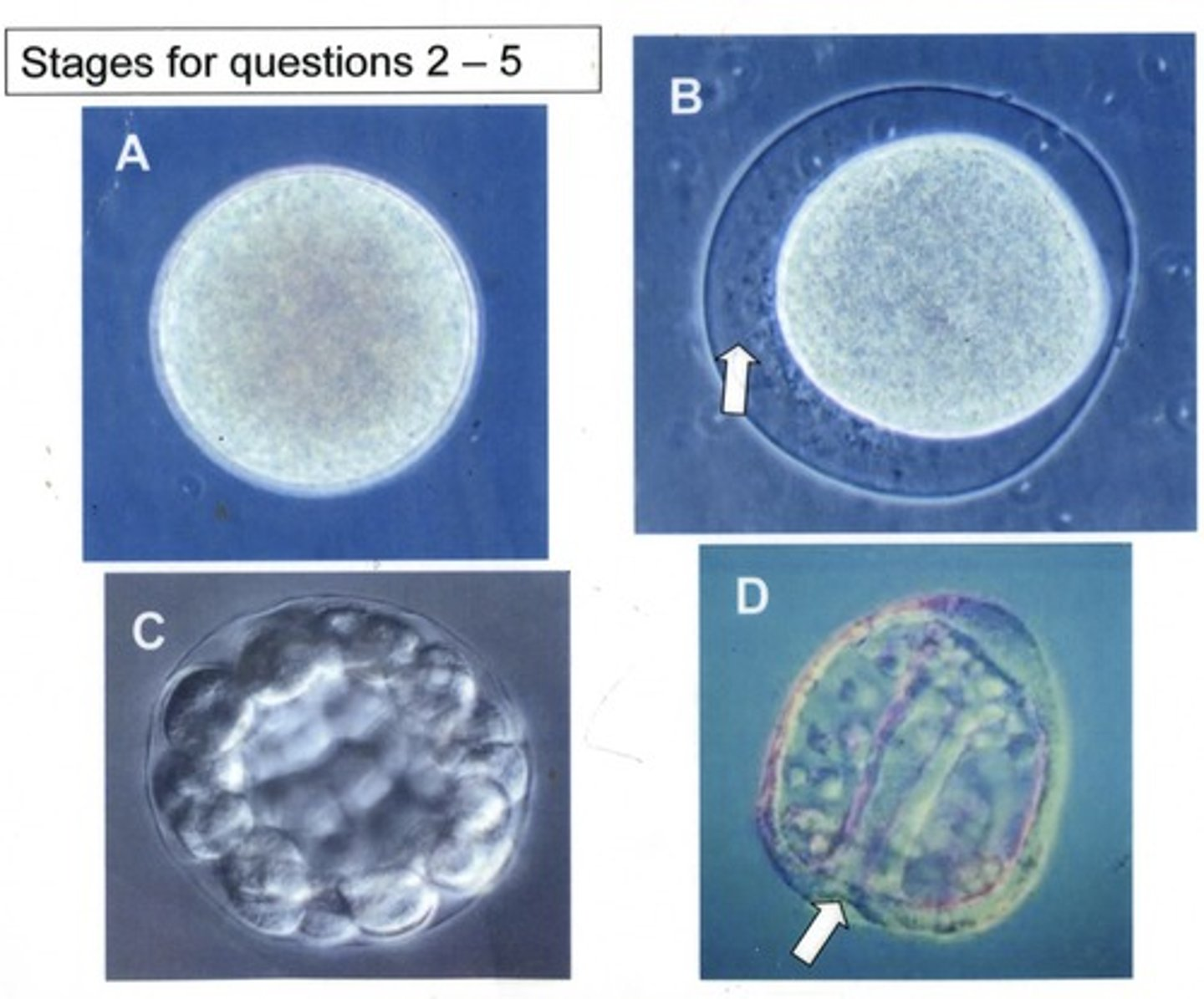
Which of these stages are found in all animals?
A,B,C
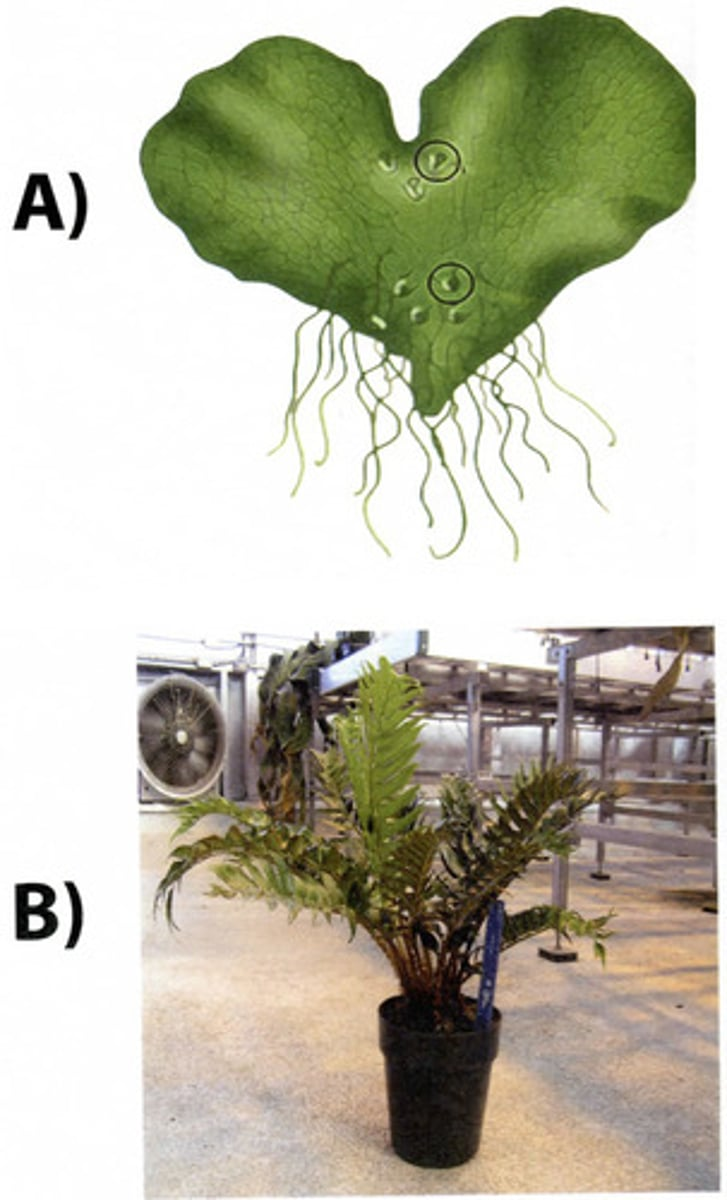
What is the ploidy level of the tissues for plants A and B above?
A=haploid , B= diploid
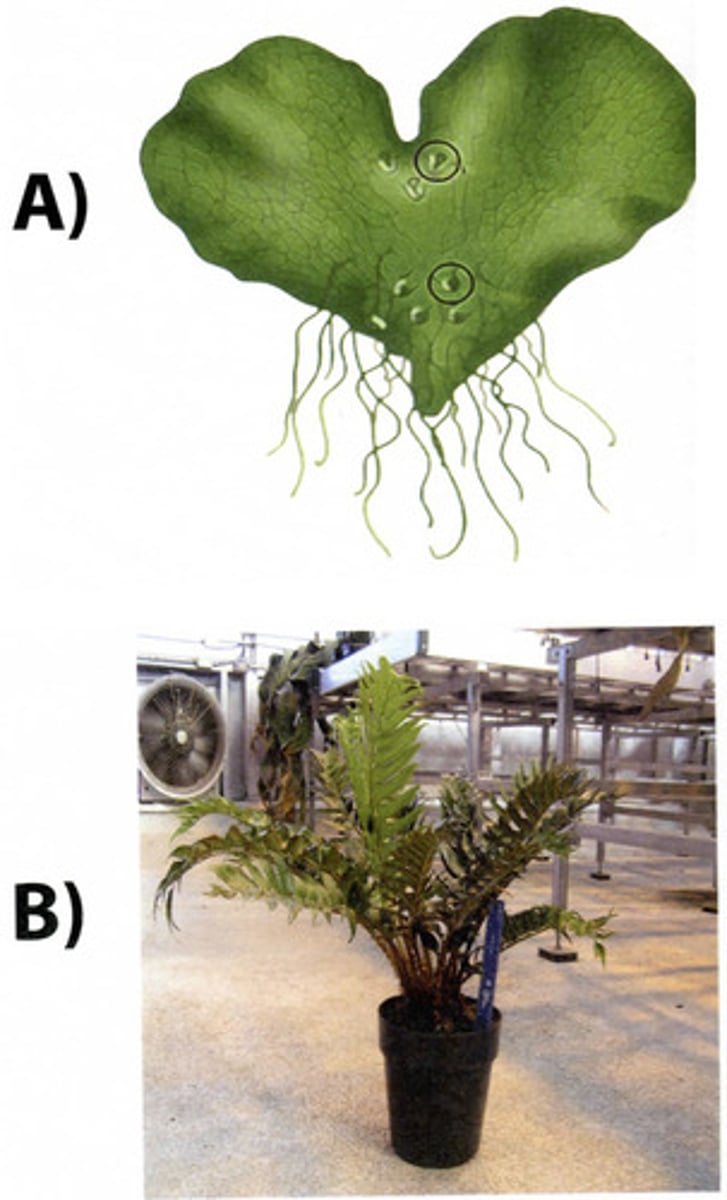
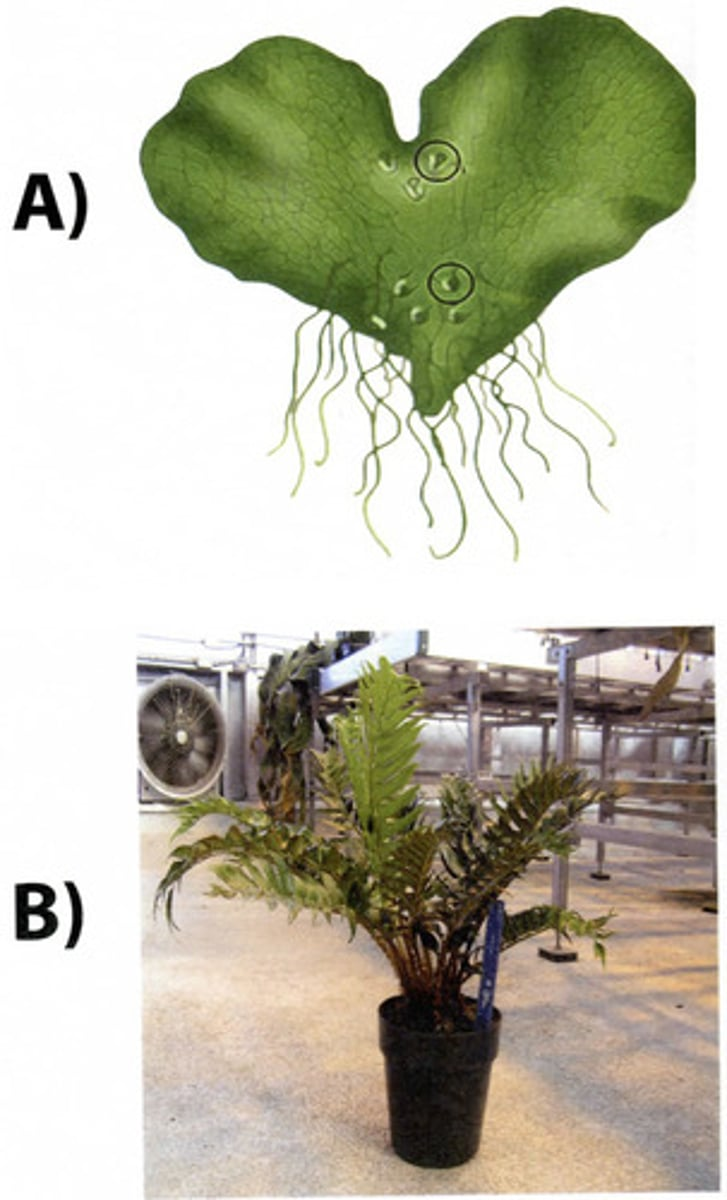
What do plants A and B produce?
A=gametes, B=spores
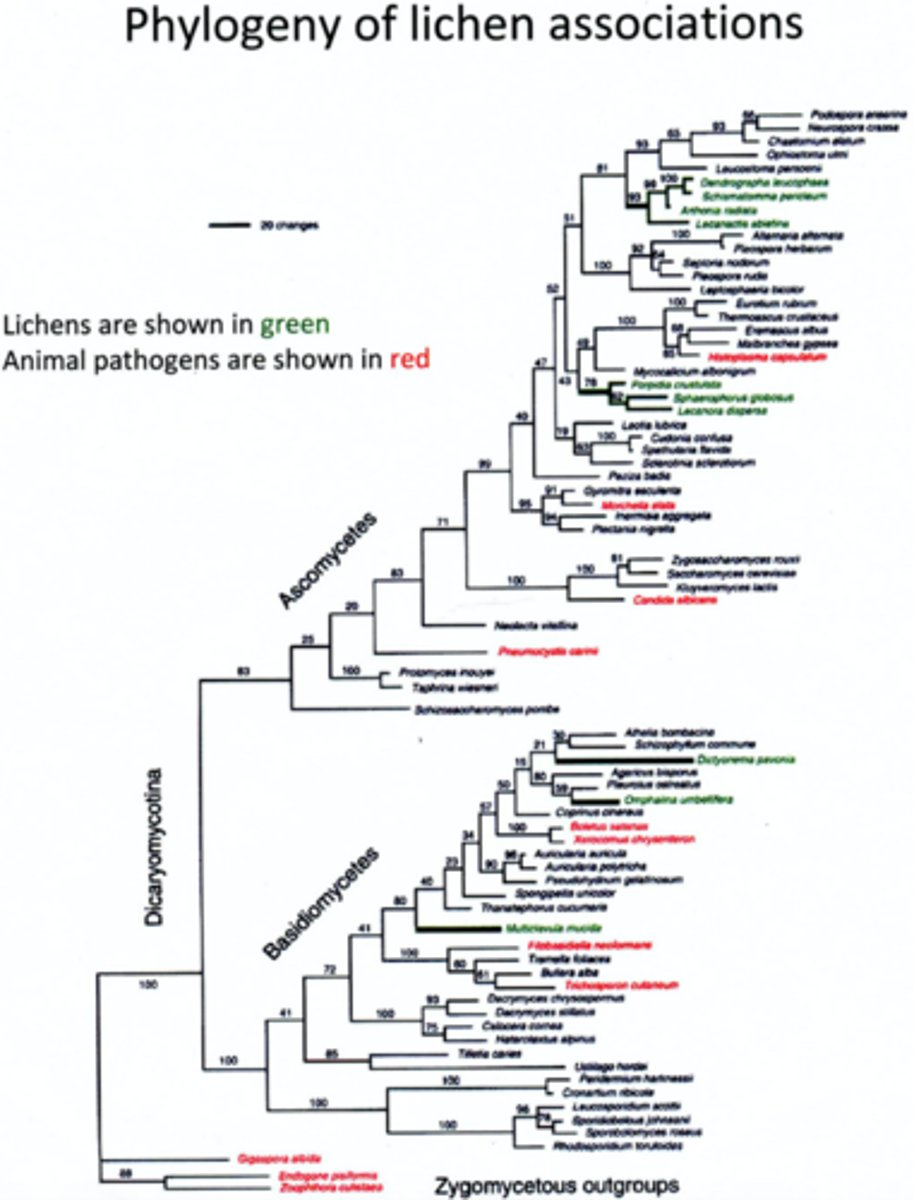
Based on the phylogeny above and the principle of parsimony, is the lichen morphology homologous across all of the lineages in which it is found?
Lichen morphology is not homologous because it is most parsimonious for lichen morphology to have evolved independently than to have a MRCA with lichen morphology that has been lost in several lineages.
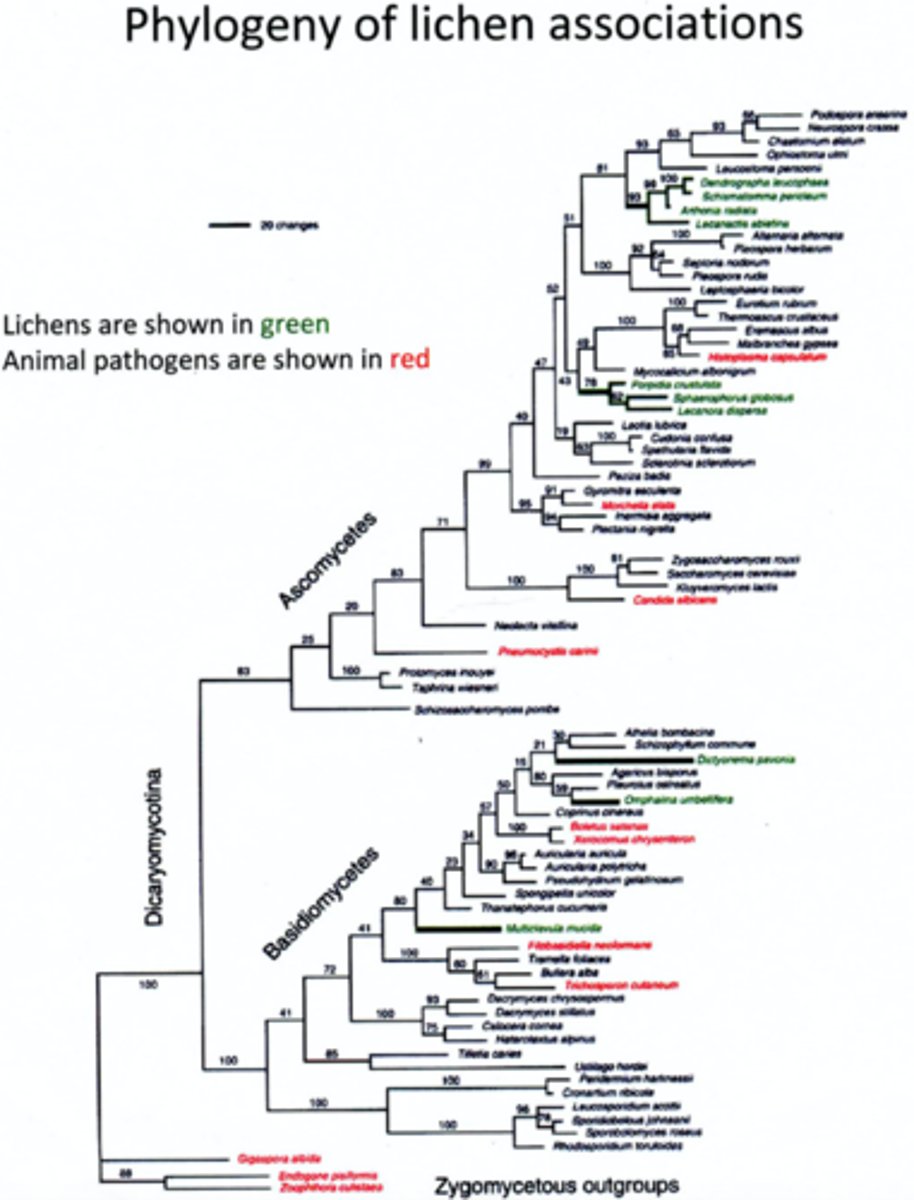
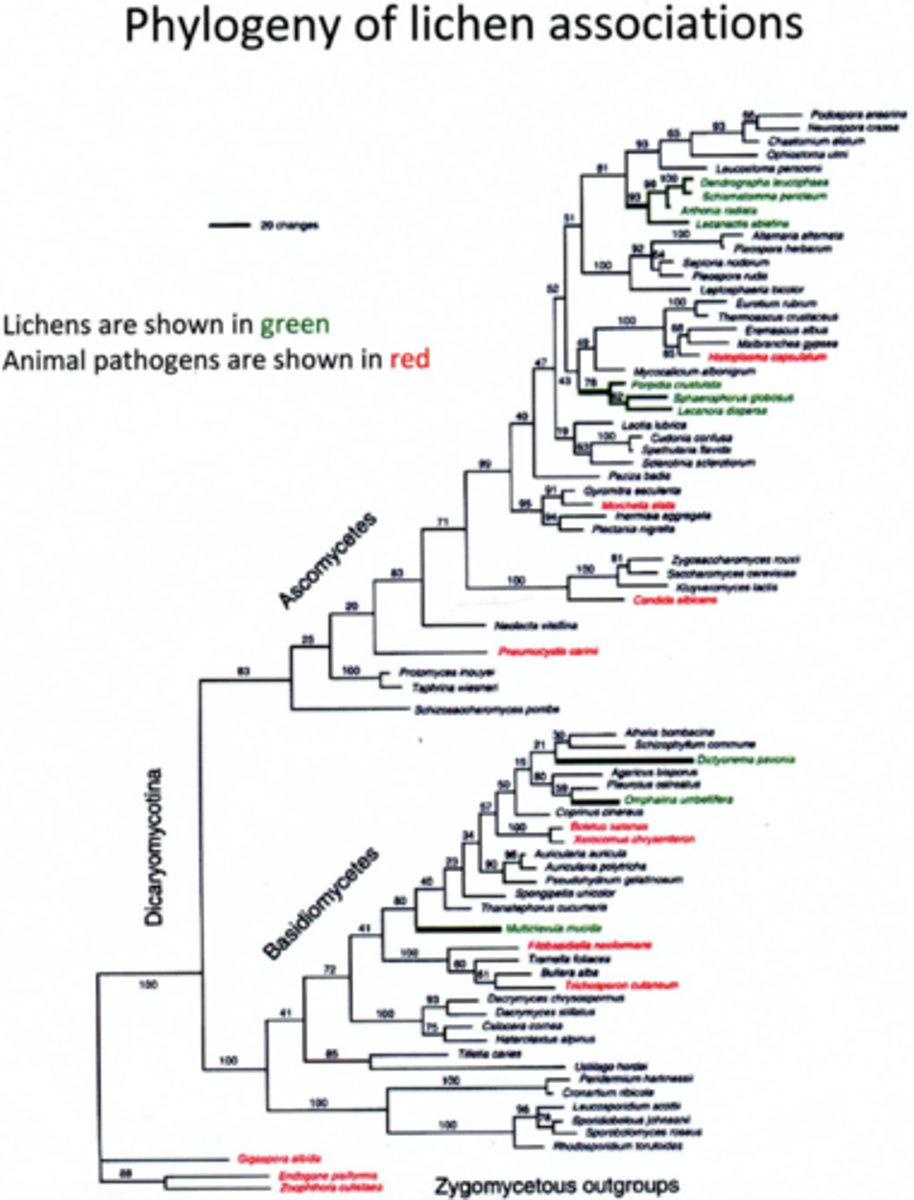
Which of the following questions would you be able to address using the phylogeny above? Explain your answer.
1) Which non-lichen fungi are most closely related to each group of lichens.
2) Which group of lichens has the highest mutation rate for the genes used to build this phylogeny.
3) Which group of lichens was the first to evolve.
You could answer questions 1 and 2. The tree is a phylogram so it gives relationships between taxa and rates of character changes. The tree does not give any sort of information about time so question 3 would not be able to be answered.
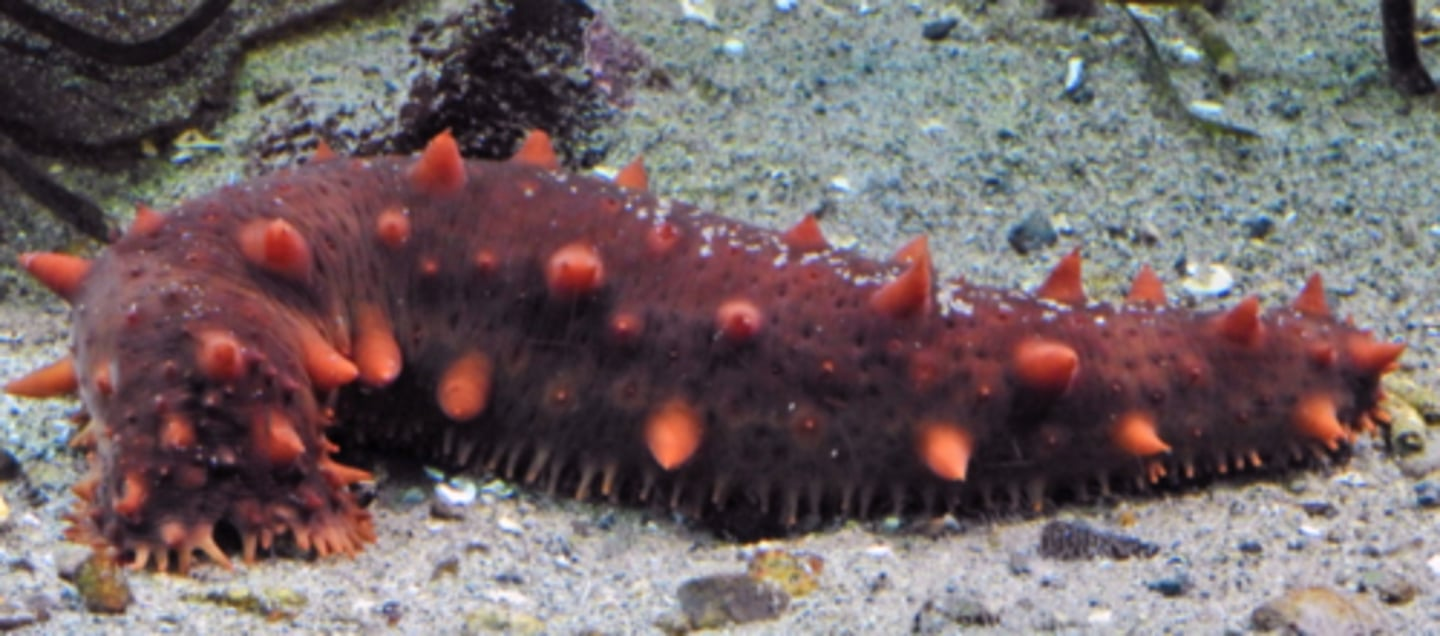

What group does the above animal belong to?
Echinoderm
Explain how you knew it was not each of the other options for the previous question.
It is not a cnidarian because it has pentaradial symmetry not radial. It is not an annelid because it is not segmented. It is not a mollusk because it does not have a large muscular foot on the bottom. It is not a chordate because it does not appear to have cephalization or a post anal tail. It also does not have siphons like a tunicate.
Lateral Gene Transfer
DNA moves from one organism to another
LGT Differences
Unidirectional, small portions of genomes, can occur across vast evolutionary distances
Trasnformation
DNA picked up from environment from lysed cell
Conjugation
Transfer of DNA from one cell to another
Transduction
Incorporation of DNA through viral particles
Microbiome
Collection of microbes that inside and on our bodies
Cilliate
Blepharisma, Paramecium, Stentor
Flagellate
Euglena, Chlamydomonas
Amoeboid
Amoeba
Epiphytes
Grow on other plants but not parasites, competition for sunlight, nutrients and water
Stem Modifications
Photosynthetic stems, reduced leaves to conserve water, storage stems, shock absorption, growth for sunlight, reflect away sunlight, have apical meristems and axillary meristems at nodes
Leaf Modifications
Can have meristems for growth (indeterminate growth), large surface area for photosynthesis, red underlayer to bounce back light for extra photosynthesis, leaves act as flower to catch insects, produce sweet nectar, reflective to reflect excess sunlight, close up for protection and exposure
Pollination
Number of flowers, size of flowers, color of flowers, symmetry of flowers, shape for pollinators, fragrance to attract pollinators
Dispersal
Flowers, fruit, seeds, vegetative/asexual
Biogeography
Euphorbiacea- Triassic, Cactaceae- Pleistocene, Didieriaceae- Pleistocene/present
Porifera
Spicules, no gut, asymmetrical. Ex: Sponges
Cnidaria
Cnidocytes, incomplete gut, planula larva, radial symmetry. Ex: Anemones, jellies, hydroids
Mollusca
Mantle, shell, radula, complete gut, bilateral symmetry. Ex: Turban snail, limpets, Kellet's whelk snail, Dorid nudibranchs, chitons, California sea hair, aeolid nudibranchs, giant rock scallop, bay muscles, smooth Washington clam
Annelida
Paired setae, segmentation, bilateral symmetry, segmentation. Ex: Feather-duster worm, rag worm, spaghetti worms, earthworm, leeches
Arthropoda
Exoskeleton, segmentation, ecdysis, bilateral symmetry, complete gut. Ex: Porcelain crab, hermit crab, gooseneck barnacle, acorn barnacle, horseshoe crab, crab, tarantula, cockroach, scorpion, shrimp, desert millipede, death feigning beetles, painted lady butterfly
Echinodermata
Water vascular system, tube feet, calcite exoskeleton, pentaradial symmetry, complete gut. Ex: Purple urchin, sea cucumber, sand dollar, brittle star, bat star, plaster star, chocolate chip star
Chordata
Notochord, post anal tail, dorsal hollow nerve chord, pharyngeal slits, endostyle/thyroid, bilateral symmetry, complete gut, segmentation. Ex: Tunicates
Blastula
Hollow ball of cells, in all animals, Porifera only have this stage (monoblastic)
Pentaradial Symmetry
5 planes of symmetry, only in Echinodermata
Spicules
Hardened structures made by cells that serve as support structure, in Porifera
Cnidocytes
Specialized stinging cells, only in Cnidaria
Ecdysis
Shedding of exoskeleton, molting of cuticle, in Nematoda and Arthropoda
Segmentation
Body is split up into repeated units, in Annelida, Arthropoda, and Chordata
Trocophore Larva
Small, free swimming larvae with cilia, in Mollusca and Annelida
Paired Setae
Bristles that segment and anchor the body, only in Annelida
Water Vascular System
Contract muscles around ampulae which forces water into tube feet extending them pushing against ground and relax to retract, only in Echinodermata
Bilateral Symmetry
One plane of symmetry, in all Bilateria except Echinodermata
Notochord
cartilaginous skeletal rod that supports embryo and some adult chordates, only in Chordata
Protostomes
Blastopore becomes mouth
Deuterostomes
Blastopore becomes anus
Cephalization
Concentration of sense organs and nerve cells in single place in animal's body, in those that have bilateral symmetry