Veterinary Parasitology CH2 - Parasites That Infect and Infest Domestic Animals
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 2 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Monogentic Trematodes (Flukes)
Do not alternate generations
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms), Class: Trematoda (flukes), Subclass: Monogenea
Ectoparasites of fish, amphibians and reptiles
Adults hatch out of eggs
In high numbers can cause fin rot, anemia
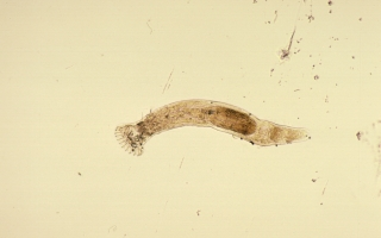
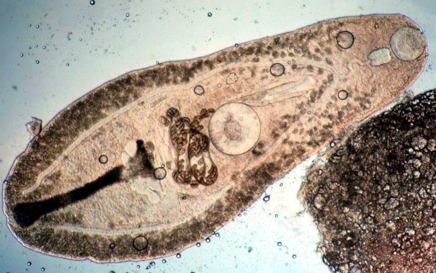
Digenetic Trematodes (Flukes)
Alternate between sexual and asexual generations
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms), Class: Trematoda (flukes), Subclass: Digenea
Endoparasites of large and small animals
Flat, leaf-shaped, infect mostly GI, also lung and blood
Eggs can be seen in feces
Have both larval and adult stages, often in different hosts
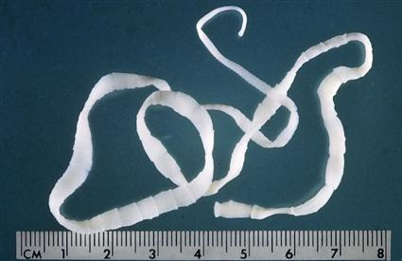
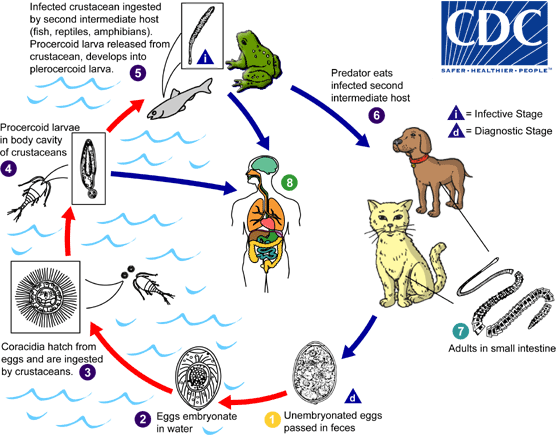
Eucestodes (True Tapeworms)
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms), Class: Eucestoda (true tapeworms)
Ribbon-like, found in GI tract of definitive hosts
Lack an alimentary canal, absorb nutrients through tegument (skin)
Eggs can be seen in fecal flotation
Larval forms can be found in various tissues of intermediate hosts and cause harm
Cotyloda (Pseudotapeworms)
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flatworms), Class: Cotyloda (pseudotapeworms)
Ribbon-like, found in GI tract of definitive hosts
Eggs can be seen in fecal flotation
Larval forms can be found in various tissues of intermediate hosts (microscopic crustaceans, fish and reptiles) but don't cause harm to domestic animals
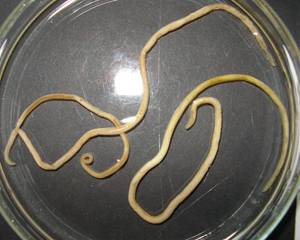
Nematodes (Roundworms)
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Nematoda
Long, not segmented, most numerous and varied of domestic worm parasites. Can cause significant disease in domestic animals
Eggs and larvae can be seen in fecal flotation
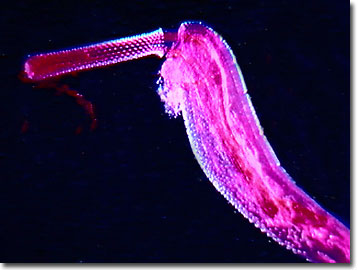
Acanthocephalans (Thorny-Headed Worms)
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Acanthceophala
Long, not segmented, contain spiny proboscis used to attach to host tissue
Lack an alimentary canal, absorb food through tegument
Very uncommon to see adult parasites
Most often seen in GI tract
Eggs can be seen in fecal flotation
Hirudineans (Leeches)
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Annelida (segmented worm), Class: Hirudinea
Blood-feeding, ringed ectoparasites of wild and domestic animals
Mostly fresh-water, some marine and land varieties

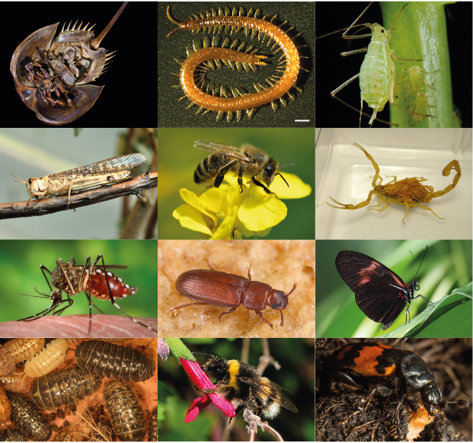
Arthropods
Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Arthropoda (jointed legs)
Largest phylum in all of the animal kingdom
Contains pentastomes, crustaceans, centipedes, millipedes, insects, mites, ticks, scorpions and spiders
May be causal agents, intermediate hosts, vectors, produce toxins or venoms

Protozoans
Kingdom: Protista
All are unicellular protozoans
Categorized by their movement: flagellates, amoebae, apicomplexans and ciliates
Can cause significant pathologies to all animals including humans